-
最全面的Mybatis教程,从“开局”到“通关”(二)
前言

本文为SSM框架 【Mybatis】 相关知识,MyBatis 是一款优秀的半自动的ORM持久层框架,下边将对
Mybatis的简介、Mybatis的CRUD实现,Mybatis的配置文件,Mybatis的日志配置,resultMap详解,分页实现,注解式开发,Lombok的使用,关联映射,动态SQL,Mybatis缓存等进行详尽介绍~
🚩 Are you ready❓ Let’s Go ❗️📌博主主页:小新要变强 的主页
👉Java全栈学习路线可参考:【Java全栈学习路线】最全的Java学习路线及知识清单,Java自学方向指引,内含最全Java全栈学习技术清单~
👉算法刷题路线可参考:算法刷题路线总结与相关资料分享,内含最详尽的算法刷题路线指南及相关资料分享~
👉Java微服务开源项目可参考:企业级Java微服务开源项目(开源框架,用于学习、毕设、公司项目、私活等,减少开发工作,让您只关注业务!)↩️本文上接:最全面的Mybatis教程,从“开局”到“通关”(一)
目录
SSM框架 【Mybatis】(二)

七、分页实现
分页(Paging):即有很多数据,我们就需要分页来分割数据,可提高整体运行性能,增强用户使用体验需求等。
不使用分页将遇到的问题:
- 客户端问题:数据太多影响用户的体验感且也不方便操作查找,甚至出现加载太慢的问题。
- 服务器问题:数据太多会造成内存溢出,且对服务器的性能也不友好。
1️⃣limit分页
🍀语法
-- 语法:select * from xxx limit startIndex,pageSize select * from user limit 3;- 1
- 2
mybatis的sql语句如果有多个参数,需要用map封装。
🍀Mapper接口
List<User> selectLimit(Map<String,Integer> map);- 1
🍀xxxMapper.xml
<select id="selectLimit" parameterType="map" resultMap="UserMap"> select * from mybatis.user limit #{startIndex},#{pageSize} select>- 1
- 2
- 3
🍀测试
Test.java:
public class UserDaoTest { @Test public void limitTest(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); map.put("startIndex",0); map.put("pageSize",2); List<User> list=mapper.selectLimit(map); for (User u: list) { System.out.println(u); } sqlSession.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
2️⃣RowBounds分页
这种方法官方不推荐。
🍀Mapper接口
List<User> selectRowBounds();- 1
🍀xxxMapper.xml
<select id="selectRowBounds" resultMap="UserMap"> select * from mybatis.user select>- 1
- 2
- 3
🍀测试
@Test public void selectRowBounds(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(0,2); List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.wang.dao.UserMapper.selectRowBounds" ,null,rowBounds); for (User user : list) { System.out.println(user); } sqlSession.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
八、注解式开发
- 注解的本质是使用反射,底层是代理模式(见设计模式)。
- 使用注解来映射简单语句会使代码显得更加简洁,但对于稍微复杂一点的语句,Java 注解不仅力不从心,还会让你本就复杂的 SQL语句更加混乱不堪。
- 因此,如果你需要做一些很复杂的操作,最好用 XML 来映射语句。
1️⃣注解式查找
🍀Mapper接口
@Select("select * from mybatis.user") List<User> selectAll();- 1
- 2
🍀注册绑定
mybatis-config.xml:
<mappers> <mapper class="com.wang.dao.UserMapper"/> mappers>- 1
- 2
- 3
🍀测试
@Test public void selectAll(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); //底层主要应用反射 UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); List<User> list=mapper.selectAll(); for (User user : list) { System.out.println(user); } sqlSession.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
2️⃣注解式CRUD
🍀设置自动提交
MybatisUtils.java:
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){ return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); }- 1
🍀Mapper接口
//多个参数情况下,有两种解决方式,一个map封装,另一种是注解Param @Select("select * from mybatis.user where id=#{id}") User selectUserById(@Param("id") int id); @Select("select * from mybatis.user") List<User> selectAll(); @Insert("insert into mybatis.user() values(#{id},#{name},#{password}) ") boolean insertUser(User u); @Update("update user set name=#{name},pwd=#{password} where id = #{id}") boolean updateUser(User u); @Delete("delete from mybatis.user where id=#{id}") boolean deleteUser(@Param("id") int id);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
🍀测试
@Test public void selectAll(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); //底层主要应用反射 UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); // Listlist=mapper.selectAll(); // for (User user : list) { // System.out.println(user); // } /** User u=mapper.selectUserById(1); System.out.println(u); */ // boolean isInserted=mapper.insertUser(new User(4,"图拉真","dgsdgs")); // if (mapper.updateUser(new User(6,"寒江雪",null))) if (mapper.deleteUser(6)) for (User user : mapper.selectAll()) { System.out.println(user); } sqlSession.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
3️⃣@Param注解
这个注解是为SQL语句中参数赋值而服务的。@Param的作用就是给参数命名,比如在mapper里面某方法A(int id),当添加注解后A(@Param(“userId”) int id),也就是说外部想要取出传入的id值,只需要取它的参数名userId就可以了。将参数值传如SQL语句中,通过#{userId}进行取值给SQL的参数赋值。
- 基本类型的参数和String类型,需要加上这个注解
- 引用类型不需要加
- 如果只有一个基本类型的参数,可以省略
- 我们在sql中引用的就是@Param(“xxx”)中设定的属性名
实例一:@Param注解基本类型的参数
🍀Mapper接口
public User selectUser(@Param("userName") String name,@Param("password") String pwd);- 1
🍀xxxMapper.xml
<select id="selectUser" resultMap="User"> select * from user where user_name = #{userName} and user_password=#{password} select>- 1
- 2
- 3
其中where user_name = #{userName} and user_password = #{password}中的userName和password都是从注解@Param()里面取出来的,取出来的值就是方法中形式参数 String name 和 String pwd的值。
实例二:@Param注解JavaBean对象
SQL语句通过@Param注解中的别名把对象中的属性取出来然后复制🍀Mapper接口
public List<User> getAllUser(@Param("user") User u);- 1
🍀xxxMapper.xml
<select id="getAllUser" parameterType="com.vo.User" resultMap="userMapper"> select from user t where 1=1 and t.user_name = #{user.userName} and t.user_age = #{user.userAge} select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
注意点:
- 当使用了@Param注解来声明参数的时候,SQL语句取值使用#{},${}取值都可以。
- 当不使用@Param注解声明参数的时候,必须使用的是#{}来取参数。使用${}方式取值会报错。
- 不使用@Param注解时,参数只能有一个,并且是Javabean。在SQL语句里可以引用JavaBean的属性,而且只能引用JavaBean的属性。
九、Lombok插件使用
Lombok是一个可以通过简单的注解形式来帮助我们简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的Java代码的工具,通过使用对应的注解,可以在编译源码的时候生成对应的方法。
1️⃣Lombok安装
🍀(1)IDEA左上角File->Settings->Plugins
🍀(2)搜索Lombok,下载安装
🍀(3)导入maven
pom.xml:
<dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <version>1.18.10version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
2️⃣使用Lombok
Lombok的支持:
@Getter and @Setter @FieldNameConstants @ToString @EqualsAndHashCode @AllArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor and @NoArgsConstructor @Log, @Log4j, @Log4j2, @Slf4j, @XSlf4j, @CommonsLog, @JBossLog, @Flogger, @CustomLog @Data @Builder @SuperBuilder @Singular @Delegate @Value @Accessors @Wither @With @SneakyThrows @val @var experimental @var @UtilityClass Lombok config system Code inspections Refactoring actions (lombok and delombok)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
常用支持:
- @Data支持: 无参构造,getter&setter,toString,hashCode,equals
- @AllArgsConstructor: 有参构造
- @NoArgsConstructor: 无参构造
使用方法:
在具体的实体类上加相应的注解。
十、Mybatis关联映射
以多个学生对应一个老师为例,存在:
- 学生关联老师,多对一关系
- 老师管理集合,一对多关系
1️⃣sql建表
create table `teacher`( `id` int not null, `name` varchar(30) default null, primary key(`id`) ) engine=InnoDB default charset=utf8; insert into teacher values (1,'王老师'); create table `student`( `id` int not null, `name` varchar(30) default null, `tid` int not null, primary key(`id`), key `FK_tid` (`tid`), constraint `FK_tid` foreign key(`tid`) references `teacher`(`id`) ) engine=InnoDB default charset=utf8;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
2️⃣测试环境搭建
🍀(1)导入Lombok
🍀(2)新建Teacher,Student实体类
🍀(3)新建Mapper接口
🍀(4)在resources新建com->xxx->dao文件夹
🍀(5)新建xxxMapper.xml文件
🍀(6)在mybatis-config.xml中注册绑定xxxMapper.xml
🍀(7)在TeacherMapper接口中创建selectAll()方法
🍀(8)在TeacherMapper.xml中写对应的查询
🍀(9)新建测试类,在测试类中测试使用
3️⃣按照查询嵌套处理多对一
🍀实体类
Student.java:
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Student { private int id; private String name; private Teacher teacher; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Teacher.java:
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Teacher { private int id; private String name; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
🍀Mapper接口
List<Student> selectAll();- 1
🍀xxxMapper.xml
<resultMap id="student_teacher" type="Student"> <result property="id" column="id"/> <result property="name" column="name"/> <association property="teacher" column="tid" javaType="Teacher" select="getTeacher"/> resultMap> <select id="selectAll" resultMap="student_teacher"> select * from mybatis.student select> <select id="getTeacher" resultType="Teacher"> select * from mybatis.teacher where id=#{tid} select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
🍀测试
@Test public void selectAll(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); List<Student> studentList = mapper.selectAll(); for (Student s: studentList) { System.out.println(s); } sqlSession.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
4️⃣按照结果嵌套处理多对一
🍀Mapper接口
List<Student> selectAll2();- 1
🍀xxxMapper.xml
<select id="selectAll2" resultMap="S_T"> select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname from mybatis.student s,mybatis.teacher t where s.tid=t.id select> <resultMap id="S_T" type="Student"> <result property="id" column="sid"/> <result property="name" column="sname"/> <association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher"> <result property="name" column="tname"/> association> resultMap>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
🍀测试
@Test public void selectAll(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); List<Student> studentList = mapper.selectAll(); for (Student s: studentList) { System.out.println(s); } sqlSession.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
5️⃣一对多关系的处理
🍀实体类
Student.java:
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Student { private int id; private String name; private int tid; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Teacher.java:
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Teacher { private int id; private String name; //老师拥有多个学生 private List<Student> students; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
🍀Mapper接口
public interface TeacherMapper { List<Teacher> selectAll(); //获取指定老师下的所有学生 Teacher getTeacher(@Param("tid")int id); Teacher getTeacher2(@Param("tid")int id); List<Student> getStudents(@Param("tid")int id); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
🍀xxxMapper.xml
<select id="selectAll" resultType="Teacher"> select * from mybatis.teacher select> <select id="getTeacher" resultMap="S_T"> select t.id tid, t.name tname,s.name sname from mybatis.teacher t,mybatis.student s where s.tid=tid and tid=#{tid} select> <resultMap id="S_T" type="Teacher"> <result property="id" column="tid"/> <result property="name" column="tname"/> <collection property="students" ofType="Student"> <result property="name" column="sname"/> <result property="tid" column="tid"/> collection> resultMap> <select id="getTeacher2" resultMap="student_teacher"> select * from mybatis.teacher where id=#{tid} select> <resultMap id="student_teacher" type="Teacher"> <result property="id" column="id"/> <result property="name" column="name"/> <collection property="students" column="id" ofType="Student" select="getStudents"/> resultMap> <select id="getStudents" resultType="Student"> select * from mybatis.student where tid=#{tid} select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
🍀测试
@Test public void selectAll(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); List<Student> studentList = mapper.selectAll(); for (Student s: studentList) { System.out.println(s); } sqlSession.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
十一、Mybatis动态SQL
1️⃣动态SQL概述
MyBatis提供了对SQL语句动态的组装能力,大量的判断都可以在 MyBatis的映射XML文件里面配置,以达到许多我们需要大量代码才能实现的功能,大大减少了我们编写代码的工作量。
动态SQL的元素:
元素 作用 备注 if 判断语句 单条件分支判断 choose、when、otherwise 相当于Java中的 case when语句 多条件分支判断 trim、where、set 辅助元素 用于处理一些SQL拼装问题 foreach 循环语句 在in语句等列举条件常用 2️⃣if元素
if元素相当于Java中的if语句,它常常与test属性联合使用。现在我们要根据name去查找学生,但是name是可选的,如下所示:
<select id="findUserById" resultType="com.wang.entity.User"> select id,username,password from user where 1 =1 <if test="id != null"> AND id = #{id} if> <if test="username != null and username != ''"> AND username = #{username} if> <if test="password != null and password != ''"> AND password = #{password} if> select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
3️⃣where元素
上面的select语句我们加了一个
1=1的绝对true的语句,目的是为了防止语句错误,变成SELECT * FROM student WHERE这样where后没有内容的错误语句。这样会有点奇怪,此时可以使用< where>元素。<select id="findUserById" resultType="com.wang.entity.User"> select id,username,password from user <where> <if test="id != null"> AND id = #{id} if> <if test="username != null and username != ''"> AND username = #{username} if> <if test="password != null and password != ''"> AND password = #{password} if> where> select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
4️⃣trim元素
有时候我们要去掉一些特殊的SQL语法,比如常见的and、or,此时可以使用trim元素。trim元素意味着我们需要去掉一些特殊的字符串,prefix代表的是语句的前缀,而prefixOverrides代表的是你需要去掉的那种字符串,suffix表示语句的后缀,suffixOverrides代表去掉的后缀字符串。
<select id="select" resultType="com.wang.entity.User"> SELECT * FROM user <trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND"> <if test="username != null and username != ''"> AND username LIKE concat('%', #{username}, '%') if> <if test="id != null"> AND id = #{id} if> trim> select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
5️⃣choose、when、otherwise元素
有些时候我们还需要多种条件的选择,在Java中我们可以使用switch、case、default语句,而在映射器的动态语句中可以使用choose、when、otherwise元素。
<select id="select" resultType="com.wang.entity.User"> SELECT * FROM user WHERE 1=1 <choose> <when test="name != null and name != ''"> AND username LIKE concat('%', #{username}, '%') when> <when test="id != null"> AND id = #{id} when> choose> select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
6️⃣set元素
在update语句中,如果我们只想更新某几个字段的值,这个时候可以使用set元素配合if元素来完成。注意: set元素遇到,会自动把,去掉。
<update id="update"> UPDATE user <set> <if test="username != null and username != ''"> username = #{username}, if> <if test="password != null and password != ''"> password = #{password} if> set> WHERE id = #{id} update>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
7️⃣foreach元素
foreach元素是一个循环语句,它的作用是遍历集合,可以支持数组、List、Set接口。
<select id="select" resultType="com.wang.entity.User"> SELECT * FROM user WHERE id IN <foreach collection="ids" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="id"> #{id} foreach> select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- collection配置的是传递进来的参数名称。
- item配置的是循环中当前的元素。
- index配置的是当前元素在集合的位置下标。
- open和 close配置的是以什么符号将这些集合元素包装起来。
- separator是各个元素的间隔符。
8️⃣foreach批量插入
<insert id="batchInsert" parameterType="list"> insert into `user`( user_name, pass) values <foreach collection="users" item="user" separator=","> (#{user.username}, #{user.password}) foreach> insert>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
9️⃣SQL片段
有时候可能某个 sql 语句我们用的特别多,为了增加代码的重用性,简化代码,我们需要将这些代码抽取出来,然后使用时直接调用。
提取SQL片段:
<sql id="if-title-author"> <if test="title != null"> title = #{title} if> <if test="author != null"> and author = #{author} if> sql>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
引用SQL片段:
<select id="queryBlogIf" parameterType="map" resultType="blog"> select * from blog <where> <include refid="if-title-author">include> where> select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
十二、Mybatis缓存
1️⃣Mybatis缓存简介
- 为什么要使用缓存? 每次查询都要连接数据库,比较耗资源,我们把查询到的数据暂存到内存里面,下次查询的时候,从内存读取, 这个地方就叫缓存。
- 什么样的数据适用于缓存? 经常查询且不经常改变的数据
Mybatis系统默认定义了两级缓存:
- 默认情况下,只有一级缓存开启(SqlSession缓存,也称为本地缓存)
- 二级缓存需要手动配置,它是基于namespace级别的缓存
- Mybatis定义了缓存接口Cache,可以通过实现Cache接口来自定义二级缓存
2️⃣ 一级缓存
🍀一级缓存是sqlsession级别的缓存
- 在操作数据库时,需要构造sqlsession对象,在对象中有一个数据结构(HashMap)用于存储缓存数据
- 不同的sqlsession之间的缓存区域是互相不影响的。
🍀一级缓存工作原理
一级缓存工作原理图解:
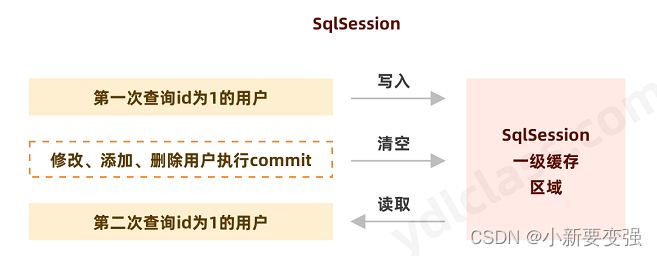
- 第一次发起查询sql查询用户id为1的用户,先去找缓存中是否有id为1的用户,如果没有,再去数据库查询用户信息。得到用户信息,将用户信息存储到一级缓存中
- 如果sqlsession执行了commit操作(插入,更新,删除),会清空sqlsession中的一级缓存,避免脏读
- 第二次发起查询id为1的用户,缓存中如果找到了,直接从缓存中获取用户信息
- MyBatis默认支持并开启一级缓存
🍀一级缓存测试步骤
- (1)开启日志
- (2)测试在一个Session中查询两次
- (3)查看日志输出
🍀一级缓存演示
Mapper接口:User getUserById(int id);- 1
xxxMapper.xml:
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="User"> select * from mybatis.user where id=#{id} select>- 1
- 2
- 3
Test.java:
@Test public void getUserById(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User u=mapper.getUserById(1); System.out.println(u); System.out.println("============="); User user=mapper.getUserById(1); System.out.println(user); System.out.println(u==user); sqlSession.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
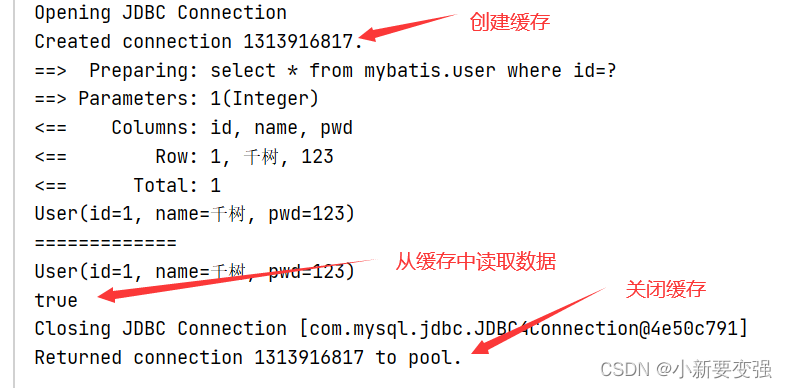
🍀缓存失效的情况- 当sqlSession不同
- 当sqlSession对象相同的时候,查询的条件不同,原因是第一次查询时候,一级缓存中没有第二次查询所需要的数据
- 当sqlSession对象相同,两次查询之间进行了插入的操作
- 当sqlSession对象相同,手动清除了一级缓存中的数据
🍀一级缓存生命周期
- MyBatis在开启一个数据库会话时,会创建一个新的SqlSession对象,SqlSession对象中会有一个新的Executor对象,Executor对象中持有一个新的PerpetualCache对象;当会话结束时,SqlSession对象及其内部的Executor对象还有PerpetualCache对象也一并释放掉。
- 如果SqlSession调用了close()方法,会释放掉一级缓存PerpetualCache对象,一级缓存将不可用。
- 如果SqlSession调用了clearCache(),会清空PerpetualCache对象中的数据,但是该对象仍可使用。
- SqlSession中执行了任何一个update操作(update()、delete()、insert()),都会清空PerpetualCache对象的数据,但是该对象可以继续使用。
3️⃣二级缓存
🍀二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存
- 多个sqlsession去操作同一个mapper的sql语句,多个sqlsession可以共用二级缓存,所得到的数据会存在二级缓存区域
- 二级缓存是跨sqlsession的
- 二级缓存相比一级缓存的范围更大(按namespace来划分),多个sqlsession可以共享一个二级缓存
🍀二级缓存实现原理
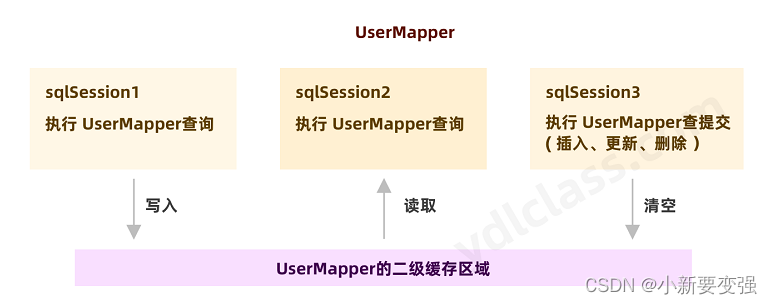
- 首先要手动开启MyBatis二级缓存
- 在config.xml设置二级缓存开关
<settings> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> settings>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 还要在具体的mapper.xml开启二级缓存
<cache eviction="LRU" flushInterval="100000"/>- 1
- 2
🍀禁用二级缓存
在statement中可以设置useCache=false,禁用当前select语句的二级缓存,默认情况为true
<select id="getStudentById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="Student" useCache="false">- 1
在实际开发中,针对每次查询都需要最新的数据sql,要设置为useCache=“false” ,禁用二级缓存。
🍀flushCache标签:刷新缓存(清空缓存)
<select id="getStudentById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="Student" flushCache="true">- 1
一般下执行完commit操作都需要刷新缓存,flushCache="true 表示刷新缓存,可以避免脏读。
🍀二级缓存应用场景
- 对于访问多的查询请求并且用户对查询结果实时性要求不高的情况下,可采用MyBatis二级缓存,降低数据库访问量,提高访问速度,如电话账单查询。
- 根据需求设置相应的flushInterval:刷新间隔时间,比如三十分钟,24小时等。
🍀二级缓存局限性
MyBatis二级缓存对细粒度的数据级别的缓存实现不好,比如如下需求:对商品信息进行缓存,由于商品信息查询访问量大,但是要求用户每次都能查询最新的商品信息,此时如果使用MyBatis的二级缓存就无法实现当一个商品变化时只刷新该商品的缓存信息而不刷新其它商品的信息,因为MyBatis的二级缓存区域以mapper为单位划分,当一个商品信息变化会将所有商品信息的缓存数据全部清空。解决此类问题需要在业务层根据需求对数据有针对性缓存。
🍀使用二级缓存
(1)开启全局缓存
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>- 1
- 2
(2)在要使用二级缓存的Mapper.xml中,写标签
<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
(3)测试
@Test public void getUserById2(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); UserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User u=mapper.getUserById(1); System.out.println(u); sqlSession.close(); System.out.println("============"); User user = mapper2.getUserById(1); System.out.println(user==u); sqlSession2.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
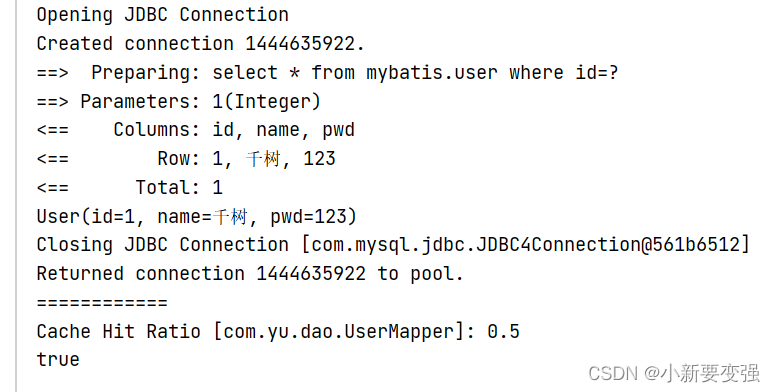
(2)问题
我们需要实体类序列化,否则会抛出异常
(4)总结
- 二级缓存在同一个Mapper下有效
- 所有的数据都会先放在一级缓存中
- 当会话提交或者关闭,数据会被转存到二级缓存中
4️⃣ 缓存原理
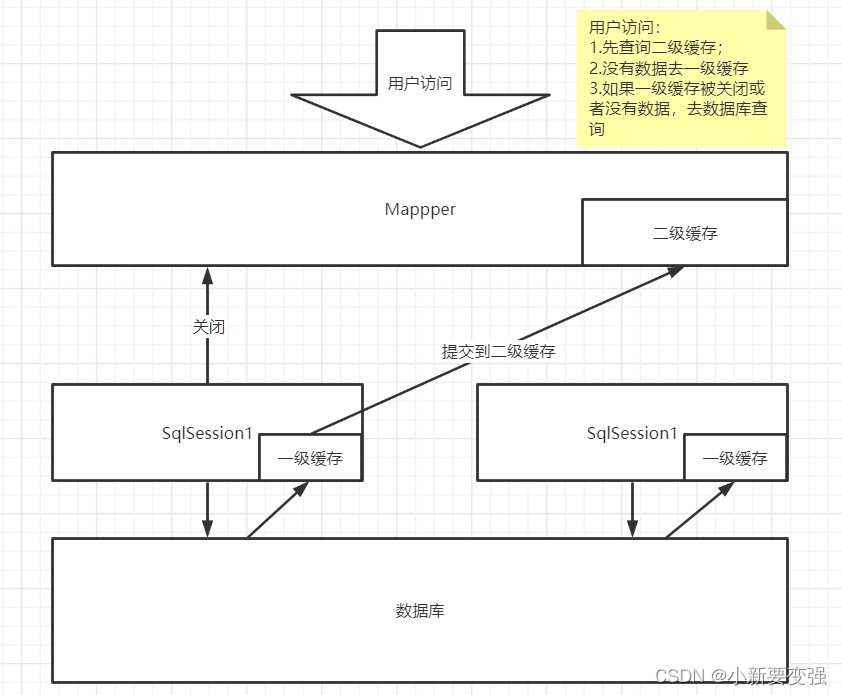
5️⃣自定义缓存EhCache
🍀EhCache简介
EhCache 是一个纯Java的进程内缓存框架,具有快速、精干等特点,是Hibernate中默认CacheProvider。Ehcache是一种广泛使用的开源Java分布式缓存。主要面向通用缓存,Java EE和轻量级容器。
🍀EhCache使用
(1)导包
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.cachesgroupId> <artifactId>mybatis-ehcacheartifactId> <version>1.2.2version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
(2)写入配置文件(resources->ehcache.xml)
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"> <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir/ehcache"/> <defaultCache maxEntriesLocalHeap="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" maxEntriesLocalDisk="10000000" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"> <persistence strategy="localTempSwap"/> defaultCache> <cache name="HelloWorldCache" maxElementsInMemory="1000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="5" timeToLiveSeconds="5" overflowToDisk="false" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/> ehcache>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
(3)在Mapper中指定
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>- 1
(4)测试
@Test public void getUserById2(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); UserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User u=mapper.getUserById(1); System.out.println(u); sqlSession.close(); System.out.println("============"); User user = mapper2.getUserById(1); System.out.println(user==u); sqlSession2.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
🍀自定义缓存
只要实现了org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache接口,就能定义自己的缓存,但是实现比较复杂,只需要会使用就行,ehcache是继承了AbstractEhcacheCache,该类已经实现了Cache接口。
public class MyCache implements Cache { @Override public String getId() { return null; } @Override public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { } @Override public Object getObject(Object key) { return null; } @Override public Object removeObject(Object key) { return null; } @Override public void clear() { } @Override public int getSize() { return 0; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
🍀实际开发中使用的缓存
在实际开发中,我们更多的使用Redis来做缓存。
后记

👉Java全栈学习路线可参考:【Java全栈学习路线】最全的Java学习路线及知识清单,Java自学方向指引,内含最全Java全栈学习技术清单~
👉算法刷题路线可参考:算法刷题路线总结与相关资料分享,内含最详尽的算法刷题路线指南及相关资料分享~
👉Java微服务开源项目可参考:企业级Java微服务开源项目(开源框架,用于学习、毕设、公司项目、私活等,减少开发工作,让您只关注业务!) -
相关阅读:
FPGA工程师面试——常用名词解释
电力巡检/电力抢修行业解决方案:AI+视频技术助力解决巡检监管难题
深度学习模型部署全流程-模型部署
【Redis学习笔记】第五章 Linux环境安装Redis
【C语言程序设计】--C语言(一)计算机思维导论
Linux三剑客:awk的实用案例
测试C语言static关键字的作用
基于DoS攻击能量分级的ICPS综合安全控制与通信协同设计
内行才知道的大数据分析平台
XSCTF联合招新【真是阳间题】(MSIC+Crypto)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42146402/article/details/127825705
