-
m基于matlab的TDSCDMA系统性能仿真
目录
1.算法概述
TD-SCDMA的中文含义为时分复用同步码分多址接入,是由中国第一次提出、在无线传输技术(RTT)的基础上完成并已正式成为被ITU接纳的国际移动通信标准。这是中国移动通信界的一次创举和对国际移动通信行业的贡献,也是中国在移动通信领域取得的前所未有的突破 。
TD-SCDMA中的TD指时分复用,也就是指在TD-SCDMA系统中单用户在同一时刻双向通信(收发)的方式是TDD(时分双工),在相同的频带内在时域上划分不同的时段(时隙)给上、下行进行双工通信,可以方便地实现上、下行链路间的灵活切换。例如根据不同的业务对上、下行资源需求的不同来确定上、下行链路间的时隙分配转换点,进而实现高效率地承载所有3G对称和非对称业务。与FDD模式相比,TDD可以运行在不成对的射频频谱上,因此在当前复杂的频谱分配情况下它具有非常大的优势。TD-SCDMA通过最佳自适应资源的分配和最佳频谱效率,可支持速率从8kb/s到2Mb/s以及更高速率的语音、视频电话、互联网等各种3G业务TD-SCDMA的发展始于1998年初,当时在国家邮电部的直接领导下,由原电信科学技术研究院组织队伍在 SCDMA技术的基础上,研究和起草符合IMT-2000要求的TDSCDMA建议草案。该标准草案以智能天线、同步码分多址、接力切换、时分双工为主要特点,于ITU征集IMT-2000第三代移动通信无线传输技术候选方案的截止日1998年6月30日提交到ITU,从而成为IMT2000的15个候选方案之一。ITU综合了各评估组的评估结果。在1999年11月举行的赫尔辛基ITU-RTG8/1第18次会议上和2000年5月举行的伊斯坦布尔ITU-R全会上,TD-SCDMA被正式接纳为CDMATDD制式的方案之中国无线通信标准研究组(CWTS)作为代表中国的区域性标准化组织,自1999年5月加入3GPP后,经过4个月的充分准备,与项目协调组(3 GPPPCG)、技术规范组(TSG)进行了大量协调工作,在同年9月向3GPP建议将TD- SCDMA纳入3GPP标准规范的工作内容。1999年12月在法国尼斯举行的3GPP会议上,提案被无线接入网(3 GPPTSGRAN)全会所接受,正式确定将TD- SCDMA纳入 Release200(后拆分为R4和R5)的工作计划中,并将 TD-SCDMA简称为即低码片速率TDD方案(Low Code rate, LCRTDD) [4] 。
在TD-SCDMA系统中,用到了以下几种主要关键技术 :
(1)时分双工方式(Time Division Duplexing);
(2)联合检测(Joint Detection);
(3)智能天线(Smart Antenna);
(4)上行同步(Uplink Synchronous);
(5)软件无线电(Soft Radio);
(6)动态信道分配(Dynamic Channel Allocation);
(7)功率控制(Power control);
(8)接力切换(Baton Handover);
(9)高速下行分组接入技术(High Speed Downlink Packet Access) 。
2.仿真效果预览
matlab2022a仿真测试如下:
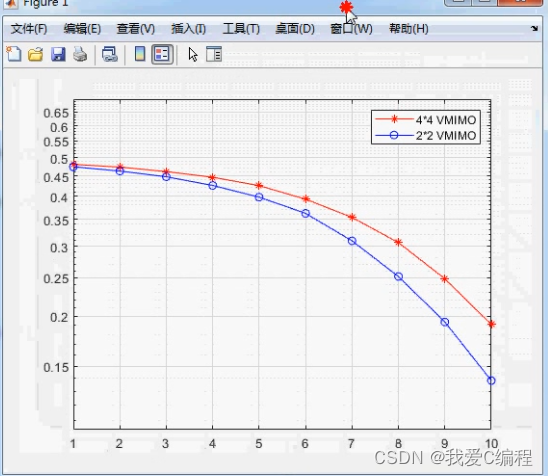
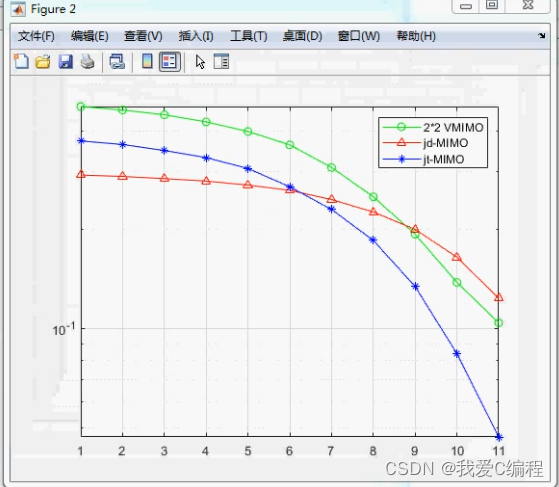
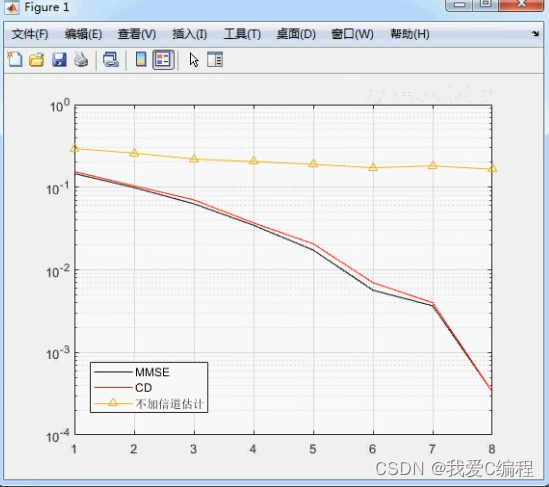
3.核心MATLAB代码预览
- snr_indb=1:8;
- for k=1:length(snr_indb)
- snr=10^(snr_indb(k)/10);
- sgma=1;
- eb=2*(sgma^2)*snr;
- LC=31;
- echip=eb/LC;
- N=1000;%number of bits transmitted
- %creat PN codes
- fbconnection=[0 1 0 0 1];
- mseq=m_sequence(fbconnection);
- fbconnection1=[0 0 1 0 1];
- fbconnection2=[0 1 1 1 1];
- goldseq=gold_seq(fbconnection1,fbconnection2);
- %N=2^length(fbconnection)-1;
- ind1=find(mseq==0);
- mseq(ind1)=-1;
- ind2=find(goldseq==0);
- goldseq(ind2)=-1; %creat 31*31 gold sequence
- temp=goldseq;
- pn_seq1=temp(3,:);
- pn_seq2=temp(4,:);
- pn_seq3=temp(7,:);
- pn_seq4=temp(10,:);
- pn_seq5=temp(15,:);
- pn_seq6=temp(20,:);
- pn_seq7=temp(26,:);
- pn_seq8=temp(31,:);
- % comput matrix R
- pp=[pn_seq1;pn_seq2;pn_seq3;pn_seq4;pn_seq5;pn_seq6;pn_seq7;pn_seq8];
- RR=(1/LC)*pp*pp';
- RR1=inv(eb*eye(8));
- R=inv(RR+RR1);
- %generate codes
- for i=1:N
- temp1=rand;
- if(temp1<0.5),dsource1(i)=-1;
- else dsource1(i)=1;
- end;
- temp2=rand;
- if(temp2<0.5),dsource2(i)=-1;
- else dsource2(i)=1;
- end;
- temp3=rand;
- if(temp3<0.5),dsource3(i)=-1;
- else dsource3(i)=1;
- end;
- temp4=rand;
- if(temp4<0.5),dsource4(i)=-1;
- else dsource4(i)=1;
- end;
- temp5=rand;
- if(temp5<0.5),dsource5(i)=-1;
- else dsource5(i)=1;
- end;
- temp6=rand;
- if(temp6<0.5),dsource6(i)=-1;
- else dsource6(i)=1;
- end;
- temp7=rand;
- if(temp7<0.5),dsource7(i)=-1;
- else dsource7(i)=1;
- end;
- temp8=rand;
- if(temp8<0.5),dsource8(i)=-1;
- else dsource8(i)=1;
- end;
- end;
- number_of_err=0;
- number_of_err1=0;
- number_of_err2=0;
- for i=1:N
- %将每个bit repeat LC=31 times
- for j=1:LC
- repeatdata1(j)=dsource1(i);
- repeatdata2(j)=dsource2(i);
- repeatdata3(j)=dsource3(i);
- repeatdata4(j)=dsource4(i);
- repeatdata5(j)=dsource5(i);
- repeatdata6(j)=dsource6(i);
- repeatdata7(j)=dsource7(i);
- repeatdata8(j)=dsource8(i);
- end;
- for ii=0:2^8-1
- j=1;aa=ii;
- while aa~=0
- bk(j,ii+1)=rem(aa,2);
- aa=floor(aa/2);
- j=j+1;
- end
- end
- bk=bk*2-1;
- %tranmit signal is:
- trans_sig1=sqrt(echip)* repeatdata1.*pn_seq1;
- trans_sig2=sqrt(echip)* repeatdata2.*pn_seq2;
- trans_sig3=sqrt(echip)* repeatdata3.*pn_seq3;
- trans_sig4=sqrt(echip)* repeatdata4.*pn_seq4;
- trans_sig5=sqrt(echip)* repeatdata5.*pn_seq5;
- trans_sig6=sqrt(echip)* repeatdata6.*pn_seq6;
- trans_sig7=sqrt(echip)* repeatdata7.*pn_seq7;
- trans_sig8=sqrt(echip)* repeatdata8.*pn_seq8;
- %add AWGN noise
- noise=sgma*randn(1,LC);
- % receive signal
- for j=1:LC
- rtemp(j)=trans_sig1(j)+trans_sig2(j)+trans_sig3(j)+trans_sig4(j)+trans_sig5(j)+trans_sig6(j)+trans_sig7(j)+trans_sig8(j);
- end;
- r=rtemp+noise;
- r1=r;r2=r;r3=r;r4=r;r5=r;r6=r;r7=r;r8=r;
- %CD JUDGE
- I1=sum(r1.*pn_seq1);
- I2=sum(r2.*pn_seq2);
- I3=sum(r3.*pn_seq3);
- I4=sum(r4.*pn_seq4);
- I5=sum(r5.*pn_seq5);
- I6=sum(r6.*pn_seq6);
- I7=sum(r7.*pn_seq7);
- I8=sum(r8.*pn_seq8);
- % DD JUDGE
- I=R*[I1,I2,I3,I4,I5,I6,I7,I8]';
- y=[I1,I2,I3,I4,I5,I6,I7,I8]';
- for ii=1:2^8
- c(ii)=2*(bk(:,ii))'*y-(bk(:,ii))'*R*bk(:,ii);
- end
- [m,mm]=max(c);
- bb=bk(:,mm);
- if(bb(1)~=dsource1(i)),number_of_err2=number_of_err2+1;end;
- if(bb(2)~=dsource2(i)),number_of_err2=number_of_err2+1;end;
- if(bb(3)~=dsource3(i)),number_of_err2=number_of_err2+1;end;
- if(bb(4)~=dsource4(i)),number_of_err2=number_of_err2+1;end;
- if(bb(5)~=dsource5(i)),number_of_err2=number_of_err2+1;end;
- if(bb(6)~=dsource6(i)),number_of_err2=number_of_err2+1;end;
- if(bb(7)~=dsource7(i)),number_of_err2=number_of_err2+1;end;
- if(bb(8)~=dsource8(i)),number_of_err2=number_of_err2+1;end;
- % DD make decision
- if(I(1)<0), desion1=-1;
- else desion1=1;
- end;
- if(I(2)<0), desion2=-1;
- else desion2=1;
- end;
- if(I(3)<0), desion3=-1;
- else desion3=1;
- end;
- if(I(4)<0), desion4=-1;
- else desion4=1;
- end;
- if(I(5)<0), desion5=-1;
- else desion5=1;
- end;
- if(I(6)<0), desion6=-1;
- else desion6=1;
- end;
- if(I(7)<0), desion7=-1;
- else desion7=1;
- end;
- if(I(8)<0), desion8=-1;
- else desion8=1;
- end;
- if(desion1~=dsource1(i)),number_of_err=number_of_err+1;end;
- if(desion2~=dsource2(i)),number_of_err=number_of_err+1;end;
- if(desion3~=dsource3(i)),number_of_err=number_of_err+1;end;
- if(desion4~=dsource4(i)),number_of_err=number_of_err+1;end;
- if(desion5~=dsource5(i)),number_of_err=number_of_err+1;end;
- if(desion6~=dsource6(i)),number_of_err=number_of_err+1;end;
- if(desion7~=dsource7(i)),number_of_err=number_of_err+1;end;
- if(desion8~=dsource8(i)),number_of_err=number_of_err+1;end;
- %CD MAKE DECISION
- % CD make decision
- if(I1<0), desion11=-1;
- else desion11=1;
- end;
- if(I2<0), desion21=-1;
- else desion21=1;
- end;
- if(I3<0), desion31=-1;
- else desion31=1;
- end;
- if(I4<0), desion41=-1;
- else desion41=1;
- end;
- if(I5<0), desion51=-1;
- else desion51=1;
- end;
- if(I6<0), desion61=-1;
- else desion61=1;
- end;
- if(I7<0), desion71=-1;
- else desion71=1;
- end;
- if(I8<0), desion81=-1;
- else desion81=1;
- end;
- if(desion11~=dsource1(i)),number_of_err1=number_of_err1+1;end;
- if(desion21~=dsource2(i)),number_of_err1=number_of_err1+1;end;
- if(desion31~=dsource3(i)),number_of_err1=number_of_err1+1;end;
- if(desion41~=dsource4(i)),number_of_err1=number_of_err1+1;end;
- if(desion51~=dsource5(i)),number_of_err1=number_of_err1+1;end;
- if(desion61~=dsource6(i)),number_of_err1=number_of_err1+1;end;
- if(desion71~=dsource7(i)),number_of_err1=number_of_err1+1;end;
- if(desion81~=dsource8(i)),number_of_err1=number_of_err1+1;end;
- end
- err(k)=number_of_err/(3*N)%MMSE ber
- err1(k)=number_of_err1/(3*N)%CD ber
- err2(k)=number_of_err2/(3*N)
- end
- %plot(snr_indb,err);
- semilogy(snr_indb,err,'k');%MMSE ber
- grid on;
- hold on;
- semilogy(snr_indb,err1,'r');%CD ber
- hold on
- semilogy(snr_indb,err2,'^-')
- legend('MMSE','CD','不加信道估计');
- 01_006_m
4.完整MATLAB程序
V
-
相关阅读:
一篇全面而且透彻的RabbitMQ性能优化指南
IDEA新建SpringBoot项目时启动编译报错:Error:java: 无效的源发行版: 17
简述php文件上传原理
健康防猝指南1:体重和减肥的秘密
java面试题整理《redis篇》八
如何使用飞书快捷指令无感记账,ios版
自定义spring-boot-starter
零售超市如何应对消费者需求?非常全面!
解读宁波IATF16949认证:开启成功之门的钥匙️
2022年7月小结
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/hlayumi1234567/article/details/127892581
