-
神经网络拟合图像:Implicit Neural Representations with Periodic Activation Functions
1. Implicit Neural Representations with Periodic Activation Functions
0. 什么是隐式神经表示
就是说用一个神经网络表示一个函数。
隐式神经表示(Implicit Neural Representations)是指通过神经网络的方式将输入的图像、音频、以及点云等信号表示为函数的方法[1] 。
对于输入x找到一个合适的网络F使得网络F能够表征函数Φ由于函数Φ是连续的,从而使得原始信号是连续的、可微的。这么干的好处在于,可以获取更高效的内存管理,得到更加精细的信号细节,并且使得图像在高阶微分情况下仍然是存在解析解的,并且为求解反问题提供了一个全新的工具。
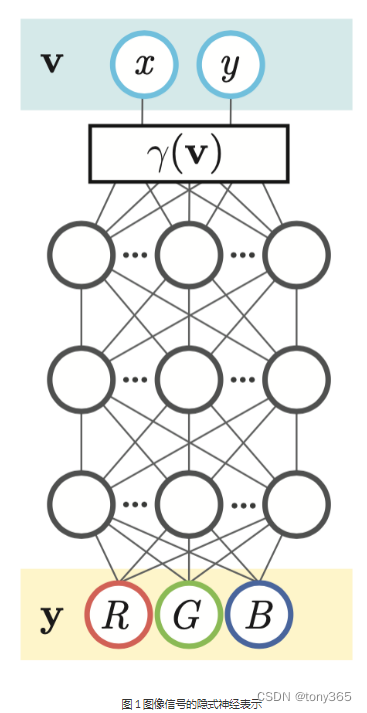
以图像信号的隐式神经表示举例:
对于图像v而言,对于每个图像平面内的像素点存在像素的坐标(x,y),同时存在每个像素的RGB值,使用一个神经网络学习坐标(x,y)和RGB值的关系,得到训练后的网络Φ。这里的Φ就是图像v的隐式神经表示。
[1]https://www.ipanqiao.com/entry/713
1. 了解SineLayer的初始化,还是没了解。。。
本文提出使用 sin 函数代替常规的relu等激活函数,来拟合更复杂的信息,sin 函数的使用增加了网络的结构复杂度,同时也提高了网络的表现能力。加入sin 函数后网络的参数初始化很重要,没有好的初始化会导致比较差的效果。
作者通过一系列证明推导出一个比较好的参数初始化方案。
初始化方案的关键思想是保持通过网络的激活的分布,这样初始化时的最终输出就不依赖于层数。
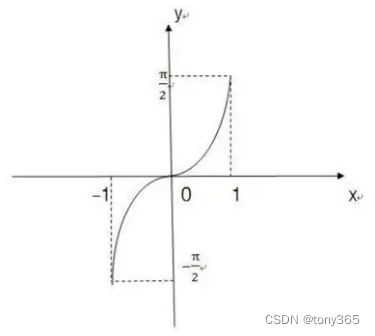
正弦函数y=sin x在[-π/2,π/2]上的反函数,叫做反正弦函数,记作arcsinx。
表示一个正弦值为x的角,该角的范围在[-π/2,π/2]区间内。
定义域[-1,1] ,值域[-π/2,π/2]。(1) arcsinx是 (主值区)上的一个角(弧度数) 。
(2) 这个角(弧度数)的正弦值等于x,即sin(arcsinx)=x.
2. 均匀分布

3. Lemma 1.1
通过 arc sin函数和 均匀分布的知识,可以理解论文中的Lemma1.1 的推导过程。
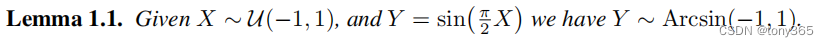
其中 PDF 和 cdf 分别是
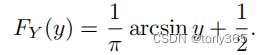
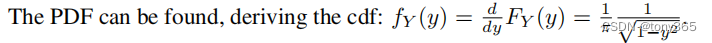
等等证明,没看太懂,直接看code吧
4. 一个简单实验, 拟合图像
4.1 网络模型代码如下,就是全连接网络,
但是激活函数是sine函数,另外就是SineLayer的初始化方法比较重要,论文中有大量证明。
class SineLayer(nn.Module): # See paper sec. 3.2, final paragraph, and supplement Sec. 1.5 for discussion of omega_0. # If is_first=True, omega_0 is a frequency factor which simply multiplies the activations before the # nonlinearity. Different signals may require different omega_0 in the first layer - this is a # hyperparameter. # If is_first=False, then the weights will be divided by omega_0 so as to keep the magnitude of # activations constant, but boost gradients to the weight matrix (see supplement Sec. 1.5) def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, bias=True, is_first=False, omega_0=30): super().__init__() self.omega_0 = omega_0 self.is_first = is_first self.in_features = in_features self.linear = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=bias) self.init_weights() def init_weights(self): with torch.no_grad(): if self.is_first: self.linear.weight.uniform_(-1 / self.in_features, 1 / self.in_features) else: self.linear.weight.uniform_(-np.sqrt(6 / self.in_features) / self.omega_0, np.sqrt(6 / self.in_features) / self.omega_0) def forward(self, input): return torch.sin(self.omega_0 * self.linear(input)) def forward_with_intermediate(self, input): # For visualization of activation distributions intermediate = self.omega_0 * self.linear(input) return torch.sin(intermediate), intermediate class Siren(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features, hidden_layers, out_features, outermost_linear=False, first_omega_0=30, hidden_omega_0=30.): super().__init__() self.net = [] self.net.append(SineLayer(in_features, hidden_features, is_first=True, omega_0=first_omega_0)) for i in range(hidden_layers): self.net.append(SineLayer(hidden_features, hidden_features, is_first=False, omega_0=hidden_omega_0)) if outermost_linear: final_linear = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features) with torch.no_grad(): final_linear.weight.uniform_(-np.sqrt(6 / hidden_features) / hidden_omega_0, np.sqrt(6 / hidden_features) / hidden_omega_0) self.net.append(final_linear) else: self.net.append(SineLayer(hidden_features, out_features, is_first=False, omega_0=hidden_omega_0)) self.net = nn.Sequential(*self.net) def forward(self, coords): coords = coords.clone().detach().requires_grad_(True) # allows to take derivative w.r.t. input output = self.net(coords) return output, coords def forward_with_activations(self, coords, retain_grad=False): '''Returns not only model output, but also intermediate activations. Only used for visualizing activations later!''' activations = OrderedDict() activation_count = 0 x = coords.clone().detach().requires_grad_(True) activations['input'] = x for i, layer in enumerate(self.net): if isinstance(layer, SineLayer): x, intermed = layer.forward_with_intermediate(x) if retain_grad: x.retain_grad() intermed.retain_grad() activations['_'.join((str(layer.__class__), "%d" % activation_count))] = intermed activation_count += 1 else: x = layer(x) if retain_grad: x.retain_grad() activations['_'.join((str(layer.__class__), "%d" % activation_count))] = x activation_count += 1 return activations- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
4.2 获取到图像
def laplace(y, x): grad = gradient(y, x) return divergence(grad, x) def divergence(y, x): div = 0. for i in range(y.shape[-1]): div += torch.autograd.grad(y[..., i], x, torch.ones_like(y[..., i]), create_graph=True)[0][..., i:i + 1] return div def gradient(y, x, grad_outputs=None): if grad_outputs is None: grad_outputs = torch.ones_like(y) grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [x], grad_outputs=grad_outputs, create_graph=True)[0] return grad def get_cameraman_tensor(sidelength): img = Image.fromarray(skimage.data.camera()) transform = Compose([ Resize(sidelength), ToTensor(), Normalize(torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor([0.5])) ]) img = transform(img) return img import cv2 img0 = get_cameraman_tensor(128) img0 = img0.cpu().permute(1,2,0).numpy().astype(np.float32) #img1 = (img0 - img0.min()) / (img0.max() - img0.min()) plt.imshow(img0, 'gray') plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
4.3 训练
模型的输入是 像素坐标,输出是像素值
通过训练后即用网络参数来拟合一张图像class ImageFitting(Dataset): def __init__(self, sidelength): super().__init__() img = get_cameraman_tensor(sidelength) self.pixels = img.permute(1, 2, 0).view(-1, 1) self.coords = get_mgrid(sidelength, 2) def __len__(self): return 1 def __getitem__(self, idx): if idx > 0: raise IndexError return self.coords, self.pixels- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
训练方法比较常规
siz = 128 cameraman = ImageFitting(siz) dataloader = DataLoader(cameraman, batch_size=1, pin_memory=True, num_workers=0) img_siren = Siren(in_features=2, out_features=1, hidden_features=256, hidden_layers=3, outermost_linear=True) img_siren.cuda() total_steps = 2501 # Since the whole image is our dataset, this just means 500 gradient descent steps. steps_til_summary = 2500 optim = torch.optim.Adam(lr=1e-4, params=img_siren.parameters()) model_input, ground_truth = next(iter(dataloader)) model_input, ground_truth = model_input.cuda(), ground_truth.cuda() for step in range(total_steps): model_output, coords = img_siren(model_input) loss = ((model_output - ground_truth) ** 2).mean() if not step % steps_til_summary: print("Step %d, Total loss %0.6f" % (step, loss)) img_grad = gradient(model_output, coords) img_laplacian = laplace(model_output, coords) fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(18, 6)) axes[0].imshow(model_output.cpu().view(siz, siz).detach().numpy(), 'gray') axes[1].imshow(img_grad.norm(dim=-1).cpu().view(siz, siz).detach().numpy(), 'gray') axes[2].imshow(img_laplacian.cpu().view(siz, siz).detach().numpy(), 'gray') plt.show() optim.zero_grad() loss.backward() optim.step()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
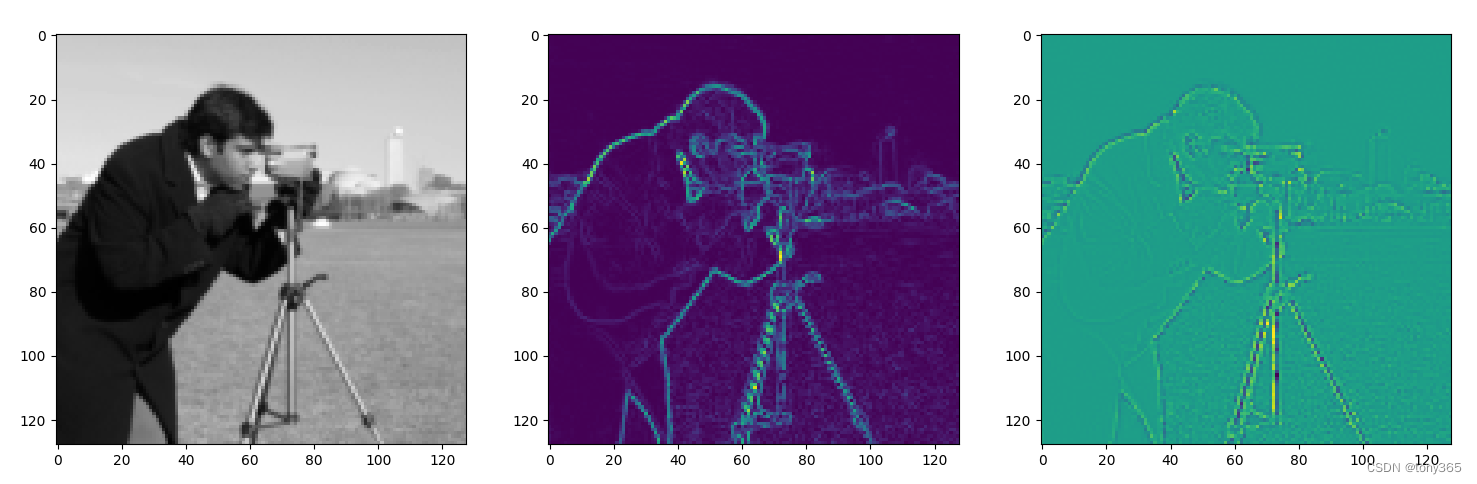
得到拟合的图像,一阶梯度图,二阶laplace 图像。
-
相关阅读:
金九银十投递:美团、滴滴、360,面经回馈与经验分享(附学习路线+思维导图+刷题指南)
『FPGA通信接口』LVDS接口(4)LVDS接收端设计
PDF被限制会出现什么情况?
B. Catching Cheaters(最长公共子序列变形)
基于Yolov8的交通标志牌(TT100K)识别检测系统
【算法leetcode】2325. 解密消息(rust和go重拳出击)
WebGL 与 WebGPU比对[5] - 渲染计算的过程
RMAN-05021
【微信小程序开发】自定义组件以及页面布局设计
Linux学习——线程的取消和互斥
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/tywwwww/article/details/127884385