-
高光谱解混和图片去噪(Matlab代码实现)
👨🎓个人主页:研学社的博客
💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录

💥1 概述
本文讲解了图像被混合噪声污染时的高光谱解混算法。还可以减少噪音。噪声可能包括线带、高斯噪声和脉冲噪声。它解决了以下优化问题:
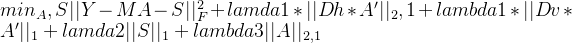
M : 混合矩阵。它是包含端部的光谱特征的矩阵;
Y : 噪声高光谱图像。这是发送到解混算法的图像。
A : 丰度矩阵。
S :稀疏噪声。它表示脉冲噪声以及线带。
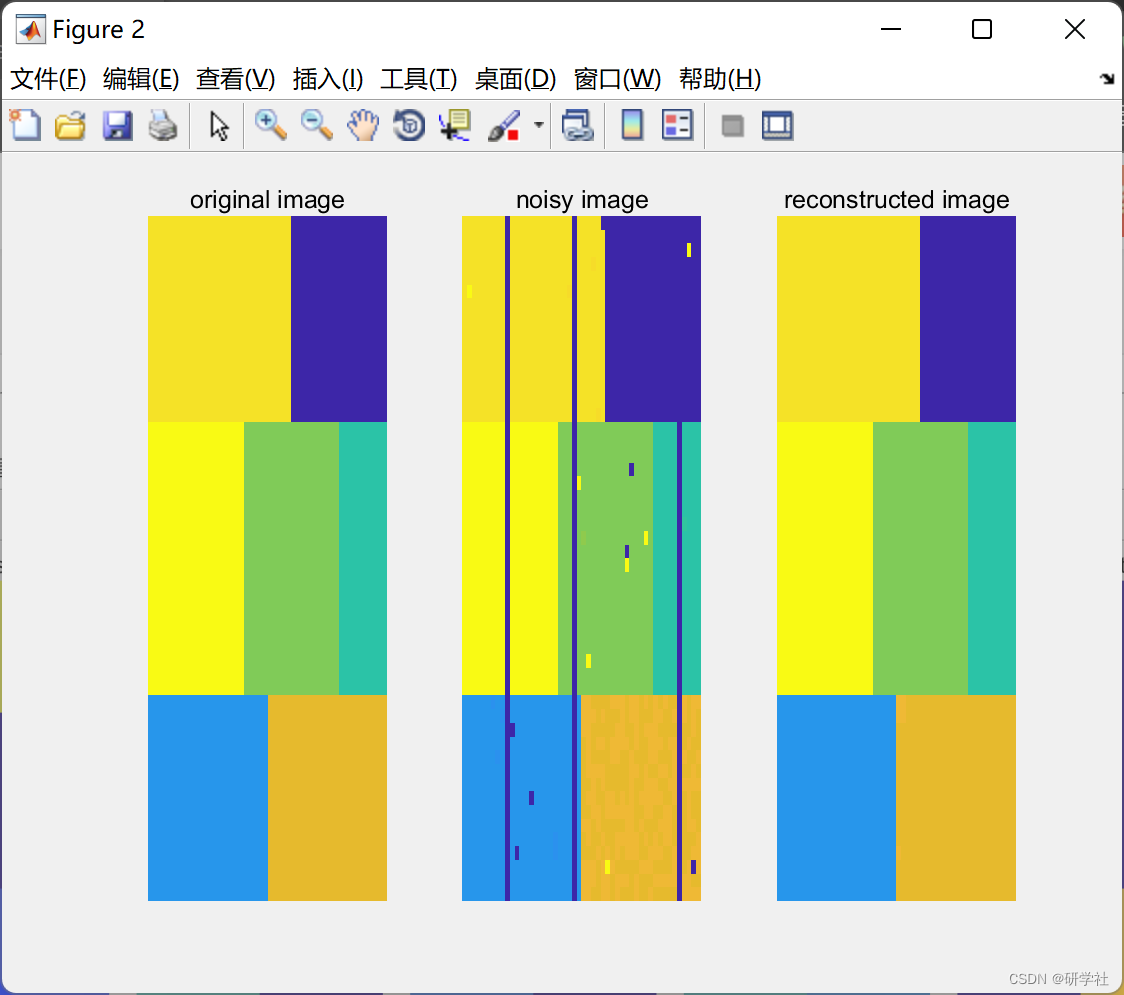
Dh, Dv :二维水平和垂直有限差分算子。📚2 运行结果

部分代码:
%% showing original, noisy, and denoised image
figure;
band=1;
subplot(131);
imagesc(img(:,:,band)); axis 'off'; title('original image');
subplot(132);
imagesc(noisy2(:,:,band)); axis 'off'; title('noisy image');
subplot(133)
imagesc(rec(:,:,band)); axis 'off'; title('reconstructed image');end
%% This is the main function
function A=funJSTV(M,Y,opts)lambda1=opts.lambda1;
lambda2=opts.lambda2; lambda3=opts.lambda3;
mu1=opts.mu1; mu2=opts.mu2;iter=opts.iter; m=opts.m; n=opts.n;
[~,e]=size(M); [~,p]=size(Y);Dh=TVmatrix(m,n,'H'); %horizontal total variation
Dv=TVmatrix(m,n,'V'); %vertical total variation
D=Dh'*Dh+Dv'*Dv;
MtM=M'*M;
A=zeros(e,p);
B1=zeros(p,e);B2=B1; Y1=Y; B3=zeros(e,p);%% main iteration
for i =1:iter
for j=1:5
P=softTh(Dh*(A')+B1,lambda1/mu1);
Q=softTh(Dv*(A')+B2,lambda1/mu1);
R=softThL21(A+B3,lambda3/mu2);
S=softTh(Y1-M*A,1/lambda2);
RHS=(mu1*(P-B1)')*Dh+ (mu1*(Q-B2)')*Dv+ M'*(Y1-S) + mu2*(R-B3);
[a,~]=pcg(@afun,RHS(:),1e-15,5);
A=reshape(a,e,p);
B1=B1+Dh*(A')-P;
B2=B2+Dv*(A')-Q;
B3=B3+A-R;
A=max(0,A);
end
Y1=Y1+Y-M*A-S;
end
function y = afun(x)
X=reshape(x,e,p);
temp=MtM*X+mu1*X*D +mu2*X;
%temp=mtimesx(MtM,X,'BLAS')+mu1*mtimesx(X,D,'BLAS');
y=temp(:);
end
end
%% Soft-thresholding for L21-norm minimization
function X=softThL21(B,lambda)
[m,~]=size(B);
D= spdiags(sqrt(sum(B.^2,2))-lambda/2,0,m,m);
X=max(0,D)*normrGood(B);end
%% Simple soft-thresholding
function X=softTh(B,lambda)
X=sign(B).*max(0,abs(B)-(lambda/2));
end
%% Total variation
function opD=TVmatrix(m,n,str)if str=='H' % This will give matrix for Horizontal Gradient
D = spdiags([-ones(n,1) ones(n,1)],[0 1],n,n);
D(n,:) = 0;
D = kron(D,speye(m));
elseif str=='V' %This will give matrix for Verticle Gradient
D = spdiags([-ones(m,1) ones(m,1)],[0 1],m,m);
D(m,:) = 0;
D = kron(speye(n),D);
end
opD=D;end
%% PSNR calculation
function [cpsnr,psnr]=myPSNR(org,recon,skip)
%skip : to skip some boundary lines
org=org(skip+1:end-skip,skip+1:end-skip,:);
recon=recon(skip+1:end-skip,skip+1:end-skip,:);
[m, n,~]=size(org);if strcmp(class(org),class(recon))
sse=squeeze(sum(sum((org-recon).^2))); %square sum of error
mse=sse./(m*n); %mean square error of each band.
maxval=squeeze(max(max(org)));
psnr= 10*log10( (maxval.^2) ./mse);
cpsnr=mean(psnr);
end
end%% histogram equilization of each band
function img=myhisteq(img)
%make each band in zero to one range
for i=1:size(img,3)
img(:,:,i)=mat2gray(img(:,:,i));
end
end
%% add Gaussian noise of given SNR
function [noisy,sigma]=addGaussianNoise(img,snr)
%This function will add Gaussian noise of given SNR.
%img is image in size
noisy=zeros(size(img));
for i=1:size(img,3)
band=img(:,:,i);
varNoise= norm(band(:))^2/(length(band(:)) * (10^ (snr/10)));
noisy(:,:,i)=band+sqrt(varNoise)*randn(size(band));
end
sigma=sqrt(varNoise);end
🎉3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
[1]Hyperspectral Unmixing in the Presence of Mixed Noise using Joint-Sparsity and Total-Variation by Hemant Kumar Aggarwal, Angshul Majumdar, in IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing (JSTARS), 2016
🌈4 Matlab代码实现
-
相关阅读:
PPT的只读模式如何设置和取消?
Oracle 2019c安装闪退解决过程
c++里对 new 、delete 运算符的重载
基于SSM+Vue的网络教学平台的设计与实现的设计与实现
FullCalendar日历组件:进行任务增删改,参考gitee例子修改
react 使用 craco库 配置 @ 路径,以及 jsconfig.json或者tsconfig.json 配置智能提示
读懂“渠道分销数字化转型”,纷享销客用5个核心角色驱动力解构
C: . 与 -> 的区别
【计算机视觉】1. 计算机视觉基础理论知识和框架(Basic Concepts)
Vue3框架中CompositionAPI的基本使用(第十课)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46039719/article/details/127875914