-
刷题日记【第十一篇】-笔试必刷题【小易的升级之路+找出字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符+微信红包+计算字符串的编辑距离】
1.计算字符串的编辑距离【动态规划编程题】
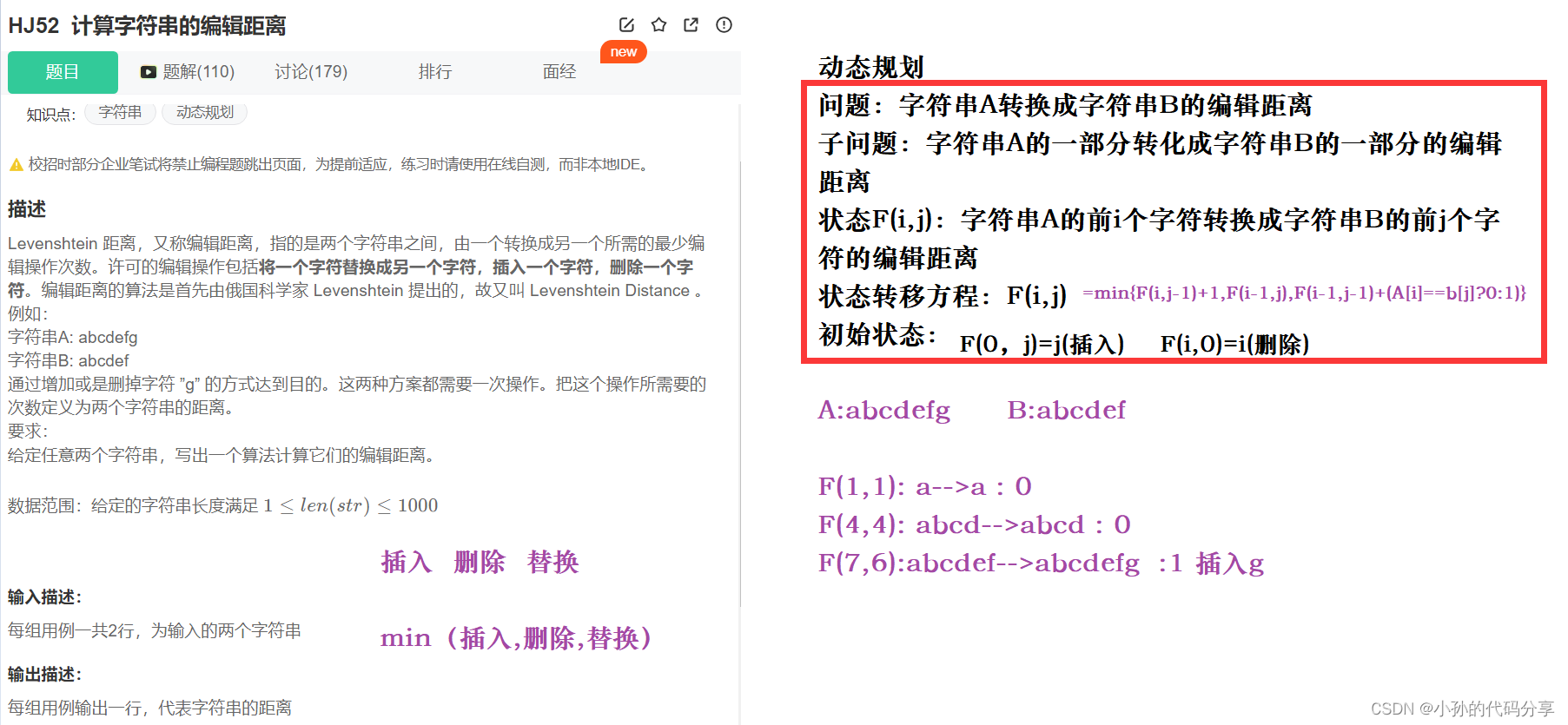
import java.util.Scanner; import java.io.*; // 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息 public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{ BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String str1 ; while((str1=reader.readLine())!=null){ String str2 = reader.readLine(); System.out.println(getDistance(str1,str2)); } } public static int getDistance(String str1, String str2) { char[] ch1 = str1.toCharArray(); char[] ch2 = str2.toCharArray(); int len1 = ch1.length; int len2 = ch2.length; //定义一个矩阵 int[][] dist = new int[len1 + 1][len2 + 1]; //初始状态 F(i,0) = i F(0,j) = j for (int i = 0; i <= len1; ++i) { dist[i][0] = i; } for (int j = 0; j <= len2; ++j) { dist[0][j] = j; } for (int i = 1; i <= len1; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j <= len2; ++j) { //F[i,j] = min(F(i-j,j)+1,F(i,j-1)+1,F(i-1,j-1)+(ch1[i]==ch2[j]?0:1)) // 插入 删除 替换 dist[i][j] = Math.min(dist[i - 1][j] + 1, dist[i][j - 1] + 1); //在和替换比较 if (ch1[i - 1] == ch2[j - 1]) { dist[i][j] = Math.min(dist[i ][j], dist[i - 1][j - 1]); } else { dist[i][j] = Math.min(dist[i ][j], dist[i - 1][j - 1]+1); } } } return dist[len1][len2]; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
2.微信红包

import java.util.*; public class Gift { public int getValue(int[] gifts, int n) { // write code here int mid = gifts.length / 2; int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < gifts.length; i++) { if (gifts[i] == gifts[mid]) { count++; } } if (count > mid) { return gifts[mid]; } return 0 ; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
3.找出字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符
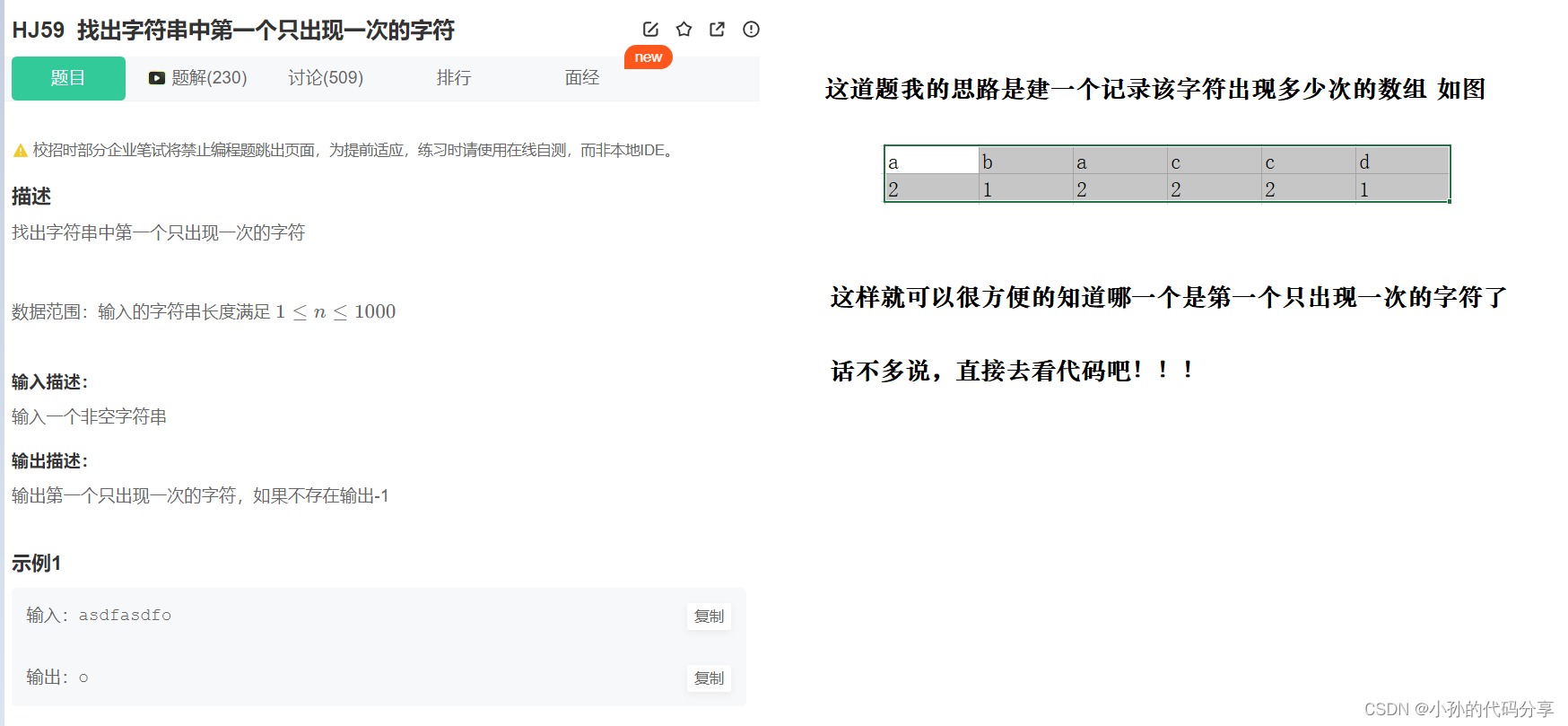
import java.util.Scanner; // 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息 public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String str = in.nextLine(); int[] arr = new int[str.length()]; for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++){ arr[i]= count(str,str.charAt(i)); } for(int j =0;j<arr.length;j++){ if(arr[j]==1){ System.out.println(str.charAt(j)); break; } if(none(arr)==-1){ System.out.println(-1); break; } } } public static int none(int[] arr){ int count = 0; for(int i= 0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(arr[i]!=1){ count++; } } if(count==arr.length){ return -1; } return 0; } public static int count(String str,char ch){ int count = 0; for(int i =0;i<str.length();i++){ if(str.charAt(i)==ch){ count++; } } return count; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
4.小易的升级之路
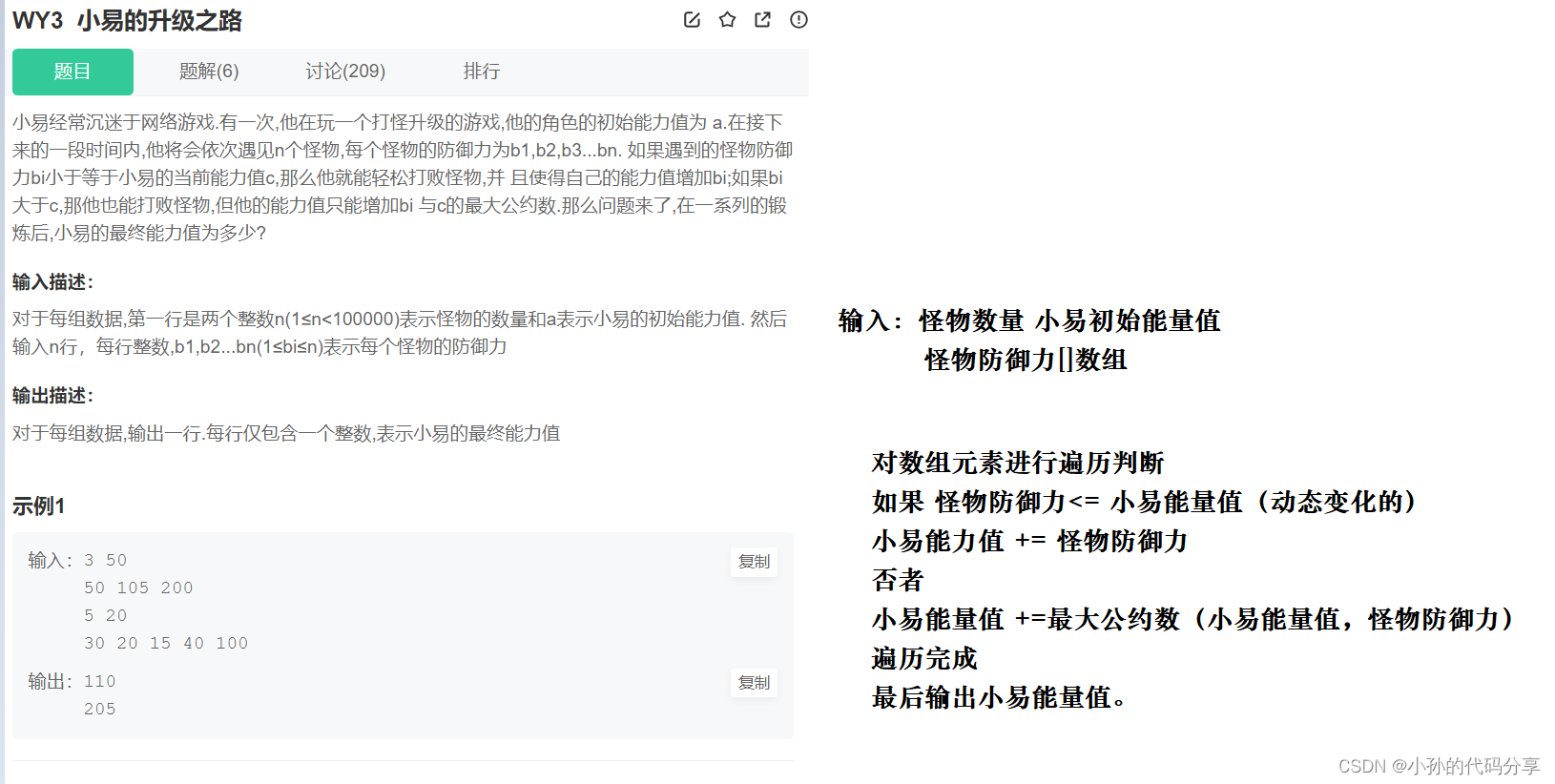
import java.util.Scanner; // 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息 public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); // 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别 while (in.hasNextInt()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 case int n = in.nextInt(); int c = in.nextInt(); int[] arr = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { arr[i] = in.nextInt(); } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (arr[i] <= c) { c += arr[i]; } else { c += zdgy(c, arr[i]); } } System.out.println(c); } } public static int zdgy(int c, int arr) { for (int i = c; i > 0; i--) { if (arr % i == 0 && c % i == 0) { return i; } } return 0 ; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
4.数据结构中具有记忆功能的是【栈】
下列数据结构具有记忆功能的是? C
A. 队列 B. 循环队列 C. 栈 D. 顺序表
记忆功能比如, 浏览器的回退功能,文本编辑器的撤销功能,都属于记忆功能
栈的LIFO特性,A函数调用B函数,B函数调用C函数,然后最后一层一层返回,这也具有记忆功能5.递归程序的优化一般为 【尾递归优化】
对递归程序的优化的一般的手段为(A) A. 尾递归优化 B. 循环优化 C. 堆栈优化 D. 停止值优化 比如快速排序和归并排序,在递归的终止条件是 l 是区间最左侧,r 是区间最右侧 //终止条件 (l >= r){return ;} //在递归终止条件处进行优化 //当区间个数较小时,采用插入排序来优化 (r - l <= 15) ---> 采用插入排序 所以这种对递归的优化一般都是 尾递归优化- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
6.时间复杂度的判断
A 红黑树插入操作的平均时间复杂度为O(logn),最坏时间复杂度为O(logn) B B+树插入操作的平均时间复杂度为O(logn),最坏时间复杂度为O(logn) C Hash表插入操作的平均时间复杂度为O(logn),最坏时间复杂度为O(n) D 排序链表插入操作的平均时间复杂度为O(n),最坏时间复杂度为O(n)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
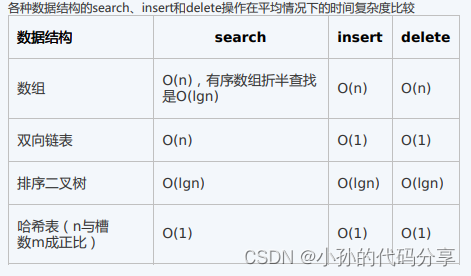
由图可知,Hash表插入操作的平均时间复杂度为O(1),最坏时间复杂度为O(1)7.为提高散列(Hash)表的查找效率,可以采取的正确措施是(II,III )
Ⅰ.增大装填(载)因子 Ⅱ.设计冲突(碰撞)少的散列函数 Ⅲ.处理冲突(碰撞)时避免产生聚集(堆积)现象- 1
- 2
- 3
散列表的查找效率取决于:散列函数、处理冲突的方法和装填因子。 冲突的产生概率与装填因子成正比,故错。
采取合适的冲突处理方法可以避免聚集现象,也提高查找效率。 -
相关阅读:
Git clone The requested URL returned error: 403 错误的解决办法
Page Cache的产生和释放
freeRTOS--任务通知
SpringMVC 11 Ajax验证用户名体验和拦截器
Echarts 3D饼图开发
【C++】6-19 方阵的转置 分数 10
YOLO物体检测-系列教程7:YOLOV3源码解读5之 Darknet
Python少儿编程小课堂(六)入门篇(6)
牛客剑指offer刷题算法篇
Docker安装mysql & redis
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_53939785/article/details/127805650
