-
Java中的字符串
🙉 作者简介: 全栈领域新星创作者 ;天天被业务折腾得死去活来的同时依然保有对各项技术热忱的追求,把分享变成一种习惯,再小的帆也能远航。
🏡 个人主页:xiezhr的个人主页
java中的字符串
一、简介
Java字符串就是Unicode字符序列。Java里没有内置的字符串类型,而是在标准的类库中提供了一个预定义类,String。每个用双引号""括起来的都是String类的一个实例。
字符串是日常开发中最常用, Java字符串的一个重要特点就是字符串不可变
二、字符串定义
2.1 直接定义字符串
String str = "www.xiezhrspace.cn"; //或者 String str; str = "www.xiezhrspace.cn";- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2.2 通过使用 String 类的构造方法来创建字符串
//① String() 初始化新创建的 String对象,使其表示空字符序列 String str = new String(); //② String(String original) 初始化新创建的String对象,使其表示与参数相同的字符序列;换句话说,新创建的字符串是参数字符串的副本。 String str = new String("www.xiezhrspace.cn") //③ String(char[] value) 分配一个新的字符串,将参数中的字符数组元素全部变为字符串。该字符数组的内容已被复制,后续对字符数组的修改不会影响新创建的字符串 char a[] = {'H','e','l','l','0'}; String sChar = new String(a); //④ String(char[] value, int offset, int count) 分配一个新的 String,它包含来自该字符数组参数一个子数组的字符。offset 参数是子数组第一个字符的索引,count 参数指定子数组的长度。该子数组的内容已被赋值,后续对字符数组的修改不会影响新创建的字符串 char a[]={'H','e','l','l','o'}; String sChar=new String(a,1,4); ...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
String提供的构造方法很多,文章只列举常用的,其余的可自行查找Java帮助文档。帮助文档的使用参照下一小节三、如何使用Java API帮助文档
3.1 帮助文档下载地址
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/
下载完解压后目录如下
3.2 帮助文档使用
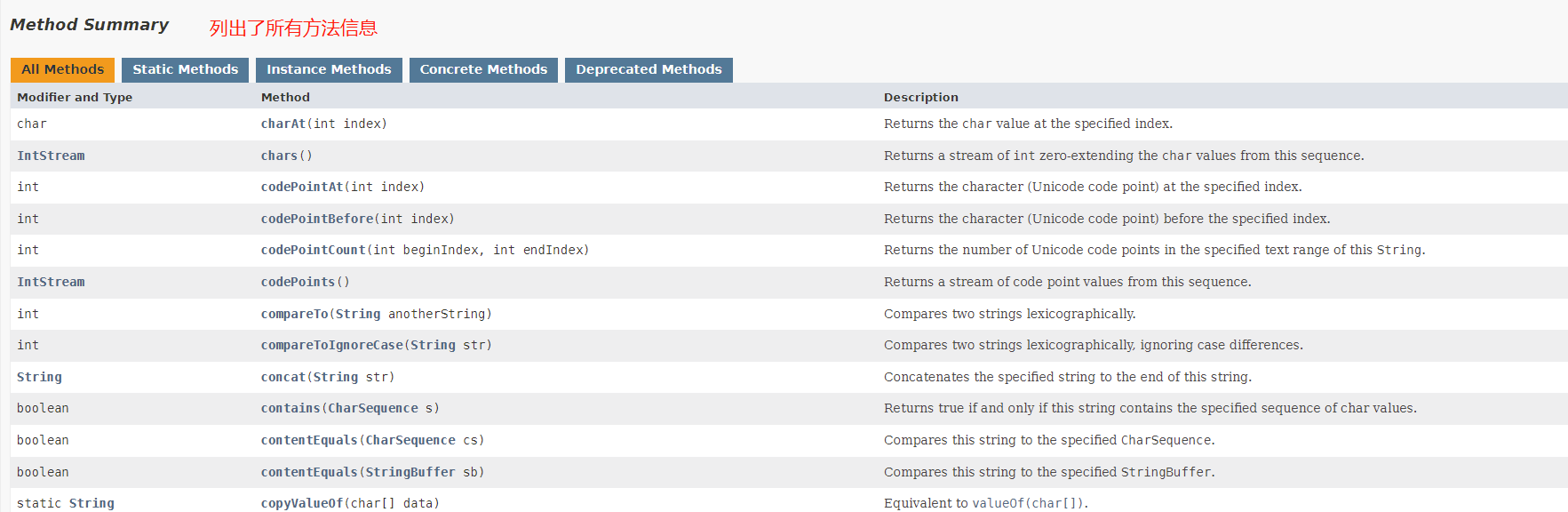
① 双击index.html打开
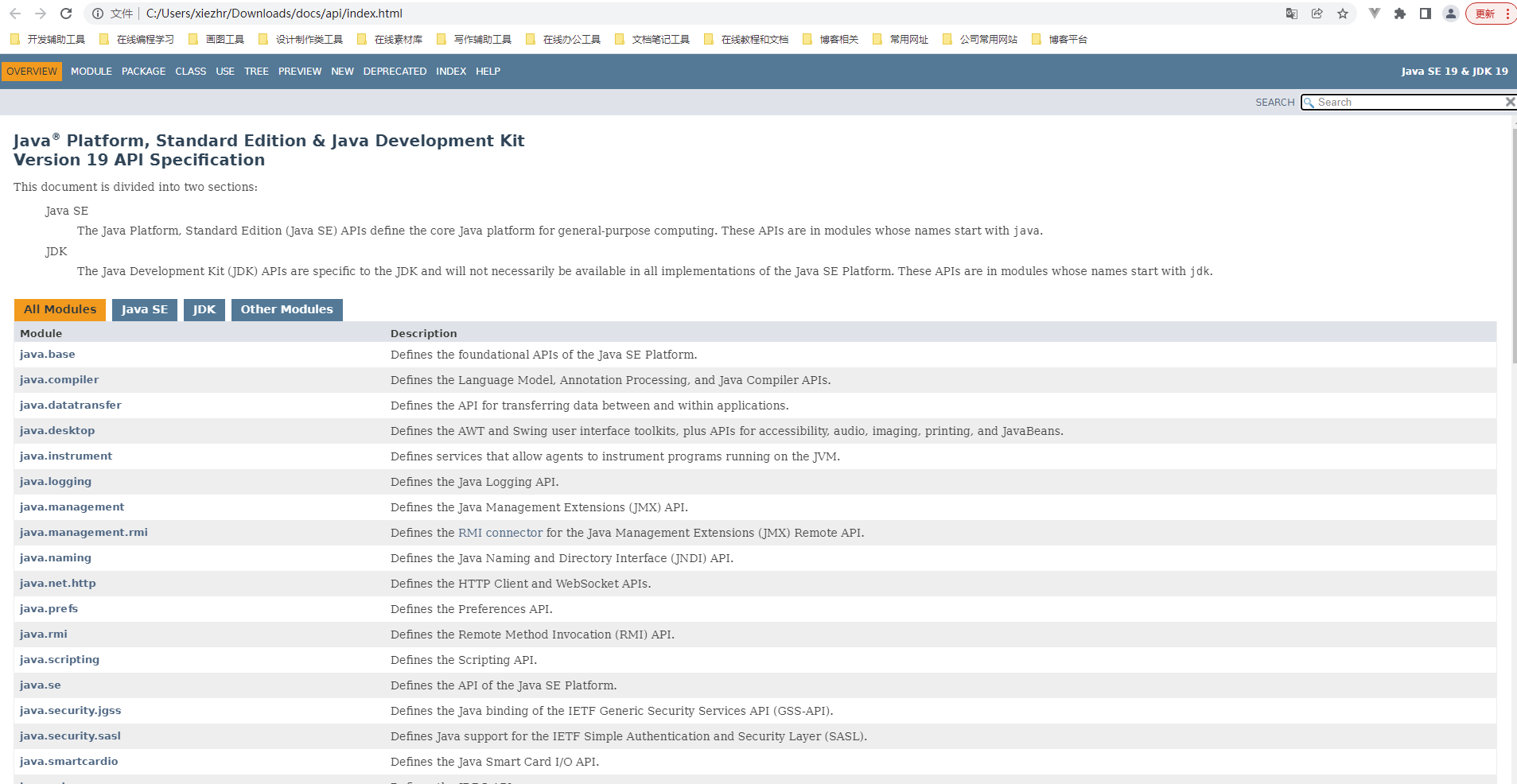
② 搜索框中输入关键字String找到java.lang包下的String
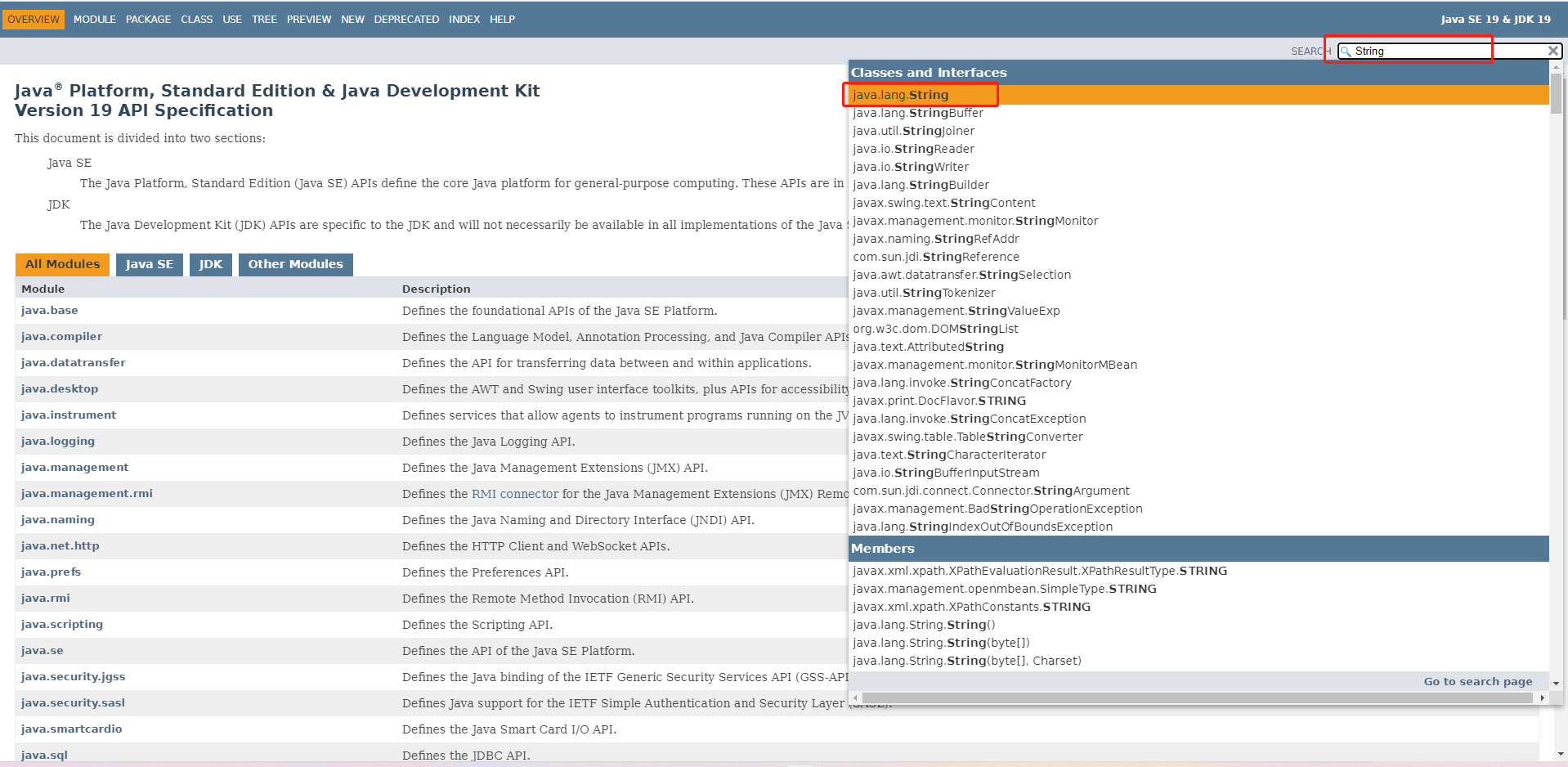
③ 查看String类的帮助信息
String类的基本信息
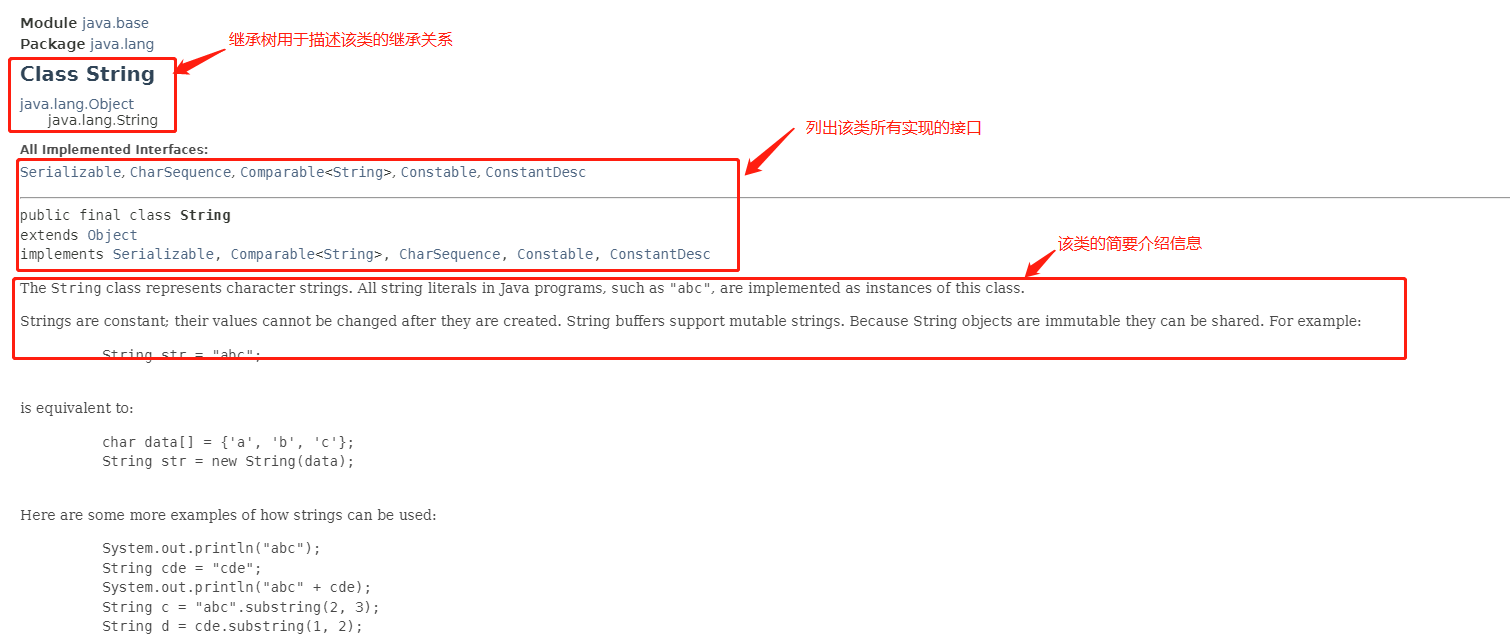
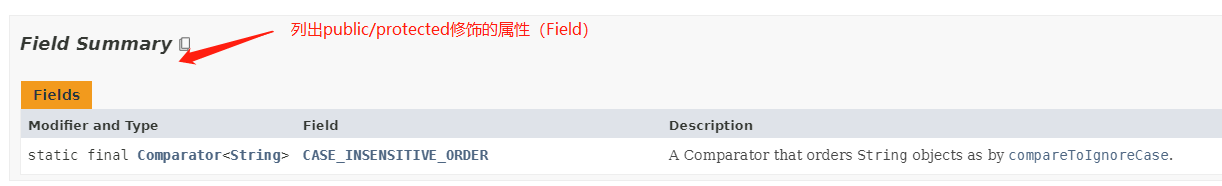
String类public/protected 修饰的属性
String类public/protected 修饰所有构造器
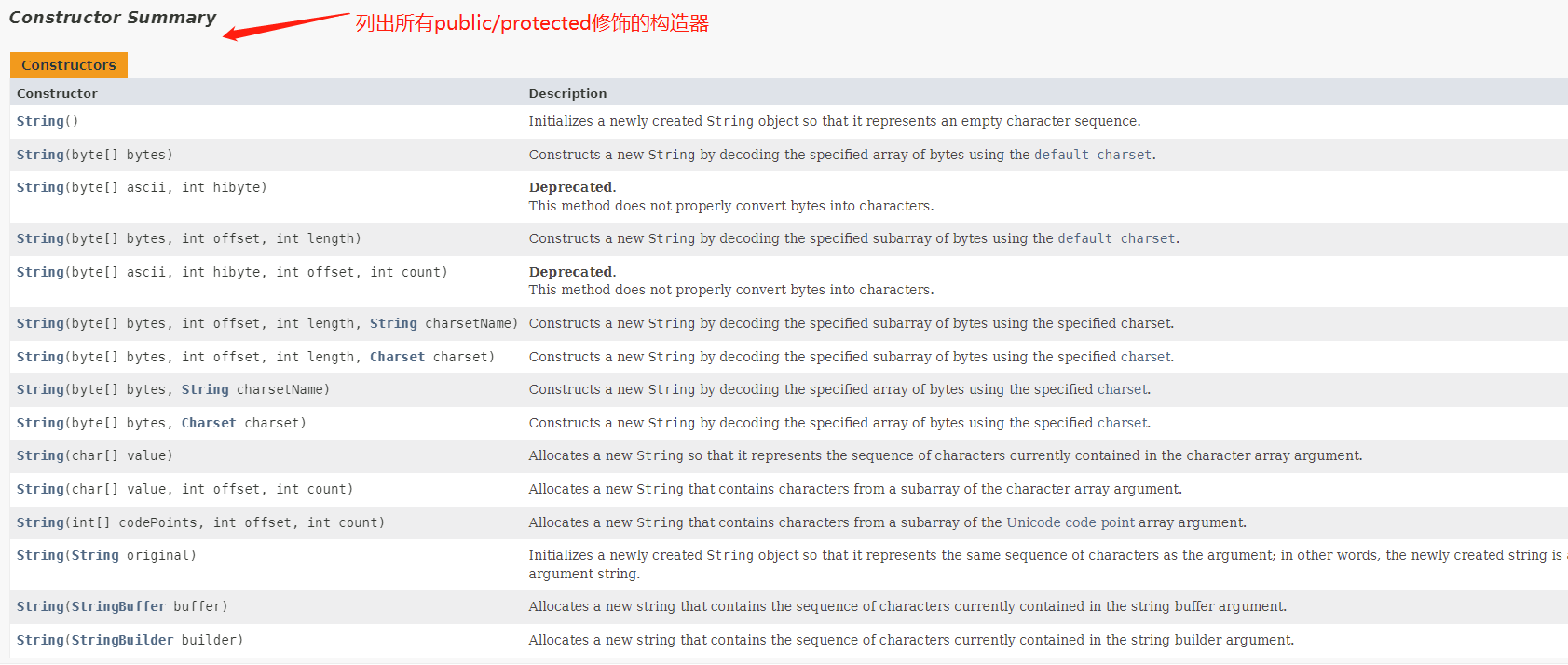
String类public/protected 修饰所有构造器
3.2 中文帮助文档
如果小伙伴看英文比较吃力,这里也提供了中文帮助文档下载地址(文档包含jdk1.6~jdk10 的帮助文档)。
注: 中文帮助文档采用的是工具翻译的,有些地方可能不准确,请结合着官方英文文档查看链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Rh-o1i-LCjEPNB4EyO9FrQ
提取码:7kms
四、 String字符串和int、double、float 的相互转换
4.1 String 转int
String 转换 int 时,String 的值一定是整数,否则会报数字转换异常(java.lang.NumberFormatException)
Integer.parseInt(String s)Integer.valueOf(String s)
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("123")); System.out.println(Integer.valueOf("345")); } } //输出结果为 123 345- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
4.2 String 转Double、Float
String 转换 Double、Float 时,String 的值一定是浮点类型,否则会报数字转换异常(java.lang.NumberFormatException)
Double.parseDouble(String s)Double.valueOf(String s)Float.parseFloat(String s)Float.valueOf(String s)
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Double.parseDouble("12.45")); System.out.println(Double.valueOf("12.45")); System.out.println(Float.parseFloat("25.68")); System.out.println(Float.valueOf("25.68")); } } //输出结果为 12.45 12.45 25.68 25.68- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
4.3 int转换为String
使用第三种方法相对第一第二种耗时比较大。在使用第一种 valueOf() 方法时,注意 valueOf 括号中的值不能为空,否则会报空指针异常(NullPointerException)
String.valueOf( Integer i)Integer.toString( Integer i)"" + Integer i
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(String.valueOf(123)); System.out.println(Integer.toString(345)); System.out.println(456 + ""); } } //输出结果为 123 345 456- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
4.3 Double、Float转换为String
使用第三种方法相对第一第二种耗时比较大。在使用第一种 valueOf() 方法时,注意 valueOf 括号中的值不能为空,否则会报空指针异常(NullPointerException)
String.valueOf(Double d)Double.toString(Double d)"" + Double dString.valueOf(Float d)Float.toString(Float d)"" + Float f
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(String.valueOf(20.48d)); System.out.println(Double.toString(20.48d)); System.out.println(20.48d + ""); System.out.println(String.valueOf(10.24f)); System.out.println(Float.toString(10.24f)); System.out.println(10.24f + ""); } } } } //输出结果为 20.48 20.48 20.48 10.24 10.24 10.24- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
五、字符串拼接
5.1 使用连接运算符“+”
str1+str2public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("微信公众号:" + "XiezhrSpace"); } } //输出 微信公众号:XiezhrSpace- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
5.2 使用 concat() 方法
str1.concat(str2)public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("个人博客:".concat("www.xiezhrspace.cn")); } } // 输出 个人博客:www.xiezhrspace.cn- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
六 、获取字符串长度
str.length()public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "公众号:XiezhrSpace"; String str2 = "个人博客:www.xiezhrspace.cn"; System.out.println("str1长度:"+str1.length()); System.out.println("str2长度:"+str2.length()); } } //输出 str1长度:15 str2长度:23- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
七、字符串大小写转换
str.toLowerCase()将字符串中的字母全部转换为小写,非字母不受影响str.toUpperCase()将字符串中的字母全部转换为大写,非字母不受影响
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str ="Hello World!"; System.out.println("原始字符串:"+str); System.out.println("使用toLowerCase() 方法之后为:" + str.toLowerCase()); System.out.println("使用toUpperCase() 方法之后为:" + str.toUpperCase()); } } //输出 原始字符串:Hello World! 使用toLowerCase() 方法之后为:hello world! 使用toUpperCase() 方法之后为:HELLO WORLD!- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
八 、去除字符串中的空格
字符串中存在的首尾空格一般情况下都没有任何意义,如字符串“ Hello ”,但是这些空格会影响到字符串的操作,如连接字符串或比较字符串等,所以应该去掉字符串中的首尾空格,这需要使用 String 类提供的 trim() 方法
str.trim()str.replace((char) 12288, ' '); str.trim()
注意:
trim()只能去掉字符串中前后的半角空格(英文空格),而无法去掉全角空格(中文空格)。
这时候我们只能先将全角空格替换为半角空格再进行操作,其中替换是 String 类的replace()方法- 12288 是中文全角空格的 unicode 编码
//字符串中的每个空格占一个位置,直接影响了计算字符串的长度 public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = " hello "; System.out.println(str.length()); // 输出 7 System.out.println(str.trim().length()); // 输出 5 } } //输出 7 5- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
//去除全角空格实例 public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = " hello"; //带有全角的空格没有去掉 System.out.println(str.trim().length()); //去除全角空格 System.out.println(str.replace((char) 12288, ' ').trim().length()); } } //输出 6 5- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
九 、截取字符串
substring(int beginIndex)//指定位置截取到字符串结尾substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex)是截取指定范围的内容
substring() 方法是按字符截取,而不是按字节截取
①
substring(int beginIndex)//调用时,括号中是需要提取字符串的开始位置,方法的返回值是提取的字符串 public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "关注XiezhrSpace公众号"; System.out.println(str.substring(2)); } } //输出 XiezhrSpace公众号- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
②
substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex)//方法中的 beginIndex 表示截取的起始索引,截取的字符串中包括起始索引对应的字符; //endIndex 表示结束索引,截取的字符串中不包括结束索引对应的字符 public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "关注XiezhrSpace公众号"; System.out.println(str.substring(2,13)); } } //输出 XiezhrSpace- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
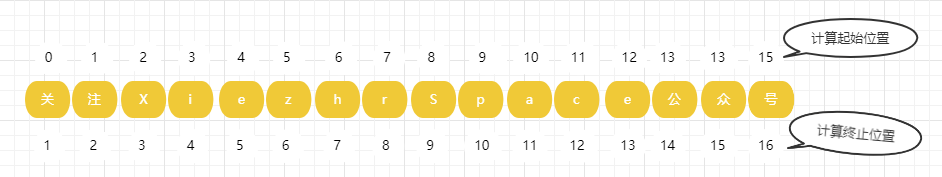
注意:, 对于开始位置 beginIndex, Java 是基于字符串的首字符索引为 0 处理的,但是对于结束位置 endIndex,Java 是基于字符串的首字符索引为 1 来处理的 。具体如下图所示
十、分割字符串
-
str.split(String sign) -
str.split(String sign,int limit) -
str 为需要分割的目标字符串。
-
sign 为指定的分割符,可以是任意字符串。
-
limit 表示分割后生成的字符串的限制个数,如果不指定,则表示不限制,直到将整个目标字符串完全分割为止。
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "苹果,香蕉,猕猴桃,梨"; String arr1[] = str.split(","); String arr2[] = str.split(",",3); System.out.println("①分割所有水果"); for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr1[i]); } System.out.println("②分割取前两个水果,其余不分割"); for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr2[i]); } } } //输出 ①分割所有水果 苹果 香蕉 猕猴桃 梨 ②分割取前两个水果,其余不分割 苹果 香蕉 猕猴桃,梨- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
对于
.,|,$,&,*,.,^等转义字符,程序中使用时,需要加上\\。 实例如下public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "苹果|香蕉|猕猴桃|梨"; String str2 = "黄色$橙色$红色$白色"; String arr1[] = str1.split("\\|"); String arr2[] = str2.split("\\$"); System.out.println("分割以|分割的水果:"); for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr1[i]); } System.out.println("分割以$为分隔符的颜色:"); for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr2[i]); } } } //输出结果 分割以|分割的水果: 苹果 香蕉 猕猴桃 梨 分割以$为分隔符的颜色: 黄色 橙色 红色 白色- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
//多层分隔符解析 public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "xiezhr相关信息^个人公账号|XiezhrSpace$个人博客|www.xiezhrspace.cn"; String arr1[] = str.split("\\^"); String arr2[] = arr1[1].split("\\$"); String arr3[] ={}; System.out.println(arr1[0]); for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) { arr3= arr2[i].split("\\|"); for (int i1 = 0; i1 < arr3.length; i1++) { System.out.println(arr3[i1]); } } } } //输出 xiezhr相关信息 个人公账号 XiezhrSpace 个人博客 www.xiezhrspace.cn- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
十一、字符串替换
str.replace(char oldChar, char newChar)将目标字符串中的指定字符(串)替换成新的字符(串)
- oldChar 表示被替换的字符串
- newChar 表示用于替换的字符串
str.replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement)将目标字符串中匹配某正则表达式的第一个子字符串替换成新的字符串
- regex 表示正则表达式
- replacement 表示用于替换的字符串
str.replaceAll(String regex, String replacement)将目标字符串中匹配某正则表达式的所有子字符串替换成新的字符串
- regex 表示正则表达式
- replacement 表示用于替换的字符串
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 ="个人公众号:XiezhrSpace"; String str2 ="xiezhr love programming"; System.out.println("原始字符串:" + str1); System.out.println("替换后:"+str1.replace(":", "|")); System.out.println("原始字符串:" + str2); System.out.println("替换后:"+str2.replace("programming", "anime")); } } //输出 原始字符串:个人公众号:XiezhrSpace 替换后:个人公众号|XiezhrSpace 原始字符串:xiezhr love programming 替换后:xiezhr love anime- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str ="中国移动:https://www.10086.cn/ 10086:https://www.10086.cn/"; System.out.println("匹配成功:"); System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("10086", "xiezhrspace")); System.out.println("未匹配成功:"); System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("mobile", "xiezhrspace")); } } //输出 匹配成功: 中国移动:https://www.xiezhrspace.cn/ 10086:https://www.10086.cn/ 未匹配成功: 中国移动:https://www.10086.cn/ 10086:https://www.10086.cn/- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str ="中国移动:https://www.10086.cn/ 10086:https://www.10086.cn/"; System.out.println("匹配成功:"); System.out.println(str.replaceAll("10086", "xiezhrspace")); System.out.println("未匹配成功:"); System.out.println(str.replaceAll("mobile", "xiezhrspace")); } } //输出 匹配成功: 中国移动:https://www.xiezhrspace.cn/ xiezhrspace:https://www.xiezhrspace.cn/ 未匹配成功: 中国移动:https://www.10086.cn/ 10086:https://www.10086.cn/- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
十二、字符串比较
str1.equals(str2)
str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2)
str1.compareTo(str2);12.1 equals()
逐个地比较两个字符串的每个字符是否相同。如果两个字符串具有相同的字符和长度,它返回 true,否则返回 false。字符大小写不同,返回false
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 ="xiezhr"; String str2 = new String("xiezhr"); String str3 = "XIEZHR"; System.out.println("str1与str2比较结果:" + str1.equals(str2)); System.out.println("str1与str3比较结果:" + str1.equals(str3)); } } //输出结果 str1与str2比较结果:true str1与str3比较结果:false- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
12.2 equals() 与 == 比较字符
== 比较引用地址是否相同,equals() 比较字符串的内容是否相同
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 ="xiezhr"; String str2 = new String("xiezhr"); System.out.println("使用equals方法比较的结果:"); System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); System.out.println("使用==比较的结果:"); System.out.println(str1 == str2); } } //输出 使用equals方法比较的结果: true 使用==比较的结果: false- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
12.3 equalsIgnoreCase()
字符串与指定的对象比较,不考虑大小写
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 ="xiezhr"; String str2 ="XIEZHR"; String str3 = new String("xiezhr"); System.out.println("str1与str2通过equalsIgnoreCase比较结果:" + str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2)); System.out.println("str1与str3通过equalsIgnoreCase比较结果:" + str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str3)); } } //输出 str1与str2通过equalsIgnoreCase比较结果:true str1与str3通过equalsIgnoreCase比较结果:true- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
12.4 compareTo() 与 compareToIgnoreCase()
基于字符串各个字符的 Unicode 值,按字典顺序(ASCII码顺序)比较两个字符串的大小
如果第一个字符和参数的第一个字符不等,结束比较,返回他们之间的长度差值(ASCII码差值)
如果第一个字符和参数的第一个字符相等,则以第二个字符和参数的第二个字符做比较,以此类推,直至不等为止,返回该字符的ASCII码差值
如果两个字符串不一样长,可对应字符又完全一样,则返回两个字符串的长度差值
compareToIgnoreCase方法可以忽略大小写- 如果参数字符串等于此字符串,则返回值 0;
- 如果此字符串小于字符串参数,则返回一个小于 0 的值;
- 如果此字符串大于字符串参数,则返回一个大于 0 的值。
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 ="xiezhr"; String str2 ="XIEZHR"; String str3 = new String("xiezhr"); String str4 = "xiezhr"; String str5 ="xiezhrspace"; System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2)); System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str3)); System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str4)); System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str5)); System.out.println(str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2)); } } //输出 32 0 0 -5 0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
十三、 字符串查找
13.1 charAt()
字符串本质上是由一个个字符组成的字符数组,因此它也有索引,索引跟数组一样从零开始。charAt() 方法可以在字符串内根据指定的索引查找字符
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str ="www.xiezhrspace.cn"; System.out.println(str.charAt(0)); System.out.println(str.charAt(4)); System.out.println(str.charAt(5)); System.out.println(str.charAt(12)); } } //输出 w x i a- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
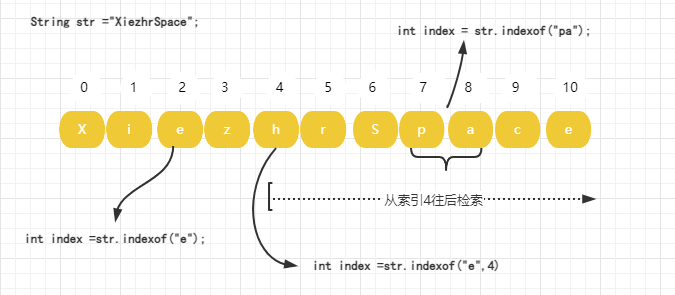
13.2 indexOf()
①public int indexOf(int ch): 返回指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1
②public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex): 返回从 fromIndex 位置开始查找指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1
③int indexOf(String str): 返回指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1
④int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex): 返回从 fromIndex 位置开始查找指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1- ch – 字符,Unicode 编码。
- fromIndex – 开始搜索的索引位置,第一个字符是 0 ,第二个是 1 ,以此类推。
- str – 要搜索的子字符串
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str ="XiezhrSpace"; System.out.println(str.indexOf("e")); System.out.println(str.indexOf("pa")); System.out.println(str.indexOf("e", 4)); } } //输出 2 7 10- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
13.3 lastlndexOf()
用于返回字符(串)在指定字符串中最后一次出现的索引位置,如果能找到则返回索引值,否则返回 -1
lastlndexOf 方法的四种形式
-
public int lastIndexOf(int ch): 返回指定字符在目标字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,如果指定字符串中没有指定的字符,返回 -1。 -
public int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex): 返回指定字符在目标字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引处开始进行反向搜索,如果目标字符串中没有指定字符,返回 -1。 -
public int lastIndexOf(String str): 返回指定子字符串在目标字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,如果目标字符串中没有指定字符,返回 -1。 -
public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex): 返回指定子字符串在目标符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始反向搜索,如果目标字符串中没有指定的字符,返回 -1。
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = new String("个人博客:www.xiezhrspace.cn"); String str1 = "xiezhr"; String str2 = "cn"; System.out.print("查找指定字符 w 在目标字符str中最后出现的位置 :" ); System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf( 'w' )); System.out.print("从第2个位置查找指定字符 w在目标字符串str最后出现的位置 :" ); System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf( 'w', 14 )); System.out.print("指定子字符串 str1 在目标字符串str最后出现的位置:" ); System.out.println( str.lastIndexOf( str1 )); System.out.print("从第7个位置开始查找指定字符串 str1在目标字符串中最后出现的位置 :" ); System.out.println( str.lastIndexOf( str1, 7 )); System.out.print("指定字符串 str2 在目标字符串str最后出现的位置 :" ); System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf( str2 )); } } //输出 查找指定字符 w 在目标字符str中最后出现的位置 :7 从第2个位置查找指定字符 w在目标字符串str最后出现的位置 :7 指定子字符串 str1 在目标字符串str最后出现的位置:9 从第7个位置开始查找指定字符串 str1在目标字符串中最后出现的位置 :-1 指定字符串 str2 在目标字符串str最后出现的位置 :21- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
13.4 contains()
查找字符串中是否包含目标字符(串)
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "xiezhrspace"; System.out.println(str.contains("xiezhr")); System.out.println(str.contains("cn")); } } //输出 true false- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
十四、字符串按指定字符集转byte序列
14.1 getBytes()
按指定的字符集将字符串编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中
14.2 getBytes(String charsetName)
默认字符集将字符串编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "网名xiezhr"; byte[] bytes1 = null; byte[] bytes2 = null; byte[] gbks = null; byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(); try { bytes1 = str.getBytes("utf-8"); bytes2 = str.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"); gbks = str.getBytes("GBK"); }catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e){ System.out.println("不支持的字符集"+e.getMessage()); } System.out.println("按默认字符集将字符串转byte数组:"); for (byte aByte : bytes) { System.out.print(aByte+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("按utf-8编码将字符串转bytes数组:"); for (byte b1 : bytes1) { System.out.print(b1+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("按ISO-8859-1编码将字符串转bytes数组:"); for (byte b2 : bytes2) { System.out.print(b2+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("按GBK编码将字符串转bytes数组:"); for (byte gbk : gbks) { System.out.print(gbk+" "); } } } //输出 按默认字符集将字符串转byte数组: -25 -67 -111 -27 -112 -115 120 105 101 122 104 114 按utf-8编码将字符串转bytes数组: -25 -67 -111 -27 -112 -115 120 105 101 122 104 114 按ISO-8859-1编码将字符串转bytes数组: 63 63 120 105 101 122 104 114 按GBK编码将字符串转bytes数组: -51 -8 -61 -5 120 105 101 122 104 114- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
十五、字符复制
15.1 getChars()
将字符从字符串复制到目标字符数组
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin)- srcBegin – 字符串中要复制的第一个字符的索引。
- srcEnd – 字符串中要复制的最后一个字符之后的索引。
- dst – 目标数组。
- dstBegin – 目标数组中的起始偏移量
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String Str1 = new String("www.xiezhrspace.cn"); char[] Str2 = new char[15]; try { Str1.getChars(4, 15, Str2, 3); System.out.print("复制的字符串为:" ); System.out.println(Str2 ); } catch( Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } } //输出,新字符串Str2 是从第三位复制的 复制的字符串为: xiezhrspace- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
15.2 copyValueOf()
将字符数组中指定字符复制到目标字符
①
public static String copyValueOf(char[] data)- data – 字符数组
②
public static String copyValueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count)- data – 字符数组
- offset – 子数组的初始偏移量
- count – 子数组的长度
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { char[] str1 ={'w','w','w',':','x','i','e','z','h','r','s','p','a','c', 'e','.','c','n' }; String str2 = null; String str3 = null; System.out.println(str2.copyValueOf(str1)); System.out.println(str3.copyValueOf(str1, 4, 11)); } } //输出 www:xiezhrspace.cn xiezhrspace- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
十六、空字符串与null
一个比较容易混淆的知识点。空串是长度为0的字符串,null表示没有引用任何对象
16.1 空字符串与null的区别
- String str = null ;
表示声明一个字符串对象的引用,但指向为null,也就是说还没有指向任何的内存空间; - String str = “”;
表示声明一个字符串类型的引用,其值为""空字符串,这个str引用指向的是空字符串的内存空间; - String str = new String();
创建一个字符串对象的默认值为""
/** 字符串对象与null的值不相等,且内存地址也不相等; 空字符串对象与null的值不相等,且内存地址也不相等; new String()创建一个字符串对象的默认值为"" **/ public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = new String(); String str2 = null; String str3 = ""; System.out.println(str1==str2); System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); System.out.println(str2==str3); System.out.println(str3.equals(str2)); System.out.println(str1==str3); System.out.println(str1.equals(str3)); } } //输出 false //内存地址的比较,返回false false //值的比较,返回false false //内存地址的比较,返回false false //值的比较,返回false false //内存地址的比较,返回false true //值的比较,返回true- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
16.2 非空判断
执行下面代码,会抛出java.lang.NullPointerException 。这也是我们日常开发中经常见到的报错。
所以,字符串非空判断显得尤为重要public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = null; str.length(); } } // 报空指针异常 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException at StringTest.main(StringTest.java:5)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
非空判断一般包含空字符串和null判断,常见的判断方法主要有以下几种
① 最多人使用的一个方法, 直观, 方便, 但效率很低
注: s==null 判断需要写在前面,要不然还是会报NullPointerExceptionif(!(s == null || s.equals(""))){ System.out.println("业务逻辑代码"); }; //或者 if(str !=null &&!"".equals(str)){ System.out.println("业务逻辑代码"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
②比较字符串长度, 效率比第一种方法高
if(!(str==null||str.length()==0)){ System.out.println("业务逻辑代码"); } if(str!=null&&str.length()!=0){ System.out.println("业务逻辑代码"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
③ Java SE 6.0 才开始提供的方法, 效率和方法②差不多, 但出于兼容性考虑, 推荐使用方法二
if(!(str==null||str.isEmpty())){ System.out.println("业务逻辑代码"); } if(str!=null&& !str.isEmpty()){ System.out.println("业务逻辑代码"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
16.3 StringUtils的isBlank与isEmpty
与java.lang这个包作用类似,Commons Lang 包是由apache 提供的jar包。这一组API也是提供一些基础的、通用的操作和处理
官方下载地址:https://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-lang/download_lang.cgi
maven 包引用<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId> <artifactId>commons-lang3artifactId> <version>3.9version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
commons-lang3 提供了很多常用的基础操作处理,包括字符串、日期、数组等等。
由于本文主要是说字符串String,所以我们只对其中的StringUtils的isBlank与isEmpty 方法说明。判断字符串为空,一般会遇到 null 、“” 、字符串中间有空格 " ", 下面是两个方法处理结果
①
public static boolean isBlank(String str)import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils; public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank(null)); System.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank("")); System.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank(" ")); System.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank(" ")); System.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank("\t \n \f \r")); System.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank("\\")); System.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank("公众号XiezhrSpace")); System.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank(" 公众号XiezhrSpace ")); } } //输出 true true true true true false false false- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
②
public static boolean isEmpty(String str)import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils; public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty(null)); System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty("")); System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty(" ")); //StringUtils 中空格作非空处理 System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty(" ")); System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty("\t \n \f \r")); System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty("\\")); System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty("公众号XiezhrSpace")); System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty(" 公众号XiezhrSpace ")); } } //输出 true true false false false false false false- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
当然了,StringUtils工具类还有对应的isNotBlank和isNotEmpty 方法,意思是不为空。
十七、String、StringBuilder、StringBuffer
具体区别可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/itchuxuezhe_yang/article/details/89966303 这篇博文,写的还是挺好的。
17.1 比较
String类是不可变类,即一旦一个 String 对象被创建以后,包含在这个对象中的字符序列是不可改变的;StringBuffer和StringBuilder支持可变字符串;StringBuilder和StringBuffer功能基本相似,方法也差不多;StringBuffer是线程安全的,而StringBuilder则没有实现线程安全功能;StringBuilder由于没有实现线程安全,所以效率要比StringBuffer高;
17.2 继承结构
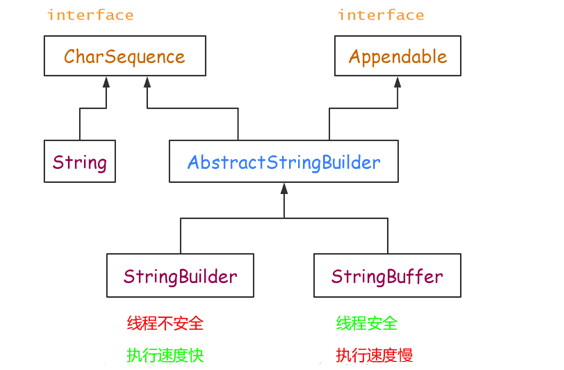
17.3 使用场景选择
- 操作少量的数据使用 String。
- 单线程操作大量数据使用 StringBuilder(大多数情况推荐使用)。
- 多线程操作大量数据使用 StringBuffer。
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { StringBuilder sbd = new StringBuilder(); StringBuffer sbf = new StringBuffer(); String str1 ="xiezhr个人信息:"; String str2 ="博客:www.xiezhrspace.cn"; String str3 ="公众号:XiezhrSpace"; String str =str1+str2+str3; sbd.append(str1); sbd.append(str2); sbd.append(str3); sbf.append(str1); sbf.append(str2); sbf.append(str3); System.out.println("String拼接字符串:"); System.out.println(str); System.out.println("StringBuilder拼接字符串:"); System.out.println(sbd.toString()); System.out.println("StringBuffer拼接字符串:"); System.out.println(sbf.toString()); } } //输出 String拼接字符串: xiezhr个人信息:博客:www.xiezhrspace.cn公众号:XiezhrSpace StringBuilder拼接字符串: xiezhr个人信息:博客:www.xiezhrspace.cn公众号:XiezhrSpace StringBuffer拼接字符串: xiezhr个人信息:博客:www.xiezhrspace.cn公众号:XiezhrSpace- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
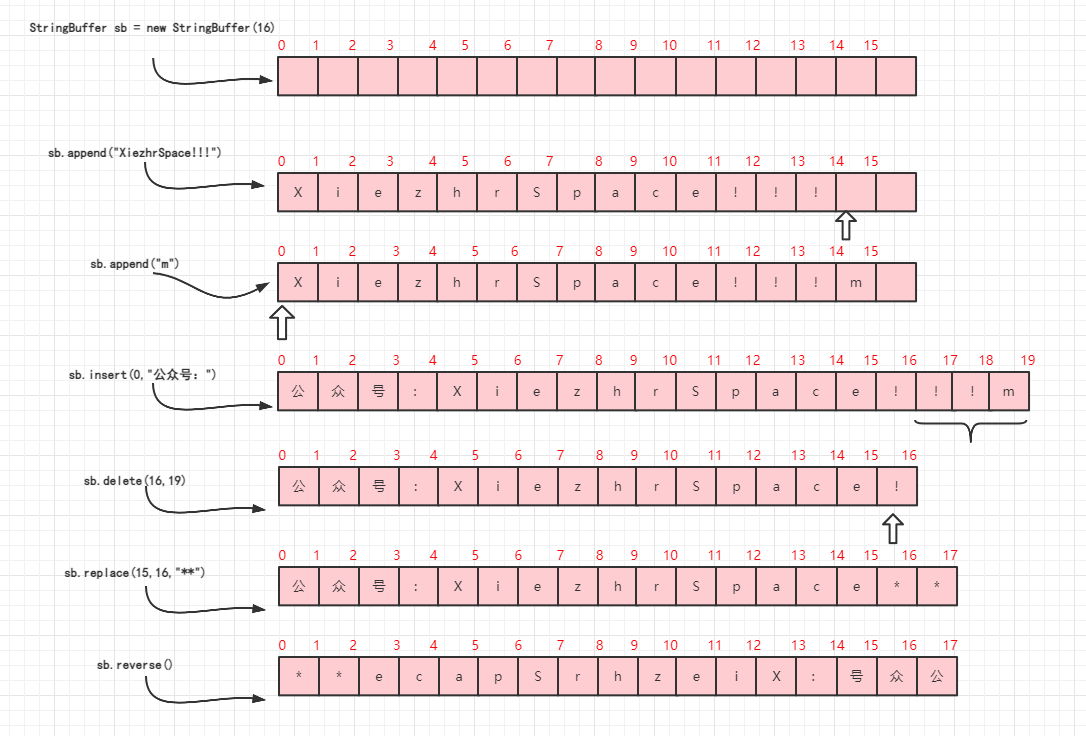
17.4 StringBuffer 常用函数
append(String s)//追加一个字符串
reverse()//将字符串反转
delete(int start, int end)//删除指定位置字符串
insert(int offset, String str)//在指定位置插入字符串
replace(int start, int end, String str)//将指定位置字符串替换为新字符串public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); sb.append("XiezhrSpace!!!"); System.out.println(sb); sb.append("m"); System.out.println(sb); sb.insert(0,"公众号:"); System.out.println(sb); sb.delete(16,19); System.out.println(sb); sb.replace(15,16,"**"); System.out.println(sb); sb.reverse(); System.out.println(sb); } } //输出 XiezhrSpace!!! XiezhrSpace!!!m 公众号:XiezhrSpace!!!m 公众号:XiezhrSpace! 公众号:XiezhrSpace** **ecapSrhzeiX:号众公- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
本期到此结束,我们下期再见~(●’◡’●)
-
相关阅读:
Redis的hash数据类型——Redis
JMeter参数化4种实现方式
数据结构——二叉树1
Python 给视频添加水印
PMP_强化练习题(二)180题(附答案及解析)
vue中调用高德地图
公益培训报名小程序
Python&SQL应用随笔4——PySpark创建SQL临时表
MySql学习笔记11——DBA命令介绍
2023高教社杯数学建模国赛C题思路解析+代码+论文
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/rong0913/article/details/127716281
