-
【math】Hiden Markov Model 隐马尔可夫模型了解
Introduction to Hidden Markov Model
Introduction
- Markov chains were first introduced in 1906 by Andrey Markov
- HMM was developed by L. E. Baum and coworkers in the 1960s
- HMM is simplest dynamic Bayesian network and a directed graphic model
- Application: speech recognition, PageRank(Google), DNA analysis, …
Markov chain
A Markov chain is “a stochastic model describing a sequence of possible events in which the probability of each event depends only on the state attained in the previous event”.
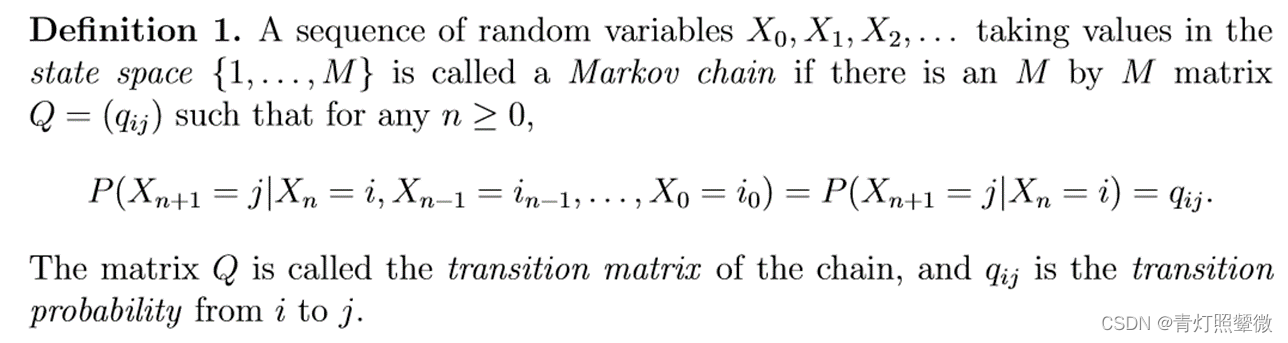
Space or time can be either discrete(𝑋_𝑡:t=0, 1, 2,…) or continuous(𝑋_𝑡:t≥0). (we will focus on Markov chains in discrete space an time)Example for Markov chain:
- transition matrix 𝑄 :
- 5-step transition matrix is 𝑄^5 :

Hidden Markov Model(HMM)
HMM is a statistical Markov model in which the system being modeled is assumed to be a Markov process with unobserved (i.e. hidden) states.
State: x = (x1, x2, x3) ; Observation: y = (y1, y2, y3); Transition matrix: A = (aij); Emission matrix: B = (bij)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
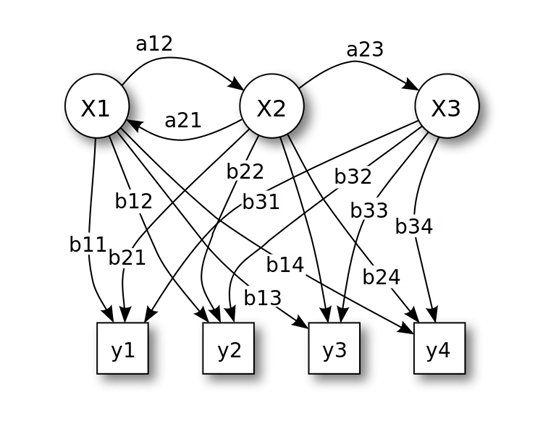
Example:

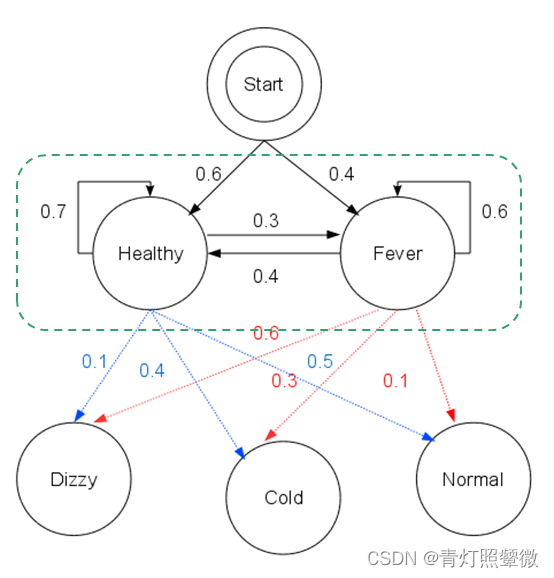
Three Questions
- Given the model 𝜆=[𝐴, 𝐵,𝜋], how to calculate the probability of producing the observation 𝒚={𝑦 1 _1 1,𝑦 2 _2 2,…,𝑦 𝑛 _𝑛 n | 𝑦 𝑖 _𝑖 i∈𝑂}? In other words, how to evaluate the matching degree between the model and the observation ?
- Given the model 𝜆=[𝐴, 𝐵,𝜋] and the observation 𝒚={𝑦 1 _1 1,𝑦 2 _2 2,…,𝑦 𝑛 _𝑛 n| 𝑦 𝑖 _𝑖 i∈𝑂}, how to find most probable state 𝒙={𝑥 1 _1 1,𝑥 2 _2 2,…,𝑥 𝑛 _𝑛 n |𝑥 𝑖 _𝑖 i∈𝑆} ? In other words, how to infer the hidden state from the observation ?
- Given the observation 𝒚={𝑦 1 _1 1,𝑦 2 _2 2,…,𝑦 𝑛 _𝑛 n | 𝑦 𝑖 _𝑖 i∈𝑂}, how to adjust model parameters 𝜆=[𝐴, 𝐵,𝜋] to maximize to the probability 𝑃(𝒚│𝜆) ? In other words, how to train the model to describe the observation more accurately ?
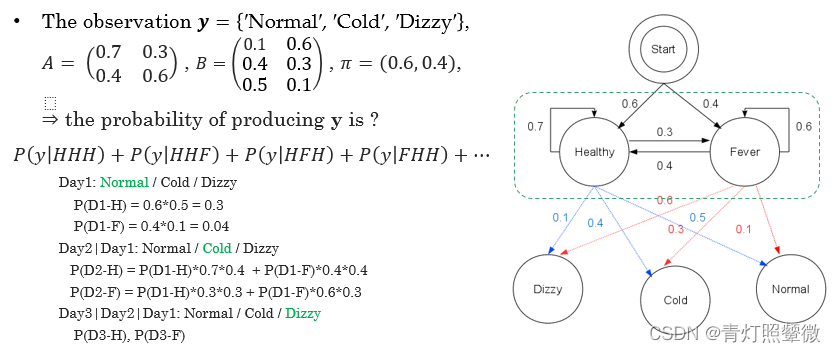
Q1: evaluate problem – Forward algorithm
Q1: how to evaluate the matching degree between the model and the observation ? ( forward algorithm)
- the probability of observing event 𝑦 1 _1 1: 𝑃 𝑖 0 _{𝑖0} i0 = 𝑃 𝑖 _𝑖 i (𝑂=𝑦 1 {_1} 1) = 𝜋 𝑖 𝑏 1 𝑖 _{𝑖}𝑏_{1𝑖} ib1i
- the probability of observing event 𝑦 𝑗 + 1 _{𝑗+1} j+1 (𝑗≥1): 𝑃 𝑖 𝑗 _𝑖𝑗 ij=𝑏 𝑗 , 𝑖 + 1 _{𝑗,𝑖+1} j,i+1 ∑ 𝑘 _𝑘 k𝑃 𝑖 , 𝑗 − 1 _{𝑖,𝑗−1} i,j−1 𝑎 𝑖 𝑗 _{𝑖𝑗} ij
- 𝑃(𝒚)=∑
𝑘
_{𝑘}
k 𝑃
𝑖
𝑗
_{𝑖𝑗}
ij∗𝑎
𝑗
0
_{𝑗0}
j0
Q2: decode problem – Viterbi algorithm
Q2: how to infer the hidden state from the observation ? (Viterbi algorithm)
Observation 𝒚=(𝑦 1 _1 1, 𝑦 2 _2 2,…, 𝑦 𝑇 _𝑇 T), initial prob. 𝝅=(𝜋 1 _1 1,𝜋 2 _2 2,…, 𝜋 𝐾 _𝐾 K), transition matrix 𝐴, emission matrix 𝐵.
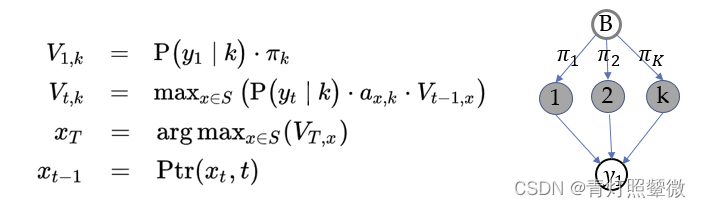
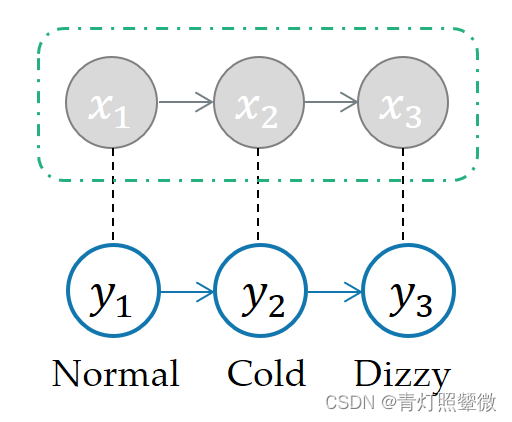
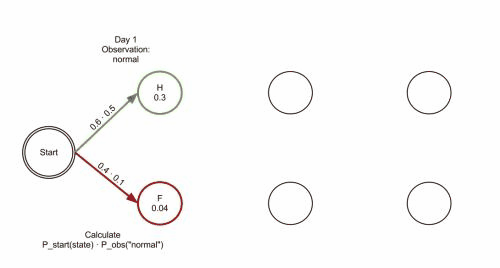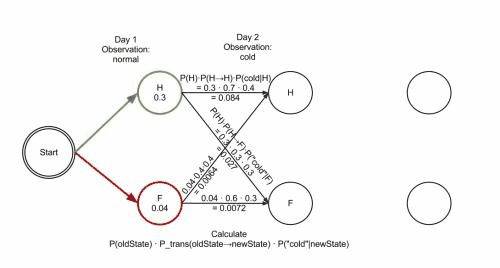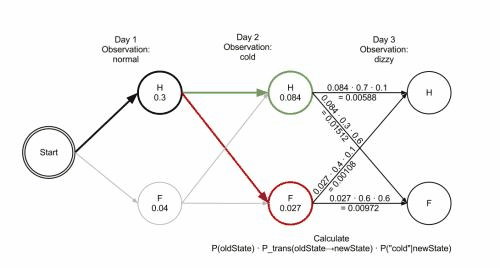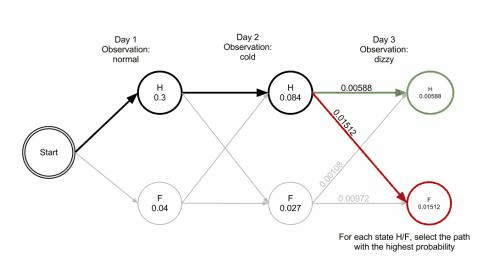
Viterbi algorithm(optimal solution) backtracking method; It retains the optimal solution of each choice in the previous step and finds the optimal selection path through the backtracking method.Example:
- The observation 𝒚={“′Normal′, ′Cold′, ′Dizzy′” } , 𝜆=[𝐴, 𝐵,𝜋], the hidden state 𝒙={𝑥
1
_1
1,𝑥
2
_2
2,𝑥
3
_3
3}= ?
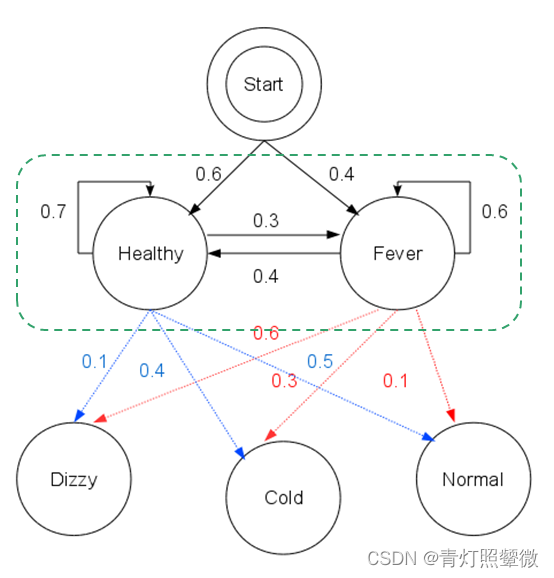
Q3: learn problem – Baum-Welch algorithm
Q3: how to train the model to describe the observation more accurately ? (Baum-Welch algorithm)
The Baum–Welch algorithm uses the well known EM algorithm to find the maximum likelihood estimate of the parameters of a hidden Markov model given a set of observed feature vectors.
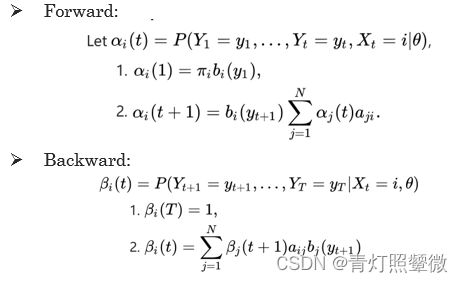
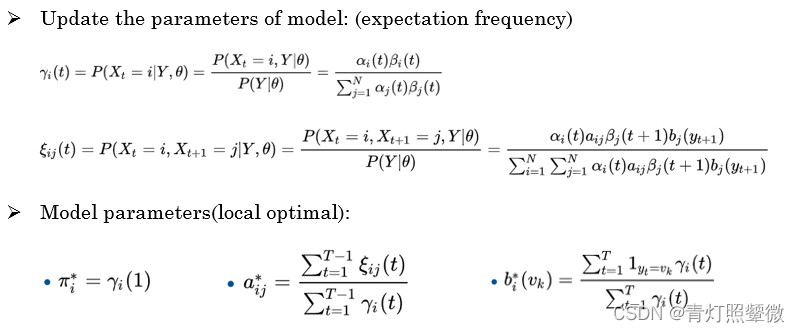
Baum–Welch algorithm(forward-backward alg.) It approximates the optimal parameters through iteration.
- (1) Likelihood function :
𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑃(Y,𝐼|𝜆) - (2) Expectation of EM algorithm:
𝑄(𝜆,𝜆 ̂ )= ∑ 𝐼 _𝐼 I 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑃(𝑌,𝐼|𝜆)𝑃(𝑌,𝐼|𝜆 ̂ ) - (3) *Maximization of EM algorithm:
max 𝑄(𝜆,𝜆 ̂ )
use Lagrangian multiplier method and take the partial derivative of Lagrangian funcition。
Application
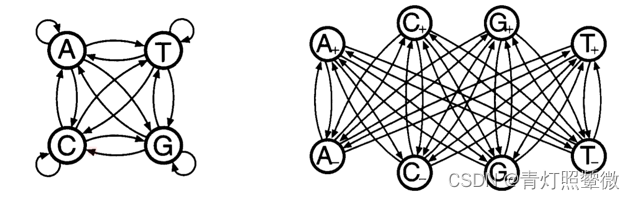
CpG island:
- In the human genome wherever the dinucleotide CG occurs, the C nucleotide is typically chemically modified by methylation.
- around the promoters or ‘start’ regions
- CpG is typically a few hundred to a few thousand bases long.


three questions: of CpG island: - Given the model of distinguished the CpG island, how to calculate the probability of the observation sequence ?
- Given a short stretch of genomic sequence, how would we decide if it comes from a CpG island or not ?
- Given a long piece of sequence, how would we find the CpG islands in it?
reference:
- Markov chain Defination
- A Revealing Introduction to Hidden Markov Models
- Top 10 Algorithms in Data Mining
- An Introduction to Hidden Markov Models for Biological Sequences
- python-hmmlearn-example
- Viterbi algorithm
- Baum-Welch blog
- Biological Sequence Analysis. Probabilistic Models of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. R. Durbin, S. Eddy, A. Krogh and G. Mitchison
未完待续…
-
相关阅读:
K8S之prometheus-operator监控
(C++版本)ros2发布者节点publisher示例源代码(改良版)
输出比较功能中的pwm以及其他功能的区分
Spring Ioc源码分析系列--@Autowired注解的实现原理
服务器出现了一个新软件,一帮大佬吵起来了!
MS-TCN lipreading运行中的问题
ubuntu与win之间共享文件夹
SQL学习--SQL函数基础用法
redis 持久化机制
基于SSM+Vue的订餐系统设计与实现
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_32872729/article/details/127866599