-
机器学习笔记 十八:基于3种方法的随机森林模型分析房屋参数重要性
将机器学习笔记 十六:基于Boruta算法的随机森林(RF)特征重要性评估与本篇结合,对比分析。
1. 探索性数据分析
输入参数: id、date、bedrooms、bathrooms、sqft_living、sqft_lot、floors、waterfront、view、condition、grade、sqft_above、sqft_basement、yr_built、yr_renovated、zipcode、lat、long、sqft_living15、sqft_lot15、
输出参数: priceimport numpy as np import pandas as pd import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor from sklearn.svm import SVC from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, LabelEncoder from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV, cross_val_score from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score from collections import defaultdict from sklearn.metrics import r2_score import sys sys.path.insert(0, 'boruta_py-master/boruta') from boruta import BorutaPy sys.path.insert(0, 'random-forest-importances-master/src') from rfpimp import * %matplotlib inline house = pd.read_csv("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/kc_house_data.csv")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
# 查看数据是否有空 print(house.isnull().any()) # 检查类型 print(house.dtypes)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
# 删除id和date两列数据,因为他们不会使用 house = house.drop(['id', 'date'],axis=1)- 1
- 2
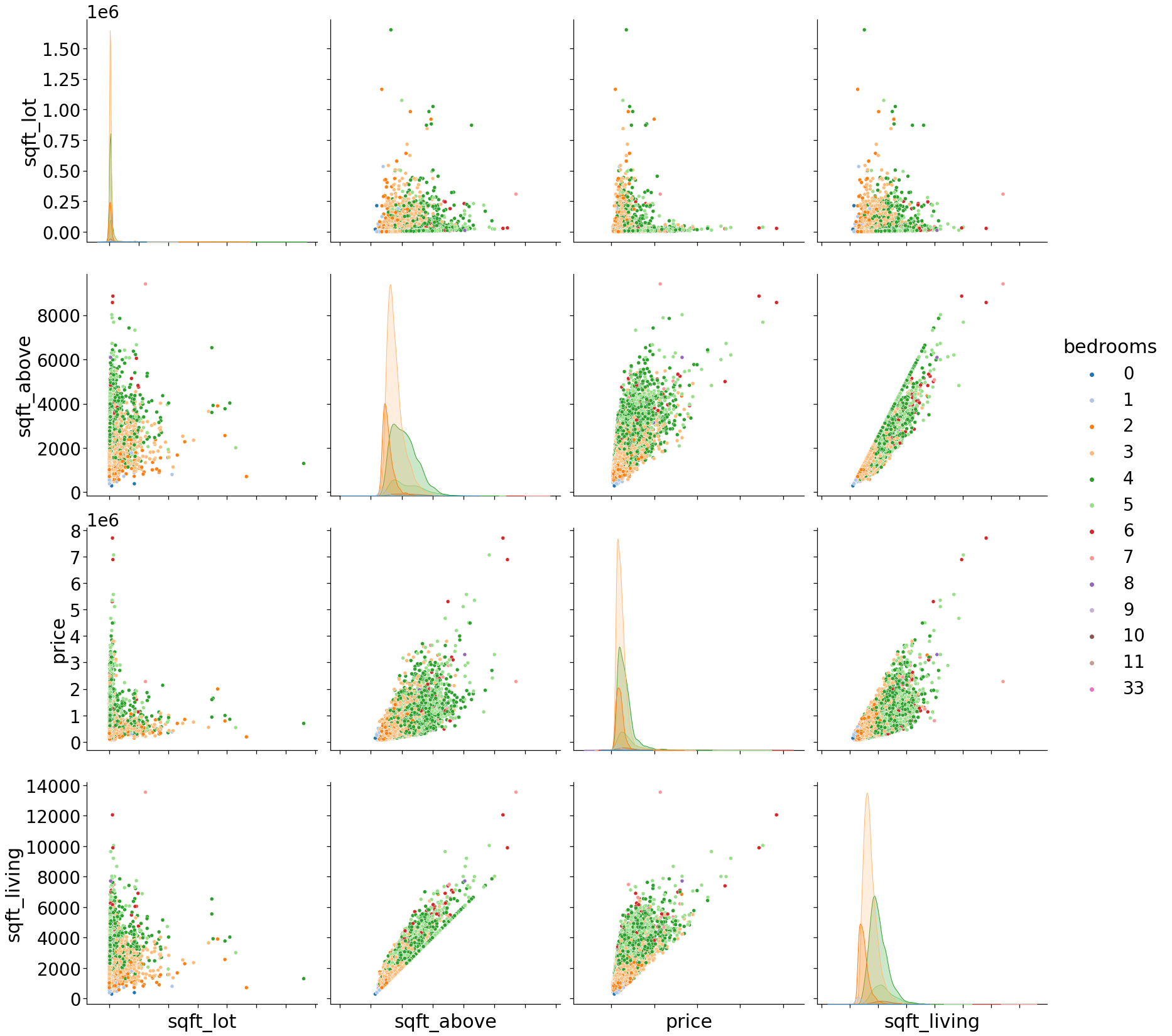
用散点图展示数据之间的相关性:
with sns.plotting_context("notebook",font_scale=2.5): g = sns.pairplot(house[['sqft_lot','sqft_above','price','sqft_living','bedrooms']], hue='bedrooms', palette='tab20',size=6) g.set(xticklabels=[]);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
绘制参数热图(相关性分析):corr = house.corr() mask = np.zeros_like(corr, dtype=np.bool) mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)] = True f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 8)) cmap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 10, as_cmap=True) sns.heatmap(corr, mask=mask, cmap=cmap, center=0, square=True, linewidths=0.5)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

1.1 数据集分割(训练集、测试集)
df_train, df_test = train_test_split(house, test_size=0.20,random_state=42) df_train = df_train[list(house.columns)] df_test = df_test[list(house.columns)] X_train, y_train = df_train.drop('price',axis=1), df_train['price'] X_test, y_test = df_test.drop('price',axis=1), df_test['price'] X_train.shape,y_train.shape,X_test.shape,y_test.shape- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
((17290, 18), (17290,), (4323, 18), (4323,))
1.2 模型拟合
def predictions (rf,X_test,y_test): # Make predictions on test data predictions = rf.predict(X_test) # Performance metrics errors = abs(predictions - y_test) print('Metrics for Random Forest Regressor') print('Average absolute error:', round(np.mean(errors), 2), 'degrees.') # Calculate mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) mape = np.mean(100 * (errors / y_test)) # Compare to baseline baseline_mape=np.mean(y_test) improvement_baseline = 100 * abs(mape - baseline_mape) / baseline_mape print('Improvement over baseline:', round(improvement_baseline, 2), '%.') # Calculate and display accuracy accuracy = 100 - mape print('Accuracy:', round(accuracy, 2), '%.') print('R2 score:',r2_score(predictions,y_test))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
rf_reg = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=200, min_samples_leaf=2, n_jobs=-1, oob_score=True, random_state=42) rf_reg.fit(X_train, y_train) predictions(rf_reg,X_test,y_test)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Metrics for Random Forest Regressor
Average absolute error: 72704.15 degrees.
Improvement over baseline: 100.0 %.
Accuracy: 86.88 %.
R2 score: 0.83817207457119222. 特征重要性比较
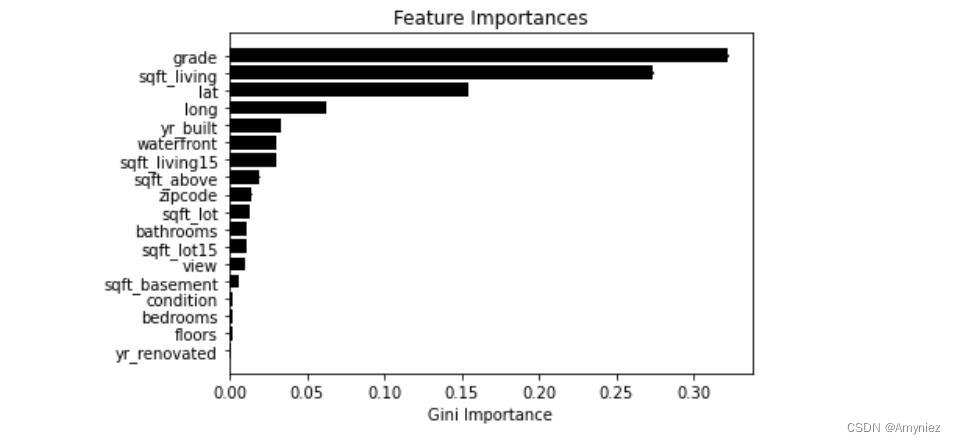
2.1 Gini Importance
features = np.array(X_train.columns) imps_gini=rf_reg.feature_importances_ std_gini = np.std([tree.feature_importances_ for tree in rf_reg.estimators_], axis=0) indices_gini = np.argsort(imps_gini) plt.title('Feature Importances') plt.barh(range(len(indices_gini)), imps_gini[indices_gini], yerr=std_gini[indices_gini],color='black', align='center') plt.yticks(range(len(indices_gini)), features[indices_gini]) plt.xlabel('Gini Importance') plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
2.2 Permutation Importance
def permutation_importances(rf, X_train, y_train, metric): baseline = metric(rf, X_train, y_train) imp = [] std = [] for col in X_train.columns: tmp=[] for i in range(10): save = X_train[col].copy() X_train[col] = np.random.permutation(X_train[col]) # permutation():按照给定列表生成一个打乱后的随机列表 m = metric(rf, X_train, y_train) X_train[col] = save tmp.append(m) imp.append(baseline - np.mean(tmp)) std.append(np.std(tmp)) return np.array(imp),np.array(std)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
np.random.seed(10) imps_perm, std_perm = permutation_importances(rf_reg, X_train, y_train,oob_regression_r2_score) features = np.array(X_train.columns) indices_perm = np.argsort(imps_perm) plt.title('Feature Importances') plt.barh(range(len(indices_perm)), imps_perm[indices_perm], yerr=std_perm[indices_perm],color='black', align='center') plt.yticks(range(len(indices_perm)), features[indices_perm]) plt.xlabel('Permutation Importance') plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
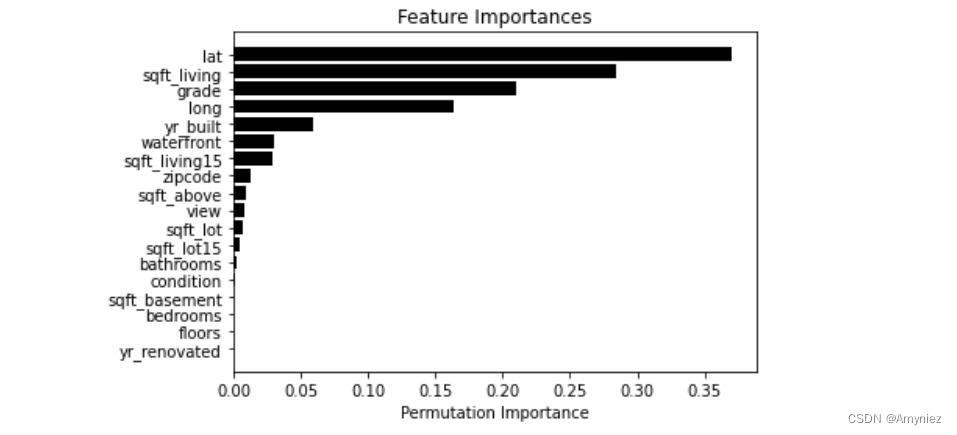
可以看出lat的重要性升高2.3 Boruta
forest_reg = RandomForestRegressor(min_samples_leaf=2, n_jobs=-1, oob_score=True, random_state=42) feat_selector_reg = BorutaPy(forest_reg, verbose=2,max_iter=50)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
np.random.seed(10) import time start = time.time() feat_selector_reg.fit(X_train.values, y_train.values) end = time.time() print(end - start)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Iteration: 1 / 50
Confirmed: 0
Tentative: 18
Rejected: 0
Iteration: 2 / 50
Confirmed: 0
Tentative: 18
Rejected: 0
Iteration: 3 / 50
Confirmed: 0
Tentative: 18
Rejected: 0
Iteration: 4 / 50
Confirmed: 0
Tentative: 18
Rejected: 0
Iteration: 5 / 50
Confirmed: 0
Tentative: 18
Rejected: 0
Iteration: 6 / 50
Confirmed: 0
Tentative: 18
Rejected: 0
Iteration: 7 / 50
Confirmed: 0
Tentative: 18
Rejected: 0
Iteration: 8 / 50
Confirmed: 13
Tentative: 0
Rejected: 5BorutaPy finished running.
Iteration: 9 / 50
Confirmed: 13
Tentative: 0
Rejected: 5
837.3257942199707print('Confirmed: \n',list(np.array(X_train.columns)[feat_selector_reg.ranking_==1])) print('\nTentatives: \n',list(np.array(X_train.columns)[feat_selector_reg.ranking_==2])) print('\nRejected: \n',list(np.array(X_train.columns)[feat_selector_reg.ranking_>=3]))- 1
- 2
- 3
Confirmed:
[‘bathrooms’, ‘sqft_living’, ‘sqft_lot’, ‘waterfront’, ‘view’, ‘grade’, ‘sqft_above’, ‘yr_built’, ‘zipcode’, ‘lat’, ‘long’, ‘sqft_living15’, ‘sqft_lot15’]Tentatives:
[‘sqft_basement’]Rejected:
[‘bedrooms’, ‘floors’, ‘condition’, ‘yr_renovated’]
3. 特征比较
3.1 Gini Importance
X_train_gini_reg=X_train[['grade','sqft_living','lat','long']] X_test_gini_reg=X_test[['grade','sqft_living','lat','long']] rf_gini_reg = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=200, min_samples_leaf=2, n_jobs=-1, oob_score=True, random_state=42) rf_gini_reg.fit(X_train_gini_reg, y_train)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
3.2 Permutation Importance
X_train_perm_reg=X_train.drop(['bedrooms','yr_renovated','floors','sqft_basement','condition','bathrooms'],axis=1) X_test_perm_reg=X_test.drop(['bedrooms','yr_renovated','floors','sqft_basement','condition','bathrooms'],axis=1) rf_perm_reg = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=200, min_samples_leaf=2, n_jobs=-1, oob_score=True, random_state=42) rf_perm_reg.fit(X_train_perm_reg, y_train)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
3.3 Boruta
X_train_boruta_reg=X_train.drop(['bedrooms','floors','condition','yr_renovated'],axis=1) X_test_boruta_reg=X_test.drop(['bedrooms','floors','condition','yr_renovated'],axis=1) rf_boruta_reg = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=200, min_samples_leaf=2, n_jobs=-1, oob_score=True, random_state=42) rf_boruta_reg.fit(X_train_boruta_reg, y_train)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
4. 模型比较
print('******************* Original Model ***********************') print('\n') predictions(rf_reg,X_test,y_test) print ('\n') print('**** Feature selection based on Gini Importance ****') print('\n') predictions(rf_gini_reg,X_test_gini_reg,y_test) print ('\n') print('**** Feature selection based on Permutation Importance *****') print('\n') predictions(rf_perm_reg,X_test_perm_reg,y_test) print ('\n') print('*********** Feature selection based on Boruta **************') print('\n') predictions(rf_boruta_reg,X_test_boruta_reg,y_test)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
******************* Original Model ***********************
Metrics for Random Forest Regressor
Average absolute error: 72704.15 degrees.
Improvement over baseline: 100.0 %.
Accuracy: 86.88 %.
R2 score: 0.8381720745711922**** Feature selection based on Gini Importance ****
Metrics for Random Forest Regressor
Average absolute error: 81288.41 degrees.
Improvement over baseline: 100.0 %.
Accuracy: 85.56 %.
R2 score: 0.8052584664901095**** Feature selection based on Permutation Importance *****
Metrics for Random Forest Regressor
Average absolute error: 72741.67 degrees.
Improvement over baseline: 100.0 %.
Accuracy: 86.77 %.
R2 score: 0.8477802122659206*********** Feature selection based on Boruta **************
Metrics for Random Forest Regressor
Average absolute error: 73254.05 degrees.
Improvement over baseline: 100.0 %.
Accuracy: 86.75 %.
R2 score: 0.8388239891237698Permutation Importance对于R2的计算是比较好的模型,Permutation Importance和Boruta都是比较好的方法。
-
相关阅读:
使用 TiDB Lightning 恢复 S3 兼容存储上的备份数据
Java 并发编程之ConcurrentHashMap源码详解
内裤洗衣机有用吗?公认好用的四大款内衣洗衣机推荐
机器学习——特征工程和评价指标
【第28天】给定一个字符串S,请你判断它是否为回文字符串 | 回文的判断
2023最新SSM计算机毕业设计选题大全(附源码+LW)之java抗包虫病药物查询与推荐系统rx40p
7-用户输入和while循环
pyqt与opencv-qt冲突解决办法
移动端H5封装一个 ScrollList 横向滚动列表组件,实现向左滑动
【Spring-5】AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean创建实例完整流程
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/amyniez/article/details/127823476