-
Java多线程探究【四线程协作】
一 线程协作——生产者和消费者模式
1.1 线程通讯
1.1.1 引子
- 应用场景——生产者和消费者问题
- 假设仓库中只能存放一件产品,生产这件生产出来的产品放入仓库,消费者将仓库中产品取走消费。
- 如果仓库中没有产品,则生产者将产品放入仓库,否则停止生产并等待,直到仓库中的产品被消费者取走为止。
- 如果仓库中放有产品,则消费者可以将产品取走消费,否则停止生产并等待,直到仓库中再次放入产品为止。
1.2 分析
- 这是一个线程同步的问题,生产者和消费者共享一个资源,并且生产者和消费者之间相互依赖,互为条件。
- 对于生产者,没有生产产品之前,要通知消费者等待;生产产品之后,又需要马上通知消费者消费。
- 对于消费者,在消费之后,要通知生产者已经结束消费,需要生产新的产品以供消费。
- 在生产者消费者之间,仅有synchronized是不够的
- synchronized 可阻止并发更新同一个资源共享,实现同步
- synchronized 不能用来实现不同线程之间的消息传递。【即 通讯】
1.3 java提供的解决方法
方法名 作用 wait() 表示线程一直等待,直到其他线程通知,与sleep不同,会释放锁 wait(long timeout) 指定等待的毫秒数 notify() 唤醒一个处于等待状态的线程 notifyAll() 唤醒同一个对象上所有的调用wait()方法的线程,优先级别高的线程优先调用 注意:以上方法均是Object类的方法,都只能在同步方法或者同步代码块中使用,否则会抛出异常IegalMonitorStateException
1.4 解决方式一:管程法通信【优化版】
- 并发协作模式“Producer Consumer Model”–>线程法
- 生产者:负责生产数据的模块(方法、对象、线程、进程)
- 消费者:负责处理数据的模块(可能是方法、对象、线程、进程)
- 缓冲区:消费者不能直接使用生产者的数据,之间存在一个超市“缓冲区”
- 生产者将生产好的数据放入缓冲区,消费者从缓冲区拿出数据
1.4.1 问题的分析
- 数组下标越界的问题
-
- 一个生产者和一个消费者是不会出现下标越界的情况。
- 消费者wait()释放对象锁权限让出CPU,只会是唯一的生产者重新拿到锁权限进行生产,这样的话不消费就生产,不生产就消费,是不会出现下标越界的。
-
- 多个消费者就会出现下标越界的情况
- wait()表示持有对象锁的线程准备释放对象锁权限和让出 cpu 资源并进入等待状态
- 。如果有多个消费者,比如X1,X2假如此时X1,X2都处于wait状态,这时容量为0了生产者拿到锁,生产者生产了1个资源让出锁,X1拿到锁消费完之后容量又刚好为0,然后X1释放锁notifyAll通知JVM去唤醒所有竞争Container对象锁的线程,如果这个锁被X2拿到,那么就会导致0–出现数组下标越界的问题,解决方案暂时只想到把消费的if(index <=0)换成while就是让消费者线程被唤醒的时候不要立刻执行下面的代码,而是再去判断当前容量。
- 因为notify唤醒沉睡的线程后,线程会接着上次的执行继续往下执行(需要注意的是,执行wait()的线程被notify唤醒的时候,只是让while循环继续往下走,如果用if的话,继续往下走意味着跳出if语句块),所以必须使用while循环阻塞。
- 判断count0或者count10的时候,要用while而不是if。线程醒来如果是在if判断里不会重新判断,直接就运行下面代码,多个消费者情况下会出现这个错误,有第一个消费者把所有商品都消费完了,数组下标为0了,但是第二个消费者线程消费时,不会重新判断数组下标,此时就会继续执行下面代码,0-1=-1,出现下标越界错误
-
while (index <= 0) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

- 先消费后生产的问题
- 生产商品和消费商品操作不符合原子性。输出语句要写在synchronized代码块里,保证操作的原子性.生产了1-10,正常来说从10开始消费,但是因为输出语句没写对位置,生产完0之后已经开始消费,但是刚pop完,准备输出语句,但是线程被夺走了
1.4.2 两个优化的地方
- 原来的生产商品和消费商品操作不符合原子性
- 输出语句要写在synchronized代码块里,保证操作的原子性
//如果没有满,就放入产品 products[count]=product; count++; System.out.println("生产了第"+product.id+"个产品");- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
//正常消费 count--; Product product=products[count]; System.out.println("消费了-->第"+product.id+"个产品");- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 数组下标越界 在多线程中要测试某个条件的变化时(尤其是用于线程通信的条件判断)不要选择if,而是选择while去判断。因为notify唤醒沉睡的线程后,线程会接着上次的执行继续往下执行(需要注意的是,执行wait()的线程被notify唤醒的时候,只是让while循环继续往下走,如果用if的话,继续往下走意味着跳出if语句块),所以必须使用while循环阻塞。
//生产者放入产品 public synchronized void push(Product product) { //如果容器满了,就需要等待消费 while(count==products.length) { //通知消费者消费,停止生产 try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } //如果没有满,就放入产品 products[count]=product; count++; System.out.println("生产了第"+product.id+"个产品"); //通知消费者消费 this.notifyAll(); } //消费者消费产品 public synchronized Product pop() { //判断是否能够消费 while(count==0) { //等待生产者生产,消费者等待 try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } //正常消费 count--; Product product=products[count]; System.out.println("消费了-->第"+product.id+"个产品"); //消费完了,通知生产者生产 this.notifyAll(); return product; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
1.4.3 完整代码
/** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/12-13:27 */ public class TestProducerConsumer { public static void main(String[] args) { SynContainer container = new SynContainer(); new Producer(container).start(); new Consumer(container).start(); } } class Producer extends Thread { //Container /*Container 类表示容器,它是一种特殊的组件,可以用来容纳其他组件, Container 又分为两种类型,分别是 Window 和 Panel;*/ SynContainer container; public Producer(SynContainer container) { this.container = container; } @Override public void run() { for(int i=1;i<=20;i++) { container.push(new Product(i)); } } } class Consumer extends Thread { SynContainer container; public Consumer(SynContainer container) { this.container = container; } @Override public void run() { for(int i=1;i<=20;i++) { container.pop(); } } } class Product { int id; public Product(int id) { this.id = id; } } class SynContainer { //需要一个容器的大小 Product[] products=new Product[10]; //容器技术器 int count=0; //生产者放入产品 public synchronized void push(Product product) { //如果容器满了,就需要等待消费 while(count==products.length) { //通知消费者消费,停止生产 try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } //如果没有满,就放入产品 products[count]=product; count++; System.out.println("生产了第"+product.id+"个产品"); //通知消费者消费 this.notifyAll(); } //消费者消费产品 public synchronized Product pop() { //判断是否能够消费 while(count==0) { //等待生产者生产,消费者等待 try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } //正常消费 count--; Product product=products[count]; System.out.println("消费了-->第"+product.id+"个产品"); //消费完了,通知生产者生产 this.notifyAll(); return product; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95

1.5 解决方式二:信号灯法
- 并非协作模式“Producer Consumer Model”–>信号灯法
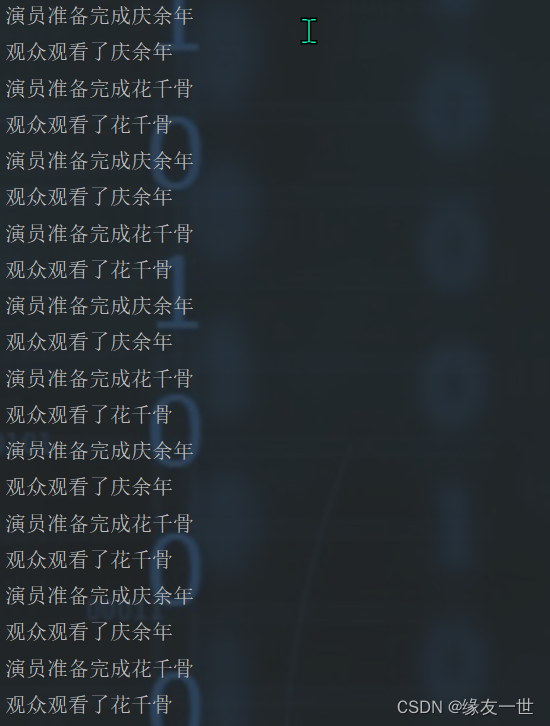
/** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/12-18:00 */ //生产者和消费者模型-->利用缓冲区解决:管城法 public class TestPW { public static void main(String[] args) { TV tv = new TV(); new Player(tv).start(); new Watcher(tv).start(); } } class Player extends Thread { TV tv; public Player(TV tv) { this.tv=tv; } @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { if(i%2==0) { this.tv.play("庆余年"); }else { this.tv.play("花千骨"); } } } } class Watcher extends Thread { TV tv; public Watcher(TV tv) { this.tv = tv; } @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<20;i++) { tv.watch(); } } } class TV { String voice;//表演的节目 boolean flag=true; //表演 public synchronized void play(String voice) { if(!flag) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } System.out.println("演员准备完成"+voice); //通知观众观看 this.notifyAll();//通知唤醒 this.voice=voice; this.flag=!this.flag; } //观看 public synchronized void watch() { //演员正在准备 if(flag) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } System.out.println("观众观看了"+voice); //通知演员表演 this.notifyAll(); this.flag=!flag; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
线程池
- 背景:经常创建和销毁、使用量特别大的资源对性能影响很大。。比如:并发情况下的线程。
- 思路:我们可以提前创建好多个线程,放入线程池中,使用时直接获取,使用完放回池中。可以避免频繁创建、销毁,实现重复利用。
- 优势:
- 提高响应速度
- 降低资源消耗
- 便于线程管理。
- 线程池的几个参数
- corePoolSize:核心池的大小
- maximumPoolSize:最大线程数
- KeepAliveTime:线程没有任务时的生命期限。
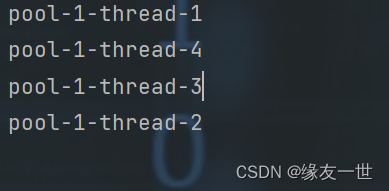
/** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/12-18:31 */ public class TestPool { public static void main(String[] args) { //1 创建服务,创建线程池。 ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); //执行 service.execute(new MyThread()); service.execute(new MyThread()); service.execute(new MyThread()); service.execute(new MyThread()); } } class MyThread implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
二 复习
2.1 创建
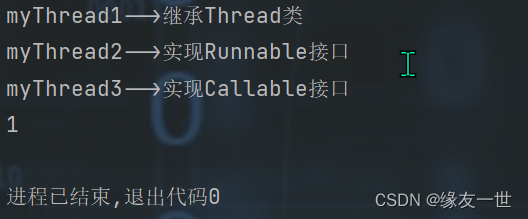
import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; /** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/12-18:36 */ public class TestReview { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { new MyThread1().start(); new Thread(new MyThread2()).start(); FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new MyThread3()); new Thread(futureTask).start(); System.out.println(futureTask.get()); } } //1 继承Thread类 class MyThread1 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("myThread1-->继承Thread类"); } } //2 实现Runnable接口 class MyThread2 implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("myThread2-->实现Runnable接口"); } } //3 实现Callable接口 class MyThread3 implements Callable<Integer> { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { System.out.println("myThread3-->实现Callable接口"); return 1; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 应用场景——生产者和消费者问题
-
相关阅读:
仪表盘自定义标题和数值样式
Virtual box中Linux挂载目录
以太网 以太网地址(MAC地址)
4.2.3 安装Windows操作系统步骤
力扣459. 重复的子字符串(kmp算法)
《改善对话读书笔记1:4R法》
JVM 优化技术
驱动 私有数据传参点灯
dom对象和jquery对象的区别及相互转换
LeetCode刷题复盘笔记——491. 递增子序列(一文搞懂回溯解决递增子序列问题)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/yang2330648064/article/details/127819005
