-
Java多线程探究【三线程同步】
线程同步
- 多个线程操作同一个资源
- 并发:同一个对象被多个线程同时操作
- 处理多线程问题,多个线程访问同一个对象,并且某些线程还想修改这个对象。这个时候我们就需要线程同步。
- 线程同步其实是一种等待机制,多个需要同时访问此对象的线程进入这个对象的等待池形成队列,等待前面的线程使用完毕,下一个线程再使用。
- 由于同一个进程的多个线程共享同一块存储空间,在带来方便的同时。也带来了访问冲突问题。为了保证数据在方法中被访问时的正确性,在访问时加入锁机制
synchronized,当一个线程获得对象的排它锁,独占资源,其他线程必须等待,使用后释放锁即可 - 存在以下问题:
- 一个线程持有锁会导致其他所有需要此锁的线程挂起。
- 在多线程竞争下,加锁,释放锁会导致比较多的上下文切换和调度延时,引起性能问题
- 如果一个优先级高的线程等待一个优先级低的线程释放锁会导致优先级倒置,引起性能问题。
1.1 三大不安全案例
1.1.1 买票
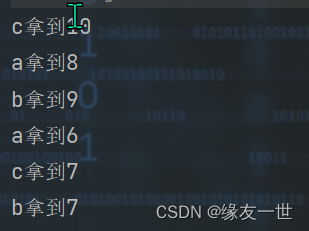
package 多线程.syn; /** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/11-22:46 */ //不安全的买票 同一个票被多个人买去 public class UnsafeBuyTicket { public static void main(String[] args) { BuyTicket buyTicket = new BuyTicket(); new Thread(buyTicket,"a").start(); new Thread(buyTicket,"b").start(); new Thread(buyTicket,"c").start(); } } class BuyTicket implements Runnable { //票 private int ticketNums=10; boolean flag=true; @Override //买票 public void run() { while(flag) { try { buy(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } private void buy() throws InterruptedException { //判断是否还有票 if(ticketNums<=0) { flag=false; return; } //模拟延时 Thread.sleep(1000); //买票 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拿到"+ticketNums--); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
1.1.2 银行取钱
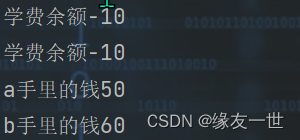
package 多线程.syn; /** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/11-22:59 */ public class UnsafeBank { public static void main(String[] args) { Account account = new Account(100, "学费"); Drawing a1 = new Drawing(account, 50, "a"); Drawing b1 = new Drawing(account, 60, "b"); a1.start(); b1.start(); } } //账户 class Account { int money; String name; public Account(int money, String name) { this.money = money; this.name = name; } } class Drawing extends Thread { Account account; int drawingMoney; int nowMoney; public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney, String name) { super(name); this.account = account; this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney; } @Override public void run() { //判断有没有钱 if(account.money-drawingMoney<0) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"钱不够了,取不了了"); return ; } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } //计算账户的余额 account.money=account.money-drawingMoney; //本人的手中的钱 nowMoney=nowMoney+drawingMoney; System.out.println(account.name+"余额"+account.money); System.out.println(this.getName()+"手里的钱"+nowMoney); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
1.1.3 线程不安全的集合
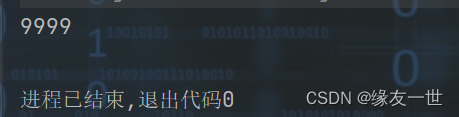
/** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/11-23:22 */ public class UnsafeList { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i=0;i<10000;i++) { new Thread(()->{ list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }).start(); } Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println(list.size()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
1.2 同步方法
- 由于我们可以通过private关键字来保证数据对象只能被方法访问,所以我们只需要针对方法提出一套机制,这套机制就是synchronized关键字,它包括两种用法:
- synchronized方法和synchronized块。
- 同步方法:
publicsynchronizedvoidmethod(intargs){} - synchronized方法控制对“对象”的访问,每个对象对应一把锁,每个synchronized方法都必须获得调用该方法的对象的锁才能执行,否则线程会阻塞方法一旦执行,就独占该锁,直到该方法返回才释放锁,后面被阻塞的线程才能获得这个锁,继续执行。
- 缺陷:若将一个大的方法申明为synchronized将会影响效率。

1.3 同步块
- 同步块:
synchronized(obj){} - Obj称之为同步监视器
- Obj可以是任何对象,但是推荐使用共享资源作为同步监视器
- 同步方法中无需指定同步监视器,因为同步方法的同步监视器就是this,就是这个对象本身,或者是class[反射中讲解]
- 同步监视器的执行过程
-
- 第一个线程访问,锁定同步监视器,执行其中代码,
-
- 第二个线程访问,发现同步监视器被锁定,无法访问
-
- 第一个线程访问完毕,解锁同步监视器
-
- 第二个线程访问,发现同步监视器没有锁,然后锁定并访问
-
1.4 synchronized的使用
1.4.1 不安全买票案例的安全化
package 多线程.syn; /** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/11-22:46 */ //不安全的买票 public class UnsafeBuyTicket { public static void main(String[] args) { BuyTicket buyTicket = new BuyTicket(); Thread a = new Thread(buyTicket, "a"); Thread b = new Thread(buyTicket, "b"); Thread c = new Thread(buyTicket, "c"); a.start(); b.start(); c.start(); } } class BuyTicket implements Runnable { //票 private int ticketNums=200; boolean flag=true; @Override //买票 public void run() { while(flag) { buy(); } } //synchronized 同步方法,锁的是this即 BuyTicket对象 private synchronized void buy() { //判断是否还有票 if(ticketNums<=0) { flag=false; return; } //模拟延时 try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } //买票 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拿到"+ticketNums--); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 在这里,我也遇到了,如果总的票数较少的情况下,票总是被同一个线程得到。在网上的解释是,偶然现象:当几个线程同时再次抢票时,还是被那个线程抢到了。如果基数太小,我们可能会得到不正确的结果,当基数变大时,越接近概率的分布。

- 当基数变大时,效果还是相当可观的

1.4.2 取钱案例的安全化
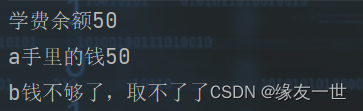
/** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/11-22:59 */ public class UnsafeBank { public static void main(String[] args) { Account account = new Account(100, "学费"); Drawing a1 = new Drawing(account, 50, "a"); Drawing b1 = new Drawing(account, 60, "b"); a1.start(); b1.start(); } } // 账户 class Account { int money; String name; public Account(int money, String name) { this.money = money; this.name = name; } } class Drawing extends Thread { Account account; int drawingMoney; int nowMoney; public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney, String name) { super(name); this.account = account; this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney; } // 默认情况下锁的时this // 这个案例我们不需要锁对象,而是需要锁定账户中的钱数 @Override public void run() { synchronized (account) { // 判断有没有钱 if (account.money - drawingMoney < 0) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "钱不够了,取不了了"); return; } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } // 计算账户的余额 account.money = account.money - drawingMoney; // 本人的手中的钱 nowMoney = nowMoney + drawingMoney; System.out.println(account.name + "余额" + account.money); System.out.println(this.getName() + "手里的钱" + nowMoney); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
1.4.3 线程不安全案例的安全化
package 多线程.syn; import java.util.ArrayList; /** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/11-23:22 */ public class UnsafeList { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i=0;i<1000;i++) { new Thread(()->{ synchronized (list) { list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }).start(); } Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println(list.size()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
1.5 补充:JUC安全类型的CopyOnWriteArrayList
package 多线程.Day03; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; /** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/12-10:22 */ public class TestJUC { public static void main(String[] args) { CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++) { new Thread(()->{ list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }).start(); } try { Thread.sleep(100); }catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(list.size()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
1.6 死锁
- 多个线程各自占有一些共享资源,并且互相等待其他线程占有的资源才能运行,而导致两个或者多个线程都在等待对方释放资源,都停止执行的情形
- 某一个"同步块"时,就可能会发生死锁同时拥有“两个以上对象的锁”的问题。
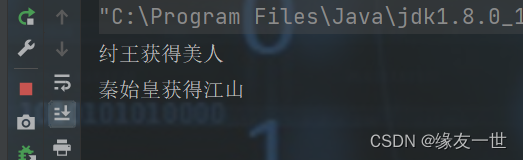
/** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/12-10:31 */ public class DeadLock { public static void main(String[] args) { new Makeup(1,"纣王").start(); new Makeup(0,"秦始皇").start(); } } class Country { } class Beauty{ } class Makeup extends Thread { //需要的资源只有一份,用static来保证只有一份 static Country country=new Country(); static Beauty beauty=new Beauty(); int choice;//选择 String Name;//拥有江山的人 public Makeup(int choice, String name) { this.choice = choice; Name = name; } @Override public void run() { try { makeup(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } //要获得就要先加锁 //两者相互僵持 private void makeup() throws InterruptedException { if(choice==0) { synchronized (country) { System.out.println(this.Name+"获得江山"); Thread.sleep(1000); synchronized (beauty) { System.out.println(this.Name+"获得美人"); } } }else { synchronized (beauty) { System.out.println(this.Name+"获得美人"); synchronized (country) { System.out.println(this.Name+"获得江山"); } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
-
程序相互僵持,一直无法结束
-
避免死锁
private void makeup() throws InterruptedException { if(choice==0) { synchronized (country) { System.out.println(this.Name+"获得江山"); Thread.sleep(1000); } synchronized (beauty) { System.out.println(this.Name+"获得美人"); } }else { synchronized (beauty) { System.out.println(this.Name+"获得美人"); } synchronized (country) { System.out.println(this.Name+"获得江山"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18

1.7 死锁的避免方法
- 产生死锁的四个必要条件:
- 互排斥条件:一个资源每次只能被一个进程使用
- 请求与保持条件:一个进程因请求资源而阻塞时,对已获得的资源保持不放
- 不剥夺条件:进程已获得的资源在末使用完之前,不能强行剥夺
- 循环等待条件:若干进程之间形成一种头尾相接的循环等待资源关系
1.8 Lock锁
-
从JDK5.0开始,Java提供了更强大的线程同步机制——通过显式定义同步锁对象来实现同步。
-
同步锁使用Lock对象充当
java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock接口是控制多个线程对共享资源进行访问的工具。 -
锁提供了对共享资源的独占访问,每次只能有一个线程对Lock对象加锁,线程开始访问共享资源之前应先获得Lock对象
-
ReentrantLock类实现了Lock,它拥有与synchronized相同的并发性和内存请义,在实现线程安全的控制中,比较常用的ReentrantLock,可以显式加锁、释放锁。
-
模板
class x { private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public void m() { lock.lock; try{ //保证线程安全的代码 }finally { lock.unlock; //如果同步代码有异常,要将unlock写入Finally语句块 } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; /** * @author 缘友一世 * date 2022/11/12-11:52 */ public class TestLock { public static void main(String[] args) { TestLock2 testLock2 = new TestLock2(); new Thread(testLock2).start(); new Thread(testLock2).start(); new Thread(testLock2).start(); } } class TestLock2 implements Runnable { private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); int ticketNums = 10; @Override public void run() { while (true) { try { lock.lock();//显示加锁 if (ticketNums > 0) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println(ticketNums--); } else { break; } } finally { lock.unlock();//解锁 } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42

1.9 synchronized&Lock
Lock synchronized Lock是显式锁 ,需要手动的开启和释放 synchronized是隐式锁,出了作用域就自动释放 Lock只有代码块锁 synchronized有代码块锁和方法锁 使用Lock锁,JVM将花费较少的时间来调度线程,性能更好。并且就有良好的拓展性 - Lock>同步代码块(已经进入了方法体分配了相应资源)>同步方法(在方法体之外)
-
相关阅读:
关于普通混凝土的组成材料,下列说法正确的是
蓝牙核心规范(V5.4)10.9-BLE 入门笔记之GAP
Restyle起来!
第15篇ESP32 idf框架 wifi联网_WiFi AP模式_手机连接到esp32开发板
秋招春招,网申在线测评中的智力测试
Privacy Policy for 高中英语
Dobbo微服务项目实战(详细介绍+案例源码) - 1.项目介绍及环境配置
Sping-AOP切面相关操作
java毕业设计健身房信息管理mp4(附源码、数据库)
基于Java电动车上牌管理系统计实现(源码+lw+部署文档+讲解等)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/yang2330648064/article/details/127814436
