-
【数据结构】11道LeetCode链表OJ练习
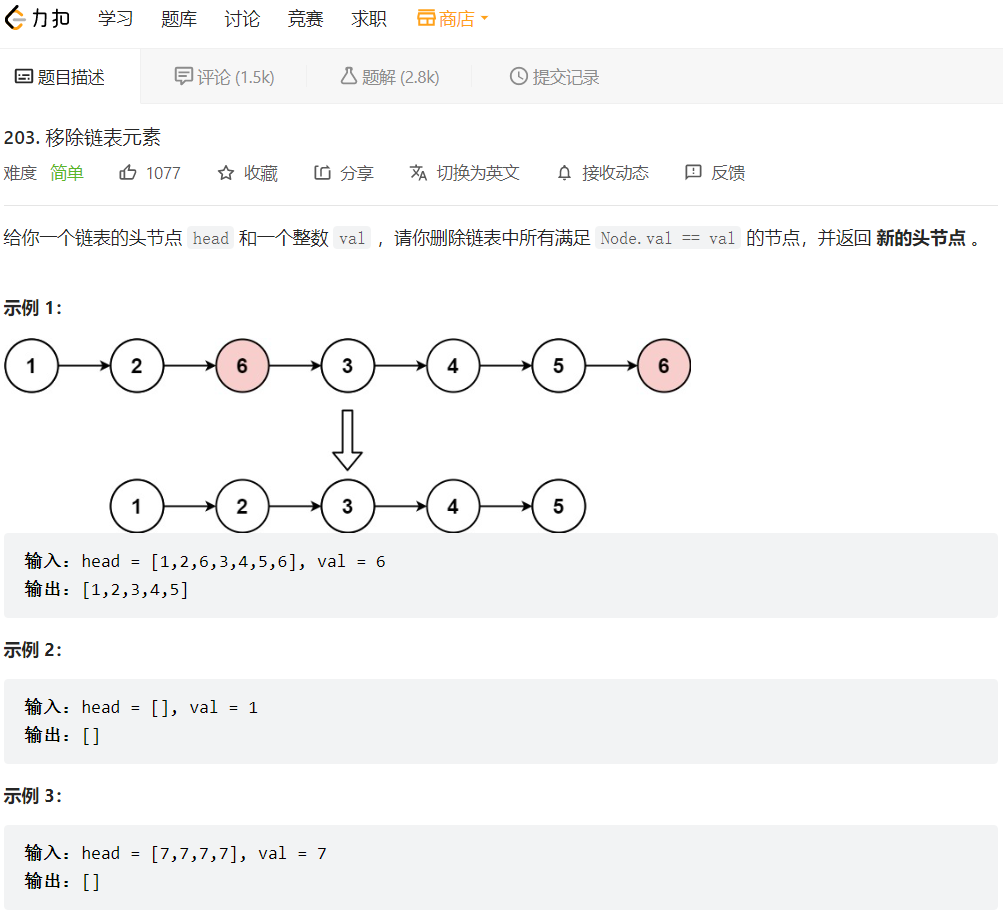
1. 移除链表元素
💝 思路:
我们可以重新定义一个申请一个新的虚拟头节点,该头节点不存储有效数据,然后我们遍历这个链表,找出数据不等于val的节点一一尾插在新的头节点之后,最后返回虚拟头节点的下一个节点即可。
💖 代码实现:
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ struct ListNode*newHead=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); newHead->next=NULL; struct ListNode*tail=newHead; struct ListNode*cur=head; while(cur) { if(cur->val!=val) { tail->next=cur; tail=cur; } cur=cur->next; } tail->next=NULL; return newHead->next; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17

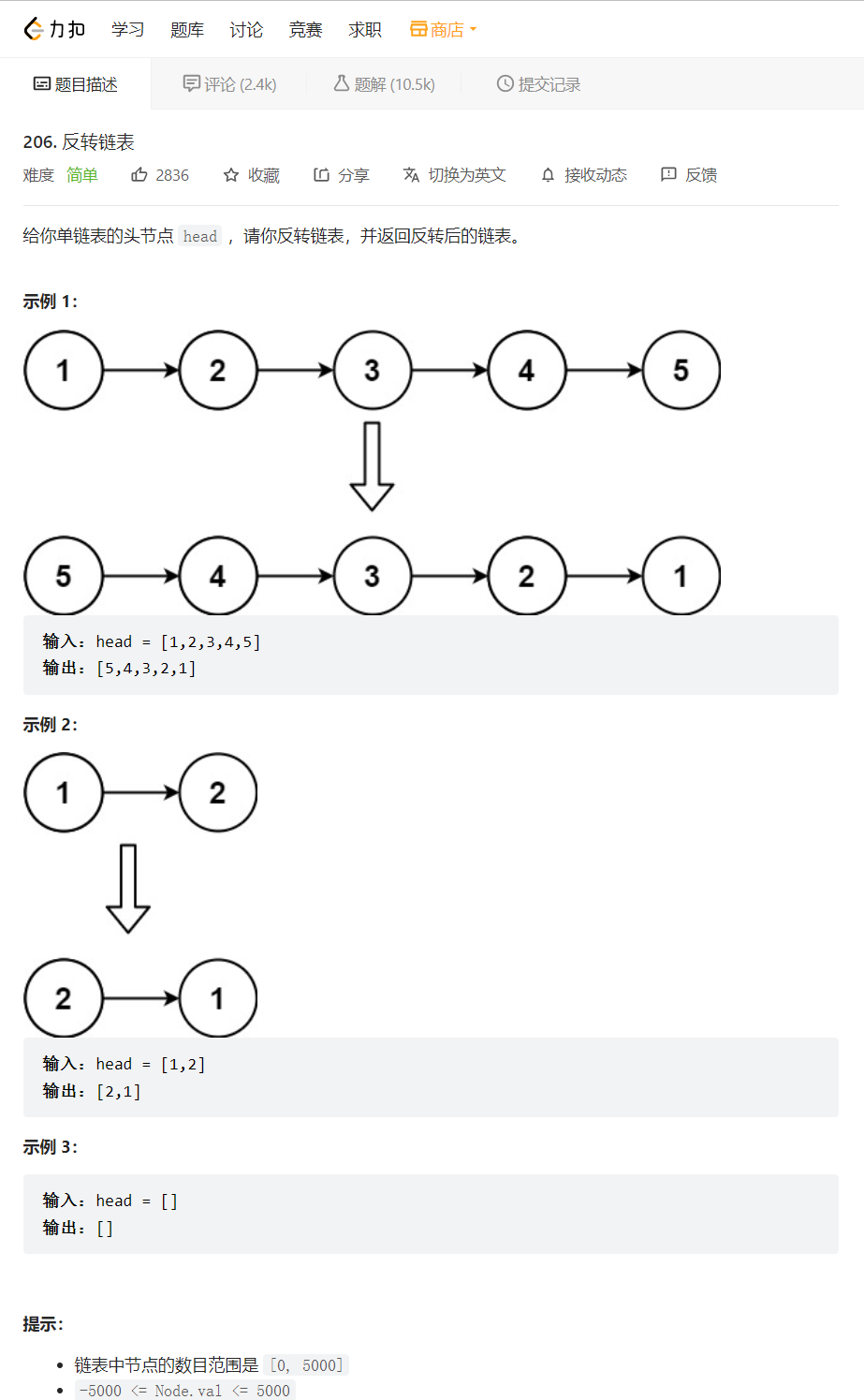
2. 反转链表
💝 思路:
要实现链表的反转,我们可以把头节点之后的节点依次头插到头节点之前即可以设置三个指针,依次迭代就可以完成。
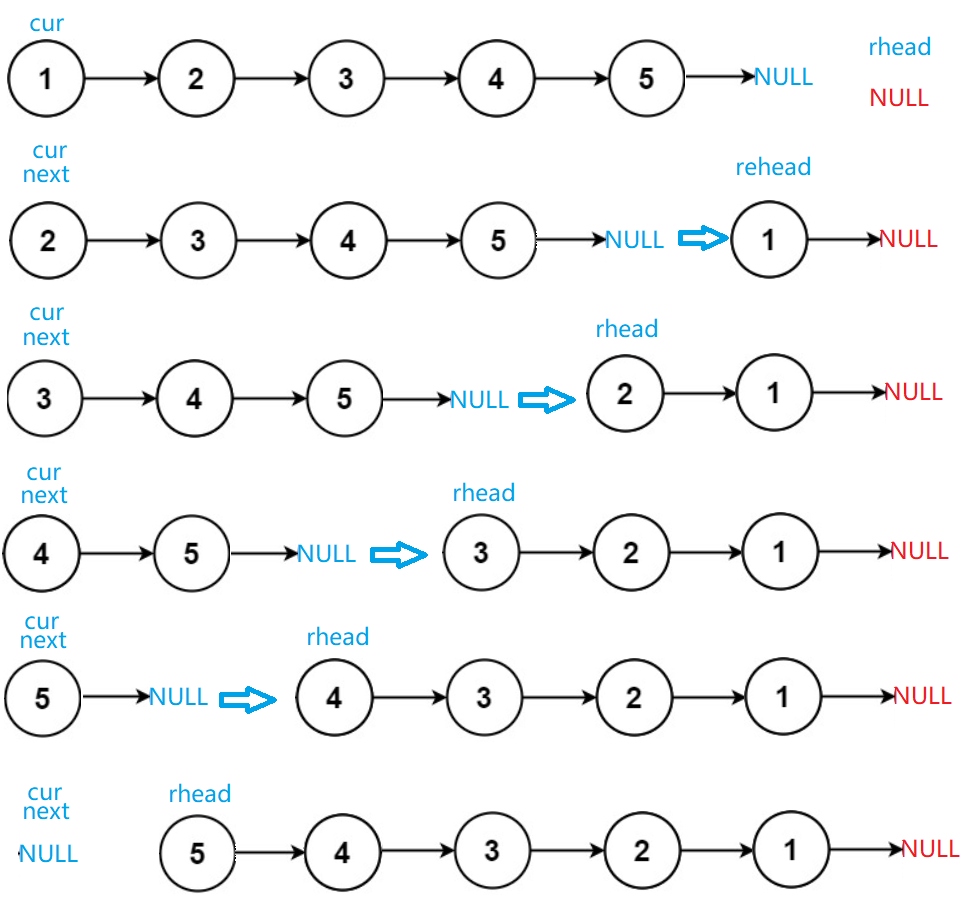
💖 代码实现:struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode*cur=head; struct ListNode*rhead=NULL; while(cur) { struct ListNode*next=cur->next; cur->next=rhead; rhead=cur; cur=next; } return rhead; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
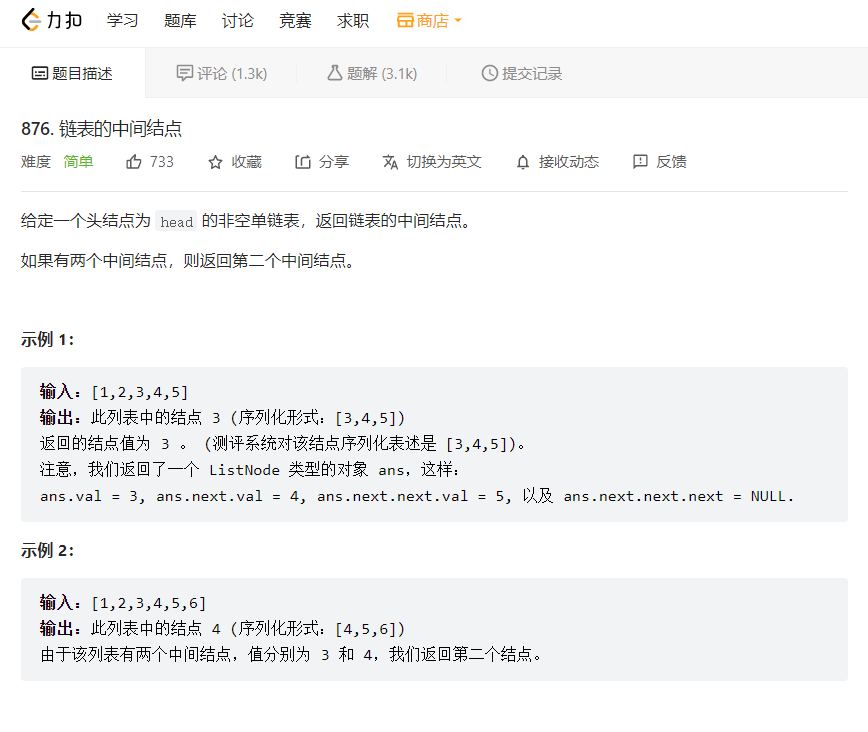
3. 链表的中间节点
💝 思路:
这道题的最优解法是快慢指针,先定义一个快指针和慢指针都指向链表的头节点,快指针次一次走两步慢指针一次走一步。如果链表节点个数为奇数,则快指针的next为空时停止循环,此时慢指针指向的节点恰好为链表的中间节点。如果节点个数为偶数,则快指针为空时停止循环,此时的慢指针的指向也恰好为链表中间节点的第二个节点。
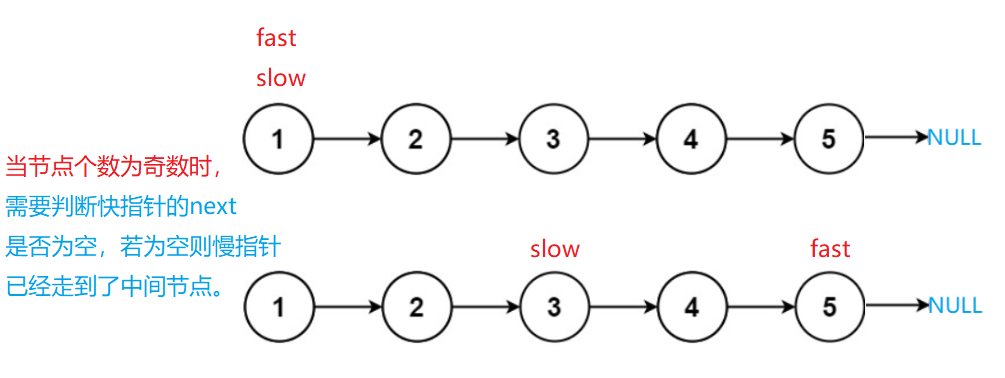

💖 代码实现:struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode*fast=head; struct ListNode*slow=head; while(fast!=NULL&&fast->next!=NULL) { fast=fast->next->next; slow=slow->next; } return slow; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
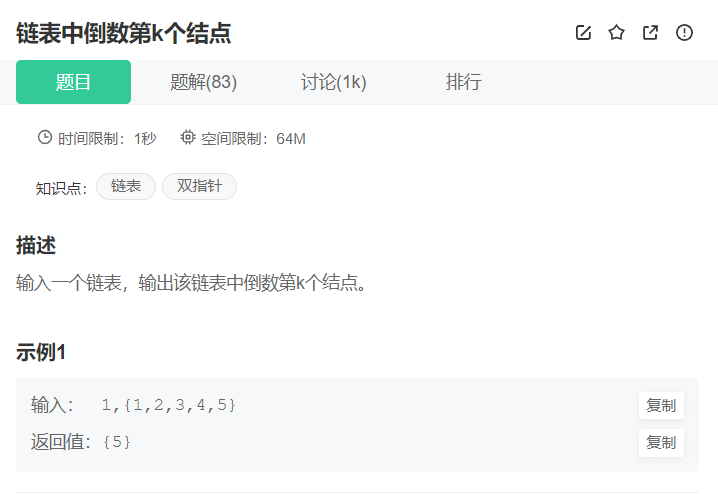
4. 链表中倒数第k个节点
💝 思路:
这道题的思路还是快慢指针,和上一个题不一样的是这个题运用到的思路不是快指针比满指针一次走的步数不同,而是先让快指针先走K步,然后慢指针和快指针一起走,当快指针指向空时,此时的慢指针的指向即为倒数第K个节点。这里需要注意的是如果K的值大于链表的长度,在快指针先走的时候就会指向0,这时候链表没有倒数第K个节点,需要返回一个空指针。
💖 代码实现:
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) { // write code here if(!pListHead) return NULL; struct ListNode*fast,*slow; fast=slow=pListHead; while(k--) { if(fast==NULL) return NULL; fast=fast->next; } while(fast) { fast=fast->next; slow=slow->next; } return slow; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
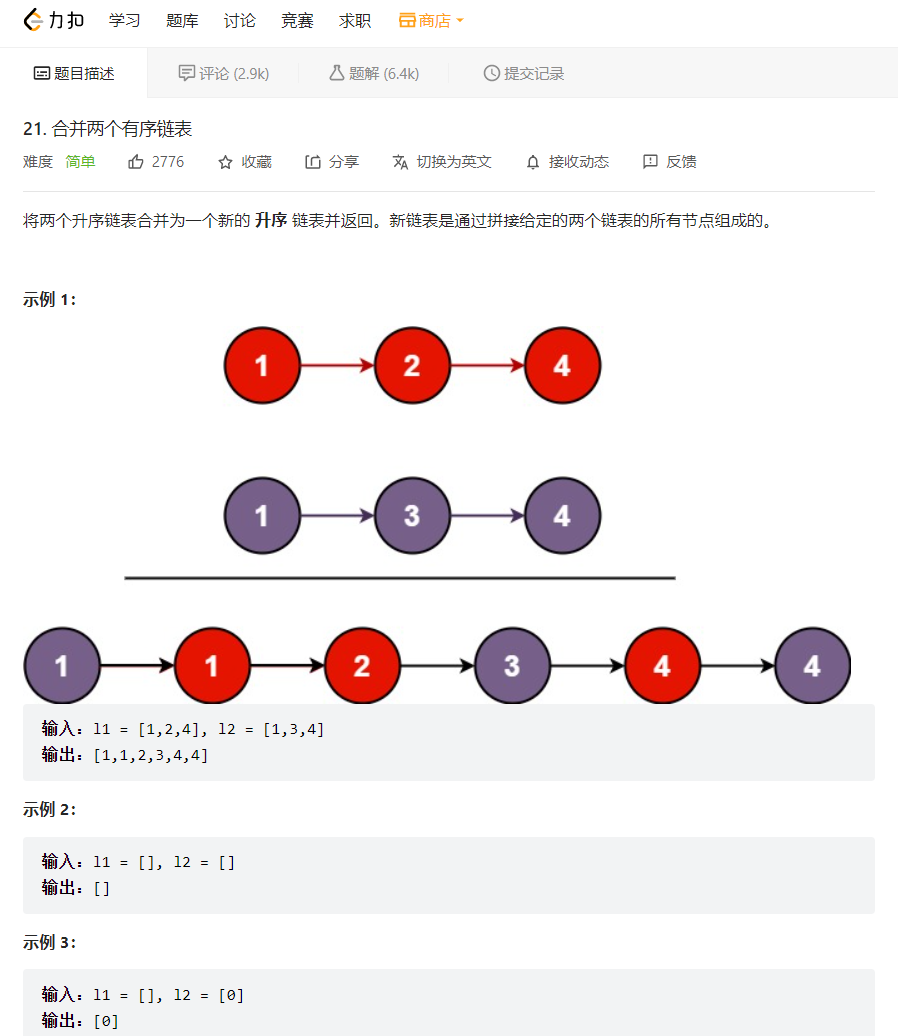
5. 合并两个有序链表
💝 思路:
这个题的思路还是双指针,先定义一个虚拟头节点,防止后面需要判空的一系列麻烦操作,同时为了能够找到新的链表的尾节点,我们还需要定义一个尾节点方便尾插,从两个链表的头节点开始比较如果list1的节点数据小于list2,则将该节点尾插到虚拟头节点的后面,同时尾节点指向新的尾,如果其中一个链表为空,则停止循环,同时将不为空的链表链接到新的链表后面,最后返回新链表的头节点的下一个节点即可。
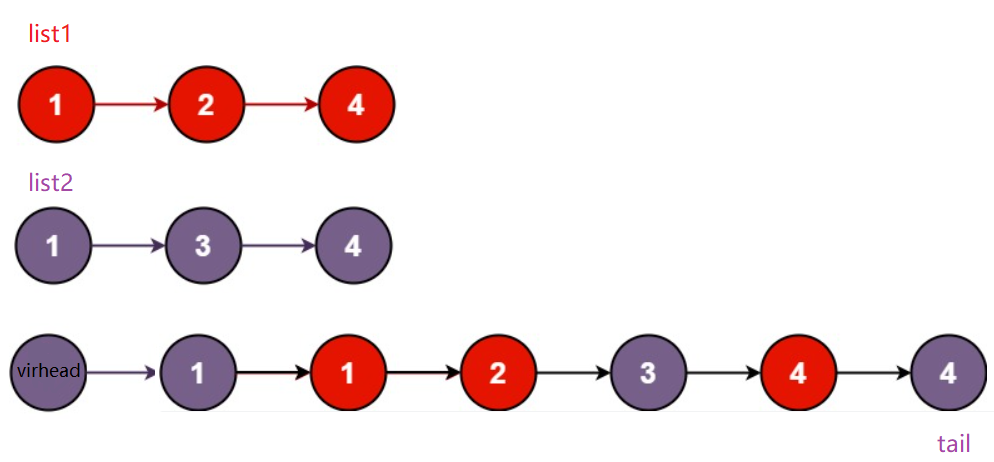
💖 代码实现:struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){ struct ListNode*virhead=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); virhead->next=NULL; struct ListNode*tail=virhead; while(list1&&list2) { if(list1->val<list2->val) { tail->next=list1; tail=tail->next; list1=list1->next; } else { tail->next=list2; tail=tail->next; list2=list2->next; } } if(!list1) tail->next=list2; if(!list2) tail->next=list1; return virhead->next; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
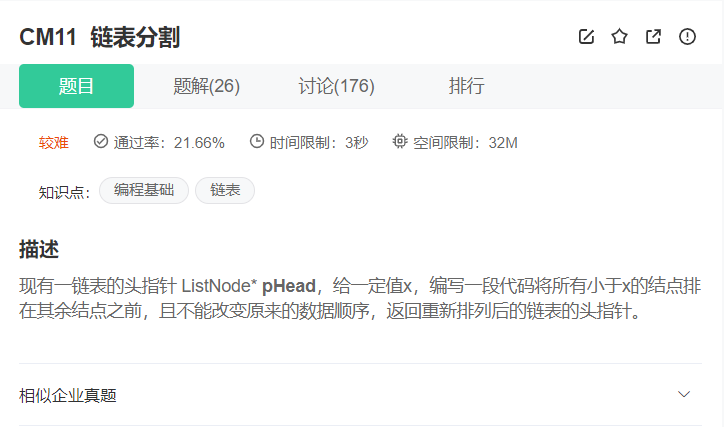
6. 链表分割
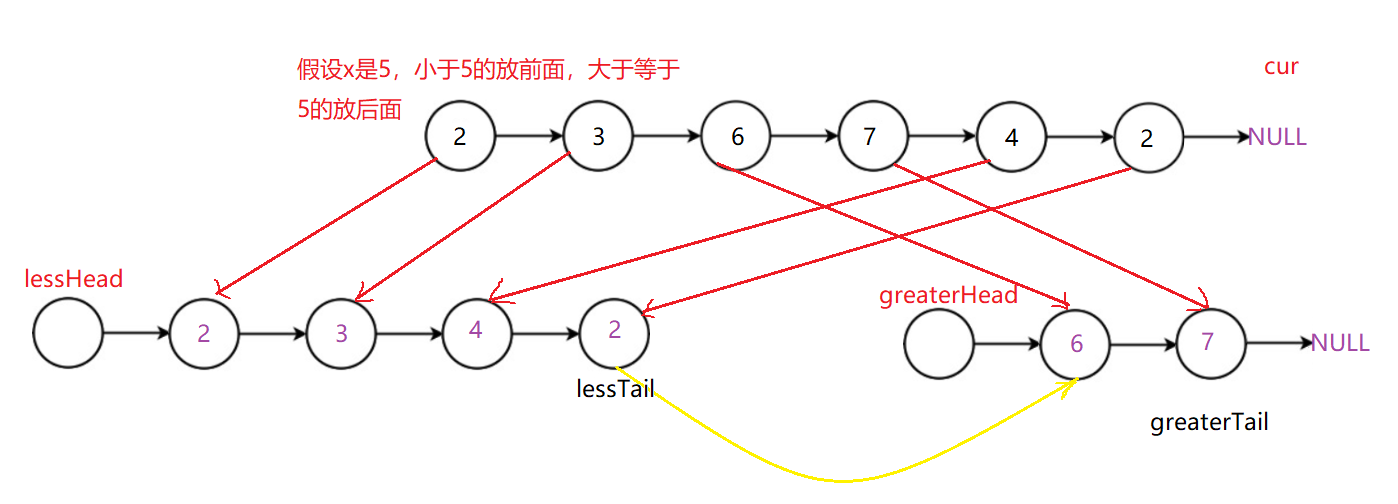
💝 思路:
要解这个题,我们的思路是:先创建两个带虚拟头节点的空链表greaterHead 和 lessHead,然后遍历题目所给我们的链表,遇到小于x的结点,尾插到lessHead链表的后面,否则的话尾插到greaterHead链表的后面。最后将两个新的链表按照lessHead->greaterHead 的顺序链接起来。最后再将此链表返回即可。在这里我们要注意的是greaterHead链表尾指针的next需要置空一下防止链表成环进入死循环。
💖 代码实现:
class Partition { public: ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) { // write code here struct ListNode*greaterHead,*greaterTail,*lessHead,*lessTail; greaterHead=greaterTail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); lessHead=lessTail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); struct ListNode*cur=pHead; while(cur) { if(cur->val<x) { lessTail->next=cur; lessTail=lessTail->next; } else { greaterTail->next=cur; greaterTail=greaterTail->next; } cur=cur->next; } greaterTail->next=NULL; lessTail->next=greaterHead->next; pHead=lessHead->next; return pHead; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
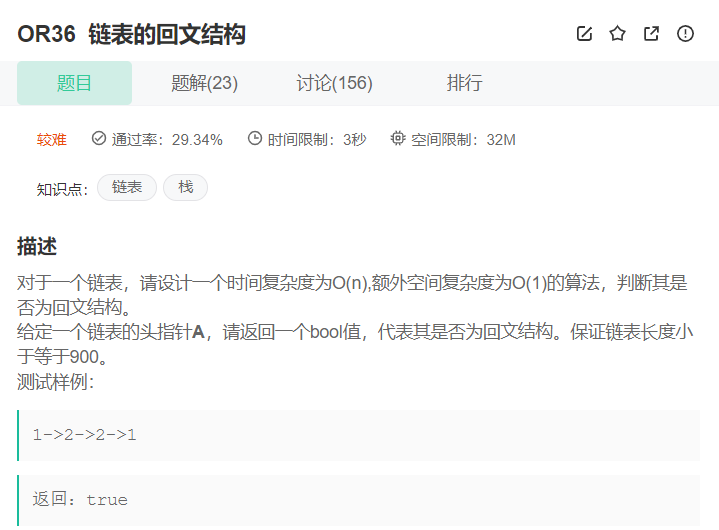
7. 链表的回文结构
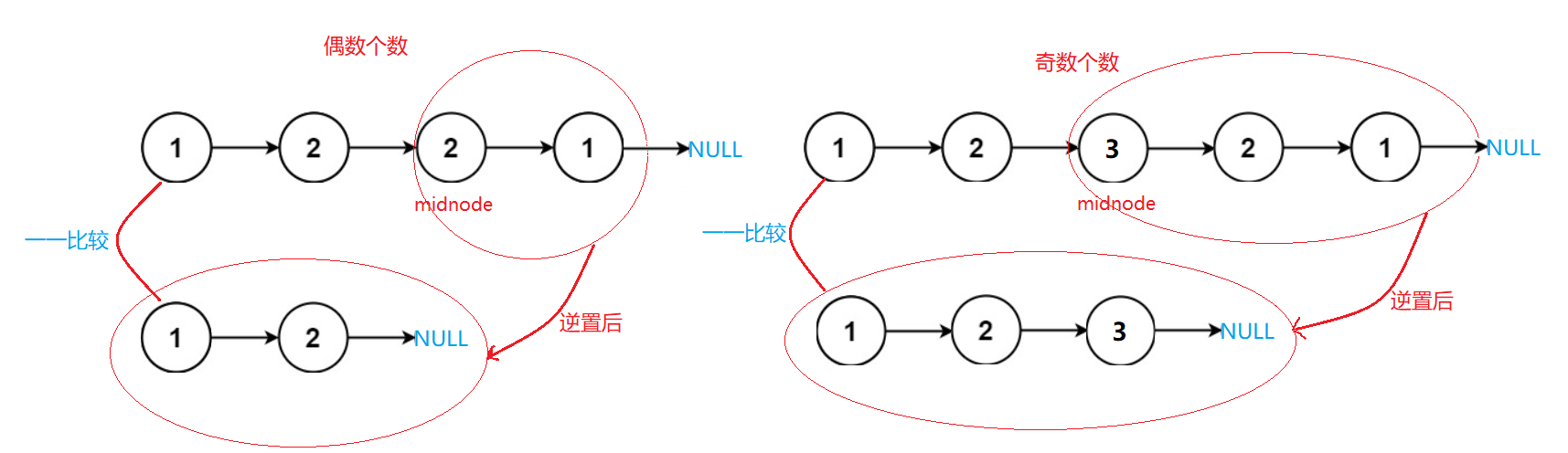
💝 思路:
要判断链表是不是回文结构,我们可以先把链表的中间结点找出,然后将中间结点后面的结点逆置,最后再将前半部分的结点和逆置了的后半部分节点一一对比,如果都相等,说明该链表是回文结构。我们在前两个题里已经实现过寻找链表的中间结点和逆置链表这两个OJ题目,这里我们只需要复用前面写过的代码即可,我们还需要注意节点个数为奇数和偶数分别应该注意的地方。
💖 代码实现:struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode*fast=head; struct ListNode*slow=head; while(fast!=NULL&&fast->next!=NULL) { fast=fast->next->next; slow=slow->next; } return slow; } struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode*cur=head; struct ListNode*rhead=NULL; while(cur) { struct ListNode*next=cur->next; cur->next=rhead; rhead=cur; cur=next; } return rhead; } class PalindromeList { public: bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) { // write code here struct ListNode*mid=middleNode(A); struct ListNode*rhead=reverseList(mid); while(A&&rhead) { if(A->val!=rhead->val) return false; A=A->next; rhead=rhead->next; } return true; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
8. 相交链表
💝 思路:
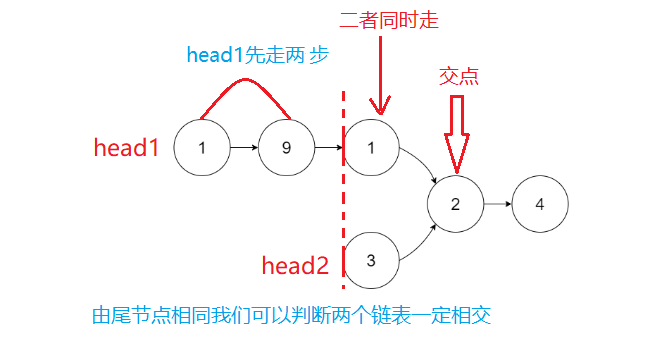
对于这道题目,我们最容易判断的就是两个链表是否相交,只需要将两个链表遍历找到他们的尾节点,如果二者的尾节点地址相同,则说明两个链表相交。其实要找他们相交的起始节点也不难:当我们判断出链表相交后,首相分别计算出两个链表的结点个数之差记为gap,然后让结点个数多的那个链表先走gap步,然后二者同时走,并且同时比较每个节点的地址是否相同,如果相同,则这个节点就是我们要找的结点。
💖 代码实现:
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) { struct ListNode*curA=headA,*curB=headB; int lenA=0,lenB=0; while(curA->next) { lenA++; curA=curA->next; } while(curB->next) { lenB++; curB=curB->next; } if(curA!=curB) return NULL; int gap=abs(lenA-lenB); struct ListNode*longList=headA,*shortList=headB; if(lenA<lenB) { longList=headB; shortList=headA; } while(gap--) { longList=longList->next; } while(longList!=shortList) { longList=longList->next; shortList=shortList->next; } return longList; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
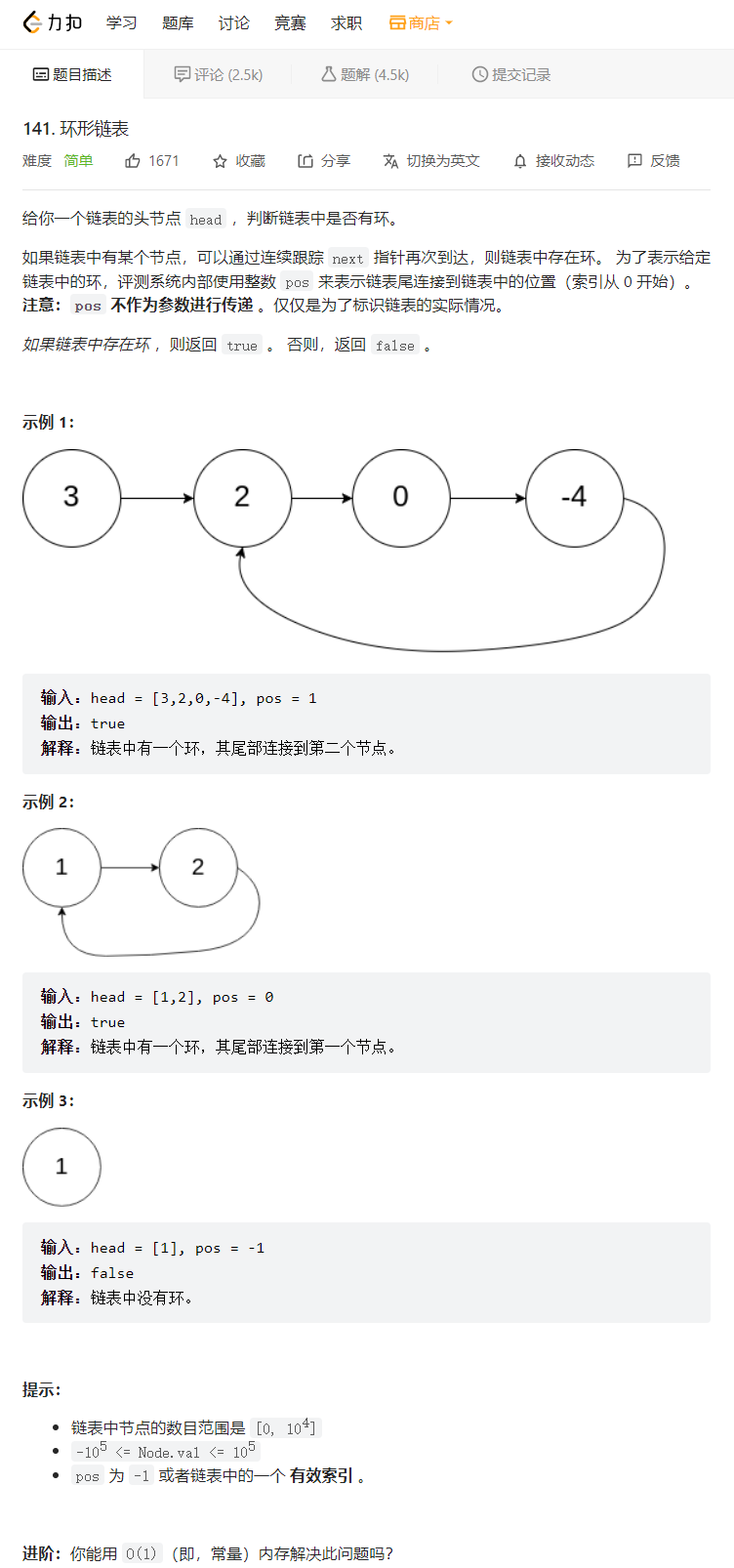
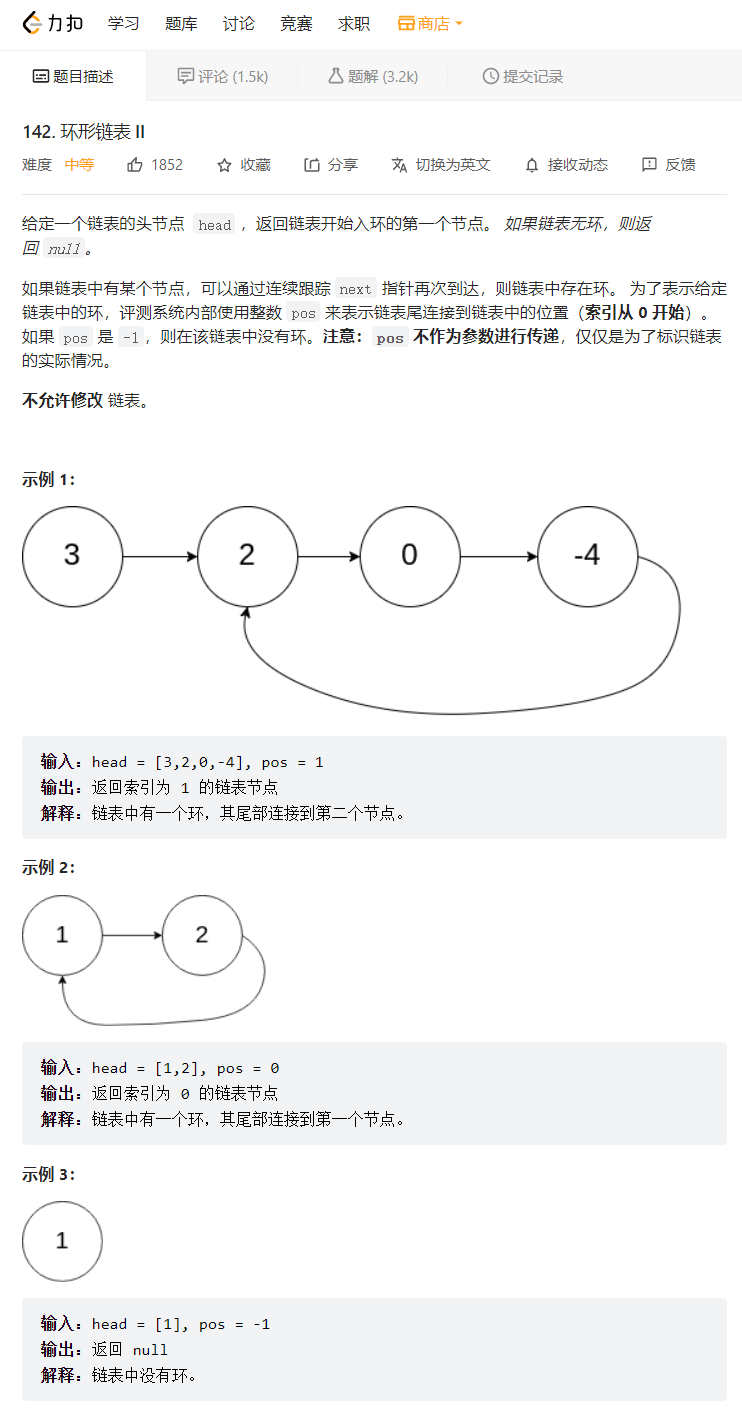
9. 环形链表
💝 思路:
这个题我们使用一种最优的解法,定义两个指针,fast和slow指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,如果最后快指针或者快指针的next指向了空,那么就说明链表是不带环的,如果在循环的过程中,慢指针追上了快指针,则说明链表是带环的那么具体是什么意思呢?我们下面来分析一下: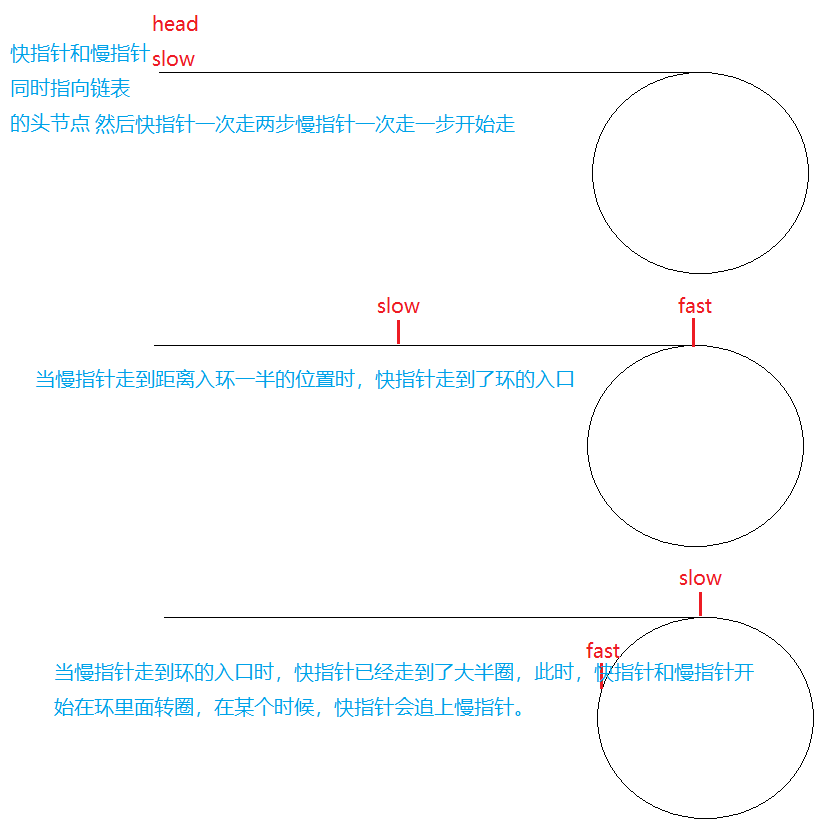
💖 代码实现:bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) { struct ListNode*fast,*slow; fast=slow=head; while(fast&&fast->next) { fast=fast->next->next; slow=slow->next; if(fast==slow) return true; } return false; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
10. 环形链表II
💝 思路一:
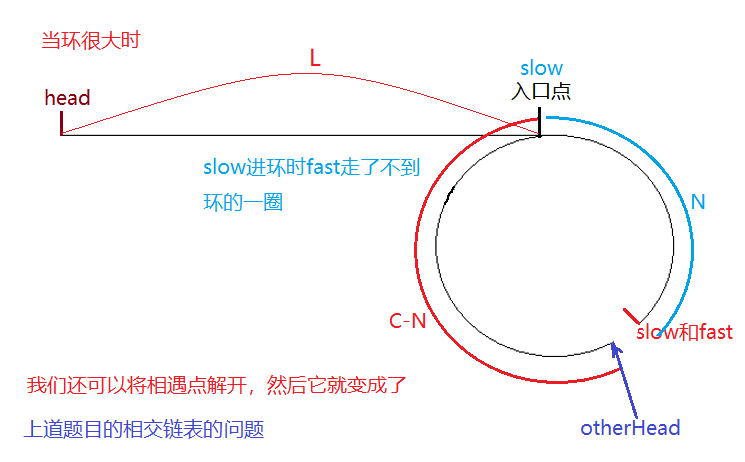
在我们讲这道题之前,我们需要把上道题目证明一下,大家在看上道题目的解析时是否想到过这么个问题,为什么两个指针都进入环后快指针一次走两步,满指针一次走一步快指针可以追上慢指针,如果快指针一次走3步走4步可不可以呢?那样是不是快指针更容易追上慢指针呢?
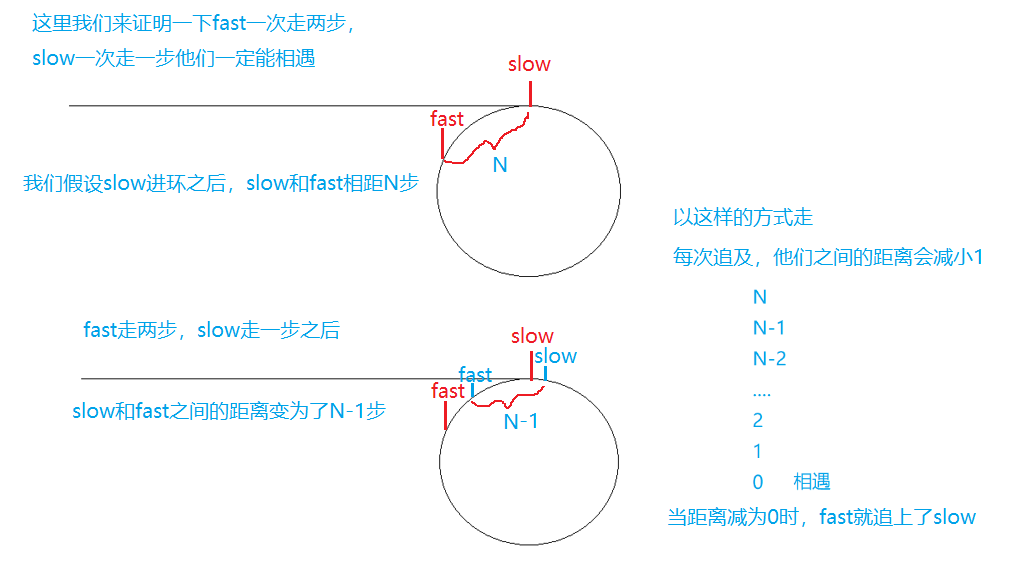
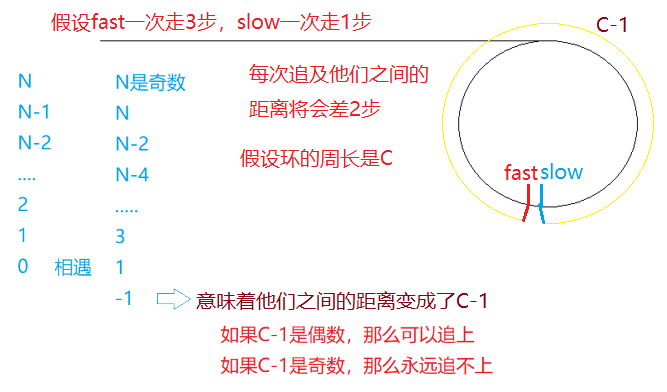
那么题目要求我们找到环的入口点又该如何找呢?这里又得用到了数学中的证明过程——我们分别以大环和小环的情况分别来证明一下
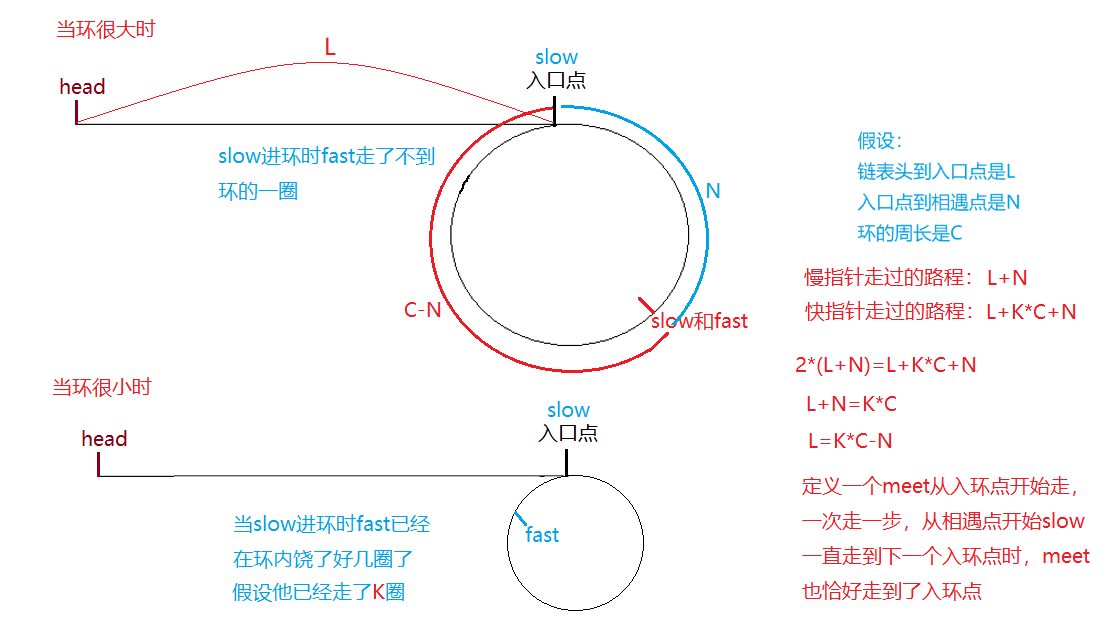
💝 思路二:
💖 代码实现(一):
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) { struct ListNode*fast,*slow; fast=slow=head; while(fast&&fast->next) { fast=fast->next->next; slow=slow->next; if(fast==slow) { struct ListNode*meet=head; while(meet!=slow) { meet=meet->next; slow=slow->next; } return meet; } } return NULL; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
💖 代码实现(二):
struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode* headA, struct ListNode* headB) { if (headA == NULL || headB == NULL) { return NULL; } struct ListNode* curA = headA, * curB = headB; int lenA = 1; //找尾节点 while (curA->next) { curA = curA->next; ++lenA; } int lenB = 1; while (curB->next) { curB = curB->next; ++lenB; } if (curA != curB) { return NULL; } struct ListNode* longList = headA, * shortList = headB; if (lenA < lenB) { longList = headB; shortList = headA; } //长的链表先走差距步 int gap = abs(lenA - lenB); while (gap--) { longList = longList->next; } //同时走找交点 while (longList != shortList) { longList = longList->next; shortList = shortList->next; } return longList; } struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode* slow = head, * fast = head; while (fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (slow == fast) { //转换相交 struct ListNode* meet = slow; struct ListNode* next = meet->next; meet->next = NULL; struct ListNode* entryNode = getIntersectionNode(head, next); //恢复环 meet->next = next; return entryNode; } } return NULL; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
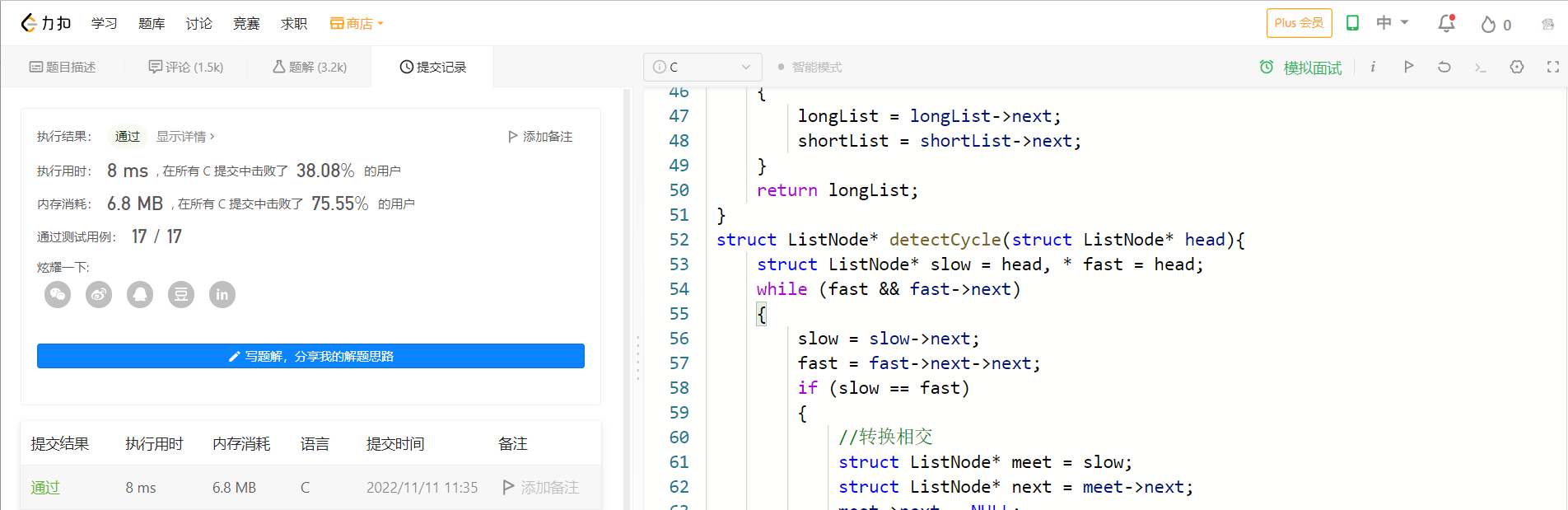
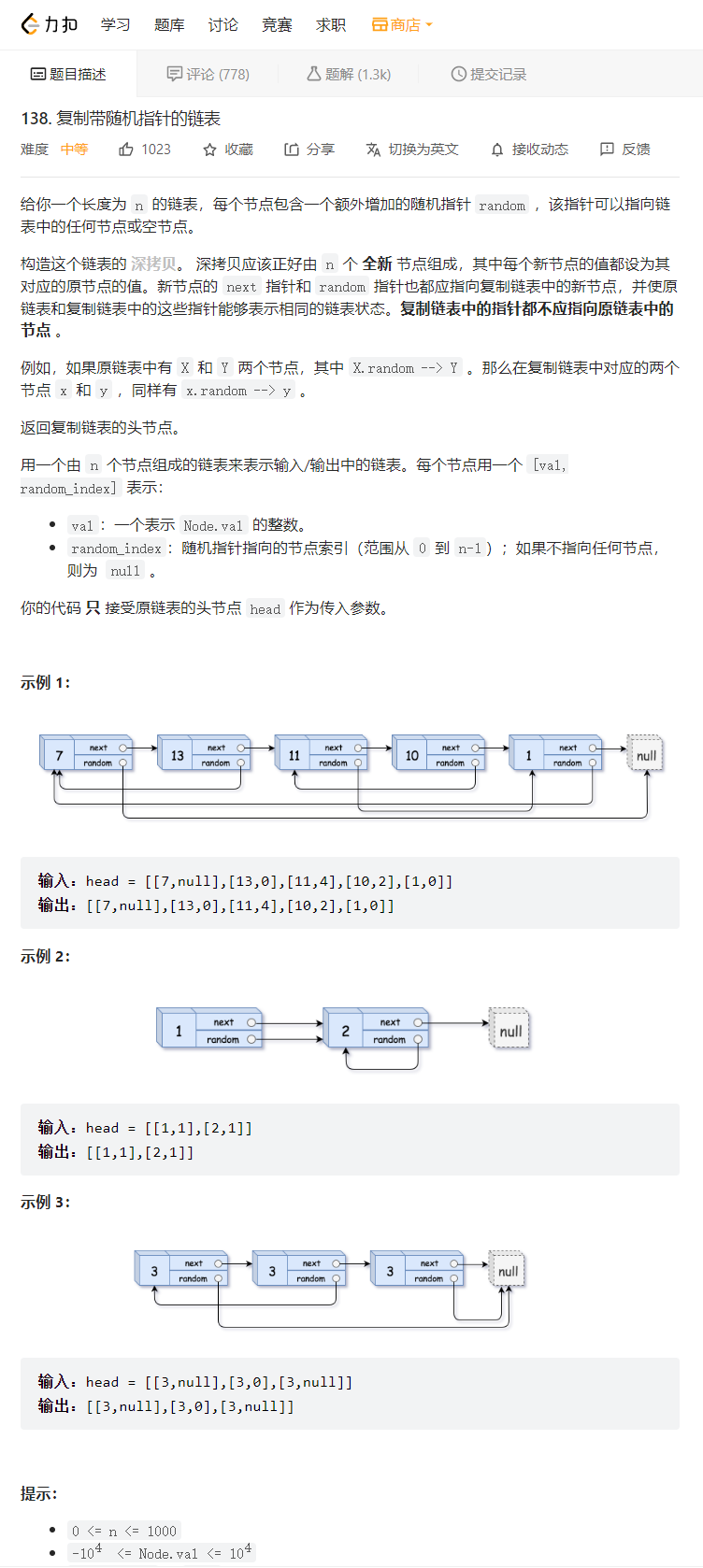
11. 复制带随机指针的链表
💝 思路:
这道题目我们可以分为三步来解:
1> 遍历一边这个链表的所有节点,将每一个结点拷贝一份链接到源节点的后面,以便我们去寻找源节点的random结点指向的结点。
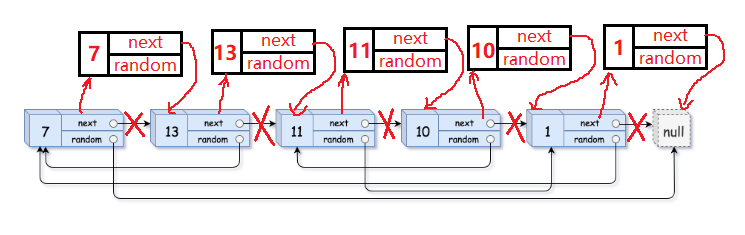
2> 通过源节点的random找到源节点的random所指向的结点,该结点的next结点即为拷贝的每一个结点的random结点所要指向的结点。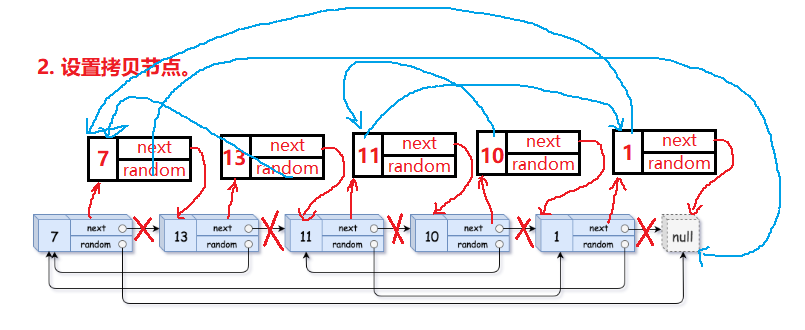
3> 将源节点后面所拷贝的结点全部解下来,然后将其链接成一个新的链表,再将原链表恢复,这道题目就大功告成了。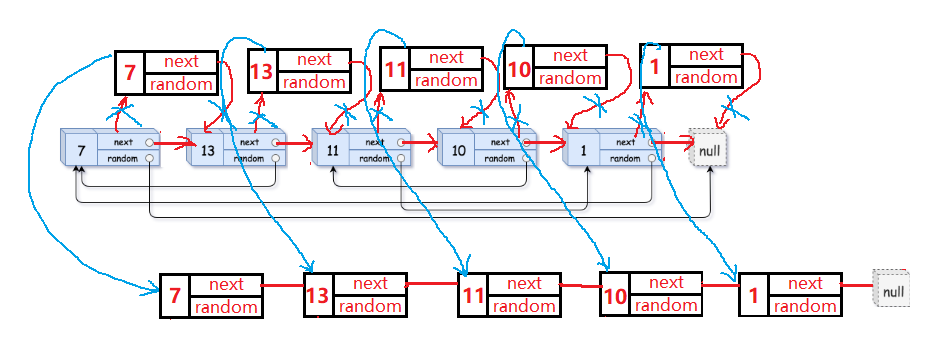
💖 代码实现:struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) { //将拷贝结点链接到源节点后面 struct Node*cur,*Next; cur=head; while(cur) { struct Node*copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); Next=cur->next; copy->val=cur->val; cur->next=copy; copy->next=Next; cur=Next; } //设置拷贝节点 cur=head; while(cur) { struct Node*copy=cur->next; if(cur->random==NULL) copy->random=NULL; else copy->random=cur->random->next; cur=copy->next; } //解下拷贝的结点 cur=head; struct Node*newHead=NULL; struct Node*newTail=newHead; while(cur) { struct Node*copy=cur->next; cur->next=copy->next; if(newHead==NULL){ newHead=copy; newTail=newHead; }else{ newTail->next=copy; newTail=newTail->next; } cur=cur->next; } return newHead; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
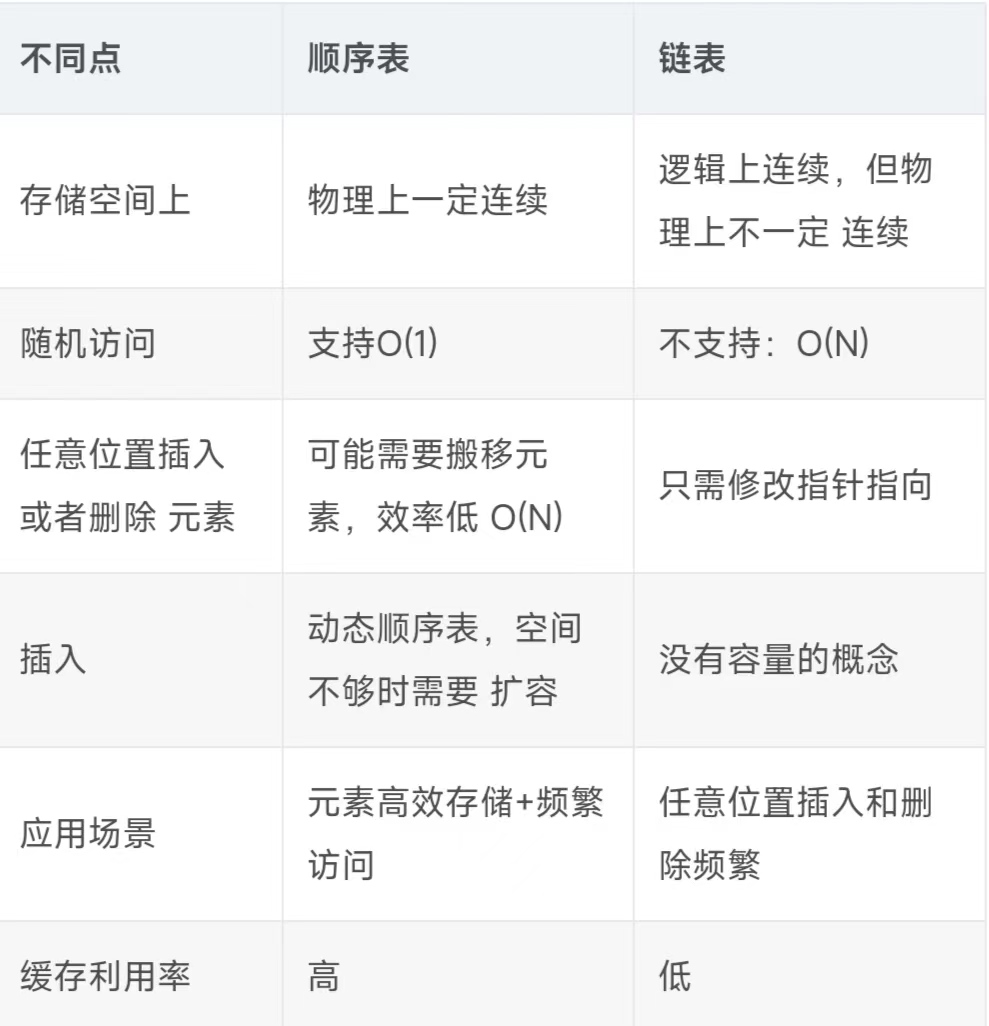
补充内容:浅谈顺序表和链表的区别
💖 下面我们来浅浅看一下链表和顺序表的区别(这里的链表指的是带头双向循环链表):
-
相关阅读:
校企合作再开新篇|哈尔滨工业大学人工智能研究院院长刘劼一行莅临云畅科技考察调研
STARTING POINT TIER 2 Oopsie
道可云元宇宙每日资讯|甸柳中心幼儿园智慧幼+元宇宙空间上线
【OpenCV 例程200篇】209. HSV 颜色空间的彩色图像分割
input控件的maxlength属性
游戏编程模式 - 原型模式、类型对象模式
CSS盒子模型
C++模板进阶
Linux高性能服务器编程 学习笔记 第十七章 系统监测工具
变分自编码器(VAE)公式推导
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_67595314/article/details/127747368