-
Java类和对象(一)
🌭专栏:JavaSE
🍧作者简介:大三学生,想要努力地变得更好!
附上一张可可爱爱的猫猫图~
🍓🍓🍓🍓🍓🍓

前言
Java是一门纯面向对象的语言。面向对象也叫OOP。Java当中一切皆对象。类和对象的知识需要慢慢地理解~可能需要多花些时间。
一、面对对象的初步认知
面向对象和面向过程
🎉面对对象:解决问题的一种思想,主要是依靠对象之间的交互完成一件事情。
举个🌰:
面对过程:关注过程
小陈想喝鸭汤。她需要买小鸭子,把小鸭子养大,杀鸭子,把鸭子砍成块,洗干净鸭肉放锅,切生姜放锅,倒料酒,水煮沸让鸭肉去腥,倒掉水,开始放各种配料调料开始炖汤,等汤炖好了,关火,等喝汤。

喝个鸭汤,差点把小陈累瘫了。按这种方式写代码,将来扩展或者维护起来会比较麻烦。
面对对象:关注对象
小陈想喝鸭汤。她走进了一家饭店:“老板,来一碗鸭汤。”喝完,付完钱,走人。

总共三个对象:小陈 饭店老板 鸭汤
小陈喝鸭汤,是通过对象之间的交互完成的。
🌺🌺
【注意】:面对过程和面对对象并不是一门语言,而是解决问题的方法,没有好坏之分,都有其专用的应用场景。
二、 类定义和使用
面对对象程序设计关注的是对象,而对象是现实生活中的实体。
要拿到对象,必须先有类。
定义了一个类,就相当于在计算机中定义了一种新的类型,与int,double类似。只不过,int和double是java语言自带的内置类型,而类是用户自定义了一个新的类型。
2.1 简单认识类
类是用来对一个实体(对象)进行描述的,主要描述该实体(对象)具有哪些属性,哪些功能行为的。描述完成后,计算机就可以识别了。
比如:洗衣机,我们在java中把它看成一个类别
属性:产品品牌、型号、产品重量、外观尺寸、颜色……
功能:洗衣、烘干……
2.2 类的定义格式
在java中定义类时,需要用到class关键字,具体语法
class 类名{
属性(或者叫成员属性、成员变量)
行为(或者叫成员方法)
}
举例如下
- class WashMachine{
- public String brand;//属性
- public String type;
- public double weight;
- public double length;
- public double width;
- public double height;
- public String color;
- //功能
- public void washClothes(){
- System.out.println("洗衣服");
- }
- public void dryClothes(){
- System.out.println("脱水");
- }
- }
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- }
- }
🥑🥑 其中class为定义类的关键字,WashMachine为类的名字,{}中为类的主体。
🧃🧃🧃注意事项:
1.类目注意采用大驼峰定义
2.成员前写法统一为public
3.此处写的方法不带static关键字
4.一般一个文件当中只定义一个类,一个文件只能有一个public类
5.main方法所在的类一般使用public修饰(注意:Ecipse默认会在public修饰的类中找main方法)

6.public修饰的类名必须要和文件名相同

🍵🍵不要轻易修改public修饰的类的名称,如果要修改:
注意我用到是Idea

然后找到Refactor选项, 点击后找到Rename选项,点击后会出现这样的页面:

三、类的实例化3.1 什么是实例化
🍍🍍🍍
用类类型创建对象的过程,称为类的实例化。在Java中采用new关键字,配合类名来实例化对象。
举个例子:
- class Student{
- public String name;
- public int age;
- public void doHomeWork(){
- System.out.println("写作业");
- }
- public void playGames(){
- System.out.println("打游戏");
- }
- }
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student student=new Student();//new一个对象
- student.name="小陈";
- student.age=18;
- System.out.println(student.name+" "+student.age);
- student.doHomeWork();
- }
- }
输出结果如下:
 🍰🍰🍰注意事项:
🍰🍰🍰注意事项:1.new关键字用于创建一个对象的实例
2.使用.来访问对象中的属性和方法
3.同一个类可以创建多个实例
🍅🍅🍅🍅第三点,我们可以在原本的学生类代码上做些修改:
- class Student{
- public String name;
- public int age;
- public void doHomeWork(){
- System.out.println("写作业");
- }
- public void playGames(){
- System.out.println("打游戏");
- }
- }
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student student1=new Student();//new一个对象
- student1.name="小陈";
- student1.age=18;
- System.out.println(student1.name+" "+student1.age);
- Student student2=new Student();
- student2.name="小俊";
- student2.age=18;
- System.out.println(student2.name+" "+student2.age);
- }
- }
现在我们创建了两个实例,小陈和小俊。现在我们看一下结果:

补充:如果name和age没有赋值,也不会报错。因为他们属于成员变量,编译器会给他们默认值,如果是引用类型,默认为null;int float对应的0值,bollean默认值false char -> '\u0000'
3.2 类和对象的说明
🍓1.类是一个模型一样的东西,用来对一个实体进行描述,限定了类有哪些成员
🍉2.类是一个自定义的类型,可以用来定义变量
🍈3.一个类可以实例化出多个对象。类实例化出对象就像现实中使用建筑设计图建造出房子,类就像是设计图。实例化出的对象才能占用实际的物理空间,存储类成员变量。
3.3 引用与对象
1.当一个引用赋值为null的时候,代表:这个引用不指向任何对象。
- class Student{
- public String name;
- public int age;
- }
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student student1=new Student();//new一个对象
- student1.name=null;
- student1.age=18;
- System.out.println(student1.name+" "+student1.age);
- }
- }
输出:

2.引用不能指向引用
下面这个例子并不是引用指向引用:
- class Student{
- public String name;
- public int age;
- }
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student student1=new Student();//new一个对象
- student1.name="小陈";
- student1.age=18;
- Student student2=new Student();
- student2.name="小俊";
- student2.age=19;
- student1=student2;
- System.out.println(student1.name+" "+student1.age);
- }
- }
输出结果:

🍎这个例子代表的是 student1这个引用指向了student2这个引用指向的对象
3.一个引用不能同时指向多个对象
举例子:
- class Student{
- public int age;
- }
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student student1=new Student();
- //new一个对象
- student1.age=1;
- student1=new Student();
- student1.age=2;
- student1=new Student();
- student1.age=3;
- student1=new Student();
- student1.age=4;
- System.out.println(student1.age);
- }
- }
输出结果:

最后,student1只是指向了一个对象。所以,可以换对象,不能有多个对象。
四、this引用
4.1 为什么要有this引用
- class Student{
- public String name;
- public int age;
- public void information(String x,int y){
- name=x;
- age=y;
- }
- public void show(){
- System.out.println("姓名"+name+" 年龄"+age);
- }
- }
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student student1=new Student();
- //new一个对象
- student1.information("小陈",18);
- student1.show();
- Student student2=new Student();
- student2.information("小俊",19);
- student2.show();
- }
- }
以上代码定义了一个学生信息类,main方法中创建了三个对象,并通过类中的成员方法对对对象进行设置和打印。
🍑🍑看似没有问题,就有一点困惑。
两个对象都在调用information和show函数,但是两个函数中没有任何关于对象的说明,information和show函数如何知道打印的是那个对象的数据呢?
我们在20行的地方取断点,Debug调试:
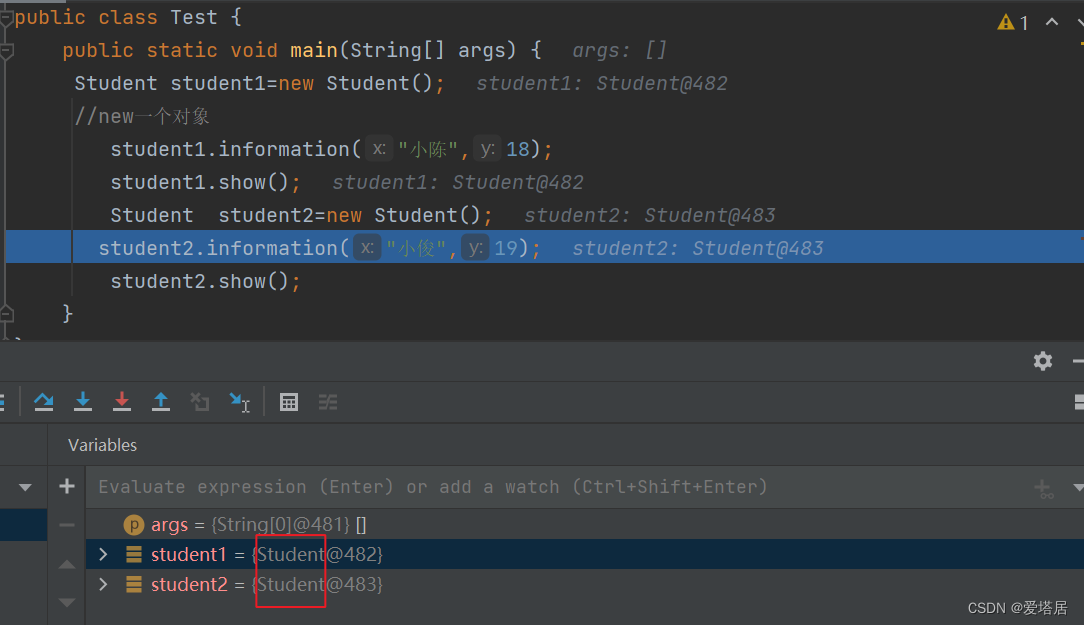
其实代码中隐藏了点东西!
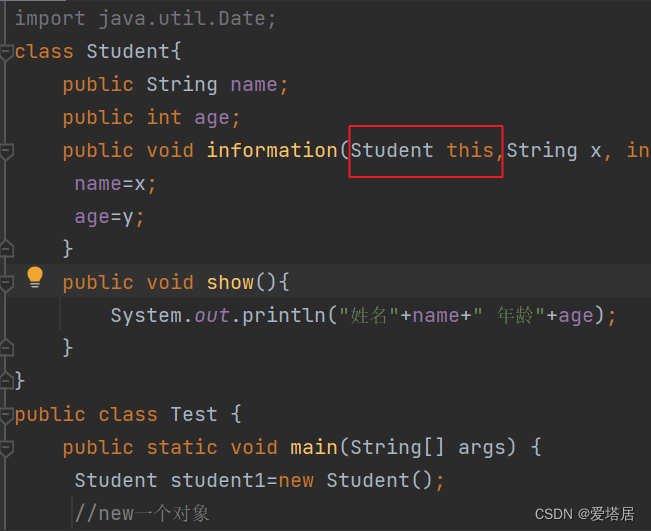
方法前面是哪个引用,就调用哪个对象的方法。this代表的是当前对象的引用。
this还有另外两种用法:
this访问构造方法
this访问成员方法
🍇🍇🍇🍇🍇🍇
这里加不加this,都没有影响。但是!我们要习惯使用this!!!
4.2 什么是this引用
this 引用指向当前对象 ( 成员方法运行时调用该成员方法的对象 ) ,在成员方法中所有成员变量的操作,都是通过该 引用去访问 。只不过所有的操作对用户是透明的,即用户不需要来传递,编译器自动完成。4.3 this引用的特性
1,this的类型:对应类类型引用,即哪个对象调用就是哪个对象的引用类型
2.this只能在“成员方法”中使用
3.在“成员方法”中,this只能引用当前对象,不能再引用其他对象
4.this是“成员方法”第一个隐藏的参数,编译器会自动传递,在成员方法执行时,编译器会负责将调用成员方法对象的引用传递给该成员方法,this负责接收
五、对象的构造及初始化
5.1 构造方法
5.1.1 概念
构造方法(也称为构造器)是一个特殊的成员方法,这个方法没有返回值,方法名和类名时一样的,在创建对象时,由编译器自动调用,并且在整个对象的生命周期内只调用一次。
Student student=new student();这是实例化对象,此时会调用对象的构造方法。如果,你写了,就调用你写的构造方法。如果,你没有写任何的构造方法,此时Java会帮我们提供一个默认的,不带参数的构造方法。public Student(){ }
- public class Date {
- public int year;//成员变量
- public int month;
- public int day;
- public Date(int year,int month,int day){
- this.year=year;
- this.month=month;
- this.day=day;
- }
- public void printDate(){
- System.out.println(year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Date d=new Date(2021,6,9);
- d.printDate();
- }
- }
注意:
1.局部变量和成员变量的区分:
局部变量在方法内。成员变量在类内,在方法外。
2.构造方法的作用就是对对象中的成员进行初始化,并不负责给对象开辟空间。
5.1.2 特性
1.名字必须与类名相同
2.没有返回值,设置为void也不行
3.创建对象时,由编译器自动调用,并且在对象的生命周期内只调用一次
4.构造方法可以重载(用户根据自己的需求提供不同参数的构造方法)
- public class Date {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- //无参构造方法
- public Date(){
- this.year=1900;
- this.month=1;
- this.day=1;
- }
- //带有三个参数的构造方法
- public Date(int year,int month,int day){
- this.year=year;
- this.month=month;
- this.day=day;
- }
- public void printDate(){
- System.out.println(year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Date d=new Date();
- d.printDate();
- }
- }
输出结果:
 5.如果用户没有显示定义,编译器会生成一份默认的构造方法,生成的默认构造方法一定是无参的。但是用户一旦定义,编译器则不再生成。
5.如果用户没有显示定义,编译器会生成一份默认的构造方法,生成的默认构造方法一定是无参的。但是用户一旦定义,编译器则不再生成。- public class Date {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- //带有三个参数的构造方法
- public Date(int year,int month,int day){
- this.year=year;
- this.month=month;
- this.day=day;
- }
- public void printDate(){
- System.out.println(year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Date d=new Date();
- d.printDate();
- }
- }
结果:
 伸个懒腰 ~
伸个懒腰 ~
6.构造方法中,可以通过this调用其他构造方法来简化代码
- public class Date {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- // 无参构造方法--内部给各个成员赋值初始值,该部分功能与三个参数的构造方法重复
- // 此处可以在无参构造方法中通过this调用带有三个参数的构造方法
- // 但是this(1900,1,1);必须是构造方法中第一条语句
- public Date(){
- //System.out.println(year); 注释取消掉,编译会失败
- this(1900, 1, 1);
- //this.year = 1900;
- //this.month = 1;
- //this.day = 1;
- }
- // 带有三个参数的构造方法
- public Date(int year, int month, int day) {
- this.year = year;
- this.month = month;
- this.day = day;
- }
- }
🍧🍧注意:
this(...)必须是构造方法中第一条语句
- public class Date {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- public Date(){
- System.out.println("year:"+year+" month:"+month+" day:"+day);
- this(1900, 1, 1);
- }
- public Date(int year, int month, int day) {
- this.year = year;
- this.month = month;
- this.day = day;
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Date date=new Date();
- }
- }
编译结果:

不能形成环
- public class Date {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- public Date(){
- this(1900, 1, 1);
- System.out.println("year:"+year+" month:"+month+" day:"+day);
- }
- public Date(int year, int month, int day) {
- this();
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Date date=new Date();
- }
- }
编译结果:
 会循环调用,编译报错。
会循环调用,编译报错。7.绝大多数情况下使用public来修饰,特殊场景下会被private修饰。
5.1.3 写构造方法的简便方法
第一步:
或者是直接使用快捷键Alt+insert
第二步:
选择第一个选项:Constructor,出现这样的页面:

第三步:
选择要哪些参数:
如果没有选择参数,就会生成以下的无参构造方法:
public Student() { }如果要选择一个参数,直接点击选项,点击OK,就能生成:
public Student(int age) { this.age = age; }如果要多个参数。按着Ctrl键,点击选项,生成:
public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; }5.2 默认初始化
Date d=new Date(2021,6,9);
在程序层面只是简单的一条语句,在JVM层面需要做好多事情:
1. 检测对象对应的类是否加载了,如果没有加载则加载2. 为对象分配内存空间3. 处理并发安全问题 。比如:多个线程同时申请对象,JVM 要保证给对象分配的空间不冲突4. 初始化所分配的空间即:对象空间被申请好之后,对象中包含的成员已经设置好了初始值。- public class Date {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- public Date(){
- System.out.println("year:"+year+" month:"+month+" day:"+day);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Date date=new Date();
- }
- }

5.设置对象头信息
6.调用构造方法,给对象中各个成员赋值
5.3 就地初始化
- public class Date {
- public int year=2022;
- public int month=11;
- public int day=11;
- public Date(){
- System.out.println("year:"+year+" month:"+month+" day:"+day);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Date date=new Date();
- }
- }

🌳🌳🌳
注意点:
1.不能这样初始化:
- public int year;
- year=2022;
2.代码编译完成后,编译器会将所有给成员初始化的这些语句添加到各个构造函数中。

-
相关阅读:
SpringBoot视图渲染技术
Win10 开机突然不断重复诊断和自动修复,安全模式也进不了,如何解决?(已解决)
基于springboot的洗衣店订单管理系统
【scikit-learn基础】--『监督学习』之 K-近邻分类
Zookeeper三台机器集群搭建
冷冻电镜聚类中心(2D Class)粒子图像的解析
文件路径中的/,\的区别和文件路径的常见用法
VSCODE 配置远程调试环境
逆变器原理
Android 指定有线网或Wifi进行网络请求
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_65683419/article/details/127777133
