-
【并发编程】线程间的通信
1.wait、notify、notifyAll
- 在多线程环境下,有时候一个线程的执行,依赖于另一个线程的某种状态的改变,这时就可以使用wait和notify或者notifyAll。
- wait和sleep的区别:wait会释放持有的锁,但是sleep不会,sleep知识让线程在指定的时间内,不去抢占cpu的资源。
- wait notify在使用的时候必须放在同步代码块里,必须拥有当前对象的锁,不能获取A对象的锁,去唤醒B对象。
- notify随机唤醒一个等待的线程,notifyAll唤醒所有在该对象上等待的线程。
public class WaitDemo { private static boolean flag = false; private static Object object = new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { new Thread(() -> { synchronized (object) { if (!flag) { try { System.out.println("flag is false"); System.out.println(object+"进入等待状态"); object.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } System.out.println("flag is true"); }).start(); Thread.sleep(2000L); new Thread(() -> { synchronized (object) { flag = true; object.notify(); System.out.println(object+"被唤醒"); } }).start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33

2.生产者消费者模型
(1)生产者消费者模型图
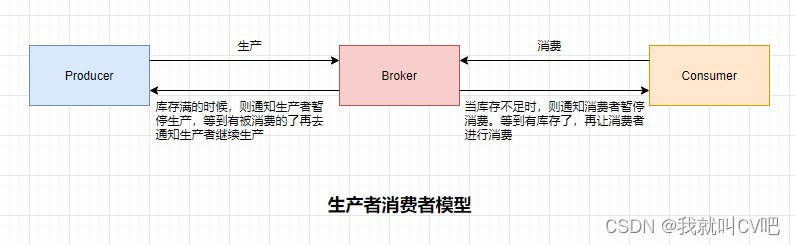
(2)编码实战
- 中间商Broker代码
public class Broker { //当前库存数 private static int num; //规定最大库存数量 private static final int TOTAL = 20; /** * 生产者生产产品存入库存 */ public synchronized void put(){ //先判断库存有没有满 if(num < TOTAL){ //库存没有满时,生产者生产 System.out.println("---库存新增一个,当前库存为:"+ ++num); //唤醒消费者消费 notifyAll(); }else{ try { //库存满时,生产这进入等待状态 System.out.println("***库存已满,生产者等待生产"); wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * 消费者消费库存 */ public synchronized void take(){ //先判断是否有库存 if(num>0){ System.out.println("---库存减少1个,当前库存为:"+ --num); //唤醒生产者 notifyAll(); }else{ try { System.out.println("***暂无库存,消费者等待消费"); wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 生产者Producer代码
public class Producer implements Runnable { private Broker broker; public Producer(Broker broker) { this.broker = broker; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { System.out.println("###生产者生产一件商品"); broker.put(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 消费者Consumer代码
public class Consumer implements Runnable { private Broker broker; public Consumer(Broker broker) { this.broker = broker; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { System.out.println("###消费者消费一件商品"); broker.take(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建中间商 Broker broker = new Broker(); //生产者线程 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { new Thread(new Producer(broker)).start(); } //消费者线程 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { new Thread(new Consumer(broker)).start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
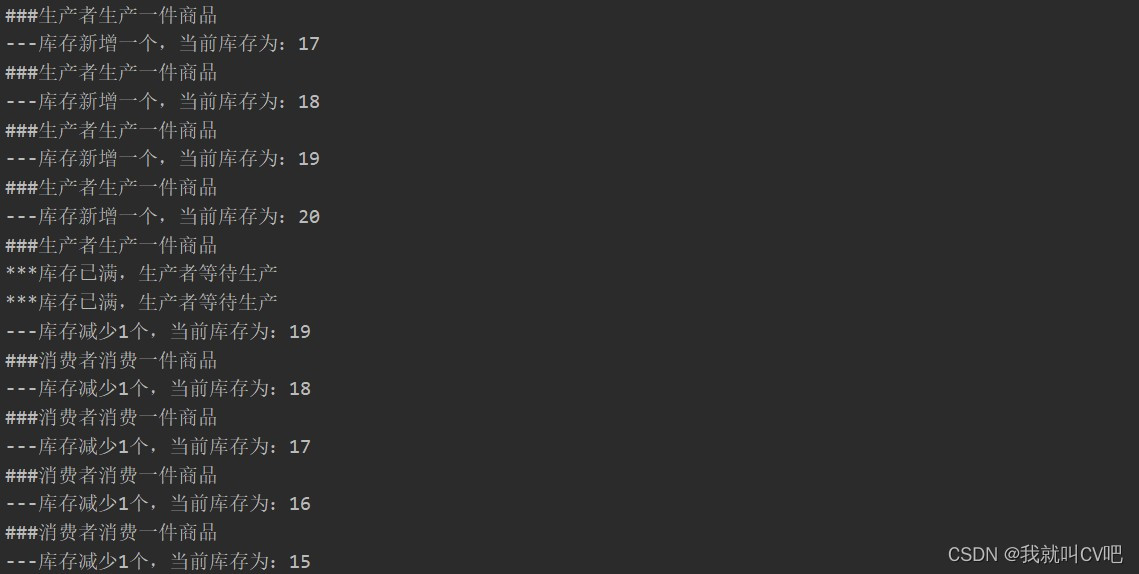
3.管道流进行线程间的通信
- 管道流进行通信其实就是以内存为媒介,一个线程去往里面存数据,一个线程去里面取数据,用于线程间的通信。
- 主要有两类
- 面向字节:【PipedOutputStream、PipedInputStream】
- 面向字符:【PipedReader、PipedWriter】
(1)字节管道流
- 编写线程ByteStreamReader类
public class ByteStreamReader implements Runnable { private PipedInputStream pipedInputStream; public ByteStreamReader(PipedInputStream pipedInputStream) { this.pipedInputStream = pipedInputStream; } @Override public void run() { try { if(pipedInputStream != null){ //读取内存中中的数据 String str = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(pipedInputStream)).lines().collect(Collectors.joining("\n")); System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取内存中的数据:"+str); } pipedInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建管道输入流 PipedInputStream pipedInputStream = new PipedInputStream(); //创建管道输出流 PipedOutputStream pipedOutputStream = new PipedOutputStream(); //输入流与输出流建立连接 pipedOutputStream.connect(pipedInputStream); //启动线程,将输入流作为参数传输进去 new Thread(new ByteStreamReader(pipedInputStream)).start(); //创建字符输入流 BufferedReader bufferedReader = null; System.out.print("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"向内存中写入数据:"); //将控制台输入的内容转化成流 bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); //写入内存 pipedOutputStream.write(bufferedReader.readLine().getBytes()); pipedOutputStream.close(); if(bufferedReader != null){ bufferedReader.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
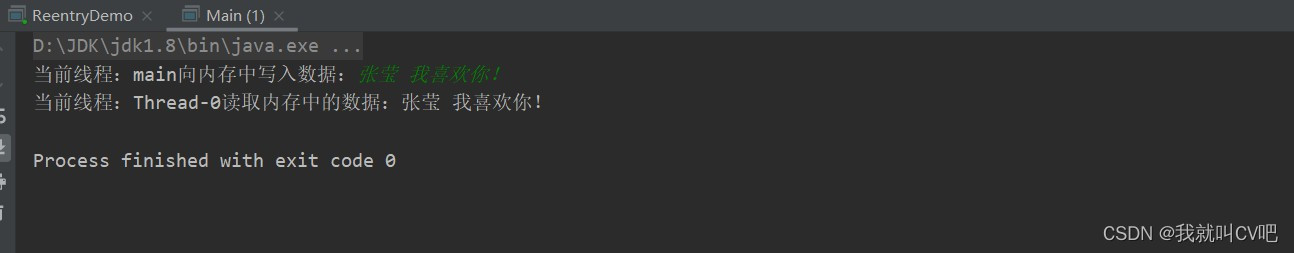
- 注意:不要在同一个线程中使用PipInputStream和PipOutputStream,会造成死锁。
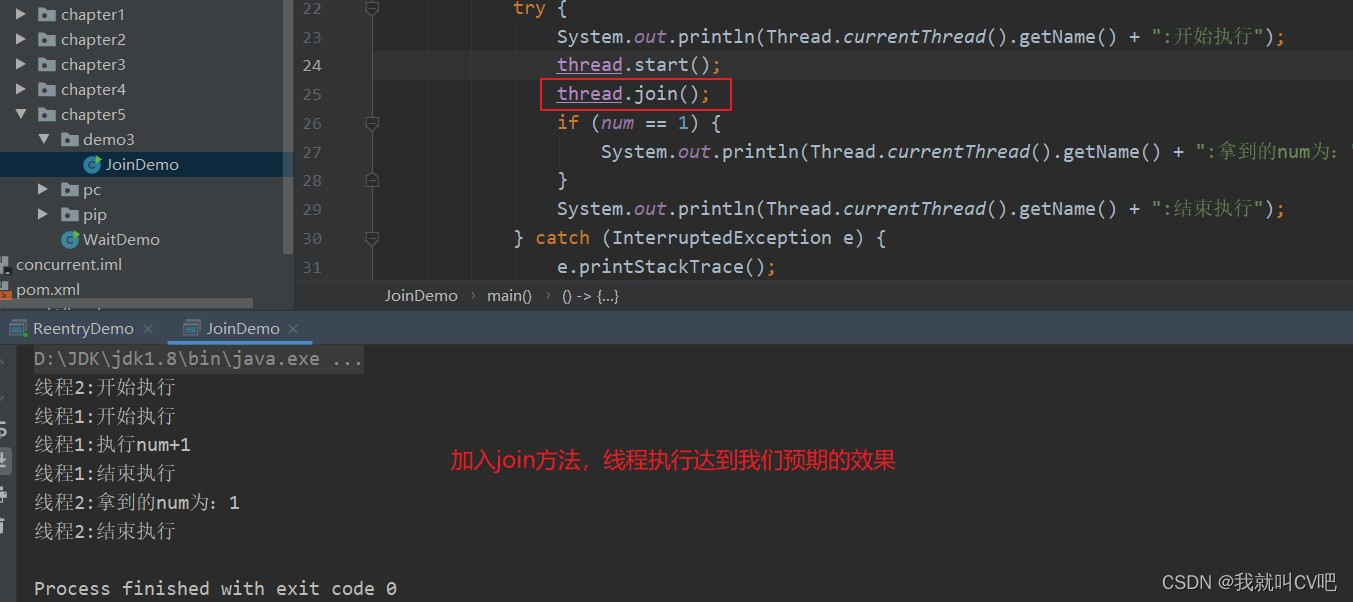
4.Thread.join()方法
(1)join()方法简介
- join()方法一共三个方法重载
public final void join() throws InterruptedException; public final synchronized void join(long millis) throws InterruptedException; public final synchronized void join(long millis, int nanos) throws InterruptedException;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 三个重载最终都掉用一个参数的版本。
- join()和join(0)是等价的,表示会一直等下去,join(非0)表示等待一段时间。
- 使用场景:线程A执行到一半,需要一个数据,这个数据需要线程B去执行修改,只有B修改完成之后,A才能继续操作。
(2)join的使用
public class JoinDemo { public static int num = 0; public void add() { num++; } public static void main(String[] args) { JoinDemo joinDemo = new JoinDemo(); Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":开始执行"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":执行num+1"); joinDemo.add(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":结束执行"); }, "线程1"); new Thread(() -> { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":开始执行"); thread.start(); /**join方法控制让线程2中的线程1先执行完成以后在执行线程2后面的操作*/ thread.join(); if (num == 1) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":拿到的num为:" + num); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":结束执行"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "线程2").start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 没有加上join()方法的运行结果
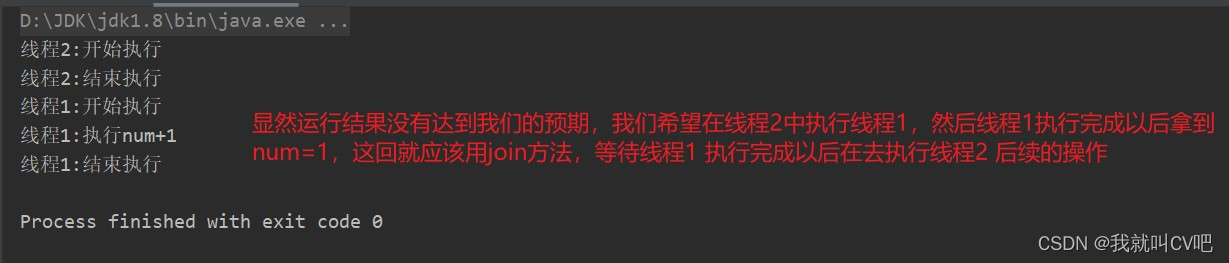
- 加上join()方法的运行结果
5.Condition详解
(1)Condition简介
- 在线程Thread类中线程之间通信是通过object类的wait()和notify()方式实现的。而ReentrantLock也有类似于wait()和notify()功能。前者是java底层级别后者是语言级别的具有更高的可控制性和扩展性。
- 二者的区别:
- Condition能够支持不响应式中断,而通过使用Object方式不支持。
- Condition能偶支持多个等待队列(new多个Condition对像),而Object方式只能支持一个。
- Condition能够支持超时时间的设置,而Object不支持。
(2)案例实战
- 简单案例
public class ConditionDemo implements Runnable{ private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private static Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); @Override public void run() { try{ lock.lock(); condition.await(); System.out.println("Thread is going on"); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(new ConditionDemo()); //启动线程 thread.start(); //睡眠2s Thread.sleep(2000); //加锁,因为condition在调用await()方法时,会释放锁资源,所以要重新加锁 lock.lock(); //唤醒 condition.signal(); //解锁 lock.unlock(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
新建的线程thread调用start()方法后执行run()方法,此时掉用lock.lock()方法进行加锁,此时线程获得锁,继续执行condition.await()方法,这个时候线程会释放刚才获得的锁资源,将线程加入到condition维护的等待队列中,等调用condition.signal()方法后,会唤醒condition等待对类中的一个线程加入到AQS对列中去,直至唤醒的线程重新获取所资源后才能继续向下执行。
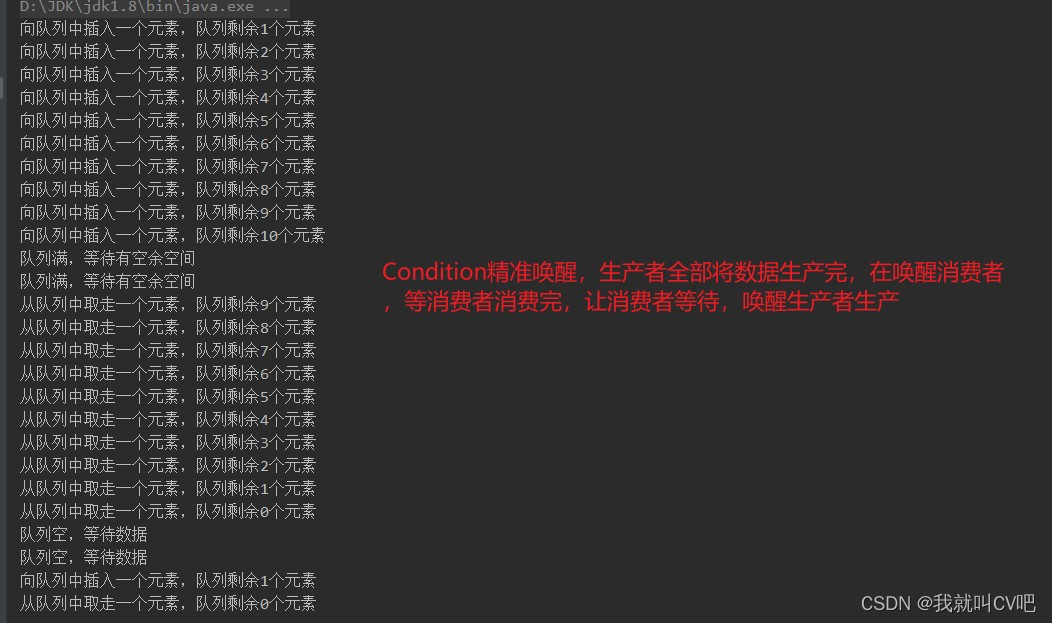
- 生产者消费者模型
public class ConditionDemo { private int queueSize=10; //定义优先队列,大小初始化为10 private PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(queueSize); //定义ReentrantLock,Condition要配合锁使用 private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //定义生产者的Condition对象 private Condition producer = lock.newCondition(); //定义消费者的Condition对象 private Condition consumer = lock.newCondition(); class Consumer extends Thread{ volatile boolean flag = true; private void consume(){ //循环调用 while(flag){ //加锁 lock.lock(); try{ /** * 如果队列是空就让消费者停止消费,进入等待状态,循环等待, * 保证不会在有消费者线程去执行await()方法 */ while(queue.isEmpty()){ try{ System.out.println("队列空,等待数据"); consumer.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { //发生异常结束方法执行 flag=false; } } //队列弹出一个元素 queue.poll(); //唤醒生产者 producer.signal(); System.out.println("从队列中取走一个元素,队列剩余"+queue.size()+"个元素"); }finally { //最后一定要进行解锁操作 lock.unlock(); } } } @Override public void run() { consume(); } } class Producer extends Thread{ volatile boolean flag = true; private void produce(){ //循环调用 while(flag){ //加锁 lock.lock(); try{ /** * 判断队列是否已满,如果队列的大小等于规定好的队列长度 * 就让生产者进行等待 */ while(queue.size() == queueSize){ try { System.out.println("队列满,等待有空余空间"); producer.await(); }catch (InterruptedException e){ //发生异常结束方法执行 flag=false; } } //生产一个元素 queue.offer(1); //每次插入一个元素 //唤醒消费者 consumer.signal(); System.out.println("向队列中插入一个元素,队列剩余"+queue.size()+"个元素"); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } } @Override public void run() { produce(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { ConditionDemo conditionDemo = new ConditionDemo(); Producer producer = conditionDemo.new Producer(); Consumer consumer = conditionDemo.new Consumer(); producer.start(); consumer.start(); producer.interrupt(); consumer.interrupt(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
-
相关阅读:
【2023年11月第四版教材】软考高项极限冲刺篇笔记(1)
精心整理高频js手写题请查收
CTF中的一些图形密码
图片转pdf格式怎么弄?
【机器学习算法】聚类分析-1 聚类是什么,我们如何确定类别间的相似性或者相异性
建模示范视频EA-027/智慧公寓系统试看片段-视频+图片版
骨灰级大 BOOS 总结出内部不传之密:多线程高并发笔记 + 视频版
POP3协议(电子邮件邮局协议)中UIDL和TOP命令在实际使用中的作用
JaveEE进阶----Spring Web MVC入门
Python文件操作2-- 小案例
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47533244/article/details/127800625