-
Hive3 - HiveSQL 特征及操作
一、HiveSQL特征
Hive SQL(HQL)与SQL的语法大同小异,基本上是相通的,对SQL掌握的可以非常快的上手使用Hive SQL。不过在一些细节上需要特别注意Hive自己特有的语法知识点,下面分别进行介绍。1. 字段数据类型
Hive数据类型整体分为两个类别:原生数据类型(primitive data type)和复杂数据类型(complex data type)。原生数据类型包括:
tinyint,smallint,int,bigint,float,double,boolean,string,timestamp,binary。复杂数据类型包括:
array数组、map映射、struct结构、union联合体。create table test_xbc( id int comment "ID", name string comment "名称" ) comment "测试表";- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
注意点:
Hive对英文字母大小写不敏感,如果定义的数据类型和文件不一致,会尝试隐式转换,但是不保证成功。2. SerDe 序列化方式
Serializer、Deserializer的简称,目的是用于在读写数据时的序列化和反序列化,其中Hive在读取文件时,会首先调用InputFormat(默认TextInputFormat),返回一条一条kv键值对记录(默认是一行对应一条记录)。然后调用SerDe(默认LazySimpleSerDe)的Deserializer,将一条记录中的value根据分隔符切分为各个字段。在写文件时,首先调用SerDe(默认LazySimpleSerDe)的Serializer将对象转换成字节序列,然后调用OutputFormat将数据写入HDFS文件系统中。既然默认的是
LazySimpleSerDe,那就肯定可以指定其他的类来处理,Hive在建表的时候可以通过row format关键字指定该参数,如果指定delimited表示使用默认的LazySimpleSerDe类来处理数据。create table test_xbc1( id int comment "ID", name string comment "名称" ) comment "测试表" row format delimited- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
如果指定其他类来处理,可以使用
serde来指定,比如:row format serde 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDe'- 1
这里的
serde还支持用户自定义SerDe类。3. 字段分隔符
Hive数据存储在HDFS文件系统中,字段与字段之间想分隔开就需要定义分隔符,建表时如果没有row format语法指定分隔符。此时字段之间默认使用的ascii编码的分割符\001。如果修改分隔符可以使用
fields terminated by和lines terminated by指定列和行之间的分隔符create table test_xbc2( id int comment "ID", name string comment "名称" ) comment "测试表" row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n'- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
除了行和列,还支持集合元素之间分隔,Map元素分隔符,比如下面数据类型:
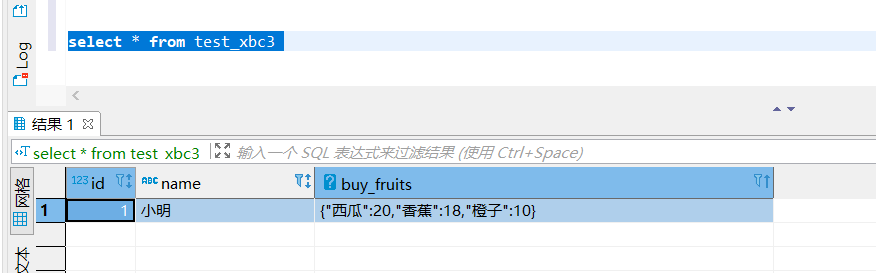
1,小明,西瓜:20;香蕉:18;橙子:10- 1
分别标识
ID、姓名、购买水果及价格, 前两个都是基础类型,后面的属于 Map 类型,此时就需要设定集合元素之间分分隔符和Map元素的分隔符:create table test_xbc3( id int, name string, buy_fruits map<string,int> ) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' collection items terminated by ';' map keys terminated by ':' ;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
4. 建表时指定存储目录
Hive创建表默认存储路径是由hive-site.xml配置文件中的hive.metastore.warehouse.dir属性指定的。默认是:/user/hive/warehouse,如果创建的表已存在数据,并且数据存在其他位置,可以通过location更改数据的存储位置:create table test_xbc3( id int comment "ID", name string comment "名称" ) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n' location '/data/data1'- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
创建测试下面数据
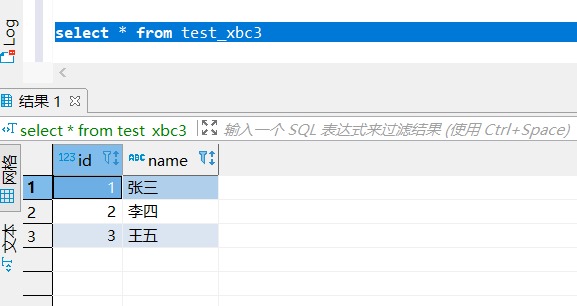
test_xbc3.txt:1,张三 2,李四 3,王五- 1
- 2
- 3
将数据上传至
/data/data1下:hadoop fs -put test_xbc3.txt /data/data1/- 1
查询数据:
select * from test_xbc3;- 1
5. 内、外部表
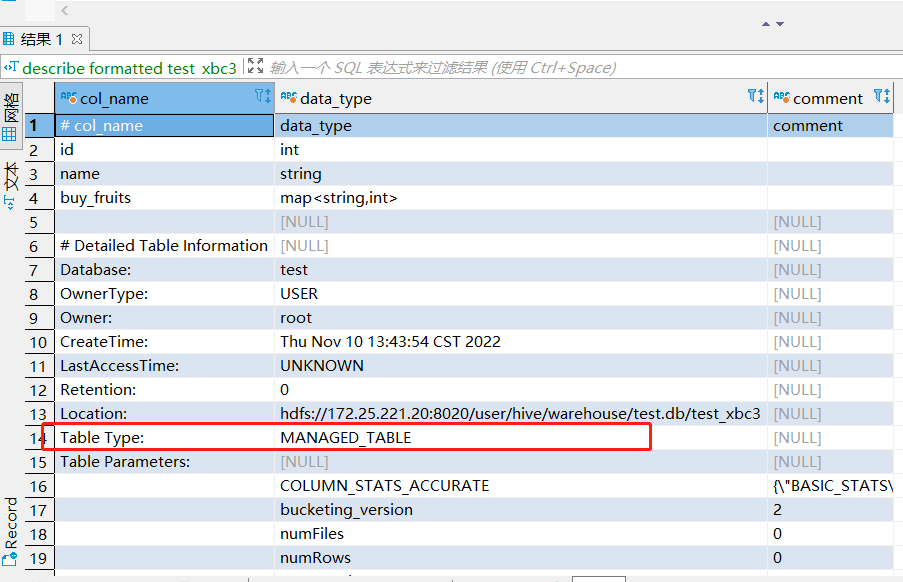
Hive中表可分为内部表和外部表,内部表也称为被Hive拥有和管理的托管表。默认情况下创建的表就是内部表,Hive拥有该表的结构和文件,删除内部表时,它会删除数据以及表的元数据。外部表只管理表元数据的生命周期,其中的数据不归Hive拥有或管理,删除外部表只会删除元数据,而不会删除实际数据。通过
describe formatted tableName;可以获取表的描述信息,其中Table Type标明了表的类型:
默认就是内部表,如果需要创建外部表,则需要使用 需要使用
external关键字:create external table test_xbc4( id int, name string ) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n' location '/data/data2';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
创建测试下面数据
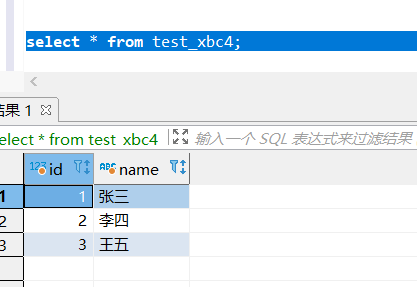
test_xbc4.txt:1,张三 2,李四 3,王五- 1
- 2
- 3
将数据上传至
/data/data2下:hadoop fs -put test_xbc4.txt /data/data1/- 1
查询数据:
select * from test_xbc4;- 1
删除表test_xbc4:drop table test_xbc4;- 1
到
HDFS中查看可以发现数据依然存在: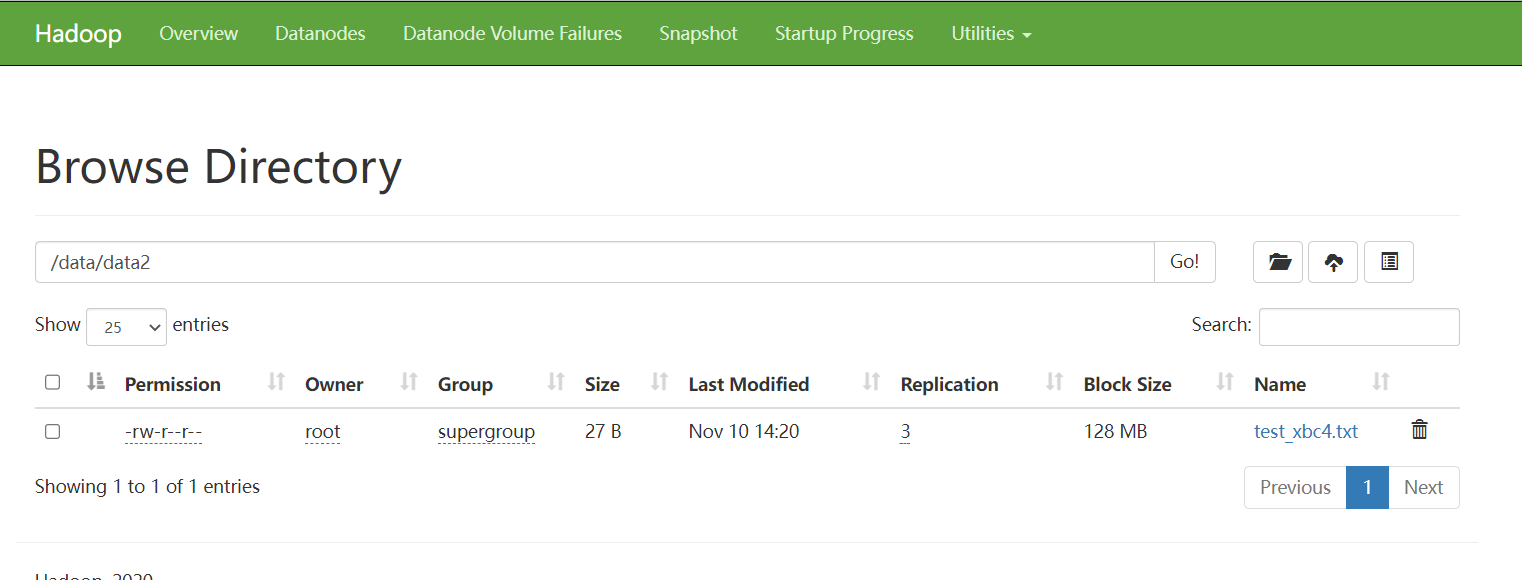
6. Hive分区表
当
Hive表的数据量大、文件多时,为了避免查询时全表扫描数据,Hive支持根据用户指定的字段进行分区,分区的字段可以是日期、地域、种类等具有标识意义的字段。根据标识字段快速定位数据分区,尽可能避免了全表扫描查询。创建分区表的语法:
create table table_name (column1 data_type, column2 data_type) partitioned by (partition1 data_type, partition2 data_type,….);- 1
比如有下面三个文件数据,分别字段表示:
ID、姓名、地区1,小明,jiangsu 2,小李,jiangsu 3,小红,jiangsu 4,小兰,jiangsu 5,张三,jiangsu 6,李四,jiangsu- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
7,王五,shandong 8,赵六,shandong 9,诸葛亮,shandong 10,曹操,shandong 11,关羽,shandong 12,周瑜,shandong- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
13,荆轲,beijing 14,嬴政,beijing 15,后羿,beijing- 1
- 2
- 3
因此,可以创建分区表,根据地区字段分区:
create table test_xbc5( id int, name string, area_name string ) partitioned by (area string) row format delimited fields terminated by "," lines terminated by '\n';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
注意:分区字段不能是表中已经存在的字段,因为分区字段最终也会以虚拟字段的形式显示在表结构上。
手动加载分区数据,将上面三个数据上传至
HDFS中: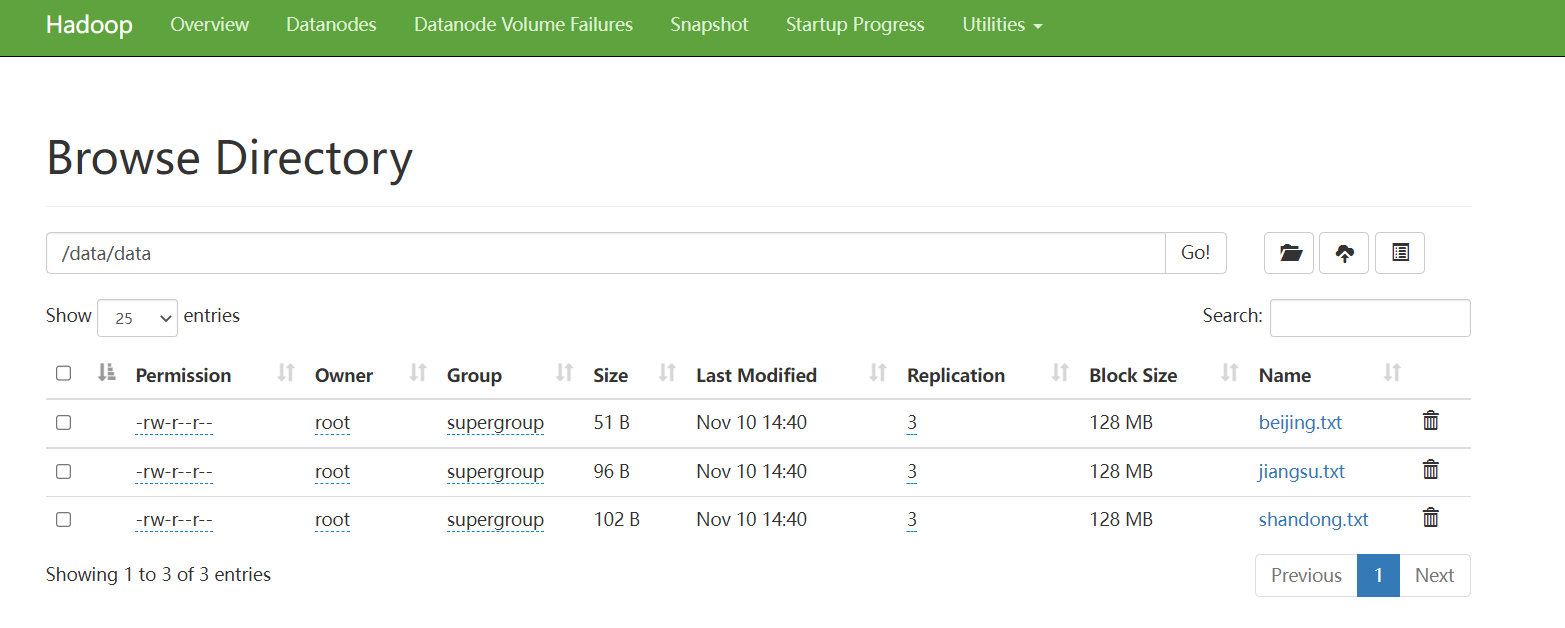
静态分区
加载数据,
load命令说明在下面第10点:load data inpath '/data/data/jiangsu.txt' into table test_xbc5 partition(area="jiangsu"); load data inpath '/data/data/shandong.txt' into table test_xbc5 partition(area='shandong'); load data inpath '/data/data/beijing.txt' into table test_xbc5 partition(area='beijing');- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
查询数据:
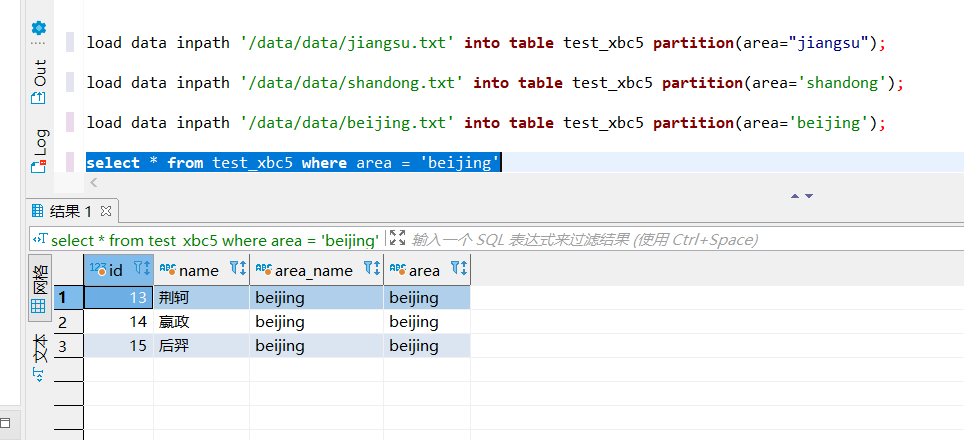
动态分区:
动态分区指的是分区的字段值是基于查询结果自动推断出来的,需要在hive会话中设置两个参数:
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true; set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict;- 1
- 2
- 3
其中
hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode分为nonstick非严格模式和strict严格模式。strict严格模式要求至少有一个分区为静态分区。创建另一张分区表:
create table test_xbc6( id int, name string, area_name string ) partitioned by (area string) row format delimited fields terminated by "," lines terminated by '\n';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
写入分区数据:
insert into table test_xbc6 partition(area) select * from test_xbc5 ;- 1
查询数据:
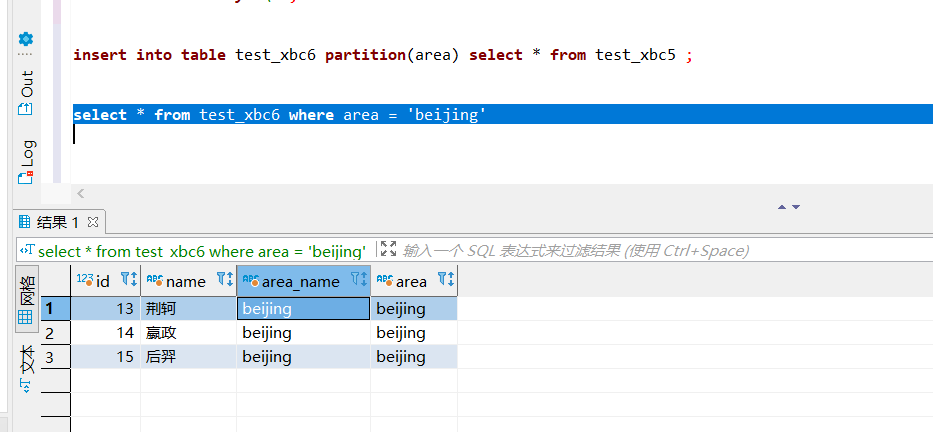
查看 HDFS 存储接口:
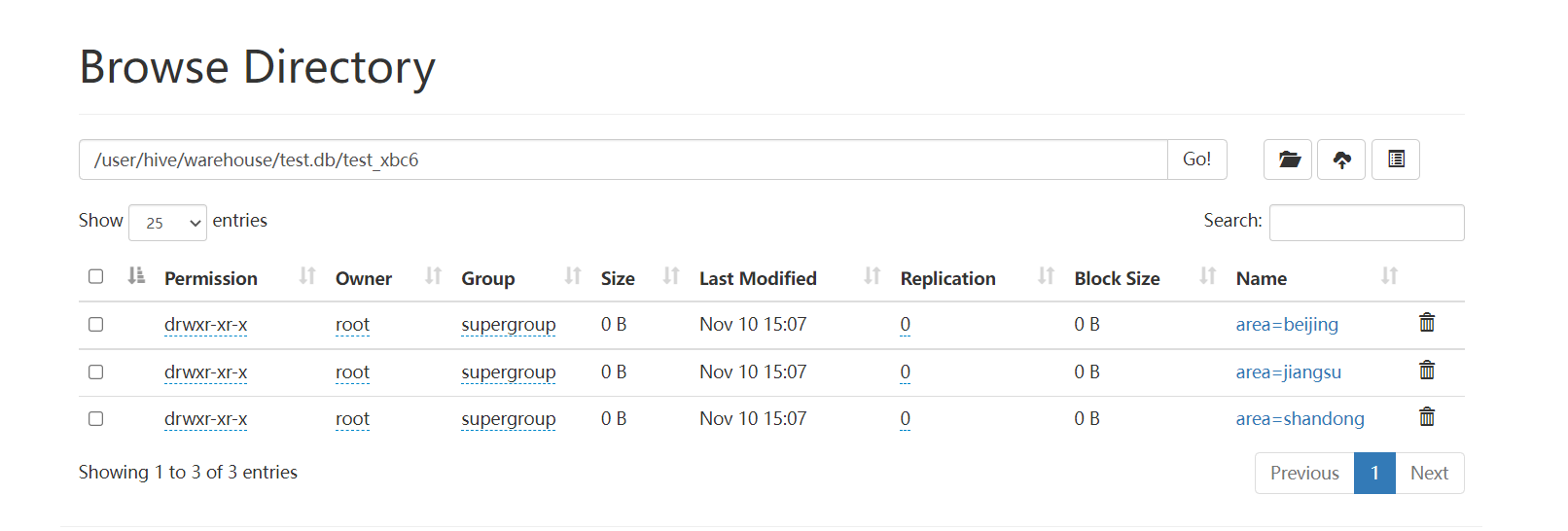
7. Hive分桶表
分桶表也叫做桶表,是一种用于优化查询而设计的表类型。该功能可以让数据分解为若干个部分进行存储,在查询时可以减少全表扫描,
JOIN时也可以提高MR程序效率,减少笛卡尔积数量。在分桶时,我们要指定根据哪个字段分桶,分桶的个数。默认规则是:
Bucket number = hash_function(bucketing_column) mod num_buckets。桶编号相同的数据会被分到同一个桶当中。分桶表的语法:
create [external] table [db_name.]table_name [(col_name data_type, ...)] clustered by (col_name) into n buckets;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
clustered by (col_name)表示根据哪个字段进行分,注意字段必须是表中已经存在的字段。into n buckets表示分为几个桶。比如有如下数据,根据 ID 分成 3 个桶。
1,小明,jiangsu 2,小李,jiangsu 3,小红,jiangsu 4,小兰,jiangsu 5,张三,jiangsu 6,李四,jiangsu 7,王五,shandong 8,赵六,shandong 9,诸葛亮,shandong 10,曹操,shandong 11,关羽,shandong 12,周瑜,shandong- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
首先先创建一个普通表,将数据加载进来:
create table test_xbc7( id int, name string, area_name string ) row format delimited fields terminated by "," lines terminated by '\n';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
将数据上传至
HDFS中的/user/hive/warehouse/test.db/test_xbc7/下。然后创建分桶表:
create table test_xbc8( id int, name string, area_name string ) clustered by(id) into 3 buckets row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
写入分桶表数据:
insert into test_xbc8 select * from test_xbc7;- 1
查询分桶表数据:
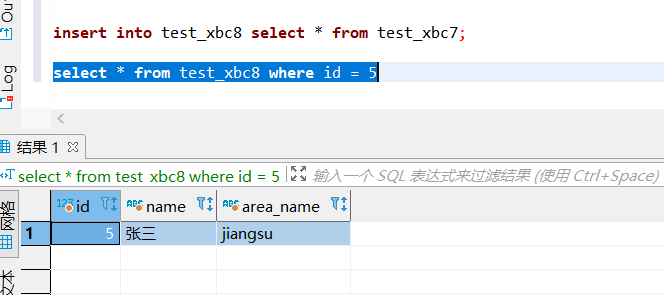
查看
HDFS存储格式:
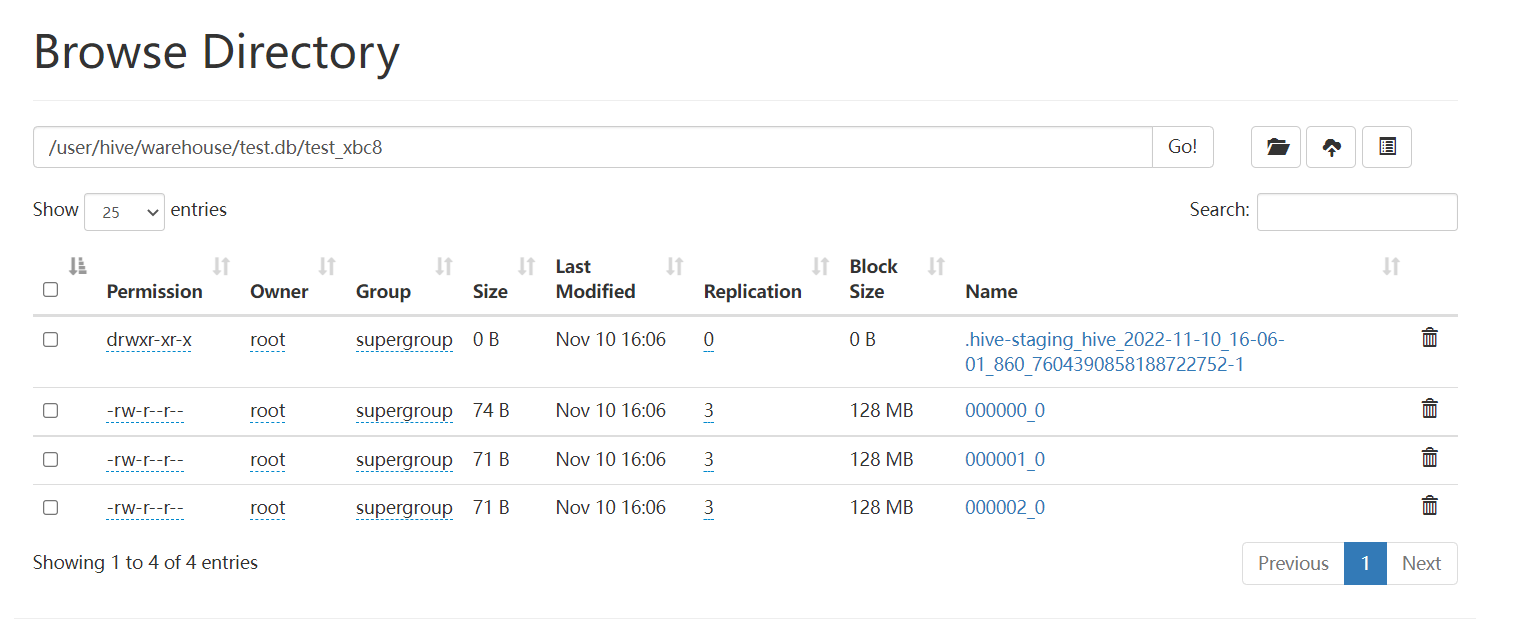
8. Hive事务表
从
Hive0.14版本开始,具有了ACID语义的事务,在此之前的版本中是不支持事务的,Hive 0.14后 ,也增加了INSERT,UPDATE和 DELETE操作,不过UPDATE和 DELETE只能在事务表上才可以操作。事务表的局限性
- 不支持
BEGIN、COMMIT、ROLLBACK操作,所有操作都是自动提交。 - 仅支持
ORC文件格式(STORED AS ORC)。 - 默认事务为关闭状态,需要配置开启使用。
- 表必须是分桶表(
Bucketed)。 - 表参数
transactional必须为true; - 外部表不能成为
ACID表,不允许从非ACID会话读取/写入ACID表。
在使用事务表前需要开启以下配置,也可以在
hive-site.xml永久配置--支持并发 set hive.support.concurrency = true; --开启分桶功能 set hive.enforce.bucketing = true; --动态分区模式为非严格 set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode = nonstrict; --事务管理器 set hive.txn.manager = org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.lockmgr.DbTxnManager; -- 在Metastore实例上运行启动线程和清理线程 set hive.compactor.initiator.on = true; -- metastore实例上运行多少个压缩程序工作线程。 set hive.compactor.worker.threads = 1;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
创建事务表:
create table test_xbc8( id int, name string, area_name string ) clustered by(id) into 3 buckets row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n' stored as orc tblproperties('transactional'='true');- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
写入数据:
insert into test_xbc8 values(1,'小明'); insert into test_xbc8 values(2,'张三');- 1
- 2
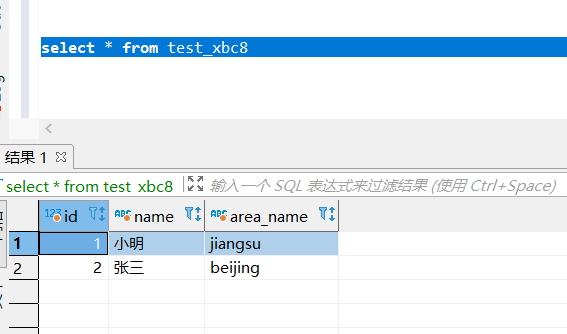
修改数据
update test_xbc8 set name = '李四' where id = 2;- 1
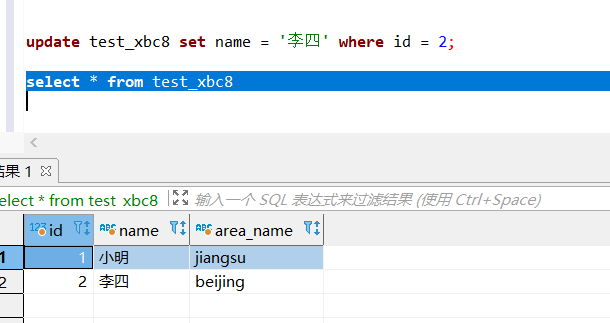
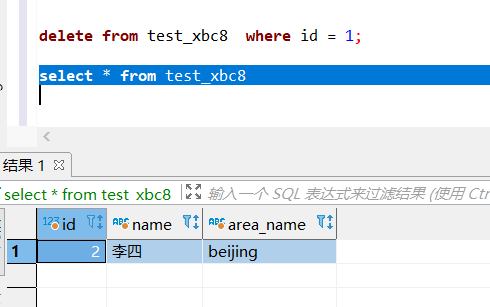
删除数据:
delete from test_xbc8 where id = 1;- 1
9. Hive视图
Hive的视图同MySQL中的视图一致,是一种虚拟表,只保存定义,不实际存储数据。
创建视图:
create view test_xbc5_view as select * from test_xbc8 where area_name = 'jiangsu';- 1
- 2
10. load 加载数据
将本机或
HDFS中的文件加载到表中,加载过程Hive不会进行任何转换,只是数据文件移动到与Hive表对应的位置下。语法:
load data [local] inpath 'filepath' [overwrite] into table tablename [partition (partcol1=val1, partcol2=val2 ...)] load data [local] inpath 'filepath' [overwrite] into table tablename [partition (partcol1=val1, partcol2=val2 ...)] [inputformat 'inputformat' serde 'serde'] (3.0 or later)- 1
- 2
- 3
local:如果不加 local 则去HDFS中找相关路径,如果加 local 则是去HiveServer2服务所在主机系统文件中查找。
filepath:待移动数据的路径
overwrite:如果加了overwrite则目标表(或者分区)中的内容会被删除,然后再添加新的数据。加载本地数据至
test_xbc5表:load data local inpath '/data/data/test_xbc5.txt' into table test_xbc5;- 1
加载
HDFS中的数据至test_xbc5表:load data inpath '/data/data/test_xbc5.txt' into table test_xbc5;- 1
加载
HDFS中的数据至test_xbc5表的某个分区:load data inpath '/data/data/test_xbc5.txt' into table test_xbc5 partition(area="jiangsu");- 1
在
Hive 3.0及更高版本中当最后一个字段是分区字段时,并且前面的字段可以和表的字段对应上,load时可以不指定分区,自动转换成为insert as select语句加载数据,例如有下面数据:1,小明,jiangsu 2,小李,jiangsu 3,小红,jiangsu 4,小兰,jiangsu 5,张三,jiangsu 6,李四,jiangsu 7,王五,shandong 8,赵六,shandong 9,诸葛亮,shandong 10,曹操,shandong 11,关羽,shandong 12,周瑜,shandong 13,荆轲,beijing 14,嬴政,beijing 15,后羿,beijing- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
创建分区表:
create table test_xbc9( id int, name string ) partitioned by (area string) row format delimited fields terminated by "," lines terminated by '\n';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
加载上面示例数据:
load data inpath '/data/data/test_xbc9.txt' into table test_xbc9;- 1
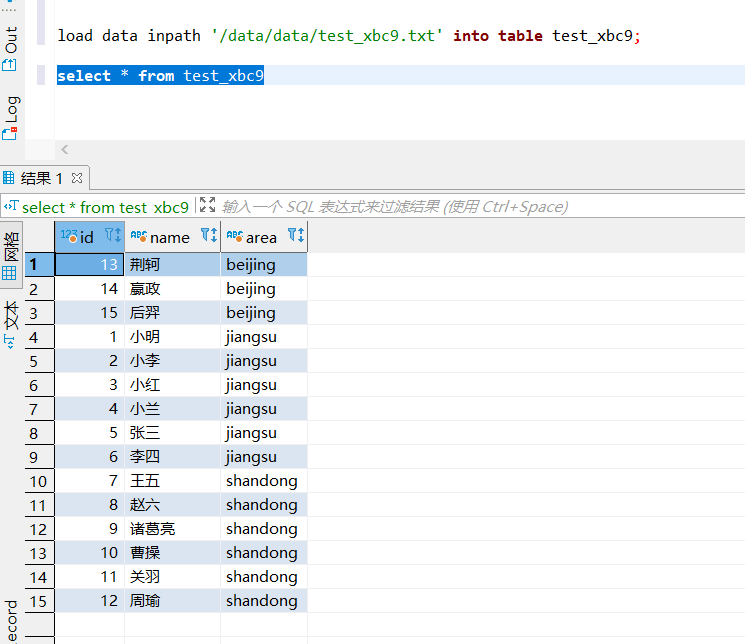
查看HDFS中的存储结构: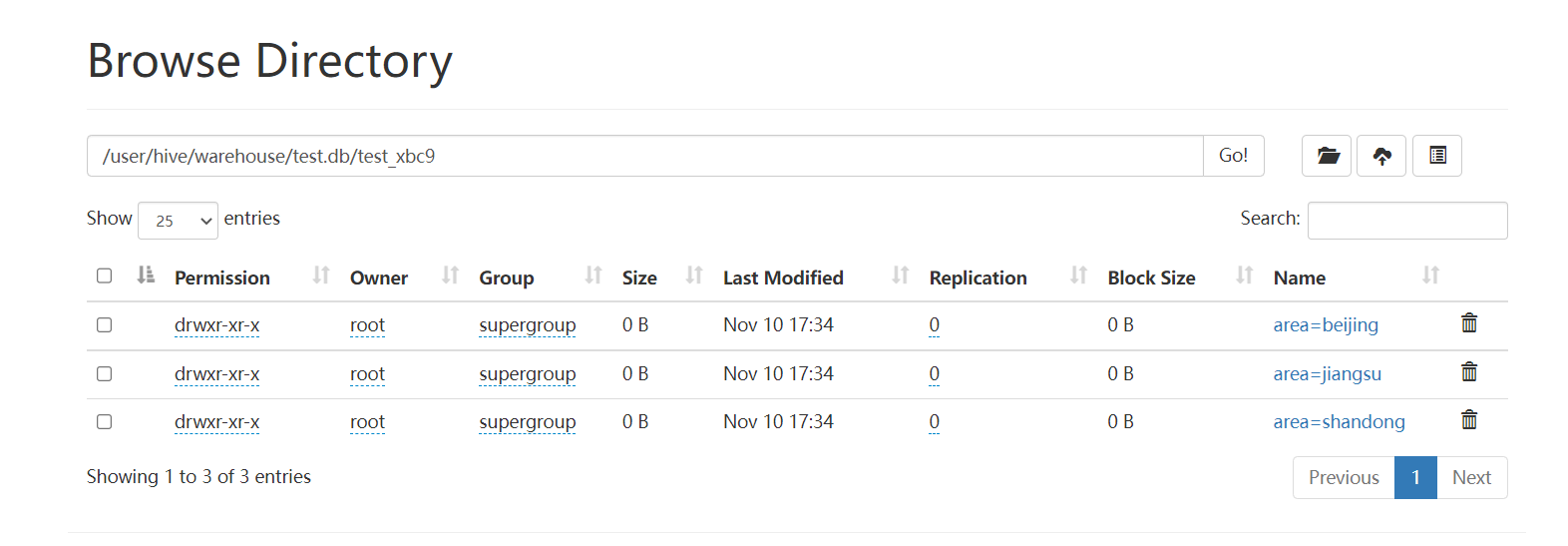
-
相关阅读:
【学习笔记37】BOM基本认识
KepServer EX6模拟仿真PlC数据以及点表的复制跟项目的迁移
始祖双碳新闻 | 2022年8月8日碳中和行业早知道
2022年度C语言面试题库汇编(含完整答案)
如何快速两个整数互质,已知的六种方法
基于LSTM+FCN处理多变量时间序列问题记录
14.Oracle中的事务
elasticsearch 索引文档相关操作
国产32位单片机 普冉PY32F002B 适用于LED灯驱,控制器等
第七章:最新版零基础学习 PYTHON 教程—Python 列表(第三节 -Python程序访问列表中的索引和值)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43692950/article/details/127784911