-
【零基础入门MyBatis系列】第八篇——使用MyBatis的小技巧
一、#{ } 和 ${ }
🌔 1、#{} 和 ${} 的区别
- #{}: 底层使用PreparedStatement。特点:先进行SQL语句的编译,然后给SQL语句的占位符问号 ? 传值。可以避免 SQL 注入的风险。
- ${} :底层使用Statement。特点:先进行SQL语句的拼接,然后再对SQL语句进行编译。存在SQL注入的风险。
🌔 2、通过简单的一个案例来分析它们的区别:我们就以一条查询语句为例
<select id="selectByCarType" resultType="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car"> select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where car_type = #{carType} </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
(1)可以看到我们此处使用的是 #{},最终是将 carType 的值传递到这个位置,加入我们调用这个方法的语句是下面这样的:
@Test public void testSelectByCarType(){ // 创建会话 SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); // 获得接口的实现类 CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); // 调用我们的方法 List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByCarType("燃油车"); // 打印查询结果 cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); // 关闭连接 sqlSession.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
底层最后执行的是
where carTyoe = "燃油车"【此处我只给出了这部分片段来说明问题】
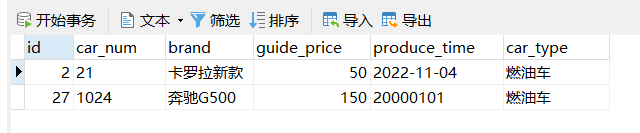
我复制了控制台打印的日志信息16:19:27.933 [main] DEBUG com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Preparing: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where car_type = ? 16:19:27.966 [main] DEBUG com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Parameters: 燃油车(String) 16:19:28.012 [main] DEBUG com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - <== Total: 4 Car{id=2, carNum='21', brand='卡罗拉新款', guidePrice=50.0, produceTime='2022-11-04', carType='燃油车'} Car{id=14, carNum='21', brand='卡罗拉新款', guidePrice=50.0, produceTime='2022-11-04', carType='燃油车'} Car{id=21, carNum='21', brand='卡罗拉新款', guidePrice=50.0, produceTime='2022-11-04', carType='燃油车'} Car{id=27, carNum='1024', brand='奔驰G500', guidePrice=150.0, produceTime='20000101', carType='燃油车'}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
(2)当我们把
car_type = #{carType}替换成car_type = ${carType}之后- 日志报告如下:【并没有复制全部的报错】
16:21:38.562 [main] DEBUG com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Preparing: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where car_type = 燃油车 16:21:38.599 [main] DEBUG com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Parameters:- 1
- 2
通过这段报告我们可以得知 >> ${参数} 就是将参数的值拼接到指定的位置上。
- 那什么时候我们会使用到 ${} 呢?
接下来我们会给出几个具体的几个案例来演示是如何使用 ${} 的
🌔 3、如果我们需要拼接表名的时候,就会使用 ${} 来传递参数
- 我们希望通过拼接的字段来选择我们使用哪个表,首先创建两张表【两张表的结构是相同的】
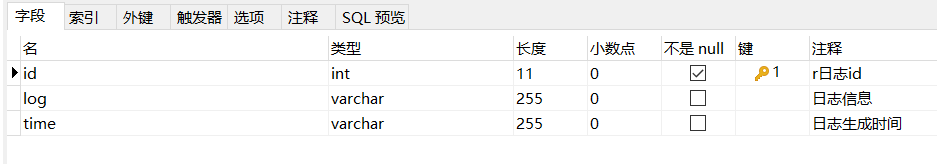
但是两张表的表名和存储的数据不同:t_log_20221104、t_log_20221105- 创建一个pojo类 Log.java
package com.powernode.mybatis.pojo; /** * @author Bonbons * @version 1.0 */ public class Log { private Integer id; private String log; private String time; public Log(){} public Log(Integer id, String log, String time) { this.id = id; this.log = log; this.time = time; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getLog() { return log; } public void setLog(String log) { this.log = log; } public String getTime() { return time; } public void setTime(String time) { this.time = time; } @Override public String toString() { return "Log{" + "id=" + id + ", log='" + log + '\'' + ", time='" + time + '\'' + '}'; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 编写我们的数据库操作接口 LogMapper 【此处我们只写一个方法,参数传递我们要拼接的日期】
package com.powernode.mybatis.mapper; import com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log; import java.util.List; /** * @author Bonbons * @version 1.0 */ public interface LogMapper { /** * 根据日期查询不同的表,查询表中所有的日志 * @param date * @return */ List<Log> selectAllByTable(String date); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 编写我们对应的映射文件 LogMapper.xml 【之所以用 * 代替是因为数据库表中字段与类属性名完全一致】
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.LogMapper"> <select id="selectAllByTable" resultType="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log"> select * from t_log_${date} </select> </mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 编写我们的测试类 LogMapperTest.java
package com.powernode.mybatis.test; import com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.LogMapper; import com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log; import com.powernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.List; /** * @author Bonbons * @version 1.0 */ public class LogMapperTest { @Test public void testSelectAllByTable(){ SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); LogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(LogMapper.class); List<Log> logs = mapper.selectAllByTable("20221105"); logs.forEach(log -> System.out.println(log)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
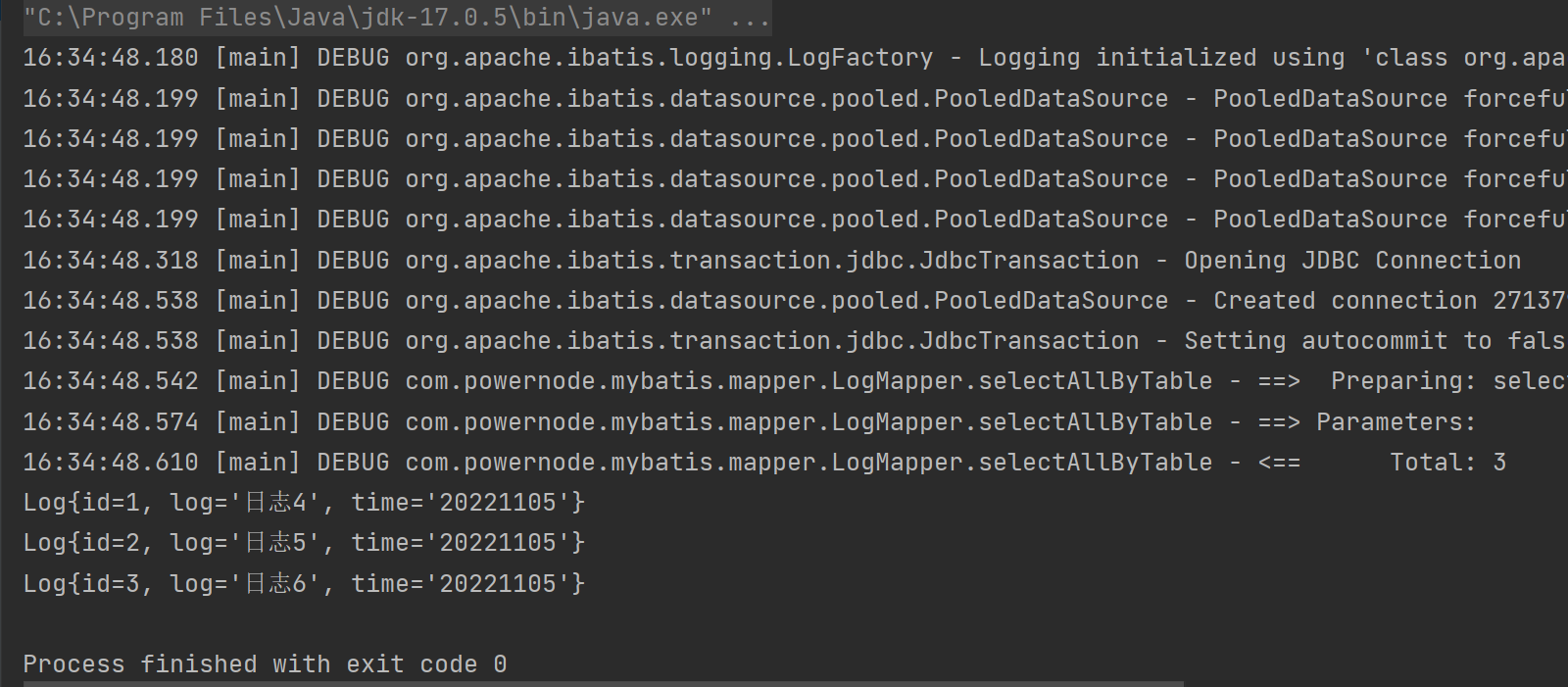
- 当我们希望将参数的值拼接到SQL语句中使用的时候 >> 我们就可以考虑使用 ${}
🌔 4、在MyBatis中如何实现批量删除呢?
- 此处我们想实现的是通过传递一个字符串来完成批量删除
- 我们有两种语句格式可以采用,一种为 or 多个条件、另一种利用in关键字
delete from t_car where id=1 or id=2 or id=3; delete from t_car where id in(1,2,3);- 1
- 2
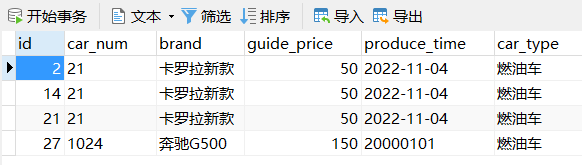
- 我们以t_car 表为例进行操作,所以此处为了简明的说明批量删除如何通过 ${} 实现,我们就只给出 接口中的方法、Mapper中的SQL语句 以及 测试代码段
(1)接口中的方法 【ids 是多个 id 构成的字符串,彼此之间用逗号分隔】
/** * 根据 id 批量删除 * @param ids 传入的id * @return 返回删除记录的条数 */ int deleteBatch(String ids);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
(2)Mapper 映射文件中的 SQL 语句
<delete id="deleteBatch"> delete from t_car where id in (${ids}) </delete>- 1
- 2
- 3
(3)写在 CarMapperTest 类中的测试方法
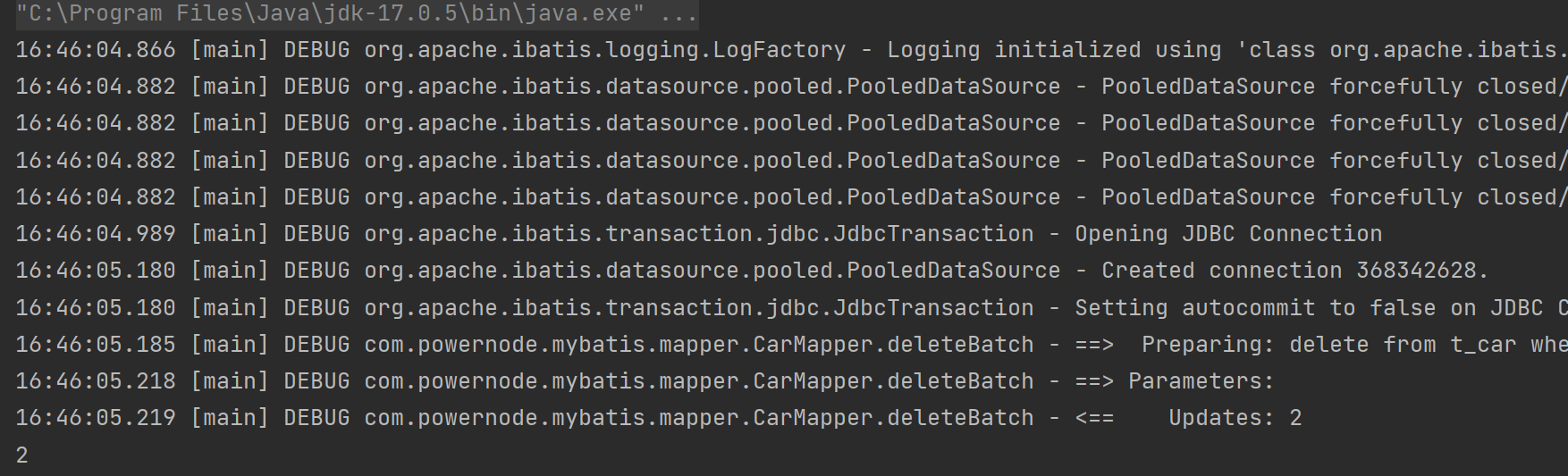
@Test public void testDeleteBatch(){ // 创建会话 SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession(); // 获得接口的实现类 CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class); // 调用删除方法 int count = mapper.deleteBatch("14,21"); System.out.println(count); // 提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); // 关闭连接 sqlSession.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
🌔 5、如何实现模糊查询呢?-
对于模糊查询的实现方式有多种,使用 #{} 和 ${} 都可以
-
对于mybatis的使用基本步骤和上面基本类似 写接口、写映射文件、写测试程序 【此时我们只给出这几种实现方法】
-
例如我们想要根据汽车的品牌查询数据:那么在Mapper文件中的SQL语句框架应该是这样的
<select id="selectByBrandLike" resultType="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car"> select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where <!--方案一:brand like '%${brand}%'--> <!--方案二: brand like concat('%', '${brand}', '%')--> <!--方案三: brand like concat('%', #{brand}, '%')--> <!--方案四: 最常用--> brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
二、typeAliases
🌔 1、什么是 typeAliases?
- 是 MyBatis 提供的一种别名处理器类。
- 当我们在Mapper中写select语句的时候都要指明返回值类型。而且我们得写对应pojo类的全限定类名。
- 很长,如果经常用的话,我们就可以在核心文件里面配置一个全局属性,给指定的全限定类名起一个别名,在映射文件中我们只使用这个别名就可以了。
🌔 2、那么我们如何来创建别名呢? 【要注意核心配置文件中标签的顺序关系】
<typeAliases> <!--最一般的方式起别名 <typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car" alias="aaa" /> <typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log" alias="bbb" /> --> <!-- 不指定别名默认为类的简名,并且不区分大小写 <typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car" /> <typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log" /> --> <!-- 指定包名,将包下所有的类都自动起别名 >> 类的简名 <package name = "com.powernode.mybatis.pojo" /> --> </typeAliases>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 此处我们给出了三种方式创建别名,好用程度是递增的 【别名是不区分大小写的】
- type 字段传递的是我们要起别名的全限定类名, alias 字段传递的别名
- 如果省略了 alias 就是用默认的别名:类的简名 【com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car >> car】
- 也可以直接将一个包下的所有类全部指定默认类名,就是通过我们的 package 标签
- 重点:我们这是为 resultType 起别名,namespace 是不能起别名的
三、Mappers
🌔 1、我们先看一下之前核心配置文件中的mappers标签都怎么写的:
<mappers> <!--sql映射文件创建好之后,需要将该文件路径配置到这里--> <mapper resource="CarMapper.xml"/> <mapper resource="LogMapper.xml"/> </mappers>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
🌔 2、如何找到Mapper映射文件的位置?
-
总共有四种方式:
- resource:从类路径中加载 【配置文件需要放到类路径当中】
- url:从指定的全限定资源路径中加载 【提供一个绝对路径,但是移植性太差】
- class:使用映射器接口实现类的完全限定类名 【接口和对应mapper文件在一个目录下】
- package:将包内的映射器接口实现全部注册为映射器 【通过package标签直接加载所有mapper文件,前提满足class中那种情况】
-
resource 案例:
<mappers> <mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/> <mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/BlogMapper.xml"/> <mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/PostMapper.xml"/> </mappers>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- url 案例:
<mappers> <mapper url="file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml"/> <mapper url="file:///var/mappers/BlogMapper.xml"/> <mapper url="file:///var/mappers/PostMapper.xml"/> </mappers>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- class 案例:
<!-- 使用映射器接口实现类的完全限定类名 --> <mappers> <mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.AuthorMapper"/> <mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.BlogMapper"/> <mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.PostMapper"/> </mappers>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- package 案例:
<!-- 将包内的映射器接口实现全部注册为映射器 --> <mappers> <package name="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper"/> </mappers>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
🌔 3、mapper标签的作用是指定SqlMapper.xml文件的路径,指定接口名有什么用呢?
-
如果你class指定是:com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper
-
那么mybatis框架会自动去com/powernode/mybatis/mapper目录下查找CarMapper.xml文件。
-
注意:也就是说:如果你采用这种方式,那么你必须保证CarMapper.xml文件和CarMapper接口必须在同一个目录下。并且名字一致。
🌔 4、如何将接口文件和Mapper文件放到一个文件夹下呢?
- 我们知道一个放在 java 中,一个放在 resource 下,但是他们都属于根目录
- 假设我们在 java文件夹下,创建一个接口 com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper【前面用 . 分隔的代表多级包】
- 但是我们在resource文件夹下是无法创建包的,如果我们点击 Directory 创建com.powernode.mybatis.mapper代表的只是一个文件夹,得写成com/powernode/mybatis/mapper 才能创建对应的多级目录,然后创建我们的 CarMapper.xml 文件
🌔 5、我们最常用package 的方式加载所有的映射文件, 要满足所有的映射文件和对应的接口在一个目录下
四、idea文件模板
🌔 1、什么是 idea 文件模板?【idea指的是IDEA集成开发环境】
就是在我们鼠标右键后点击 new,显示出来很多文件的模板,我们点击后就可快速基于模板进行开发
🌔 2、那么如何定制我们自己的 idea 文件模板呢?
File >> Settings >> Editor >> File and Code Templates >> + 创建新模板 >> Name(MyBatis核心配置文件)+Extersion(xml)
- 我们定制一个我们 mybatis-config.xml 的核心配置文件 【步骤如上,此处给出模板内容】
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!--外部资源地址--> <properties resource=" "></properties> <typeAliases> <!--pojo类包名,自动起简名--> <package name=" "/> </typeAliases> <environments default="dev"> <environment id="dev"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <!--指定xml的目录,加载目录下的所有映射文件,前提要与对应接口在一个目录下--> <package name=" " /> </mappers> </configuration>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 定义一个映射文件模板:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!--需要指定接口的全限定类名--> <mapper namespace=" "> <!--填充我们需要的SQL语句--> </mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
五、插入数据时获取自动生成的主键
- 当主键是自动生成的时候,我们传递数据时不用指定主键的值【此处以id为例】
- 那我们如何在插入数据的时候,同时获得主键的值呢?
(1)在Mapper文件中的SQL语句
<insert id="insertUseGeneratedKeys" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> insert into t_car(id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type) values(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType}) </insert>- 1
- 2
- 3
(2)test 代码块
@Test public void testInsertUseGeneratedKeys(){ CarMapper mapper = SqlSessionUtil.openSession().getMapper(CarMapper.class); Car car = new Car(); car.setCarNum("5262"); car.setBrand("BYD汉"); car.setGuidePrice(30.3); car.setProduceTime("2020-10-11"); car.setCarType("新能源"); mapper.insertUseGeneratedKeys(car); SqlSessionUtil.openSession().commit(); System.out.println(car.getId()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 就是在insert语句里添加了两个字段:
- useGeneratedKeys=“true” 代表开启使用生成的主键
- keyProperty=“id” 代表使用传入对象的那个属性来接收这个获得到的主键
-
相关阅读:
JavaScript学习小结
JRebel在IDEA中实现热部署 (JRebel实用版)
牛客小白月赛65
grpc的metadata---拦截器--验证器--状态码-yapi安装
MyBatis的各种查询功能
机器人微控制器编程(CoCube)-强化实践
程序员面试金典 - 面试题 17.12. BiNode
3.0 设计模式汇总
java 面试题
剑指 Offer II 068. 查找插入位置
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61323055/article/details/127705062