-
基于opencv的手指静脉识别(附源码)
前言
手指静脉识别技术是一种新的生物特征识别技术,它利用手指内的静脉分布图像来进行身份识别。
工作原理
是依据人类手指中流动的血液可吸收特定波长的光线,而使用特定波长光线对手指进行照射,可得到手指静脉的清晰图像。利用这一固有的科学特征,将实现对获取的影像进行分析、处理,从而得到手指静脉的生物特征,再将得到的手指静脉特征信息与事先注册的手指静脉特征进行比对,从而确认登录者的身份。本文利用OpenCV各种图像算法实现对手指静脉进行识别,使用传统的方法来处理图像,而不是深度学习方法。代码实现框架图如下所示:
直方图识别效果
两种完整实现方案源码
Matlab版本源码_传统图像处理方法:https://download.csdn.net/download/DeepLearning_/87347150
python版本源码_深度学习方法(神经网络):https://download.csdn.net/download/DeepLearning_/87347127
一、代码实现步骤
1.引入库
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import cv2 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import math import numpy import os- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
2.均值滤波(高斯滤波、高斯双边滤波)
def first_filter(img): #均值滤波 img_Blur=cv2.blur(img,(5,5)) ''' #高斯滤波 img_GaussianBlur=cv2.GaussianBlur(img,(7,7),0) #高斯双边滤波 img_bilateralFilter=cv2.bilateralFilter(img,40,75,75) ''' return img, img_Blur- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3.边缘检测
代码如下(示例):
def edge_detection(img): #img = cv2.imread(file, 0) #img = cv2.imread("01.jpg", 0) x = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_16S,1,0) y = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_16S,0,1) absX = cv2.convertScaleAbs(x)# 转回uint8 absY = cv2.convertScaleAbs(y) img_edge = cv2.addWeighted(absX,0.5,absY,0.5,0) ''' #cv2.imshow("absX", absX) #cv2.imshow("absY", absY) #cv2.imshow("Result", img_edge) #cv2.waitKey(0) #cv2.destroyAllWindows() fig = plt.figure(figsize = (30, 30)) ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2) #ax3 = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 3) ax1.imshow(img, cmap = plt.cm.gray) ax2.imshow(img_edge, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.show() ''' return img, img_edge- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
4.像素二值化
# threshold 像素两极化的阈值 def pixel_polarization(img_edge, img, threshold): for i in range(len(img_edge)): for j in range(len(img_edge[i,:])): if img_edge[i][j] > threshold: img_edge[i][j] = 255 else: img_edge[i][j] = 0 ''' fig = plt.figure(figsize = (16, 16)) ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2) ax1.imshow(img, cmap = plt.cm.gray) ax2.imshow(img_edge, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.show() ''' img_edge_polar = img_edge return img_edge_polar def positioning_middle_point(img, dst, point_pixel): h, w = img.shape w1 = w // 5 # 作为左边竖线的x坐标 w2 = (w // 5) * 4 # 作为右边竖线的x坐标 ''' print("roi width: ",h, w1, w2) ''' low_l = False high_l = False while (not low_l or not high_l) and w1 < (w // 2): for i, pix in enumerate(dst[:, w1]): if i+1 < (h // 2) and not low_l: if pix == 255: low_l = True lower_left = i elif i+1 > (h // 2) and not high_l: h_h = int(h * (3/2) - (i+1)) # 除法会带来小数,因此用int(), h/2开始对称位置找亮点 ''' print(h_h) ''' if dst[h_h, w1] == 255: high_l = True higher_left = h_h if not low_l or not high_l: w1 = w1 + 2 middle_left = (lower_left + higher_left) // 2 low_r = False high_r = False while (not low_r or not high_r) and w2 > (w // 2): for i, pix in enumerate(dst[:, w2]): if i+1 < (h // 2) and not low_r: if pix == 255: low_r = True lower_right = i elif i+1 > (h // 2) and not high_r: h_h = int(h * (3/2) - (i+1)) if dst[h_h, w2] == 255: high_r = True higher_right = h_h if not low_r or not high_r: w2 = w2 - 2 middle_right = (lower_right + higher_right) // 2 ''' dst[middle_left, w1] = point_pixel dst[middle_left+1, w1] = point_pixel dst[middle_left-1, w1] = point_pixel dst[middle_left, w1 + 1] = point_pixel dst[middle_left, w1 - 1] = point_pixel dst[middle_right, w2] = point_pixel dst[middle_right+1, w2] = point_pixel dst[middle_right-1, w2] = point_pixel dst[middle_right, w2 + 1] = point_pixel dst[middle_right, w2 - 1] = point_pixel fig = plt.figure(figsize = (16, 16)) ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2) ax1.imshow(img, cmap = plt.cm.gray) ax2.imshow(dst, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.show() ''' return dst, middle_left, middle_right, w1, w2- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
5.旋转矫正
def rotation_correction(img, dst, middle_right, middle_left, w1, w2): tangent_value = float(middle_right - middle_left) / float(w2 - w1) rotation_angle = np.arctan(tangent_value)/math.pi*180 (h,w) = img.shape center = (w // 2,h // 2) M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center,rotation_angle,1)#旋转缩放矩阵:(旋转中心,旋转角度,缩放因子) rotated_dst = cv2.warpAffine(dst,M,(w,h)) rotated_img = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(w,h)) ''' fig = plt.figure(figsize = (16, 16)) ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 1) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 2) ax3 = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 3) ax1.imshow(img, cmap = plt.cm.gray) ax2.imshow(rotated_dst, cmap = plt.cm.gray) ax3.imshow(rotated_img, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.show() ''' return rotated_dst, rotated_img def roi(rotated_img, rotated_edge, w1, w2, url): h, w = rotated_edge.shape r = range(0, h) r1 = range(0, h // 2) r2 = range(h // 2, h - 1) c = range(0, w) c1 = range(0, w // 2) c2 = range(w // 2, w-1) highest_edge = (rotated_edge[r1][:,c].sum(axis=1).argmax()) lowest_edge = (rotated_edge[r2][:,c].sum(axis=1).argmax() + (h // 2)) ''' leftest_edge = (rotated_edge[r][:,c1].sum(axis=0).argmax()) rightest_edge = (rotated_edge[r][:,c2].sum(axis=0).argmax() + (w // 2)) ''' leftest_edge = w1 rightest_edge = w2 ''' _, img_w = rotated_edge.shape half = int(img_w/2) max_right_sum = 0 max_right_i = 0 sum_img = numpy.sum(rotated_img,axis=0) for i in range(half,img_w-50): s = sum(sum_img[i:i+50]) if s > max_right_sum: max_right_sum = s max_right_i = i ''' #print(highest_edge, lowest_edge, leftest_edge, rightest_edge) #print max_right_i #rightest_edge = max_right_i + 200 #leftest_edge = 0 ''' rotated_edge[highest_edge, : ] = 200 rotated_edge[lowest_edge, : ] = 200 #150 rotated_edge[: , leftest_edge] = 200 #200 rotated_edge[: , rightest_edge] = 200 #250 rotated_croped = rotated_edge[highest_edge : lowest_edge, leftest_edge : rightest_edge] ''' rotated_croped_img = rotated_img[highest_edge : lowest_edge, leftest_edge : rightest_edge] ''' fig = plt.figure(figsize = (30, 30)) ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 2) ax3 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 3) ax4 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 4) ax1.imshow(rotated_edge, cmap = plt.cm.gray) ax2.imshow(rotated_croped, cmap = plt.cm.gray) ax3.imshow(rotated_img, cmap = plt.cm.gray) ax4.imshow(rotated_croped_img, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.show() ''' #print("rotated_croped_img type: ", rotated_croped_img) #cv2.imwrite(url, rotated_croped_img) #im = Image.fromarray(rotated_croped_img) #im.save(url) return rotated_croped_img- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
6.ROI获取
def get_imgs_roi(img_file): images = os.listdir(img_file) for i, image in enumerate(images): print(i) print(image) img_raw = cv2.imread(os.path.join(img_file, image), 0) print(img_raw.shape) ''' (h,w) = img.shape center = (w / 2,h / 2) M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center,90,1)#旋转缩放矩阵:(旋转中心,旋转角度,缩放因子) img_raw = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(w,h)) ''' #img_raw, img_edge = edge_detection(img_raw) img_raw, img_Blur = first_filter(img_raw) img_raw, img_Blur_edge = edge_detection(img_Blur) ''' fig = plt.figure(figsize = (50, 15)) ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 1) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 2) ax3 = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 3) ax1.imshow(img_raw, cmap = plt.cm.gray) ax2.imshow(img_edge, cmap = plt.cm.gray) ax3.imshow(img_Blur_edge, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.show() ''' img_Blur_edge_polar = pixel_polarization(img_Blur_edge, img_raw, 25) #二值化 img_Blur_edge_polar_midd, middle_left, middle_right, w1, w2= positioning_middle_point(img_raw, img_Blur_edge_polar, 100) img_Blur_edge_polar_midd_rotated, rotated_img = rotation_correction(img_raw, img_Blur_edge_polar_midd, middle_right, middle_left, w1, w2) # roi图像保存路径 new_file = './roi_600_2_all_320240' save_root = os.path.join(new_file,image) roi_img = roi(rotated_img, img_Blur_edge_polar_midd_rotated, w1, w2, save_root) resized_roi_img = img_resized_enhance(roi_img, save_root)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
7.建立特征
def build_filters(): """ returns a list of kernels in several orientations """ filters = [] ksize = 31 for theta in np.arange(0, np.pi, np.pi / 4): params = {'ksize':(ksize, ksize), 'sigma':3.3, 'theta':theta, 'lambd':18.3, 'gamma':4.5, 'psi':0.89, 'ktype':cv2.CV_32F} kern = cv2.getGaborKernel(**params) kern /= 1.5*kern.sum() filters.append((kern,params)) return filters def getGabor(img, filters): """ returns the img filtered by the filter list """ accum = np.zeros_like(img) for kern,params in filters: fimg = cv2.filter2D(img, cv2.CV_8UC3, kern) np.maximum(accum, fimg, accum) return accum- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
8.二值纹理特征提取
def bin_features_extract(roi_file): ''' images_roi = os.listdir(roi_file) for i, image_roi in enumerate(images_roi): print(i) print(image_roi) img_roi_raw = cv2.imread(os.path.join(roi_file, image_roi), 0) ''' img_roi_raw = cv2.imread(roi_file, 0) # Gabor滤波器 filters = build_filters() img_roi_raw_gabor = getGabor(img_roi_raw, filters) #print(img_roi_raw_gabor) #灰度归一化 #norm_resized_img = cv2.normalize(img_roi_raw_gabor, norm_resized_img, 0, 255, cv2.NORM_MINMAX) #二值化 #img_roi_raw_gabor_polar60 = img_roi_raw_gabor.copy() #img_roi_raw_gabor_polar60 = pixel_polarization(img_roi_raw_gabor_polar60, img_roi_raw, 60) img_roi_raw_gabor_polar70 = img_roi_raw_gabor.copy() img_roi_raw_gabor_polar70 = pixel_polarization(img_roi_raw_gabor_polar70, img_roi_raw, 70) ''' plt.figure(figsize = (30, 30)) plt.subplot(2, 2, 1), plt.title('img_roi_raw') plt.imshow(img_roi_raw, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.subplot(2, 2, 2), plt.title('img_roi_raw_gabor') plt.imshow(img_roi_raw_gabor, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.subplot(2, 2, 3), plt.title('img_roi_raw_gabor_polar60') plt.imshow(img_roi_raw_gabor_polar60, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.subplot(2, 2, 4), plt.title('img_roi_raw_gabor_polar70') plt.imshow(img_roi_raw_gabor_polar70, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.show() ''' return img_roi_raw_gabor_polar70 def bin_match(img1_path, img2_path): img1 = bin_features_extract(img1_path) img2 = bin_features_extract(img2_path) height, width = img1.shape size = height * width score = 0 for i in range(len(img1)): for j in range(len(img1[i,:])): if img1[i][j] == img2[i][j]: score += 1 scores = 100 * round((score / size), 4) #print(img1_path, img2_path, scores) return scores- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
9.图片分成m*n块
def cut_image(image, m, n): height, width = image.shape item_width = int(width // m) item_height = int(height // n) #box_list = [] cropped_list = [] # (left, upper, right, lower) for i in range(0,n):#两重循环,生成m*n张图片基于原图的位置 for j in range(0,m): #print((i*item_width,j*item_width,(i+1)*item_width,(j+1)*item_width)) #box = (j*item_width,i*item_height,(j+1)*item_width,(i+1)*item_height) #box_list.append(box) cropped = image[i*item_height:(i+1)*item_height, j*item_width:(j+1)*item_width] cropped_list.append(cropped) print(len(cropped_list)) #image_list = [image.crop(box) for box in box_list] return cropped_list- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
10.LBP特征提取
def LBP_feature_extrector(roi_file): images_roi = os.listdir(roi_file) # settings for LBP radius = 3 n_points = 8 * radius METHOD = 'uniform' for i, image_roi in enumerate(images_roi): print(i) print(image_roi) img_roi_raw = cv2.imread(os.path.join(roi_file, image_roi), 0) img_roi_raw_lbp = local_binary_pattern(img_roi_raw, n_points, radius, METHOD) #print(img_roi_raw_lbp.shape()) #img_roi_raw_lbp_cut = cut_image(img_roi_raw_lbp, 4, 4) #分成4*4 #分块显示 #plt.figure(figsize = (30, 30)) #print(img_roi_raw_lbp_cut.shape()) ''' score = cv2.compareHist(lbp_hist, lbp_hist, cv2.HISTCMP_BHATTACHARYYA) #score = kullback_leibler_divergence(lbp_hist, lbp_hist) print(score) ''' ''' #绘制直方图 #lbp_hist = plt.hist(img_roi_raw_lbp.ravel(),256,[0,256]) n_bins = int(img_roi_raw_lbp.max() + 1) lbp_hist = plt.hist(img_roi_raw_lbp.ravel(), density=True, bins=n_bins, range=(0, n_bins), facecolor='0.5') plt.figure(figsize = (30, 30)) plt.subplot(1, 2, 1), plt.title('img_roi_raw') plt.imshow(img_roi_raw, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.subplot(1, 2, 2), plt.title('img_roi_raw_lbp') plt.imshow(img_roi_raw_lbp, cmap = plt.cm.gray) # plt.subplot(1, 3, 3), plt.title('lbp_hist') # plt.imshow(lbp_hist) plt.show() '''- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
11.SIFT特征提取与匹配
def SIFT_detector(gray_path): images_sift = os.listdir(gray_path) for i, image_sift in enumerate(images_sift): print(i) print(image_sift) img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(gray_path, image_sift), 0) ''' #sift检测 sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create() kp = sift.detect(img,None) img_sift=cv2.drawKeypoints(img,kp,img,flags=cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS) ''' ''' #SURF检测 surf = cv2.xfeatures2d.SURF_create() kp = surf.detect(img,None) img_surf=cv2.drawKeypoints(img,kp,img,flags=cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS) ''' ''' #ORB检测,几乎没有 orb = cv2.ORB_create() kp = orb.detect(img,None) img_orb=cv2.drawKeypoints(img,kp,img,flags=cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS) ''' #KAZE检测 kaze = cv2.KAZE_create() kp = kaze.detect(img,None) img_kaze=cv2.drawKeypoints(img,kp,img,flags=cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS) #cv2.imwrite('sift_keypoints.jpg',img) plt.figure(figsize = (30, 30)) plt.subplot(1, 2, 1), plt.title('img') plt.imshow(img, cmap = plt.cm.gray) plt.subplot(1, 2, 2), plt.title('img_kaze') plt.imshow(img_kaze, cmap = plt.cm.gray) # plt.subplot(1, 3, 3), plt.title('lbp_hist') # plt.imshow(lbp_hist) plt.show() def SIFT_match(img1_path, img2_path): img1 = cv2.imread(img1_path,0) # queryImage img2 = cv2.imread(img2_path,0) # trainImage # Initiate SIFT detector sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create() # find the keypoints and descriptors with SIFT kp1, des1 = sift.detectAndCompute(img1,None) # BFMatcher with default params bf = cv2.BFMatcher() matches = bf.knnMatch(des1,des2, k=2) # Apply ratio test good = [] for m,n in matches: if m.distance < 0.75*n.distance: good.append([m]) # cv2.drawMatchesKnn expects list of lists as matches. img3 = cv2.drawMatchesKnn(img1,kp1,img2,kp2,good,None,flags=cv2.DrawMatchesFlags_NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS) plt.imshow(img3),plt.show() def FLANN_based_Matcher(img1_path, img2_path): img1 = cv2.imread(img1_path, 0) # queryImage img2 = cv2.imread(img2_path, 0) # trainImage ''' # Initiate SURF detector surf = cv2.xfeatures2d.SURF_create() # find the keypoints and descriptors with SIFT kp1, des1 = surf.detectAndCompute(img1,None) kp2, des2 = surf.detectAndCompute(img2,None) ''' ''' kaze = cv2.KAZE_create() kp1, des1 = kaze.detectAndCompute(img1, None) kp2, des2 = kaze.detectAndCompute(img2, None) # Initiate ORB detector orb = cv2.ORB_create() # find the keypoints and descriptors with ORB kp1, des1 = orb.detectAndCompute(img1,None) kp2, des2 = orb.detectAndCompute(img2,None) ''' # Initiate SIFT detector sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create() # find the keypoints and descriptors with SIFT kp1, des1 = sift.detectAndCompute(img1,None) kp2, des2 = sift.detectAndCompute(img2,None) # FLANN parameters FLANN_INDEX_KDTREE = 1 index_params = dict(algorithm = FLANN_INDEX_KDTREE, trees = 5) search_params = dict(checks=50) # or pass empty dictionary flann = cv2.FlannBasedMatcher(index_params,search_params) matches = flann.knnMatch(des1,des2,k=2) # Need to draw only good matches, so create a mask matchesMask = [[0,0] for i in range(len(matches))] #matchesMask = [] # ratio test as per Lowe's paper match_keypoints_count = 0 for i,(m,n) in enumerate(matches): if m.distance < 0.8*n.distance: matchesMask[i]=[1,0] #matchesMask.append(m) match_keypoints_count += 1 draw_params = dict(matchColor = (0,255,0), singlePointColor = (255,0,0), matchesMask = matchesMask, flags = cv2.DrawMatchesFlags_DEFAULT) #计算匹配得分,保留小数点后两位 score = 100 * round(match_keypoints_count / len(matchesMask), 4) #print('score = ', score) ''' img3 = cv2.drawMatchesKnn(img1,kp1,img2,kp2,matches,None,**draw_params) #img3 = cv2.drawMatchesKnn(img1,kp1,img2,kp2,matches,None,flags=2) plt.imshow(img3),plt.show() ''' return score- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
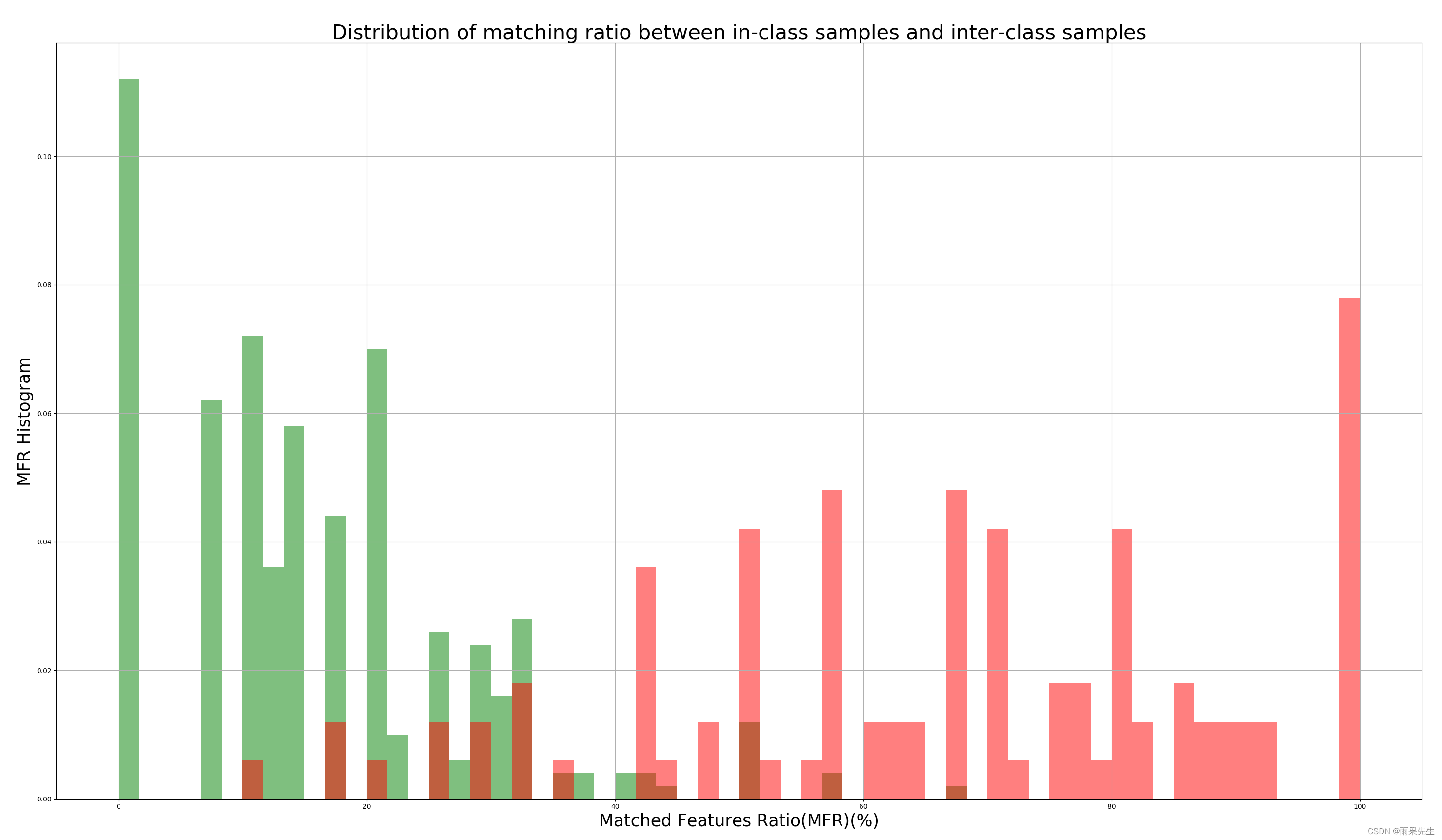
12.绘制第几组样本的类内类间距离直方图
def cal_scores(method='FLANN', flag=1): scores_list_diff = [] scores_list_same = [] #类间比较 for k in range(1,5): if k is not flag: for i in range(1,11): for j in range(1,11): #print('%s', ) strs1 = './data/roi_600_2_all_320240/600-{}-{}-1.bmp'.format(flag,i) strs2 = './data/roi_600_2_all_320240/600-{}-{}-1.bmp'.format(k,j) if method == 'FLANN': scores = FLANN_based_Matcher(strs1, strs2) scores_list_diff.append(scores) if method == 'BIN': scores = bin_match(strs1, strs2) scores_list_diff.append(scores) print(strs1,strs2, scores) #类内比较 for i in range(1,11): for j in range(1,11): #print('%s', ) strs1 = './data/roi_600_2_all_320240/600-{}-{}-1.bmp'.format(flag,i) strs2 = './data/roi_600_2_all_320240/600-{}-{}-1.bmp'.format(flag,j) if method == 'FLANN': scores = FLANN_based_Matcher(strs1, strs2) scores_list_same.append(scores) if method == 'BIN': scores = bin_match(strs1, strs2) scores_list_same.append(scores) print(strs1,strs2, scores) plt.hist(scores_list_diff, 60, range=(0,100), density=True, histtype="bar", facecolor='g', label='Inter-class', alpha=0.5) plt.hist(scores_list_same, 60, range=(0,100), density=True, histtype="bar", facecolor='r', label='In-class', alpha=0.5) plt.xlabel('Matched Features Ratio(MFR)(%)', fontsize=25) plt.ylabel('MFR Histogram', fontsize=25) plt.title('Distribution of matching ratio between in-class samples and inter-class samples', fontsize=30) #plt.text(60, .025, r'$\mu=100,\ \sigma=15$') #plt.axis([0, 1, 0, 0.03]) plt.grid(True) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
总结
我们可以将阈值设置为60进行分类。
-
相关阅读:
【java】【项目实战】[外卖十二]【完结】项目优化(前后端分离开发)
记第一次eudsrc拿到RCE(下)
ntfs是什么硬盘?ntfs硬盘如何在苹果电脑使用
《自然语言处理实战入门》 基于知识图谱的问答机器人
C/C++轻量级并发TCP服务器框架Zinx-游戏服务器开发006:基于redis查找玩家姓名+游戏业务实现总结
南通,一座在直播电商里焕新的产业带城市
【计算思维】少儿编程蓝桥杯青少组计算思维题考试真题及解析B
【英语:语法基础】B7.核心语法-英文的基础时态
外滩大会今日开幕 生成式AI成为热议话题
丁鹿学堂:从零开始手写promise(二)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/DeepLearning_/article/details/127741568
