-
代码随想录算法训练营第二十七天| LeetCode39. 组合总和、LeetCode40. 组合总和 II、LeetCode131. 分割回文串
一、LeetCode39. 组合总和
1:题目描述(39. 组合总和)
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组
candidates和一个目标整数target,找出candidates中可以使数字和为目标数target的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。candidates中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。对于给定的输入,保证和为
target的不同组合数少于150个。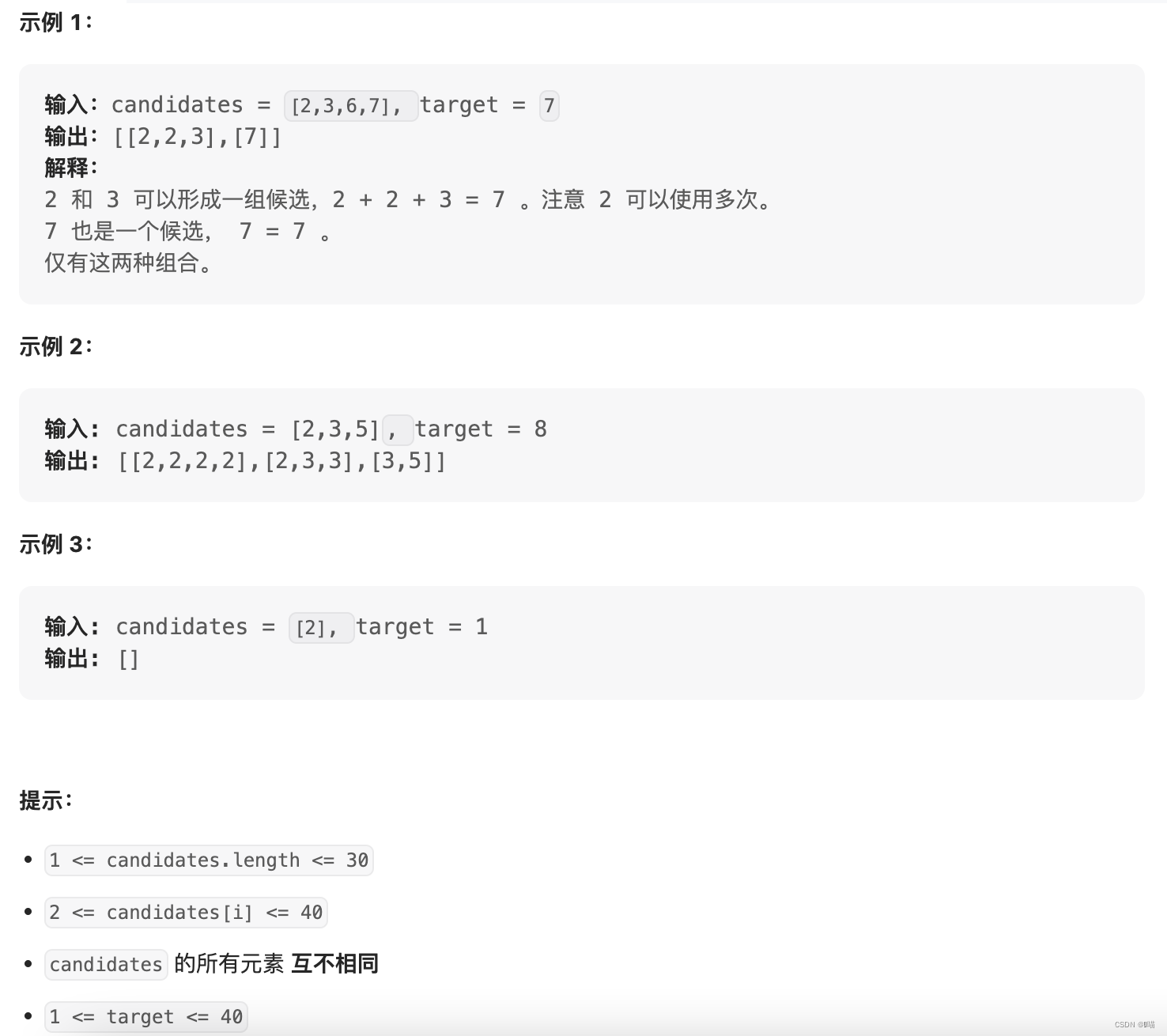
2:解题思路
- class Solution:
- def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- res = []
- path = []
- def pathSum(candidates,target,startindex):
- if sum(path) == target:
- # 当路径的元素之和等于target,就将路径加入到res中
- res.append(path[:])
- return
- elif sum(path) > target:
- # 当路径的元素之和小于target,就直接返回到上一层
- return
- # i从起始位置开始遍历
- for i in range(startindex,len(candidates)):
- path.append(candidates[i])
- # 递归调用,因为元素可以重复,所以起始位置就是当前元素的位置
- pathSum(candidates,target,i)
- # 回溯
- path.pop()
- pathSum(candidates,target,0)
- return res
二、LeetCode40. 组合总和 II
1:题目描述(40. 组合总和 II)
给定一个候选人编号的集合
candidates和一个目标数target,找出candidates中所有可以使数字和为target的组合。candidates中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用 一次 。注意:解集不能包含重复的组合。

2:解题思路
参考代码随想录:回溯算法中的去重,树层去重树枝去重,你弄清楚了没?| LeetCode:40.组合总和II_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
- class Solution:
- def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- res = []
- path = []
- # used用来标记candidates中对应下标的元素是否被使用过
- # 0表示没有被使用过,1表示被使用过
- used = [0] * len(candidates)
- candidates = sorted(candidates)
- def pathSum(candidates, target, startindex, used):
- if sum(path) == target:
- res.append(path[:])
- return
- elif sum(path) > target:
- # 当前数组的元素之和大于目标值了,直接返回上一层
- return
- for i in range(startindex, len(candidates)):
- # 进行去重,当当前元素的值等于前一个元素的值,并且前一个元素没有被使用过
- # 不再进行遍历,进入下一个元素的遍历
- if i > 0 and candidates[i-1] == candidates[i] and used[i-1] == 0:
- continue
- path.append(candidates[i])
- # 当前元素使用了,将当前元素的下标在used中相同下标对应的元素修改为1
- # 来标记当前元素被使用
- used[i] = 1
- # 每次遍历的起始位置:从当前位置的下一个位置开始
- pathSum(candidates, target, i+1, used)
- # 回溯
- path.pop()
- # 当前元素从path中移除,那么当前元素就没有被使用
- used[i] = 0
- if sum(candidates) < target:
- # 当给的数组元素之和已经小于了目标值,则直接返回
- return res
- pathSum(candidates, target, 0, used)
- return res
三、LeetCode131. 分割回文串
1:题目描述(131. 分割回文串)
给你一个字符串
s,请你将s分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回s所有可能的分割方案。回文串 是正着读和反着读都一样的字符串。

2:解题思路
参考代码随想录:带你学透回溯算法-分割回文串(对应力扣题目:131.分割回文串)| 回溯法精讲!_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
- class Solution:
- def partition(self, s: str) -> List[List[str]]:
- res = []
- path = []
- # startindex,就是切割字符串的的位置
- def division(s, startindex):
- if startindex >= len(s):
- # 当切割的位置到达字符串s的长度时
- # 字符串已经被切割完了
- # 此时将path中收集的回文字符串的子串加入到res中
- res.append(path[:])
- return
- # 每次切割,需要从起始位置开始
- for i in range(startindex, len(s)):
- # 每次切割的起始位置为startindex,结束位置为当前遍历(i)的位置
- s1 = s[startindex:i+1]
- # 判断切割出来的字符串是否为回文字符串
- if s1 == s1[::-1]:
- # 是回文字符串,就将字符串加入path中
- path.append(s1)
- else:
- # 不是回文字符串就继续向后遍历位置,进行切割
- continue
- division(s, i+1)
- # 回溯
- path.pop()
- division(s, 0)
- return res
-
相关阅读:
Vue的生命周期详解
PostgreSQL的学习心得和知识总结(八十五)|深入理解PostgreSQL数据库开源扩展pg_backtrace的使用场景和实现原理
Flink SQL解析嵌套Json数据测试过程调研
Metabase学习教程:视图-4
1.9 - Cache
Java版分布式微服务云开发架构 Spring Cloud+Spring Boot+Mybatis 电子招标采购系统功能清单
深度学习部署神器——triton inference server入门教程指北
【C++ STL】模拟实现 unordered_set/map 系列容器(对一张哈希表进行封装)
Python学习:encode()和decode()方法:字符串编码转换
EXSI 实用指南 2024 -编译环境 Mac OS 安装篇(一)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_48323589/article/details/127740337
