-
计算连续性状的PRS得分
为何要学习PRS模型
对于动植物育种而言,我之前写过PRS和MAS以及GS的关系,有老师评论说PRS更类似GS,因为它可以利用已有的GWAS信息,直接预测候选群的表型,如果按照动植物的GS方法,几十万几百万的样本做GS显然不现实,而PRS提供了这种思路,就可以利用已有的GWAS结果,通过一些质控,来预测候选群的表现(目标群体的风险得分)。当然,这里的PRS,是多基因风险得分,是预测疾病的表现,而PGS(多基因得分)更中性一点。总结如下:
- 1,如果选择显著性的点,位点少时,就可以预测只有基因型的候选群,这就是动植物的分子标记辅助选择(MAS)
- 2,如果使用所有位点,选择最优的组合,预测只有基因型的候选群,就是动植物中的基因组选择(GS)
- 3,相对于MAS和GS,PRS模型,可以考虑位点的LD质控,特别是位点少的MAS,更准确,
关于PRS系列文章中,上篇博客,介绍了PRSice软件计算二分类性状的PRS得分,本次介绍连续性状的PRS得分计算方法。
我们先把流程跑通,然后在看数据质控,PCA等协变量加入加入,LD衰减等内容。
1. 数据
数据来源《统计遗传学》第十章节:
2. 环境配置
这里使用Linux系统,使用PRSice-2.0 软件。首先把数据放到Linux系统中,把可执行文件PRSice软件放到同一个文件夹中:
注意,本操作也可以用windows系统实现,需要下载对应的PRSice-2.0 的windows版本!
$ ls 1kg_EU_qc.bed 1kg_FTOscore.log 1kg_hm3_qc.bim BMI_LDpred.txt Obesity_pheno.txt PRSice.R 1kg_EU_qc.bim 1kg_FTOscore.profile 1kg_hm3_qc.fam BMI_pheno.txt pca.eigenvec score_rs9930506.txt 1kg_EU_qc.fam 1kg_hm3_qc.bed 1kg_samples.txt BMI.txt PRSice_linux- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
3. base和target数据
3.1 base data
这里的base data是连续性状的GWAs结果,文件:
BMI.txt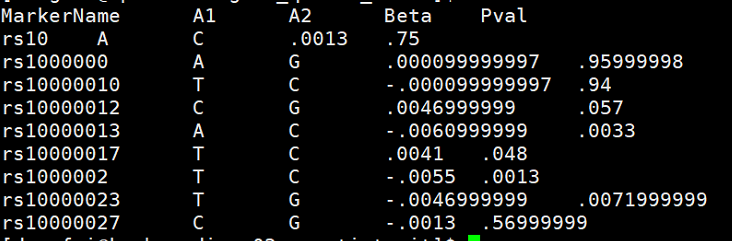
文件有行头名,每一列分别是:- SNP名称
- A1,次等位基因
- A2,主等位基因
- Beta,effect效应值
- Pval,P值
共有2336370个SNP的GWAS结果。
$ wc -l BMI.txt 2336270 BMI.txt- 1
- 2
- 3
3.2 target data
首先目标数据是二进制的plink文件:
1kg_hm3_qc:$ ls 1kg_hm3_qc.* 1kg_hm3_qc.bed 1kg_hm3_qc.bim 1kg_hm3_qc.fam- 1
- 2
- 3
目标数据中,共有1092个样本,每个样本有846484个位点。
$ wc -l 1kg_hm3_qc.fam 1092 1kg_hm3_qc.fam $ wc -l 1kg_hm3_qc.bim 846484 1kg_hm3_qc.bim- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
然后是目标文件的表型数据:
BMI_pheno.txt$ head BMI_pheno.txt FID IID BMI 0 HG00096 25.022827 0 HG00097 24.853638 0 HG00099 23.689295 0 HG00100 27.016203 0 HG00101 21.461624 0 HG00102 20.673635 0 HG00103 25.71508 0 HG00104 25.252243 0 HG00106 22.765049- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
4. 运行模型
注意,原始数据BMI.txt文件中,有9行是重复的行,所以用uniq去重一下:
uniq BMI.txt >t.txt mv t.txt BMI.txt- 1
- 2
运行模型:
Rscript PRSice.R --dir . --prsice ./PRSice_linux --base BMI.txt --target 1kg_hm3_qc --snp MarkerName --A1 A1 --A2 A2 --stat Beta --pvalue Pval --pheno-file BMI_pheno.txt --bar-levels 1 --fastscore --binary-target F --out BMI_score_all- 1
- 2
代码解释
- Rscirpt,是系统中的R脚本调用
- PRSice.R是下载的软件
- –prsice ,时指定PRSice版本,这里是PRSice_linux
- –base,基础数据,这里是GWAS的结果
- –target,是目标数据,这里是plink的二进制文件前缀名
- –snp,是gwas结果中的snp名称,根据实际文件名写
- –A1,gwas的行头名,根据实际文件名写
- –A2,gwas的行头名,根据实际文件名写
- –stat,gwas的行头名,根据实际文件名写,对应的是效应值
- –pvalue,gwas的行头名,根据实际文件名写,对应的是P值
- –pheno,是目标数据的表型数据,三列:FID,IID,表型数据
- –bar-levels 1,默认是使用所有的SNP进行PRS的计算
- –fastscore,计算PRS得分
- –binary-target F,是连续性状
- –out BMI_socre_all,输出文件名。
日志:
$ Rscript PRSice.R --dir . --prsice ./PRSice_linux --base BMI.txt --target 1kg_hm3_qc --snp MarkerName --A1 A1 --A2 A2 --stat Beta --pvalue Pval --pheno-file BMI_pheno.txt --bar-levels 1 --fastscore --binary-target F --out BMI_score_all PRSice 2.3.3 (2020-08-05) https://github.com/choishingwan/PRSice (C) 2016-2020 Shing Wan (Sam) Choi and Paul F. O'Reilly GNU General Public License v3 If you use PRSice in any published work, please cite: Choi SW, O'Reilly PF. PRSice-2: Polygenic Risk Score Software for Biobank-Scale Data. GigaScience 8, no. 7 (July 1, 2019) 2022-11-04 10:51:48 ./PRSice_linux \ --a1 A1 \ --a2 A2 \ --bar-levels 1 \ --base BMI.txt \ --beta \ --binary-target F \ --clump-kb 250kb \ --clump-p 1.000000 \ --clump-r2 0.100000 \ --fastscore \ --num-auto 22 \ --out BMI_score_all \ --pheno BMI_pheno.txt \ --pvalue Pval \ --seed 1715667869 \ --snp MarkerName \ --stat Beta \ --target 1kg_hm3_qc \ --thread 1 Initializing Genotype file: 1kg_hm3_qc (bed) Start processing BMI ================================================== Base file: BMI.txt Header of file is: MarkerName A1 A2 Beta Pval Reading 100.00% 2336260 variant(s) observed in base file, with: 358378 ambiguous variant(s) excluded 1977882 total variant(s) included from base file Loading Genotype info from target ================================================== 1092 people (525 male(s), 567 female(s)) observed 1085 founder(s) included 127366 variant(s) not found in previous data 719118 variant(s) included Phenotype file: BMI_pheno.txt Column Name of Sample ID: FID+IID Note: If the phenotype file does not contain a header, the column name will be displayed as the Sample ID which is expected. There are a total of 1 phenotype to process Start performing clumping Clumping Progress: 100.00% Number of variant(s) after clumping : 117278 Processing the 1 th phenotype BMI is a continuous phenotype 1085 sample(s) with valid phenotype Start Processing Processing 100.00% There are 1 region(s) with p-value less than 1e-5. Please note that these results are inflated due to the overfitting inherent in finding the best-fit PRS (but it's still best to find the best-fit PRS!). You can use the --perm option (see manual) to calculate an empirical P-value. Begin plotting Current Rscript version = 2.3.3 Plotting Bar Plot- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
从日志可以看出,PRSice软件,分别执行下面的步骤:
- base数据汇总,进行了质控,剩余1977882个位点
- target文件中,共有1092个个体,其中525个Male,567个female,共有719118个交叉的位点
- 执行clumping,有效个体1085,有效位点117278
5. 结果说明
结果文件:
整个模型的结果:
最优模型是:117278个位点组成的模型,PRS解释百分比是13.8%,P值是7e-37(极显著)

每个个体的PRS得分:
$ head BMI_score_all.best FID IID In_Regression PRS 0 HG00096 Yes -2.50012794e-05 0 HG00097 Yes -3.7721909e-05 0 HG00099 Yes -3.15140097e-05 0 HG00100 Yes -3.08681086e-05 0 HG00101 Yes -3.65507599e-05 0 HG00102 Yes -3.56626993e-05 0 HG00103 Yes -2.73137334e-05 0 HG00104 Yes -2.35918077e-05 0 HG00106 Yes -2.38714852e-05- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
可视化:
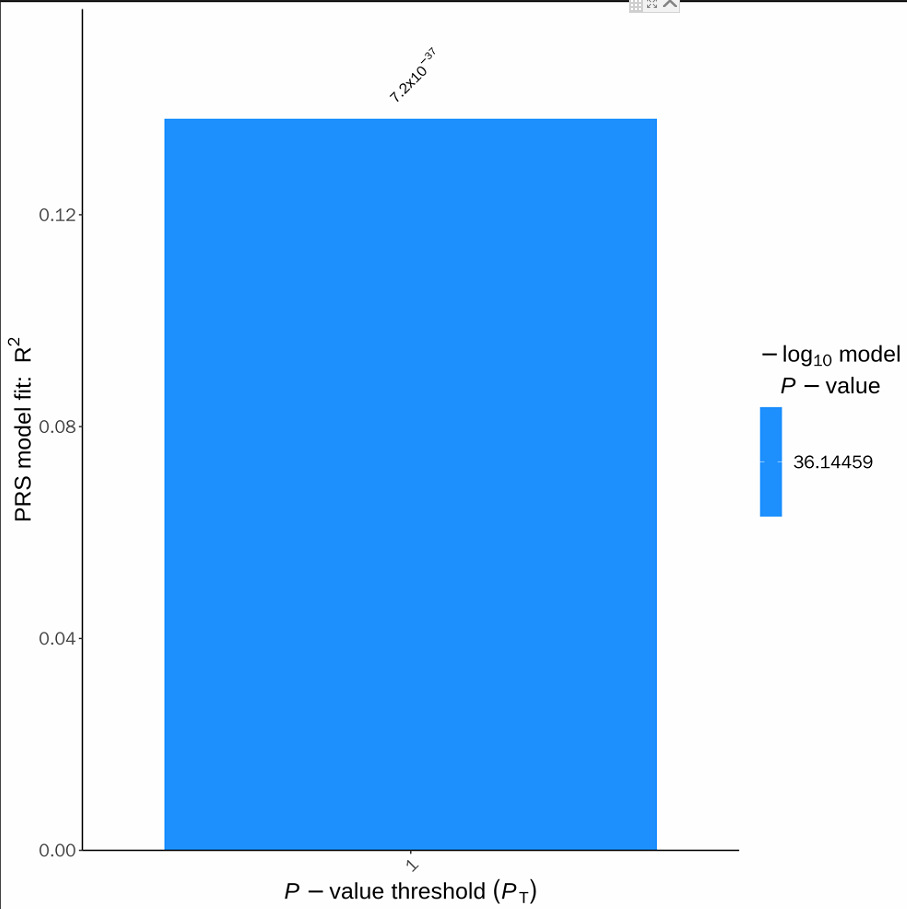
6. 梯度阈值
增加–bar-levels的梯度,分别是:
- 5e-8
- 5e-7
- 5e-6
- 5e-5
- 5e-4
- 5e-3
- 5e-2
- 5e-1
代码:
Rscript PRSice.R --dir . --prsice ./PRSice_linux --base BMI.txt --target 1kg_hm3_qc --snp MarkerName --A1A1 --A2 A2 --stat Beta --pvalue Pval --pheno-file BMI_pheno.txt --bar-levels 5e-8,5e-7,5e-6,5e-5,5e-4,5e-3,5e-2,5e-1 --fastscore --binary-targetF --out BMI_thresholds- 1
- 2
结果:

整体结果:
BMI_thresholds.summary最优的阈值是0.5,最优的位点数是90384,解释百分比是13.99%

看一下每个阈值对应的SNP个数以及解释百分比和对应的P值:BMI_thresholds.prsice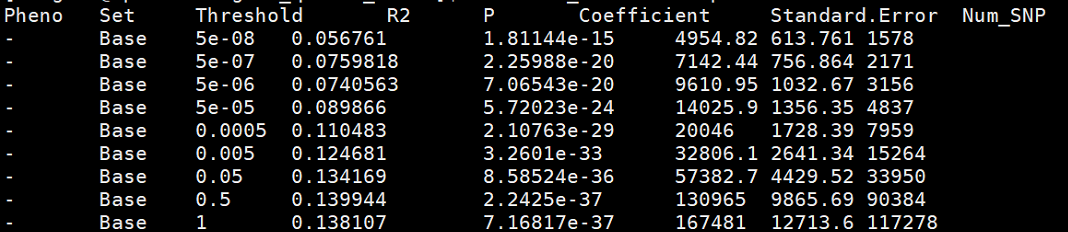
每个个体最优的PRS值:
$ head BMI_thresholds.best FID IID In_Regression PRS 0 HG00096 Yes -3.24349447e-05 0 HG00097 Yes -4.97621266e-05 0 HG00099 Yes -4.11754297e-05 0 HG00100 Yes -4.15040277e-05 0 HG00101 Yes -4.79216457e-05 0 HG00102 Yes -4.70924063e-05 0 HG00103 Yes -3.56921583e-05 0 HG00104 Yes -3.0351058e-05 0 HG00106 Yes -3.19768991e-05- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
结果可视化:
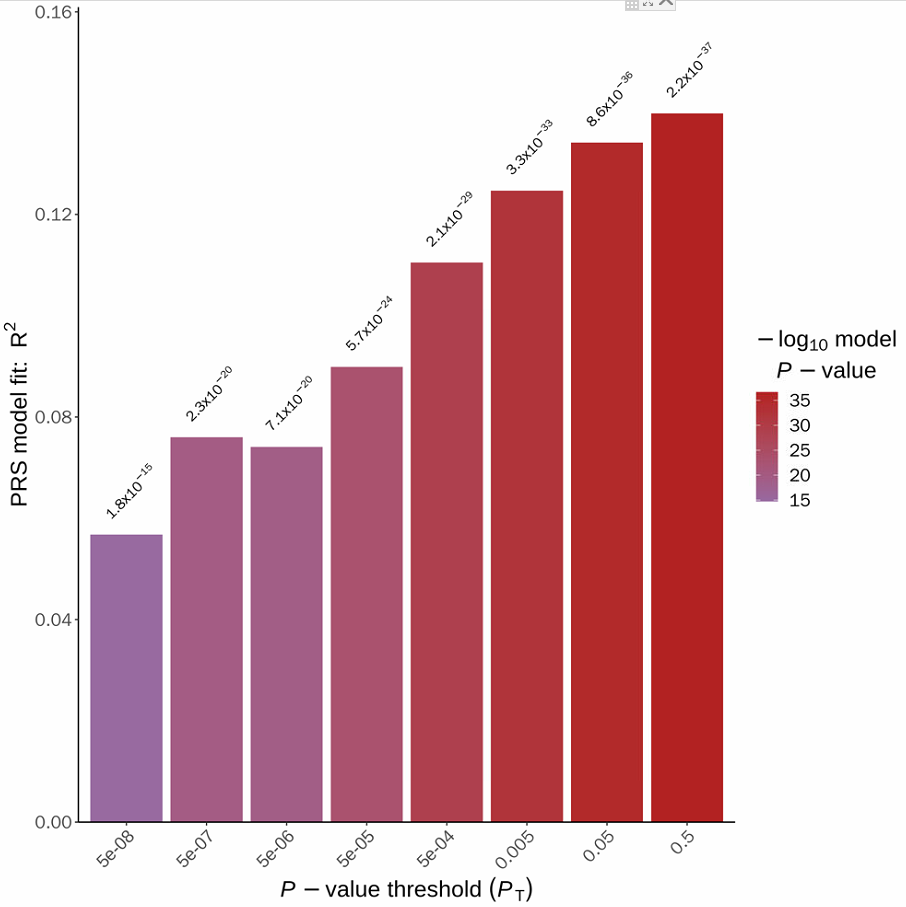
看到这里,我有一个大胆的想法:
- 1,如果选择显著性的点,位点少时,就可以预测只有基因型的候选群,这就是动植物的分子标记辅助选择(MAS)
- 2,如果使用所有位点,选择最优的组合,预测只有基因型的候选群,就是动植物中的基因组选择(GS)
相对于MAS和GS,PRS模型,可以考虑位点的LD质控,特别是位点少的MAS,更准确。
-
相关阅读:
mysql之count(*)
UVM 的精髓在于给验证人员提供了快速搭建 testbench 的途径
【算法 | 概述初识】时间复杂度和空间复杂度(我不信看完这篇文章你还不懂)
汇编语言与微机原理 期末半开卷复习整理(上)
PMSM——转子位置估算基于QPLL
14:00面试,14:06就出来了,问的问题有点变态。。。
当食品制造业遇见数字化工具,如何借助S2B2C电商系统实现企业新增长
python机器人编程——差速机器人小车的控制,控制模型、轨迹跟踪,轨迹规划、自动泊车(上)
百度知道本地搭建环境无限制采集聚合【最新版】
STM32使用串口空闲中断(IDLE)和 DMA接收一串数据流
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/yijiaobani/article/details/127682839
