-
异步编程生产实践
背景介绍
最近几个月参与了公司大屏业务,因大屏是将不同维度的数据有效整合并做可视化处理。此时对于后端来说,需要请求多个数据源并完成数据规整,最终返回前端。在此过程中,由于每个数据源返回结果的时间不确定且数据源之前可能存在关联关系,导致无法及时响应结果和任务编排混乱问题。为了解决这些问题便在项目中引入异步编程工具 asyncTool,对此工具的使用和原理做出如下记录。
正文
数据的来源可分为三种:数据库、内部接口和外部接口。当一个面板展示数据时,需要分别从数据库和接口中获取,若此时是以串行方式先从数据库读取数据再请求接口,最终合并数据,那么数据的响应是非常慢的。
多线程
在 Java 中实现多线程编程有三种实现方式
- 继承 Thread 类,并重写 run 方式
- 实现 Runnable 接口,实现 run 方法
- 实现 Callable 接口,实现 call 方法
从返回值的角度来看,有两种:无返回值的(Runnable)和有返回值的(Callable),对于大屏场景肯定需要使用有返回值的。
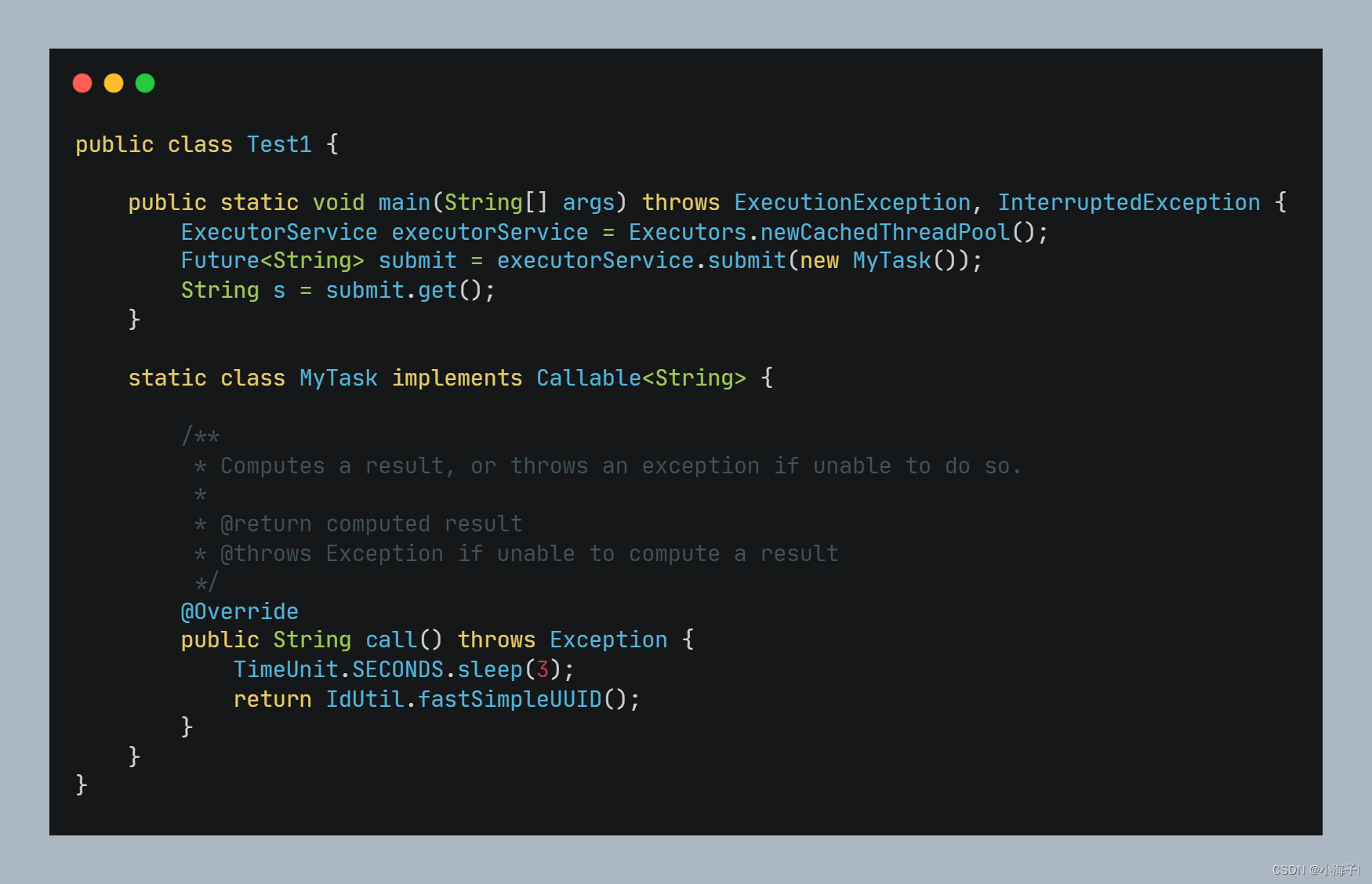
将任务提交至线程池后返回 Future, 再调用 get() 方法获取最终结果。
Future
Future 类早在 Java5 中就已存在,也是我最早接触的异步编程方案。
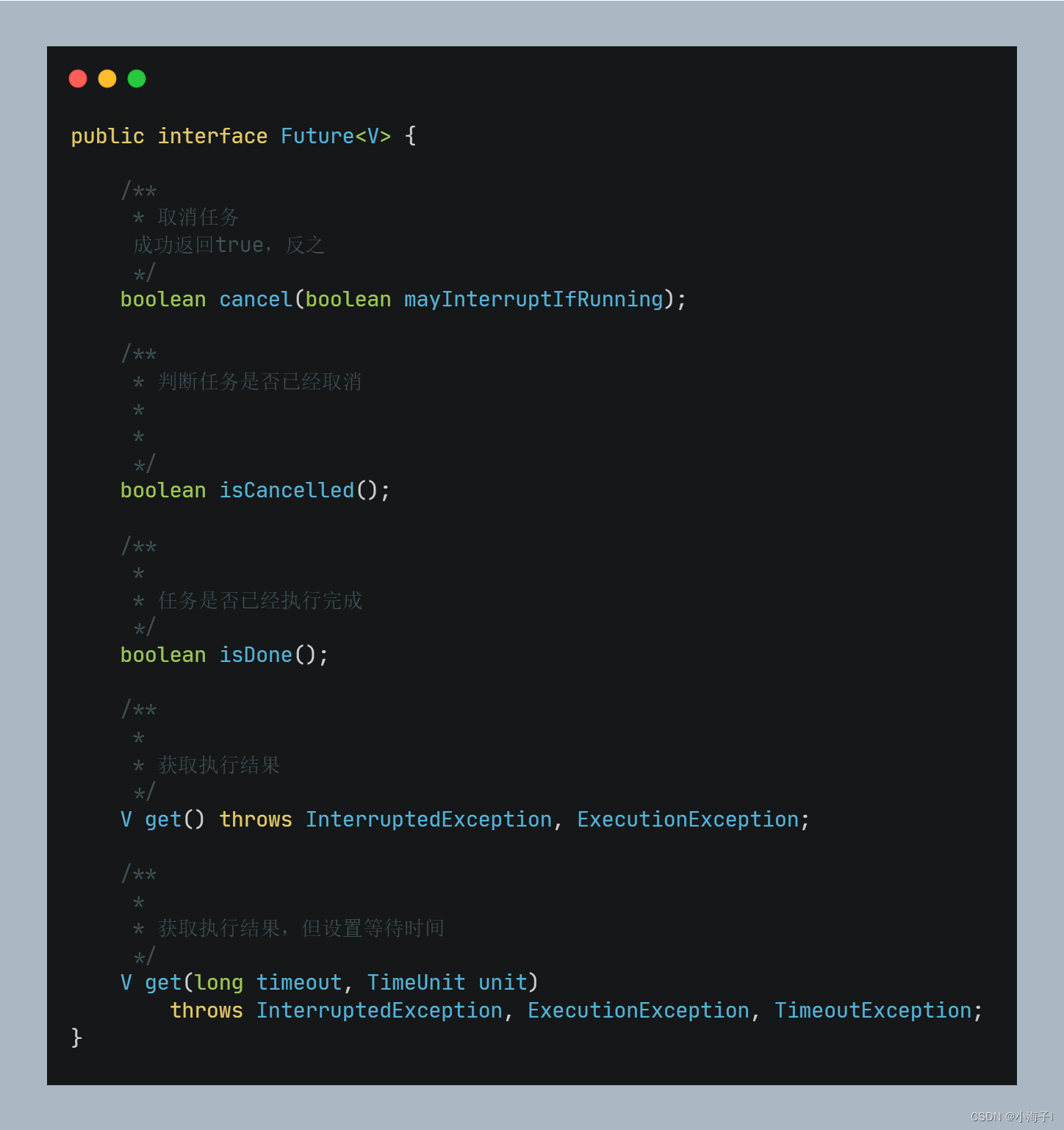
Future 适合解决一些简单且相互独立的异步场景,当存在异步任务相互依赖和流水线的场景下,实现起来就不那么方便了。
入门CompletableFuture
在 Java 8 中加入了 CompletableFuture 类,可以轻松实现任务编排。
CompletableFuture 提供了 supplyAsync 和 runAsync 方法分别用于执行有返回值的 Callable和 无返回值的 Runnable
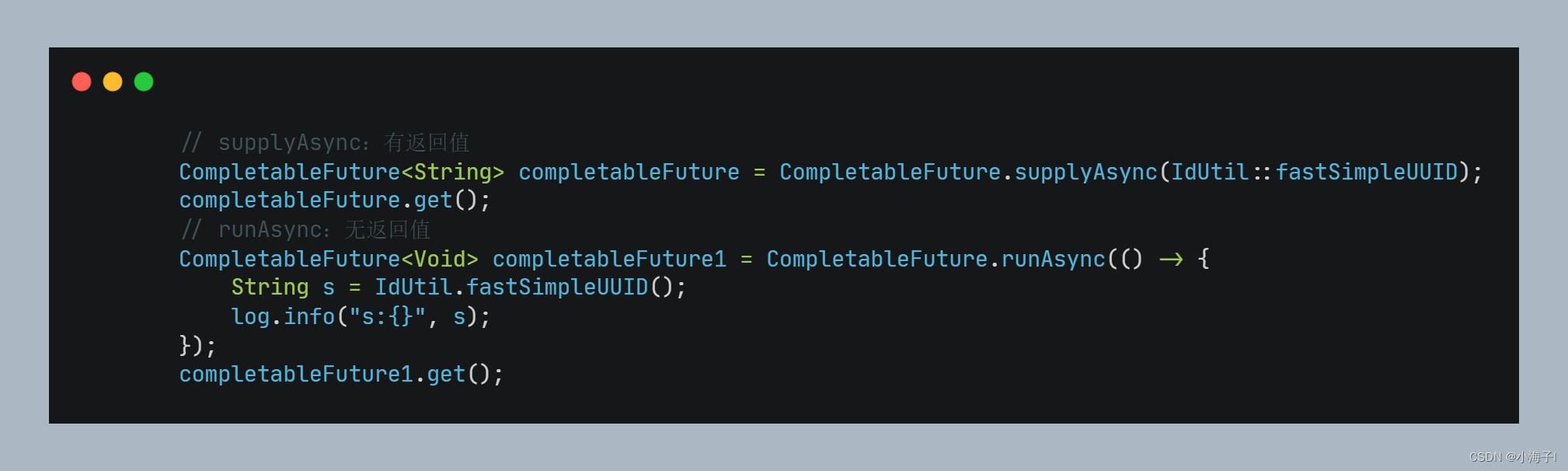
且这两种方式都提供了带有线程池的构造函数。
任务编排
API 说明 thenApply 将上一个任务的返回值作为参数传递给下一个任务 thenCompose 同上,但上一个任务的返回值是 CompletionStage 类型 thenAccept 与 thenApply 类似,但没有返回值 thenRun 无法将上一个任务的参数传递给下一个任务,且下一个任务无返回值 allOf 多个任务同时执行 anyOf 多个任务中,任意一个完成 - thenApply
/** * 第一个任务调用HTTP接口,再将结果传递给第二个任务,拼接时间戳返回 * * @throws ExecutionException ExecutionException * @throws InterruptedException InterruptedException */ static void test() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { String path = "http://localhost:8080/get?num="; CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpUtil.get(path + 1)).thenApply(res -> res + System.currentTimeMillis()); completableFuture.get(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- thenComppnse
/** * 第一个任务调用HTTP接口,再将结果(CompletionStage类型)传递给第二个任务,拼接时间戳返回 * * @throws ExecutionException ExecutionException * @throws InterruptedException InterruptedException */ static void test() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { String path = "http://localhost:8080/get?num="; CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpUtil.get(path + 1)).thenCompose(res -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> res + System.currentTimeMillis())); completableFuture.get(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- thenAccept
/** * 第一个任务调用HTTP接口,再将结果传递给第二个任务,并输出至控制台 * * @throws ExecutionException ExecutionException * @throws InterruptedException InterruptedException */ static void test() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { String path = "http://localhost:8080/get?num="; CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpUtil.get(path + 1)).thenAccept(System.out::println); completableFuture.get(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- thenRun
/** * 第一个任务调用HTTP接口,完成后第二个任务开始调用接口 * * @throws ExecutionException ExecutionException * @throws InterruptedException InterruptedException */ static void test() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { String path = "http://localhost:8080/get?num="; CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpUtil.get(path + 1)).thenRun(() -> HttpUtil.get(path + 1)); completableFuture.get(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- allOf
/** * 两个任务并行执行 * * @throws ExecutionException ExecutionException * @throws InterruptedException InterruptedException */ static void test() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); String path = "http://localhost:8080/get?num="; CompletableFuture<String> firstFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { String res = HttpUtil.get(path + 1); log.info("res:{}", res); return res; }); CompletableFuture<String> secondFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { String res = HttpUtil.get(path + 1); log.info("res:{}", res); return res; }); CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(firstFuture, secondFuture); completableFuture.get(); stopWatch.stop(); log.info("结束; time:{}", stopWatch.getTotalTimeSeconds()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- anyOf
/** * 两个任务同时执行,以最短时间内结束的为准 * * @throws ExecutionException ExecutionException * @throws InterruptedException InterruptedException */ static void test() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); // num为阻塞时间 String path = "http://localhost:8080/get?num="; CompletableFuture<String> firstFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { String res = HttpUtil.get(path + 1); log.info("res:{}", res); return res; }); CompletableFuture<String> secondFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { String res = HttpUtil.get(path + 3); log.info("res:{}", res); return res; }); CompletableFuture<Object> finishFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(firstFuture, secondFuture); finishFuture.get(); stopWatch.stop(); log.info("结束; time:{}", stopWatch.getTotalTimeSeconds()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 更多API请翻阅官方文档
结束
在实际项目中,通过使用异步编程将接口的响应时间减少了三分之二,极大的提升了用户体验。于此同时,在后期的开发过程中对于性能优化有了新的选择。在执行异步任务的过程中,最好使用自定义线程池且需实现业务隔离,防止在生产环境下出现线程堆积问题。
参考资料
-
相关阅读:
【乐吾乐3D可视化组态编辑器】相机与视角
[计算机毕业设计定制]精品微信小程序学生公寓生活管理系统|前后分离VUE[包运行成功]
C# 第三章:类、接口与结构 学习笔记
《SpringBoot篇》06.超详细热部署教学
Java8 新写法:优雅处理空值,告别冗长的 if-else!
创建型设计模式之建造者模式
swing- 使用颜色画笔装饰你的容器背景
微服务-gateway基本使用
Docker的基本使用
《计算机视觉基础知识蓝皮书》第2篇 深度学习基础
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lhc_makefunny/article/details/127723343
