-
大数据高级开发工程师——Spark学习笔记(9)
Spark内存计算框架
Spark Streaming
Spark Streaming简介
- Spark Streaming 是 Spark 核心 API 的扩展,用于构建弹性、高吞吐量、容错的在线数据流的流式处理程序。总之一句话,Spark Streaming 用于流式数据的处理。
- 数据可以来源于多种数据源:Kafka、Flume、Kinesis,或者 TCP 套接字;接收到的数据可以使用 Spark 的原语来处理,尤其是那些高阶函数:map、reduce、join、window;最终,被处理的数据可以发布到 HDFS、数据库或者在线可视化平台。
- 另外,Spark Streaming 也能和MLlib(机器学习)以及Graphx完美融合。

- Spark Streaming 是基于 Spark 的流式批处理引擎,其基本原理是把某一时间间隔的输入数据进行批量的处理,当批处理间隔缩短到秒级时, 便可以用于处理实时数据流。
- 在 Spark Streaming 中,处理数据的单位是一批而不是单条,而数据采集却是逐条进行的,因此 Spark Streaming 系统需要设置间隔,使得数据汇总到一定的量后再一并操作,这个间隔就是批处理的间隔。
- 批处理间隔是 Spark Streaming 的核心概念和关键参数,它决定了 Spark Streaming 提交作业的频率和数据处理的延迟,同时也影响着数据处理的吞吐量和性能。
Spark Streaming架构流程
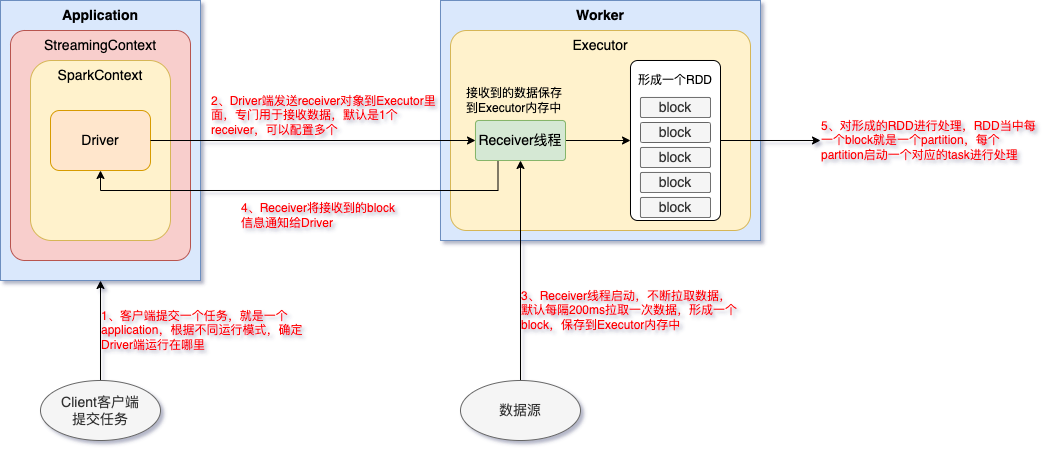
什么是DStream
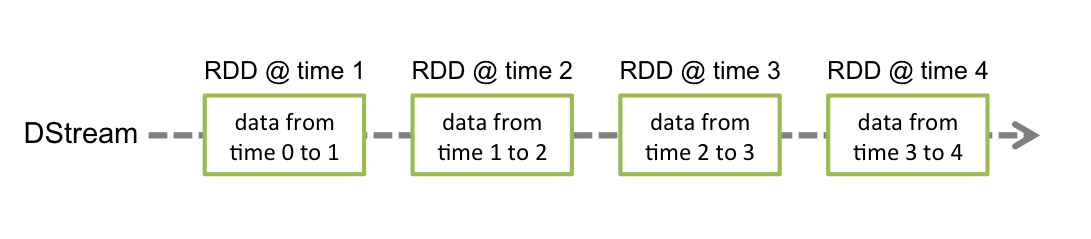
- 离线数据流或者 DStream 是 Spark Streaming 提供的基本抽象。
- 其表现为连续的数据流,这个输入数据流可以来自于源,也可以来自于转换输入流产生的已处理的数据流。
- 内部而言,一个 DStream 以一系列连续的 RDDs 所展现,这些 RDD 是 Spark 对于不变的、分布式数据集的抽象。
- 一个 DStream 中的每个 RDD 都包含来自一定间隔的数据,如下图:
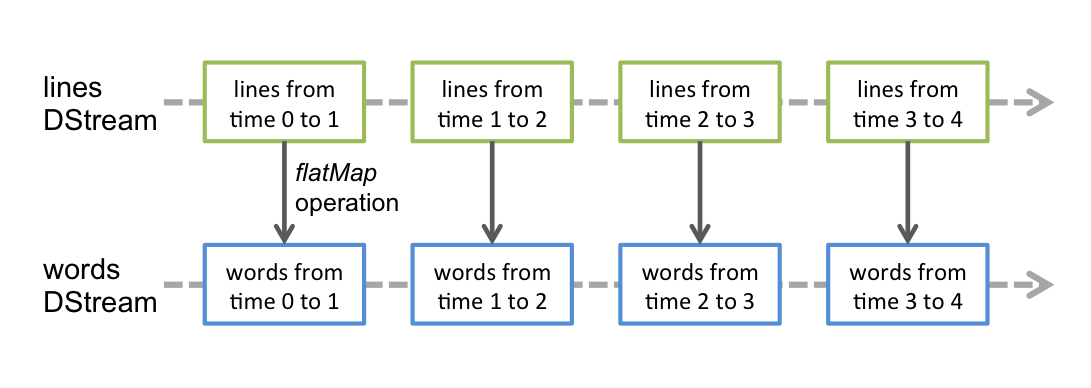
- 在 DStream 上使用的任何操作都会转换为针对底层 RDD 的操作。例如:之前那个将行的流转变为词流的例子中,flatMap 操作应用于行 DStream 的每个 RDD 上,从而产生 words DStream·的 RDD。如下图:
DStream算子操作
1. Transformations
- 实现把一个 DStream 转换成一个新的 DStream;延迟加载,不会触发任务的执行。
Transformation Meaning map(func) 对DStream中的各个元素进行func函数操作,然后返回一个新的DStream flatMap(func) 与map方法类似,只不过各个输入项可以被输出为零个或多个输出项 filter(func) 过滤出所有函数func返回值为true的DStream元素并返回一个新的DStream repartition(numPartitions) 增加或减少DStream中的分区数,从而改变DStream的并行度 union(otherStream) 将源DStream和输入参数为otherDStream的元素合并,并返回一个新的DStream. count() 通过对DStream中的各个RDD中的元素进行计数,然后返回只有一个元素的RDD构成的DStream reduce(func) 对源DStream中的各个RDD中的元素利用func进行聚合操作,然后返回只有一个元素的RDD构成的新的DStream. countByValue() 对于元素类型为KV的DStream,返回一个元素为(K,Long)键值对形式的新的DStream,Long对应的值为源DStream中各个RDD的key出现的次数 reduceByKey(func, [numTasks]) 利用func函数对源DStream中的key进行聚合操作,然后返回新的(K,V)对构成的DStream join(otherStream, [numTasks]) 输入为(K,V)、(K,W)类型的DStream,返回一个新的(K,(V,W))类型的DStream cogroup(otherStream, [numTasks]) 输入为(K,V)、(K,W)类型的DStream,返回一个新的 (K, Seq[V], Seq[W]) 元组类型的DStream transform(func) 通过RDD-to-RDD函数作用于DStream中的各个RDD,可以是任意的RDD操作,从而返回一个新的RDD updateStateByKey(func) 根据key的之前状态值和key的新值,对key进行更新,返回一个新状态的DStream reduceByKeyAndWindow 窗口函数操作,实现按照window窗口大小来进行计算 2. Output Operations
- 输出算子操作,触发任务的真正运行。
Output Operation Meaning print() 打印到控制台 saveAsTextFiles(prefix, [suffix]) 保存流的内容为文本文件,文件名为"prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". saveAsObjectFiles(prefix, [suffix]) 保存流的内容为SequenceFile,文件名为 “prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]”. saveAsHadoopFiles(prefix, [suffix]) 保存流的内容为hadoop文件,文件名为 “prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]”. foreachRDD(func) 对Dstream里面的每个RDD执行func 数据源
1. socket数据源
- 需求:Spark Streaming 实时接收 socket 数据,实现单词统计。
- 业务流程图:

- 安装 socket 服务:在 node01 节点使用 yum 安装 nc 工具(nc命令是netcat命令的简称,它是用来设置路由器,我们可以利用它向某个端口发送数据)。
sudo yum -y install nc- 1
- node01 执行命令向指定的端口发送数据
nc -lk 9999- 1
- 代码开发:
object Case01_SocketWordCount { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.ERROR) // 1. 创建SparkConf对象,注意这里至少给两个线程,一个线程没办法执行 val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName).setMaster("local[2]") // 2. 创建StreamingContext对象 val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(1)) // 3. 接收Socket数据 val socketTextStream: ReceiverInputDStream[String] = ssc.socketTextStream("node01", 9999) // 4. 对数据进行处理 val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = socketTextStream.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _) // 5. 打印结果 result.print() // 6. 开启流式计算 ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
2. HDFS数据源
- 需求:通过 Spark Streaming 监控 HDFS 上的目录,有新的文件产生,就把数据拉取过来进行处理。
- 业务流程图:

- 代码实现:
object Case02_HdfsWordCount { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.ERROR) // 1. 创建SparkConf对象 val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName).setMaster("local[2]") // 2. 创建StreamingContext对象 val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(2)) // 3. 监控hdfs目录的数据 val textFileStream: DStream[String] = ssc.textFileStream("hdfs://node01:8020/data") // 4. 对数据进行处理 val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = textFileStream.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _) // 5. 打印结果 result.print() // 6. 开启流式计算 ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
3. 自定义数据源
object Case03_CustomReceiver { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { // 1. 创建SparkConf对象,注意这里至少给两个线程,一个线程没办法执行 val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName).setMaster("local[2]") // 2. 创建StreamingContext对象 val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(1)) // 3. 调用ReceiverStream API,将自定义的Receiver传进去 val receiverStream = ssc.receiverStream(new CustomReceiver("node01", 9999)) // 4. 对数据进行处理 val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = receiverStream.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _) // 5. 打印结果 result.print() // 6. 开启流式计算 ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } } /** * 自定义Source数据源 */ class CustomReceiver(host: String, port: Int) extends Receiver[String] (StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER) with Logging { override def onStart(): Unit = { // 启动一个线程,开始接收数据 new Thread("custom-receiver") { override def run(): Unit = { receive() } }.start() } private def receive(): Unit = { var socket: Socket = null try { logInfo("Connecting to " + host + ":" + port) socket = new Socket(host, port) logInfo("Connected to " + host + ":" + port) val reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) var line: String = null while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null && !isStopped) { store(line) } reader.close() socket.close() logInfo("Stopped receiving") restart("Trying to connect again") } catch { case e: java.net.ConnectException => restart("Error connecting to " + host + ":" + port, e) case t: Throwable => restart("Error receiving data", t) } } override def onStop(): Unit = { } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
4. flume数据源
- 需求:基于 flume 采集源源不断的数据,通过 Spark Streaming 进行实时数据处理。
- flume 作为日志实时采集的框架,可以与 Spark Streaming 实时处理框架进行对接,flume 实时产生数据,Spark Streaming 做实时处理。
- Spark Streaming 对接 Flume NG 有两种方式:Poll方式、Push 方式。
Poll 方式
- 安装 flume:参考大数据高级开发工程师——数据采集框架Flume(1)
- spark-streaming与flume整合的依赖jar包 spark-streaming-flume-sink_2.11-2.3.4.jar 放到 flume 安装目录下的 lib 目录下。
- 开发 flume 配置文件:
vim spark_flume_poll.conf
a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # source a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /bigdata/install/flumedatas/spark_flume a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true # channel a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 20000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 5000 # sink a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k1.type = org.apache.spark.streaming.flume.sink.SparkSink a1.sinks.k1.hostname = node02 a1.sinks.k1.port = 8888 a1.sinks.k1.batchSize = 2000- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- node02 启动 flume 进程
cd /bigdata/install/apache-flume-1.9.0-bin/ bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/spark_flume_poll.conf -n a1 -Dflume.rootLogger=DEBUG,CONSOLE- 1
- 2
- 准备数据文件,上传到 flume 指定的文件夹,
cd /bigdata/install/flumedatas/spark_flume && vim wordcount.txt
hadoop spark hive spark hadoop sqoop spark storm- 1
- 2
- 代码开发 spark 程序 poll拉取 flume 数据:使用sparkStreaming去poll拉取flume当中的数据,并实现数据的统计计算
- 需要添加 pom 依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.sparkgroupId> <artifactId>spark-streaming-flume_2.11artifactId> <version>2.3.4version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 具体代码实现如下:
object SparkStreamingPollFlume { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { // 1. 创建SparkConf对象,注意这里至少给两个线程,一个线程没办法执行 val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName).setMaster("local[2]") // 2. 创建SparContext对象 val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf) sc.setLogLevel("WARN") // 3. 创建StreamingContext对象 val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc, Seconds(5)) ssc.checkpoint("./flume") // 4. 通过FlumeUtils调用createPollingStream方法获取flume中的数据 val pollingStream: ReceiverInputDStream[SparkFlumeEvent] = FlumeUtils.createPollingStream(ssc, "node02", 8888) // 5. 获取flume中event的body val data: DStream[String] = pollingStream.map(x => new String(x.event.getBody.array())) // 6. 切分每一行,每个单词记为1 val wordAndOne: DStream[(String, Int)] = data.flatMap(x => x.split(" ")).map((_, 1)) // 7. 相同单词出现的次数累加 val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = wordAndOne.updateStateByKey(updateFunc) // 8. 打印结果 result.print() // 9. 开启流式计算 ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } /** * @param currentValues 表示在当前批次每个单词出现的所有的1 (hadoop,1)、(hadoop,1)、...、(hadoop,1) * @param historyValues 表示在之前所有批次中每个单词出现的总次数 (hadoop,100) */ def updateFunc(currentValues: Seq[Int], historyValues: Option[Int]): Option[Int] = { val newValue: Int = currentValues.sum + historyValues.getOrElse(0) Some(newValue) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
Push方式
- 开发 flume 配置文件:
vim spark_flume_push.conf
a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # source a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /bigdata/install/flumedatas/spark_flume a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true # channel a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 20000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=5000 # sink a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k1.type = avro # 注意这里的ip需要指定的是我们spark程序所运行的服务器的ip a1.sinks.k1.hostname = 192.168.0.100 a1.sinks.k1.port = 8888 a1.sinks.k1.batchSize = 2000- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- node02 启动 flume 进程
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f conf/spark_flume_push.conf -n a1 -Dflume.rootLogger=DEBUG,CONSOLE- 1
- 开发 Spark Streaming代码,通过 push 模式消费 flume 当中的数据,代码实现如下:
object SparkStreamingPushFlume { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { // 1. 创建SparkConf对象,注意这里至少给两个线程,一个线程没办法执行 val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName).setMaster("local[2]") // 2. 创建SparContext对象 val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf) sc.setLogLevel("WARN") // 3. 创建StreamingContext对象 val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc, Seconds(5)) ssc.checkpoint("./flume") // 4. 当前应用程序部署的服务器ip地址,跟flume配置文件保持一致 val flumeStream: ReceiverInputDStream[SparkFlumeEvent] = FlumeUtils.createStream(ssc, "192.168.0.100", 8888, StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK) // 5. 获取flume中event的body val lineStream: DStream[String] = flumeStream.map(x => new String(x.event.getBody.array())) // 6. 实现单词汇总 val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = lineStream.flatMap(x => x.split(" ")).map((_, 1)) .updateStateByKey(updateFunc) // 7. 打印结果 result.print() // 8. 开启流式计算 ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } /** * @param currentValues 表示在当前批次每个单词出现的所有的1 (hadoop,1)、(hadoop,1)、...、(hadoop,1) * @param historyValues 表示在之前所有批次中每个单词出现的总次数 (hadoop,100) */ def updateFunc(currentValues: Seq[Int], historyValues: Option[Int]): Option[Int] = { val newValue: Int = currentValues.sum + historyValues.getOrElse(0) Some(newValue) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
任务提交
spark-submit \ --master spark://node01:7077 \ --deploy-mode cluster \ --supervise \ --class com.yw.spark.example.streaming.cases.Case01_SocketWordCount \ --executor-memory 1g \ --total-executor-cores 2 \ original-spark-demo-1.0.jar- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Transformation高级算子
1. updateStateByKey
- 有时,我们需要在 DStream 中跨批次维护状态(例如流计算中累加 WordCount)。针对这种情况,updateStateByKey 为我们提供了对一个状态变量的访问,用于键值对形式的 DStream。给定一个由【键,事件】构成的 DStream,并传递一个指定如何根据新的事件更新每个键对应状态的函数,它可以构建出一个新的 DStream,其内部数据为【键,状态】对。
- updateStateByKey 的结果会是一个新的 DStream,其内部的 RDD 序列是由每个时间区间对应的【键,状态】对组成的。
- updateStateByKey 操作使得我们可以在用新信息进行更新时,保持任意的状态。为使用这个功能,需要做下面两步:
- 定义状态,状态可以是一个任意的数据类型;
- 定义状态更新函数,用此函数阐明如何使用之前的状态和来自输入流的新值,对状态进行更新。
- 使用 updateStateByKey 需要对检查点目录进行配置,会使用检查点来保存状态。
- Spark Streaming接受socket数据实现所有批次的单词次数累加,代码实现如下:
object Case04_UpdateStateByKeyWordCount { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.ERROR) // 1. 创建SparkConf对象 val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName).setMaster("local[2]") // 2. 创建StreamingContext对象 val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(2)) // 3. 设置checkpoint目录 ssc.checkpoint("hdfs://node01:8020/checkpoint") // 4. 接收Socket数据 val socketTextStream: ReceiverInputDStream[String] = ssc.socketTextStream("node01", 9999) // 5. 对数据进行处理 val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = socketTextStream.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)) .updateStateByKey(updateFunc) // 6. 打印结果 result.print() // 7. 开启流式计算 ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } /** * @param currentValues 表示在当前批次每个单词出现的所有的1 (hadoop,1)、(hadoop,1)、...、(hadoop,1) * @param historyValues 表示在之前所有批次中每个单词出现的总次数 (hadoop,100) */ def updateFunc(currentValues: Seq[Int], historyValues: Option[Int]): Option[Int] = { val newValue: Int = currentValues.sum + historyValues.getOrElse(0) Some(newValue) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
2. mapWithState
- 除了使用 updateStateByKey 完成以上需求外,还可以使用 mapWithState 实现所有批次的单词次数累加
- 代码实现如下:
object Case05_MapWithStateWordCount { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.ERROR) // 1. 创建SparkConf对象 val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName).setMaster("local[2]") // 2. 创建StreamingContext对象 val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(2)) // 3. 设置checkpoint目录 ssc.checkpoint("hdfs://node01:8020/checkpoint") // 4. 接收Socket数据 val socketTextStream: ReceiverInputDStream[String] = ssc.socketTextStream("node01", 9999) val initRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = ssc.sparkContext.parallelize(List(("hadoop", 10), ("spark", 20))) val stateSpec = StateSpec.function((time: Time, key: String, currentValue: Option[Int], historyState: State[Int]) => { val sum: Int = currentValue.getOrElse(0) + historyState.getOption().getOrElse(0) val output = (key, sum) if (!historyState.isTimingOut()) { historyState.update(sum) } Some(output) }).initialState(initRDD).timeout(Durations.seconds(5)) // 5. 对数据进行处理 val result: MapWithStateDStream[String, Int, Int, (String, Int)] = socketTextStream.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)) .mapWithState(stateSpec) // 6. 打印结果 result.stateSnapshots().print() // 7. 开启流式计算 ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 小结:
- 若要清除某个key的状态,可以在自定义的方法中调用 state.remove();
- 若要设置状态超时时间,可以调用 StateSpec.function(mappingFunc).timeout() 方法设置;
- 若要添加初始化的状态,可以调用 StateSpec.function(mappingFunc).initialState(initialRDD) 方法;
- 性能比 updateStateByKey 好。
3. transform
- 需求:获取每一个批次中单词出现次数最多的前三位
- 代码实现:
object Case06_TransformWordCount { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.ERROR) // 1. 创建SparkConf对象 val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName).setMaster("local[2]") // 2. 创建StreamingContext对象 val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(2)) // 3. 接收Socket数据 val socketTextStream: ReceiverInputDStream[String] = ssc.socketTextStream("node01", 9999) // 4. 对数据进行处理 val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = socketTextStream.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)) .reduceByKey(_ + _) // 5. 对DStream进行transform操作 val sortedDstream: DStream[(String, Int)] = result.transform(rdd => { val sortedRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = rdd.sortBy(_._2, false) val top3: Array[(String, Int)] = sortedRDD.take(3) top3.foreach(println) sortedRDD }) // 6. 打印结果 sortedDstream.print() // 7. 开启流式计算 ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
4. window 操作
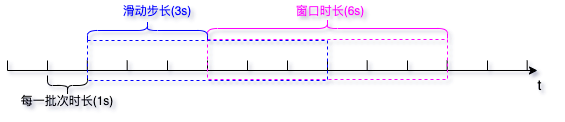
- window 操作可以设置窗口的大小和滑动窗口的间隔来动态的获取当前Streaming的允许状态,所以基于窗口的操作都是需要两个参数,分别为窗口时长以及滑动步长。
- 窗口时长:计算内容的时间范围;
- 滑动步长:隔多久触发一次计算。
- 注意:这两者必须为采集周期大小的整数倍。
- 需求:实现 WordCount,3秒一个批次,窗口12秒,滑动步长6秒。
- 代码实现:
object Case07_WindowWordCount { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.ERROR) // 1. 创建SparkConf对象 val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName).setMaster("local[2]") // 2. 创建StreamingContext对象 val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(2)) // 3. 接收Socket数据 val socketTextStream: ReceiverInputDStream[String] = ssc.socketTextStream("node01", 9999) // 4. 对数据进行处理 val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = socketTextStream.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)) .reduceByKeyAndWindow((a: Int, b: Int) => a + b, Seconds(12), Seconds(6)) // 5. 打印结果 result.print() // 6. 开启流式计算 ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
关于 window 的操作还有如下方法:
- window(windowLength, slideInterval):基于对源 DStream 窗口的批次进行计算返回一个新的 DStream;
- countByWindow(windowLength, slideInterval):返回一个滑动窗口计数流中的元素个数;
- reduceByWindow(func, windowLength, slideInterval):通过使用自定义函数整合滑动区间流元素来创建一个新的单元素流;
- reduceByKeyAndWindow(func, windowLength, slideInterval, [numTasks]):当一个 (K,V) 对的 DStream 上调用此函数,会返回一个新 (K,V) 对的 DStream,此处通过对滑动窗口中批次数据使用 reduce 函数来整合每个 key 的 value 值。
- reduceByKeyAndWindow(func, invFunc, windowLength, slideInterval, [numTasks]):这个函数是上述函数的变化版本,每个窗口的 reduce 值都是通过用前一个窗的reduce值来递增计算。通过reduce进入到滑动窗口数据并”反向reduce”离开窗口的旧数据来实现这个操作。一个例子是随着窗口滑动对keys的“加”“减”计数。通过前边介绍可以想到,这个函数只适用于”可逆的reduce函数”,也就是这些reduce函数有相应的”反reduce”函数(以参数invFunc形式传入)。如前述函数,reduce任务的数量通过可选参数来配置。
Output算子
- 输出操作指定了对流数据经转化操作得到的数据,所要执行的操作(例如把结果写入外部数据库或输出到屏幕上)。与 RDD 中的惰性求值类似,如果一个 DStream 及其派生出的 DStream 都没有执行输出操作,那么这些 DStream 就都不会被求值。如果 StreamingContext 中没有设定输出操作,整个 context 都不会启动。
- 输出操作如下:
- print():在运行流程序的驱动节点上打印 DStream 中每一批数据的最开始 10 个元素,这个用于开发和调试。
- saveAsTextFiles(prefix, [suffix]):以 text 文件形式存储这个 DStream 的内容,每一批次的存储文件名基于参数中的prefix和suffix。”prefix-Time_IN_MS[.suffix]”。
- saveAsObjectFiles(prefix, [suffix]):以 Java 对象序列化的方式将 Stream 中的数据保存为 SequenceFiles,每一批次的存储文件名基于参数中的为"prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]"。
- saveAsHadoopFiles(prefix, [suffix]):将 Stream 中的数据保存为 Hadoop files,每一批次的存储文件名基于参数中的为"prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]"。
- foreachRDD(func):这是最通用的输出操作,即将函数 func 用于产生于 stream的每一个RDD。其中参数传入的函数func应该实现将每一个RDD中数据推送到外部系统,如将RDD存入文件或者通过网络将其写入数据库。通用的输出操作foreachRDD(),它用来对DStream中的RDD运行任意计算。这和transform() 有些类似,都可以让我们访问任意RDD。在foreachRDD()中,可以重用我们在Spark中实现的所有行动操作。比如,常见的用例之一是把数据写到诸如MySQL的外部数据库中。
- 需求:将WordCount案例中得到的结果通过foreachRDD保存结果到mysql中
- 代码实现:
object Case08_WordCountForeachRDD { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.ERROR) // 1. 创建SparkConf对象,注意这里至少给两个线程,一个线程没办法执行 val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName).setMaster("local[2]") // 2. 创建StreamingContext对象 val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(1)) // 3. 接收Socket数据 val socketTextStream: ReceiverInputDStream[String] = ssc.socketTextStream("node01", 9999) // 4. 对数据进行处理 val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = socketTextStream.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _) // 5. 将结果保存到MySQL数据库中 // /*********************** 方案一 ***********************/ // result.foreachRDD(rdd => { // // 注意这里创建的对象都是在Driver端,但真正执行是在 Executor 端,所以是有问题的 // val conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://node01:3306/test", "root", "123456") // val statement = conn.prepareStatement(s"insert into wordcount(word, count) values(?, ?)") // // rdd.foreach { record => // statement.setString(1, record._1) // statement.setInt(2, record._2) // statement.execute() // } // statement.close() // conn.close() // }) // /*********************** 方案二 ***********************/ // result.foreachRDD(rdd => { // rdd.foreach { record => // // 针对每一个record创建连接,效率不高 // val conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://node01:3306/test", "root", "123456") // val statement = conn.prepareStatement(s"insert into wordcount(word, count) values(?, ?)") // // statement.setString(1, record._1) // statement.setInt(2, record._2) // statement.execute() // // statement.close() // conn.close() // } // }) // /*********************** 方案三 ***********************/ // result.foreachRDD(rdd => { // rdd.foreachPartition(it => { // // 针对每一个执行器分区创建连接 // val conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://node01:3306/test", "root", "123456") // val statement = conn.prepareStatement(s"insert into wordcount(word, count) values(?, ?)") // // it.foreach(record => { // statement.setString(1, record._1) // statement.setInt(2, record._2) // statement.execute() // }) // // statement.close() // conn.close() // }) // }) /*********************** 方案四 ***********************/ result.foreachRDD(rdd => { rdd.foreachPartition(it => { // 针对每一个执行器分区创建连接,同时使用批量提交 val conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://node01:3306/test", "root", "123456") val statement = conn.prepareStatement(s"insert into wordcount(word, count) values(?, ?)") // 关闭自动提交 conn.setAutoCommit(false) it.foreach(record => { statement.setString(1, record._1) statement.setInt(2, record._2) // 添加到每一个批次 statement.addBatch() }) // 批量提交该分区所有数据 statement.executeBatch() conn.commit() statement.close() conn.close() }) }) // 6. 开启流式计算 ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
-
相关阅读:
一起Talk Android吧(第四百二十七回:在Android中使用MQTT通信一)
4、MySql 索引浅解
Linux关于memory cgroup的几个要点
python:xlwings 操作 Excel 加入图片
Vue 中简易封装网络请求(Axios),包含请求拦截器和响应拦截器
数据结构-顺序表操作
Day18-登录与支付-登录-点击结算按钮进行条件判断
基于微信小程序的健身小助手打卡预约教学系统(源码+lw+部署文档+讲解等)
Mapper输出数据中文乱码
如何选择消息队列
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/yangwei234/article/details/127608398