-
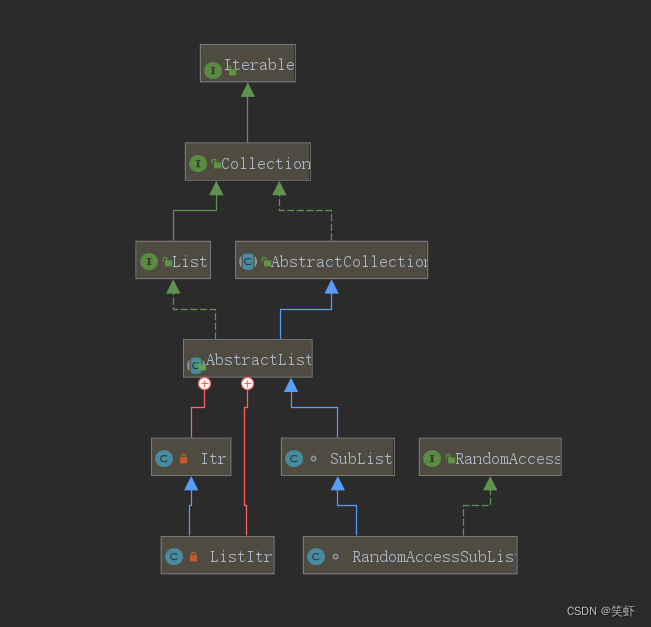
Java 集合学习笔记:AbstractList
equals(Object o)
实现 equals 对当前列表与指定对象 o 中的元素,按顺序两两对比。
- 元素数量要相等。
- 相同索引上的元素要满足:
o1.equals(o2) == true。
public boolean equals(Object o) { // 指定对象 o 与当前对象是同一个,直接返回 true if (o == this) return true; // 指定对象 o 不是 List 的实现,直接返回 false if (!(o instanceof List)) return false; // 分别取出【当前列表】和【指定列表】的迭代器。 ListIterator<E> e1 = listIterator(); ListIterator<?> e2 = ((List<?>) o).listIterator(); // 按顺序成对逐个对比元素 // 如果两个列表都有 next 则都取出来,对比。 // 对 null 单独判断。 // 如果 o1 为 null 就判断 o2 是不是 null // 如果 o1 非 null 就 o1.equals(o2) while (e1.hasNext() && e2.hasNext()) { E o1 = e1.next(); Object o2 = e2.next(); if (!(o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2))) return false; } // 成对比较完成后,再检测是否有某个列表,还有更多的元素,一多一少,则不相等。 return !(e1.hasNext() || e2.hasNext()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
hashCode()
可以看到这里的返回值是
int出负数是没跑了public int hashCode() { int hashCode = 1; for (E e : this) hashCode = 31*hashCode + (e==null ? 0 : e.hashCode()); return hashCode; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
indexOf(Object o)
和大多数的处理逻辑一至,分为 null 和 非null 两个分支。
public int indexOf(Object o) { ListIterator<E> it = listIterator(); if (o==null) { while (it.hasNext()) if (it.next()==null) return it.previousIndex(); } else { while (it.hasNext()) if (o.equals(it.next())) return it.previousIndex(); } return -1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
lastIndexOf(Object o)
与 indexOf 相反,从后往前找。找到就返回索引。
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { ListIterator<E> it = listIterator(size()); if (o==null) { while (it.hasPrevious()) if (it.previous()==null) return it.nextIndex(); } else { while (it.hasPrevious()) if (o.equals(it.previous())) return it.nextIndex(); } return -1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
clear()
调用
removeRange将指定范围内的元素,逐个删除。public void clear() { removeRange(0, size()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { ListIterator<E> it = listIterator(fromIndex); for (int i=0, n=toIndex-fromIndex; i<n; i++) { it.next(); it.remove(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
addAll(int index, Collection c)
批量添加。
- 检查给定索引是否
index < 0 || index > size() - 这是修改标记
modified只能成功添加就会为true add方法等待子类实现。当前类中直接抛锅UnsupportedOperationException();
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); boolean modified = false; for (E e : c) { add(index++, e); modified = true; } return modified; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
equals(Object o)
public boolean equals(Object o) { // 给定对象 o 与当前对象 地址相同,则是同一对象,一定相等。 if (o == this) return true; // 如果给定对象 o 都不是 List 的实现,那肯定不相等。(因为我是) if (!(o instanceof List)) return false; // 取出当前列表和给定对象的迭代器。 ListIterator<E> e1 = listIterator(); ListIterator<?> e2 = ((List<?>) o).listIterator(); // 只要两个迭代器都有元素,就一直逐个对比 while (e1.hasNext() && e2.hasNext()) { E o1 = e1.next(); Object o2 = e2.next(); // 如果我是 null 你也必须是 null (否则就不相等了) // 如果我们都不是 null,调用 equals 对比。 if (!(o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2))) return false; } // 上面都一对一对比过来了。无论谁还剩的有元素,那都说明我们不一样。 return !(e1.hasNext() || e2.hasNext()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
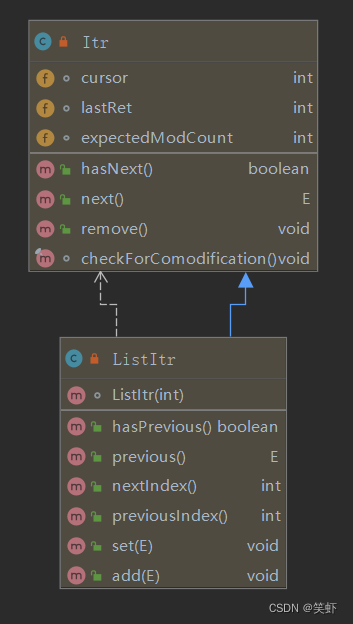
Itr
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { // 光标指向:下一个(要返回的)元素的索引。 int 类型默认值 0 int cursor = 0; // 最近一次(返回的)元素的索引; 调用 remove 后会重置为-1,表示没有指向。 int lastRet = -1; // 迭代器先记录下,列表的修改次数。后面做并发检测,如果两个值不相等,说明列表被别人动了。 // 如果是迭代器自己的修改操作 remove 它最后会同步两个数值。 int expectedModCount = modCount; // 光标没指到 public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size(); } // 返回下一个元素 public E next() { checkForComodification();// 检查并发冲突 try { int i = cursor; // 拿到要返回的元素的索引 E next = get(i);// 获取元素 lastRet = i; // 更新 lastRet 指针(这东西是给 remove 用的) cursor = i + 1; // 更新光标,指向下一次调next(要返回的)元素的索引 return next; // 返回元素 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { checkForComodification(); throw new NoSuchElementException(); } } // 移除上一次 next() 返回的元素 public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) // 还没有调用过 next throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); // 检查并发冲突 try { // 调用 AbstractList 的 remove 方法删除元素(remove 需要子类来实现) AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet); // 删除元素后,其后元素整体左移一位 cursor 也要减一才对应的上。 if (lastRet < cursor) cursor--; lastRet = -1; // 同步【迭代器】的修改计数和【列表】的修改计数。 expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } // 检查并发冲突 final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
ListItr
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> { // 按给定索引值初始化对象 ListItr(int index) { cursor = index; // 初始当前位置 } // cursor 不等于 0,表示前面还有元素。返回 true public boolean hasPrevious() { return cursor != 0; } // 与 next 相反返回列表中的上一个元素。 public E previous() { checkForComodification(); // 检查并发冲突 try { int i = cursor - 1; // 取出前一个索引 E previous = get(i);// 获取前一个元素 lastRet = cursor = i;// 更新上次操作的元素的指针 return previous; // 返回前一个元素 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { checkForComodification(); throw new NoSuchElementException(); } } // next 将返回的元素的索引 public int nextIndex() { return cursor; } // 上一个元素的索引 public int previousIndex() { return cursor-1; } // 修改(索引 lastRet 所在的)元素 public void set(E e) { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { // set 要让子类去实现 AbstractList.this.set(lastRet, e); // 可能子类会修改列表,同步一下计数 expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } // 当前位置插入元素 public void add(E e) { checkForComodification(); try { int i = cursor; AbstractList.this.add(i, e); lastRet = -1; cursor = i + 1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
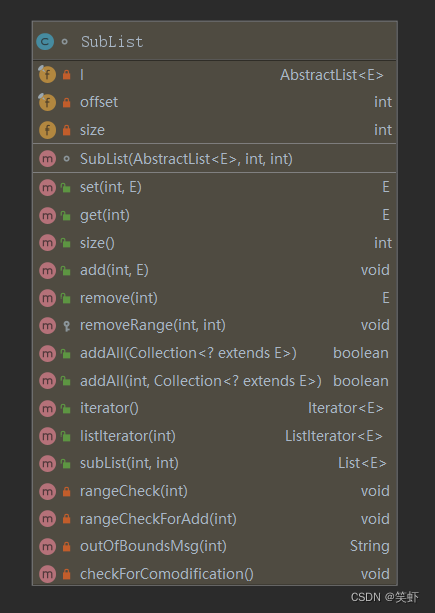
SubList
SubList 是对当前列表的片段引用。
class SubList<E> extends AbstractList<E> { private final AbstractList<E> l; private final int offset; private int size; SubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) { // 一通检测确保索引和size都正常 if (fromIndex < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex); if (toIndex > list.size()) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex); if (fromIndex > toIndex) throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex + ") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")"); l = list; // subList 引用原列表 offset = fromIndex; // 开始索引 size = toIndex - fromIndex; // 算出subList应该有的大小 this.modCount = l.modCount; // 引用修改计数 } // 调用原列表的 set,修改指定index所在的元素 public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); checkForComodification(); return l.set(index+offset, element); } // 调用原列表的 get public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); checkForComodification(); return l.get(index+offset); } public int size() { checkForComodification(); return size; } // 调用原列表的 add public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); checkForComodification(); l.add(index+offset, element); // 因为实际调用的是原列表,所以要加上偏移量 this.modCount = l.modCount; // 同步计数 size++; } // 调用原列表的 remove public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); checkForComodification(); E result = l.remove(index+offset); // 因为实际调用的是原列表,所以要加上偏移量 this.modCount = l.modCount; // 同步计数 size--; // 删除成功自然要更新 size return result; // 返回被删除的元素(与原列表行为保持一至) } // 调用原列表的 removeRange protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { checkForComodification(); l.removeRange(fromIndex+offset, toIndex+offset); this.modCount = l.modCount; size -= (toIndex-fromIndex); } public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(size, c); } // 调用原列表的 addAll public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); int cSize = c.size(); if (cSize==0) return false; checkForComodification(); l.addAll(offset+index, c); this.modCount = l.modCount; size += cSize; return true; } // 返回迭代器 public Iterator<E> iterator() { return listIterator(); } public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) { checkForComodification(); rangeCheckForAdd(index); return new ListIterator<E>() { private final ListIterator<E> i = l.listIterator(index+offset); public boolean hasNext() { return nextIndex() < size; } public E next() { if (hasNext()) return i.next(); else throw new NoSuchElementException(); } public boolean hasPrevious() { return previousIndex() >= 0; } public E previous() { if (hasPrevious()) return i.previous(); else throw new NoSuchElementException(); } public int nextIndex() { return i.nextIndex() - offset; } public int previousIndex() { return i.previousIndex() - offset; } public void remove() { i.remove(); // 当前是嵌套关系。显示表明调用的是 SubList.this SubList.this.modCount = l.modCount; size--; } public void set(E e) { i.set(e); } public void add(E e) { i.add(e); SubList.this.modCount = l.modCount; size++; } }; } public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { return new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex); } // 检测索引有没有超出 private void rangeCheck(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } // 检测索引是否在可插入元素的范围内 private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { if (index < 0 || index > size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size; } // 检测并发冲突 private void checkForComodification() { if (this.modCount != l.modCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
参考资料
-
相关阅读:
websocket学习
GPU的租用Pycharm连接远程GPU服务器跑深度学习
shell的for循环与结构化
T288401 B-莲子的机械动力学
chrome 相关设置
Netty数据存储分析和经典问题之粘包拆包解决方案
【外汇天眼】很多交易高手都容易忽视的问题:“路径依赖”!
Lua 模块 module
神经网络基本框架(torch.nn)
编程小白的自学笔记十四(python办公自动化创建、复制、移动文件和文件夹)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/jx520/article/details/127163538
