-
详解Python中的序列化(简单易懂版)
1.什么是数据序列化?
序列化 (Serialization),是指把程序中的一个类转化成一个标准化的格式。标准化的意义是这个格式可以跨程序,跨平台的被使用,而且保持其原有的内容,规范。
2.为什么要进行数据序列化呢?
(1)一致性
我们将要保存的数据,序列化成标准的格式(Json格式或者Pickle格式)。之后再反序列化回来,数据依然是原来的。保持了数据的一致性。
(2)有效性
序列化之后,可以减少内存和网络资源的占用。
(3)兼容性
将数据序列化之后,Json格式或者Pickle格式,我可以在其他平台(其他操作系统的电脑)上依然使用。
我用python对数据进行了序列化,我之后可以使用java等其他语言,对其进行反序列,然后进行使用,数据并没有发生改变。3.数据序列化的应用
(1)应用一
你的程序需要和其他程序交流,例如 平台 API, 网页请求

(2)应用二
串行任务流,每一个任务结束之后数据通过序列化传递到下一个任务。
4.JSON
JSON 是一个文件格式,也是一个标准化的数据传输方案,通常网站的后端和前端的交流,移动 APP 和云服务器的交流方式都是通过 JSON。
(1)序列化
# 导入json模块 import json simple_dict = {'name': 'zxy', 'age': 21} with open('simple_dict.txt', 'w') as file_to_write: # 进行json序列化,然后写入simple_dict.txt文件中 json.dump(simple_dict, file_to_write)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
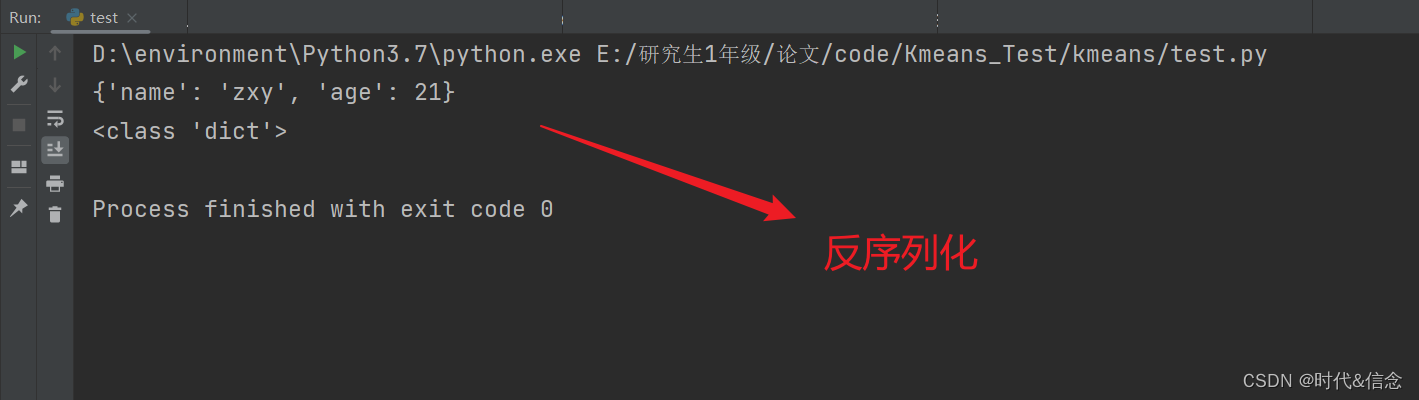
(2)反序列化
with open('simple_dict.txt', 'r') as file_to_read: loaded_simple_dict = json.load(file_to_read) print(loaded_simple_dict) print(type(loaded_simple_dict))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
(3)Json 方法的弊端
当遇到一些 Python 特定的高级数据类型的时候,Json 会因为没有标准而无法进行序列化。
会报如下错误:

5.Pickle
Pickle 和 Json 不同的是,Pickle 是 Python 专属的序列化方案,可以转化大多数 Python 的数据类型,并且储存方式是二进制(Byte Code)。二进制的储存方式只有机器才能理解,但是同时也保证了一定的数据隐秘性和高效性。
(1)序列化
import pickle import datetime abc_dict = {datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 18, 0, 0): 9682.24, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 17, 0, 0): 9411.61, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 16, 0, 0): 10858.7, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 15, 0, 0): 10195.0, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 14, 0, 0): 11378.23, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 13, 0, 0): 11810.0, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 12, 0, 0): 11338.9, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 11, 0, 0): 12090.99, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 10, 0, 0): 12577.85} with open('abc.pk', 'wb') as file_to_write: pickle.dump(abc_dict, file_to_write)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
二进制的储存方式只有机器才能理解,保证了一定的数据隐秘性和高效性。

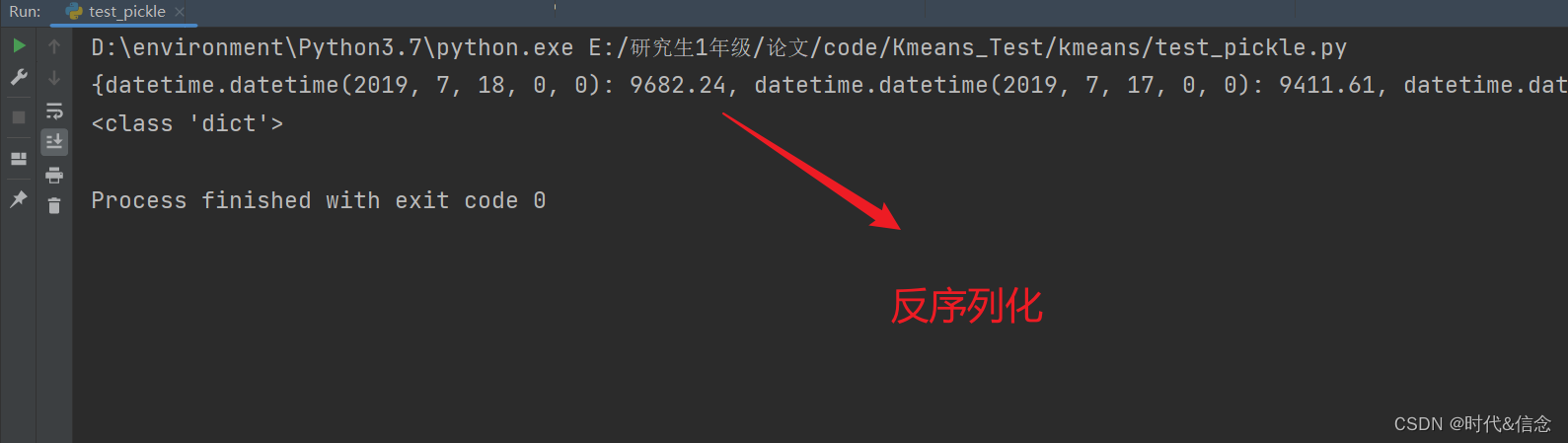
(2)反序列化
import pickle import datetime abc_dict = {datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 18, 0, 0): 9682.24, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 17, 0, 0): 9411.61, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 16, 0, 0): 10858.7, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 15, 0, 0): 10195.0, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 14, 0, 0): 11378.23, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 13, 0, 0): 11810.0, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 12, 0, 0): 11338.9, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 11, 0, 0): 12090.99, datetime.datetime(2019, 7, 10, 0, 0): 12577.85} with open('abc.pk', 'wb') as file_to_write: # pickle序列化,然后以二进制的形式存入文件中 pickle.dump(abc_dict, file_to_write) with open('abc.pk', 'rb') as file_to_read: # 以二进制的形式进行读取文件 abc_dict_pk = pickle.load(file_to_read) print(abc_dict_pk) print(type(abc_dict_pk))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
6.总结
这里两个方法的行为都是在序列化数据,所以在调用函数上感觉完全一样。
但是本质上 Json 写入文件的是字符串,而 Pickle 则是把数据转化成了二进制,两个是完全不同的处理方案。本文参考自:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/87470851
-
相关阅读:
收单外包机构备案业务类型汇总分析
poshmark前景,怎么快速提升销量!
netty系列之:在netty中使用native传输协议
设计模式(5)--模板方法模式概念要点及例子说明
大数据课程L4——网站流量项目的Hive离线批处理
java毕业生设计在线教学质量评价系统计算机源码+系统+mysql+调试部署+lw
虚拟机配置网络(主机ping、虚拟机ping不通等问题)
HTML小游戏11 —— 横版恐龙大冒险游戏(附完整源码)
mac13 intellij系列全家桶全屏键入闪烁问题
4.【opencv打开美女热舞视频以及摄像头】
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Elon15/article/details/127679212
