-
【英语:基础高阶_经典外刊阅读】L1.阅读理解—读题定位法
1.阅读理解解题方法
阅读理解在各类不同的考试中, 出题的方式也是不尽相同, 除了最常见的选择, 还会有填空、排序、判断正误、匹配、添加标题、补充句子等等.
在应对不同问题时我们需要熟练运用不同的解题方式, 看清阅读理解的出题方向, 扎实阅读解题基本功.
2.阅读理解解题常见方法
2.1.信息类——扫读
定义:查读可以为扫描式阅读, 英文叫
scanning, 是指用较短的时间快速扫视文章, 查找具体信息或相关事实与细节的阅读技巧.举个简单的例子
当你在机场看指示牌, 找登机信息时, 就需要用scanning. 再如去车站坐车, 去景点买门票, 去超市购物等, 都需要这种查阅信息的能力, 从而快速找到想要的信息.特点:功利性强, 耗时短. 查读带有明确的目的性, 是带着问题寻找答案的阅读方法, 在考试中具有很高的实用价值.
阅读理解有时会出一些图表、招聘广告、电影海报等类型的题目, 这一类题目往往比较直观, 主要考察时间、地点、数字等通过查读就可以了解的信息.
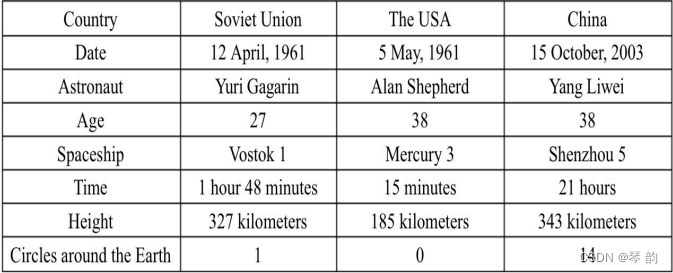
看这个表格题
-
________went into space first.
A. China
B. The USA
C. Soviet Union
D. The UK -
The Chinese astronaut stayed in space for________.
A. 1 hour 48 minutes
B. only 15 minutes
C. the shortest time
D. 21 hours
解析:
这两道题就是典型的扫读类型的题目, 只要找到题干的关键词, 然后直接去表格中快速扫视, 定位目标.第一题关键词first, 是问去的时间, 对应date那一行, 选出答案
C, Soviet Union.
第二题关键词Chinese astronaut, 直接对应着找时间就可以了, 选出答案D`.这一类题目的答题原则就是要快而准, 需要同学们更加细致, 不能马虎.
2.2.主旨类——略读
定义:略读, 英文叫skimming, 是指快速阅读文章以了解其内容大意的阅读方法, to build a quick understanding. 换句话说, 略读是要求读者有选择地进行阅读, 可跳过某些细节, 以求抓住文章的大概, 从而加快阅读速度.
特点:可以在短时间内了解文章或段落大意. 在考试中, 有助于我们在短时间内了解文章主要内容, 可以帮助学生做文章主旨、段落大意、标题概括类题目以及做出时间分配与阅读重心的判断.
这一类常见的问题包括:
文章主旨类:- What is the main idea of the passage?
- What does the story mainly tell us?
- What does the passage mainly talk about?
- The main purpose of the passage is to ______.
段落大意类:- What does paragraph 3 mainly talk about?
- What does the writer try to express in paragraph 3?
标题概括类:- What is the best title for this passage?
- Which of the following is the best title of the passage?
略读的具体操作方法如下:
- 阅读标题——标题往往最能够体现一篇文章的主旨大意.
- 大致浏览题目, 了解题目类型, 确定阅读重心和时间分配.
- 完整地阅读首段——帮助识别文章的主题和题材, 了解作者的风格和观点.
- 如果有小标题, 浏览小标题, 确定段与段之间的逻辑关系.
- 阅读接下来每个段落的第一句话, 通常第一句话都为主题句. 如果句首为问句, 那么主题句往往出现在句末.
- 留意文章中某些特定的定位信息, 例如回答有关who, what, when, why, how 等问题的语句, 以及其他信息如名词、首字母大写的单词、举例、限定性形容词 (best, worst, most等)和带有印刷效果的单词(斜体、粗体、下划线等), 方便后面做题的时候回到文章中查阅.
看个例题:
Meanwhile, things that you might expect to discourage spending — “bad” tables,crowding, high prices — don’t necessarily. Diners at bad tables — next to the kitchen door, say — spent nearly as much as others but soon fled. It can be concluded that restaurant keepers need not “be overly concerned about ‘bad’ tables”, given that they’re profitable. As for rowds, a Hong Kong study found that they increased a restaurant’s reputation, suggesting great food at fair prices. And doubling a buffet’s price led customers to say that its pizza was 11 percent tastier.What does the last paragraph talk about?
A. Tips to attract more customers.
B. Problems restaurants are faced with.
C. Ways to improve restaurants’ reputation.
D. Common misunderstandings about restaurants.2.2.1.读题定位法
-
-
相关阅读:
worthington细胞分离优化技术:优化策略
JumpServer2023漏洞复现合集
数据结构之线性表中的顺序表【详解】
最小二乘法
模拟量采集----测量输入的电压
STC15单片机-串口打印printf重定向
《mysql》--mysql约束
JDBC-环境搭建及简单介绍和使用
电脑重装系统后鼠标动不了该怎么解决
【PickerView案例12-info_plist-PCH文件介绍 Objective-C语言】
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/u012549626/article/details/127692808