-
3.pytorch学习:conv2d——2d卷积
目录
自建一个tensor理解卷积
- import torch
- from torch import nn
- input = torch.tensor([[[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]],
- [[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]],
- [[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]]], dtype=torch.float32)
- print(input.shape)
- input = torch.reshape(input, (-1, 3, 5, 5))
- print(input.shape)
- class ZiDingYi(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(ZiDingYi, self).__init__()
- self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=6, kernel_size=3, stride=(1, 1), padding=0)
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.conv1(x)
- return x
- zidingyi = ZiDingYi()
- print(zidingyi)
- output = zidingyi(input)
- print(output)
自创一个tensor张量,为了与图像相符合,采用了三通道、高与宽的形式。
- input = torch.tensor([[[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]],
- [[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]],
- [[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]]], dtype=torch.float32)
- print(input.shape)
- input = torch.reshape(input, (-1, 3, 5, 5))
- print(input.shape)
注意的点1:
输入的整数系统默认识别为长整型(long),这种数据类型神经网络不能接收,必须强制转换为浮点型,其中torch下给出了浮点型的数据类型。
dtype=torch.float32注意的点2:
不知道新增维度的值时可以给-1让系统自己运算。
input = torch.reshape(input, (-1, 3, 5, 5))继承nn.Module父类,利用super()调用父类中的__init__()
- class ZiDingYi(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(ZiDingYi, self).__init__()
- self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=6, kernel_size=3, stride=(1, 1), padding=0)
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.conv1(x)
- return x
其中2d卷积的参数,收到的通道数,输出的通道数,卷积核大小(可以给int,也可以给元组,此处给的int),步长(可以给int,也可以给元组,此处给的元组),填充大小。
forward()函数负责利用__init__()的属性,传入输入值并返回输出值。
结果:
- torch.Size([3, 5, 5])
- torch.Size([1, 3, 5, 5])
- ZiDingYi(
- (conv1): Conv2d(3, 6, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
- )
- tensor([[[[ 0.7182, 2.4224, 0.9817],
- [ 1.7839, 2.5734, 1.2106],
- [ 1.8459, 1.5189, 1.4425]],
- [[ 0.1448, -0.0430, 0.0554],
- [-0.7607, -0.3164, -1.1233],
- [ 0.9714, 0.2079, 1.0055]],
- [[-0.4258, -0.7102, -0.6917],
- [-0.3210, -0.1598, -0.8339],
- [-2.5572, -1.2985, -1.3247]],
- [[ 0.4376, -0.4646, -1.1285],
- [ 0.1640, 0.0108, 0.2103],
- [-0.5246, -0.5199, 0.1915]],
- [[ 1.2390, 1.2742, 1.0452],
- [ 0.5466, 0.6744, 1.8741],
- [-0.0987, -0.1915, -1.2585]],
- [[-0.7630, 0.5245, -0.3805],
- [-0.2918, 0.1074, -0.2167],
- [ 0.1180, 0.4456, 0.2908]]]], grad_fn=
) - Process finished with exit code 0
观察结果符合特征图大小计算公式:
输出高=((输入高+2×填充大小-卷积核大小)/步长大小)+1
加入图像数据集
- import torch
- import torchvision
- from torch import nn
- from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
- input = torch.tensor([[[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]],
- [[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]],
- [[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]]], dtype=torch.float32)
- print(input.shape)
- input = torch.reshape(input, (-1, 3, 5, 5))
- print(input.shape)
- class ZiDingYi(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(ZiDingYi, self).__init__()
- self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=6, kernel_size=3, stride=(1, 1), padding=0)
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.conv1(x)
- return x
- zidingyi = ZiDingYi()
- print(zidingyi)
- output = zidingyi(input)
- print(output)
- dataset_transforms = torchvision.transforms.Compose([torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
- torchvision.transforms.Normalize((0.4915, 0.4823, 0.4468),
- (0.2470, 0.2435, 0.2616))])
- train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root="./dataset", train=True, download=True, transform=dataset_transforms)
- train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, drop_last=False)
- for data in train_dataloader:
- imgs, labels = data
- output2 = zidingyi(imgs)
- print(imgs.shape)
- print(output2.shape)
结果:
- torch.Size([3, 5, 5])
- torch.Size([1, 3, 5, 5])
- ZiDingYi(
- (conv1): Conv2d(3, 6, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
- )
- tensor([[[[-0.3747, 1.3237, -0.4478],
- [ 0.7121, 1.4943, 0.4299],
- [ 0.4241, -0.6195, -0.0987]],
- [[-0.7136, -1.2816, -1.1319],
- [-1.2081, -1.2827, -0.4157],
- [-0.6310, -0.6770, -0.0811]],
- [[-0.8652, 0.0879, -0.4910],
- [-1.2453, 0.2760, 0.0546],
- [-0.8033, -0.5222, -0.3930]],
- [[-0.1145, 0.3100, -0.8689],
- [ 1.0125, 0.6360, -0.2982],
- [-0.6484, -1.0439, -0.3103]],
- [[-0.3132, -0.5373, -1.3907],
- [ 0.4211, -1.0112, -0.5164],
- [-1.5543, -0.2601, -0.3318]],
- [[-0.4129, -1.6505, -0.0648],
- [ 0.1058, 0.1305, 0.3511],
- [ 0.6991, -0.3641, 0.6684]]]], grad_fn=
) - Files already downloaded and verified
- torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
- torch.Size([64, 6, 30, 30])
- torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
- torch.Size([64, 6, 30, 30])
- torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
- torch.Size([64, 6, 30, 30])
- torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
- torch.Size([64, 6, 30, 30])
- ————————————后面省略——————————————
其中64为批处理大小,通道数由3转化为6,特征图从32高宽转为30高宽,符合计算公式。
- torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
- torch.Size([64, 6, 30, 30])
tensorboard查看卷积后的图片
- import torch
- import torchvision
- from torch import nn
- from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
- from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
- input = torch.tensor([[[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]],
- [[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]],
- [[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
- [1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
- [5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
- [2, 1, 0, 1, 1]]], dtype=torch.float32)
- print(input.shape)
- input = torch.reshape(input, (-1, 3, 5, 5))
- print(input.shape)
- class ZiDingYi(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(ZiDingYi, self).__init__()
- self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=6, kernel_size=3, stride=(1, 1), padding=0)
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.conv1(x)
- return x
- zidingyi = ZiDingYi()
- print(zidingyi)
- output = zidingyi(input)
- print(output)
- dataset_transforms = torchvision.transforms.Compose([torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
- torchvision.transforms.Normalize((0.4915, 0.4823, 0.4468),
- (0.2470, 0.2435, 0.2616))])
- train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root="./dataset", train=True, download=True, transform=dataset_transforms)
- train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, drop_last=False)
- writer = SummaryWriter("./logs")
- step = 0
- for data in train_dataloader:
- imgs, labels = data
- output2 = zidingyi(imgs)
- print(imgs.shape)
- # torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
- print(output2.shape)
- # torch.Size([64, 6, 30, 30])
- # 这个是显示不出来的,需要reshape一下,转化为3通道
- writer.add_images(tag="input", img_tensor=imgs, global_step=step)
- output_reshape = torch.reshape(output2, (-1, 3, 30, 30))
- writer.add_images(tag="output", img_tensor=output_reshape, global_step=step)
- step += 1
- writer.close()
进入Terminal终端
tensorboard --logdir=logs- (pytorch) D:\project\pytorch_learn>tensorboard --logdir=logs
- TensorFlow installation not found - running with reduced feature set.
- Serving TensorBoard on localhost; to expose to the network, use a proxy or pass --bind_all
- TensorBoard 2.10.1 at http://localhost:6006/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
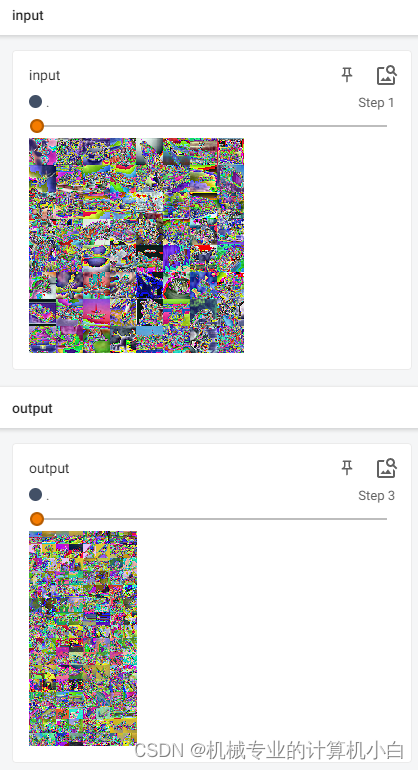
input是归一化后的图片,归一化后灰度值会有负数,显示的时候负数置0,变黑色。
output是卷积处理后的图片,每个卷积核可以视为一个滤波器。

其中同一行会有两个形状的图片,那是因为一个图片三个通道,经过卷积操作变成了6个通道,但是由于图片只能三个通道的时候显示出来(为了在tensorboard上观察),故进行了reshape操作:
output_reshape = torch.reshape(output2, (-1, 3, 30, 30))(64,6,30,30)reshape成了(128,3,30,30)
6通道变成了两个3通道,由两个图片显示出来。
-
相关阅读:
GUN介绍
已解决python -m pip install --upgrade pip命令升级报错
tomcat启动后,执行一个方法作为监听
Spring学习笔记6 Bean的实例化方式
2022年全球市场激光直接成像系统(LDI)总体规模、主要生产商、主要地区、产品和应用细分研究报告
SpringBoot3基础:最简项目示例
Linux Netlink通信机制详解
【谷粒商城 - k8s、devOps专栏】
python 参数内存地址相关
C陷阱与缺陷 第7章 可移植性缺陷 7.9 大小写转换
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/wzfafabga/article/details/127695823
