-
回溯算法题目
1.lc77 组合
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回范围 [1, n] 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
你可以按 任何顺序 返回答案。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combinations/
输入:n = 4, k = 2
输出:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]//组合问题 //用过的不能再用,通过startindex实现 //每个元素只能取一次,通过dfs(satrtindex+1)实现 class Solution { private: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> path; void dfs(int n,int k,int startindex) { if(path.size()==k) { res.push_back(path); return; } for(int i = startindex;i<=n;i++) { path.push_back(i); dfs(n,k,i+1); path.pop_back(); } } public: vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) { dfs(n,k,1); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
2.lc216 组合总和 III
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合,且满足下列条件:
只使用数字1到9
每个数字 最多使用一次
返回 所有可能的有效组合的列表 。该列表不能包含相同的组合两次,组合可以以任何顺序返回。输入: k = 3, n = 7
输出: [[1,2,4]]
解释:
1 + 2 + 4 = 7
没有其他符合的组合了。https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-iii/
//组合问题 //要用startindex+1确保每个数字只用一次 //通过一维的path和二维的res保存中间结果和最后结果 //判断中止的条件时path中元素的个数是否达到k个 //通过判断path中元素的sum值来决定是否将path传到res //dfs中需要传入k,n,startindex //疑问:需不需要一个变量记录path中已有变量的sum class Solution { private: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> path; void dfs(int k,int n,int startindex) { if(path.size()==k) //决定树的深度 { int sum = 0; for(int i = 0;i<k;i++) { sum+=path[i]; } if(sum==n) res.push_back(path); return; } for(int i = startindex;i<=9;i++) //决定树的宽度 { path.push_back(i); dfs(k,n,i+1); path.pop_back(); } } public: vector<vector<int>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) { dfs(k,n,1); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
3.lc17 电话号码的字母组合
//首先要解决数字和对应字母之间的映射关系:定义一个string类型的数组来实现 //树的宽度为该层数字对应的字符串的长度,高度为digits的长度。 //要传入dfs的是digits,phone_map,index //判断中止的条件是index为digits的长度 class Solution { private: vector<string> res; string path; const string phone_map[10]={"","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"}; void dfs(string digits,int index) { if(index==digits.size()) { res.push_back(path); return; } for(int i = 0;i<phone_map[digits[index]-'0'].size();i++) { path.push_back(phone_map[digits[index]-'0'][i]); dfs(digits,index+1); path.pop_back(); } } public: vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) { if(digits.size()==0) return res; dfs(digits,0); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
4.lc39 组合总和
//依旧是组合问题,源数组无重复,但是可以重复选取 //和之前的"组合总和 III"主要区别在于源数组中的数能否重复的选取 //这个区别的话通过dfs中startindex不加1来实现 //这样的话中止条件需要通过path数组中已有元素的和是否超过target来判断 //为了实现实现上面的判断就需要在dfs中传入参数时,传入一个sum表示当前path的元素的和 //树的宽度为当前startindex下可以选取的元素数量 class Solution { private: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> path; void dfs(vector<int>& candidates,int target, int sum, int starindex) { if(sum>target) return; if(sum==target) { res.push_back(path); return; } for(int i = starindex;i<candidates.size();i++) { sum+=candidates[i]; path.push_back(candidates[i]); dfs(candidates,target,sum,i); sum-=candidates[i]; path.pop_back(); } } public: vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) { // dfs(candidates,target,sum,starindex); dfs(candidates,target,0,0); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
5.lc40 组合总和 II
//这个跟上一个lc39 组合总和很像,区别在于本题源数组可以有重复,而对于数组中每个元素只可以取一次
//为了不重复还是需要用到startindex,到这里发现组合问题都需要startindex哈,到后面的排列问题就不需要了
//由于源数组中有重复元素,即使用了startindex依旧需要去重,这时如果考虑最后去重会花很多时间,可能导致超时吧
//于是乎,可以先对源数组排一下序,然后用一个used记录元素是否用过
//如果当前元素和前一个元素相等,而且used前一个元素时true代表什么呢?代表这俩在一个树枝上
//如果当前元素和前一个元素相等,而前一个元素used为false代表什么呢?代表这俩在同一层上
// 1 1 1 2 4 target=5 同一层上的情况直接跳过,因为它能贡献的情况,前面那个和他相同的值也能提供,并且提供更多
//树的宽度是startindex右边的数的大小,高度通过不限制但是sum超过target剪枝
//写代码时注意先排序,另外去掉同层的情况要写在循环中,class Solution { vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> path; void dfs(vector<int>& candidates,int target,vector<bool>& used,int sum, int startindex) { if(sum>target) return; if(sum==target) { res.push_back(path); return; } for(int i = startindex;i<candidates.size();i++) { if(i>0&&candidates[i-1]==candidates[i]&&used[i-1]==false) continue; sum+=candidates[i]; path.push_back(candidates[i]); used[i] = true; dfs(candidates,target,used,sum,i+1); sum-=candidates[i]; path.pop_back(); used[i] = false; } } public: vector<vector<int>> combinationSum2(vector<int>& candidates, int target) { sort(candidates.begin(),candidates.end()); vector<bool> used(candidates.size(), false); // dfs(candidates,target,sum,startindex) dfs(candidates,target,used,0,0); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
6.lc131 分割回文串
//切割问题
//可切割的位置就是每个字符之后
//树的宽为startindex右边数量,深度不定
//终止条件根据startindex是否到最后一个元素后面确定
//一个很大的问题时如何表示分割线//注:substr第一个参数是起始位置,第二个参数是长度
class Solution { private: vector<vector<string>> res; vector<string> path; bool ishui(string s,int start,int end) { bool flag = true; for(int i = start,j = end;i<j;i++,j--) { if(s[i]!=s[j]) flag = false; } return flag; } void dfs(string s,int startindex) { if(startindex==s.size()) { res.push_back(path); return; } for(int i = startindex;i<s.size();i++) { if(ishui(s,startindex,i)) { string str = s.substr(startindex,i-startindex+1); path.push_back(str); } else continue; dfs(s,i+1); path.pop_back(); } } public: vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) { // dfs(s,startindex) dfs(s,0); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
7.lc3 复原 IP 地址

//复杂一点的分割问题
//在分割问题的基础上,区别在于要加dian
//对于加dian,要求每一段范围为0-255,且不含前导0
//要确保加三个点分成四段,还是通过startindex当作点,增加一个变量记录当前的点数
//树的宽度为startindex右边的数量,深度不定
//中止条件:indexnum等于3class Solution { private: vector<string> res; void dfs(string s, int startindex,int indexnum) { if(indexnum==3) { if(isValid(s,startindex,s.size()-1)) { res.push_back(s); } return ; } for(int i = startindex;i<s.size()-1;i++) { if(isValid(s,startindex,i)) { s.insert(s.begin()+i+1,'.'); indexnum++; dfs(s,i+2,indexnum); indexnum--; s.erase(s.begin()+i+1); } else break; } } bool isValid(string s,int start,int end) { if(start>end) return false; if (s[start] == '0' && start != end) { // 0开头的数字不合法 return false; } int num = 0; for(int i=start;i<=end;i++) { if(s[i]-'0'>9 || s[i]-'0'< 0) return false; num= num*10 + (s[i]-'0'); if(num>255) return false; } return true; } public: vector<string> restoreIpAddresses(string s) { // dfs(s,startindex,indexsum); if (s.size() < 4 || s.size() > 12) return res; dfs(s,0,0); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
8.lc78 子集
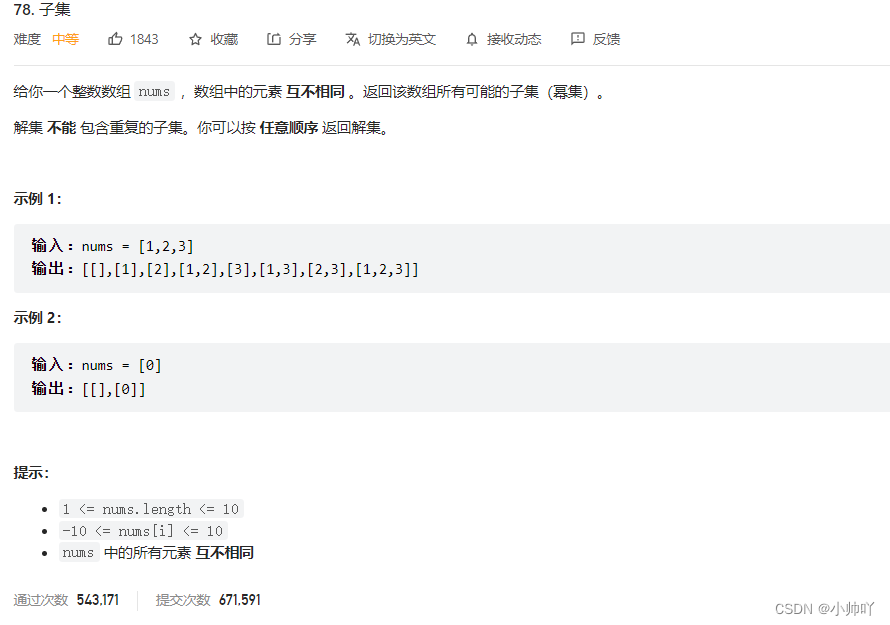
//子集问题
//在组合问题基础上,需要将每个节点的结果保存下来
//回顾一下组合问题用startindex确保不重复,dfs的时候加1class Solution { private: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> path; void dfs(vector<int> nums,int startindex) { res.push_back(path); if(startindex==nums.size()) { return; } for(int i = startindex;i<nums.size();i++) { path.push_back(nums[i]); dfs(nums,i+1); path.pop_back(); } } public: vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) { // dfs(nums,startindex); dfs(nums,0); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
9.lc90 子集 II
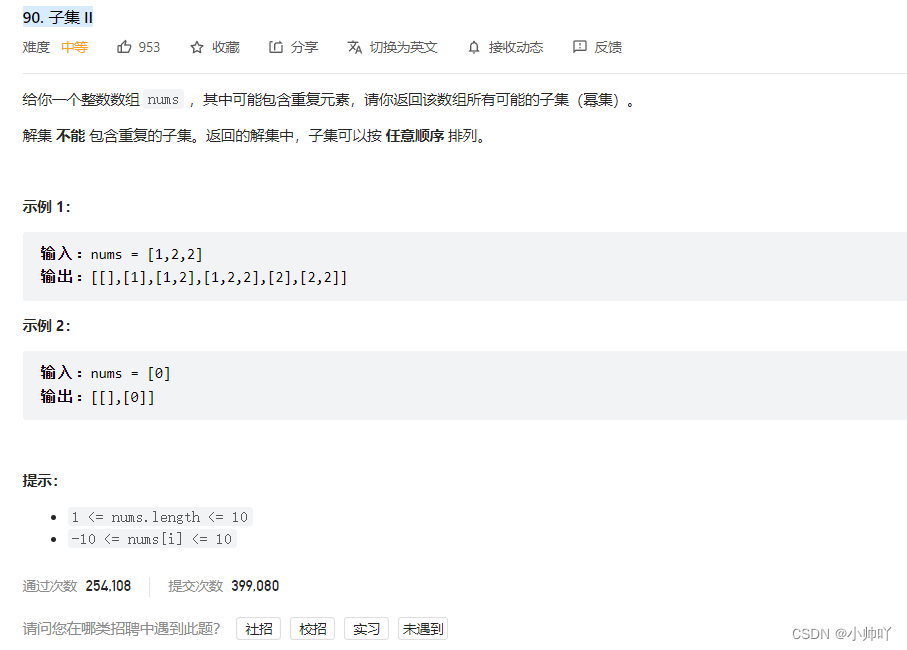
//还是子集问题,区别在于这次源数组中可以有重复元素,需要加入used数组,排序方式对结果去重class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> path; void dfs(vector<int>& nums,vector<bool>& used,int startindex) { res.push_back(path); if(startindex==nums.size()) return; for(int i = startindex;i<nums.size();i++) { if(i>0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1]&&used[i-1]==false) continue; path.push_back(nums[i]); used[i]=true; dfs(nums,used,i+1); path.pop_back(); used[i] = false; } } vector<vector<int>> subsetsWithDup(vector<int>& nums) { vector<bool> used(nums.size(),false); sort(nums.begin(),nums.end()); // dfs(nums,used,startindex); dfs(nums,used,0); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
10.lc491 递增子序列

//和前面的子集问题十分类似
//要注意的是不能对数组进行排序,那么怎么实现去重呢,方法就是用一个哈希表存同一层的树结点
//当判断是否要往一个path中加数据时,要看当前值和path中最后一个数的大小的比较以及看同层是否出现过该数值class Solution { private: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> path; void dfs(vector<int> nums,int startindex) { if(path.size()>1) res.push_back(path); if(startindex==nums.size()) return ; unordered_set<int> u; //注意不要定义在循环中 for(int i = startindex;i<nums.size();i++) { if((!path.empty()&&nums[i]<path.back())||u.find(nums[i])!=u.end()) continue; else { u.insert(nums[i]); path.push_back(nums[i]); dfs(nums,i+1); path.pop_back(); } } } public: vector<vector<int>> findSubsequences(vector<int>& nums) { // dfs(nums,startindex); dfs(nums,0); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
11.lc46 全排列

//排列问题
//不用startindex了
//那么如何去重呢,就需要用到used数组了我想,之前组合问题中对于源数组中有重复元素时用到used数组进行去重class Solution { private: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> path; void dfs(vector<int> nums,vector<bool> used,int u) { if(u==nums.size()) { res.push_back(path); return ; } for(int i = 0;i<nums.size();i++) { if(used[i]==false) { path.push_back(nums[i]); used[i] = true; dfs(nums,used,u+1); used[i] = false; path.pop_back(); } } } public: vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) { vector<bool> used(nums.size(),false); // dfs(nums,used,u); dfs(nums,used,0); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
12.lc47 全排列 II
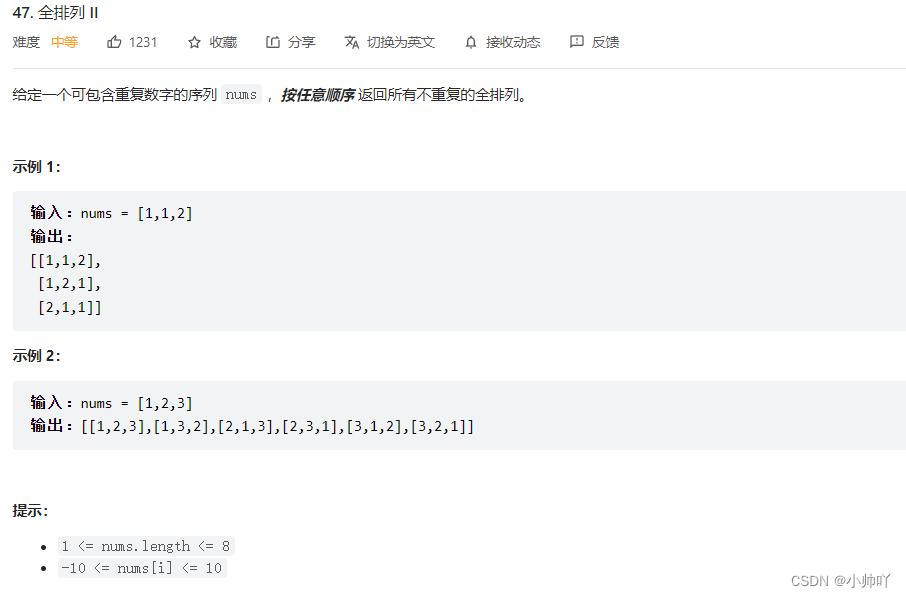
//全排列问题进阶,与上题不同在于源数组中有重复的元素
//如果还和上次那样的代码会出现什么问题呢,会出现重复//怎么解决呢?初步想法是和组合问题中这种情况类似,先排序然后针对同层的元素用used数组判断是否要跳过
class Solution { private: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> path; void dfs(vector<int> nums,vector<bool> used,int u) { if(u==nums.size()) { res.push_back(path); return; } for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++) { if(i>0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1]&&used[i-1]==false) continue; if(used[i]==false) { path.push_back(nums[i]); used[i] = true; dfs(nums,used,u+1); used[i] = false; path.pop_back(); } } } public: vector<vector<int>> permuteUnique(vector<int>& nums) { vector<bool> used(nums.size(),false); sort(nums.begin(),nums.end()); // dfs(nums,used,u); dfs(nums,used,0); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
13.lc51 N 皇后

//主要是dg和udg数组的运用,dg和udg代表正负斜线的截距
//dg[u+i]即y = -x + b
//udg[u-i+n]即y = x+b 之所以加n是因为不然会出现负数的下标,这样都加n也可以一一对应上
//--------->
//|
//|
//|
//>class Solution { private: bool col[20],dg[20],udg[20]; vector<vector<string>> res; vector<string> path; void dfs(int u,int n) { if(u==n) { res.push_back(path); return; } for(int i = 0;i< n;i++) { if(!col[i]&&!dg[u+i]&&!udg[u-i+n]) { string s; for(int j = 0;j<n;j++) { if(j==i) s+="Q"; else s+="."; } path.push_back(s); col[i]=true; dg[u+i] = true; udg[u-i+n] =true; dfs(u+1,n); path.pop_back(); col[i] = false; dg[u+i] = false; udg[u-i+n] = false; } else{ continue; } } } public: vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) { dfs(0,n); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
14.lc112 路径总和
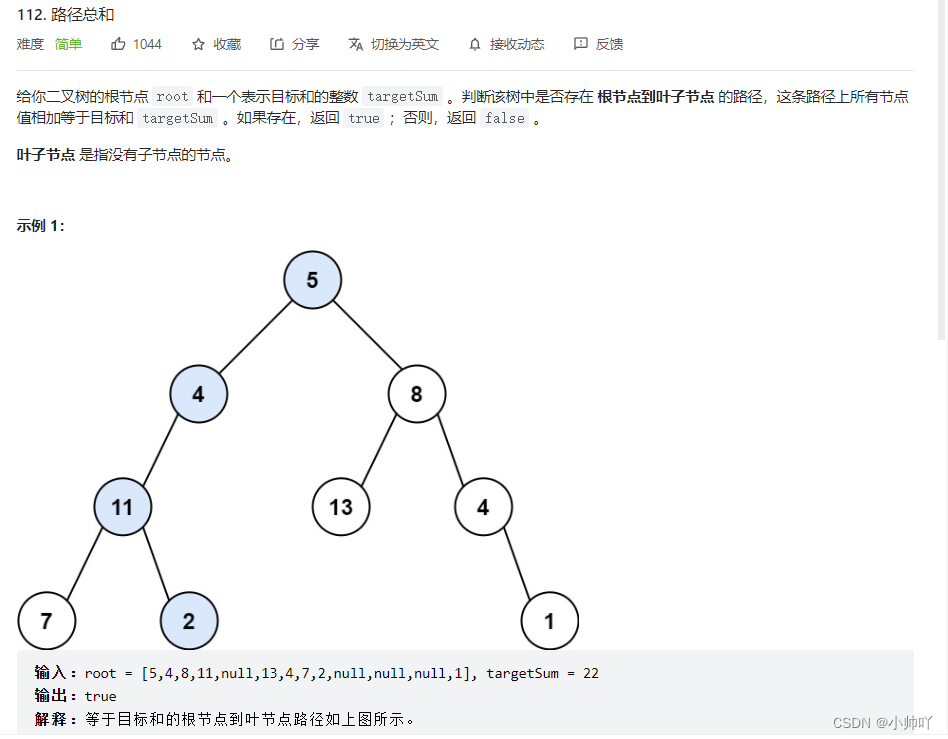
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { int sum = 0; bool flag = false; void dfs(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) { sum += root->val; if(root->left!=nullptr) hasPathSum(root->left,targetSum); if(root->right!=nullptr) hasPathSum(root->right,targetSum); if(root->left==nullptr&&root->right==nullptr) { if(sum==targetSum) flag = true; } sum-=root->val; } public: bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) { if(root==nullptr) return false; dfs(root,targetSum); return flag; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
15.lc113 路径总和 II
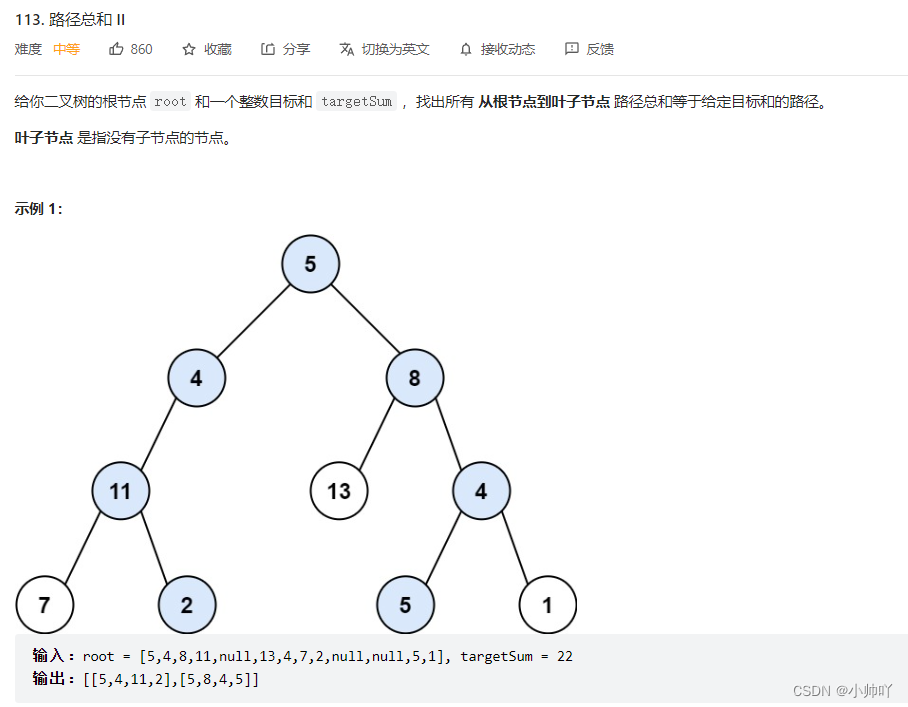
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ //和112.路径总和的区别在于要存一下路径 //应该也不难,试一试 class Solution { private: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> path; int sum = 0; void dfs(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) { sum += root->val; path.push_back(root->val); if(root->left!=nullptr) dfs(root->left,targetSum); if(root->right!=nullptr) dfs(root->right,targetSum); if(root->left==nullptr&&root->right==nullptr) { if(sum==targetSum) { res.push_back(path); } } sum-=root->val; path.pop_back(); } public: vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) { if(root==nullptr) return res; dfs(root,targetSum); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
16.lc22 括号生成
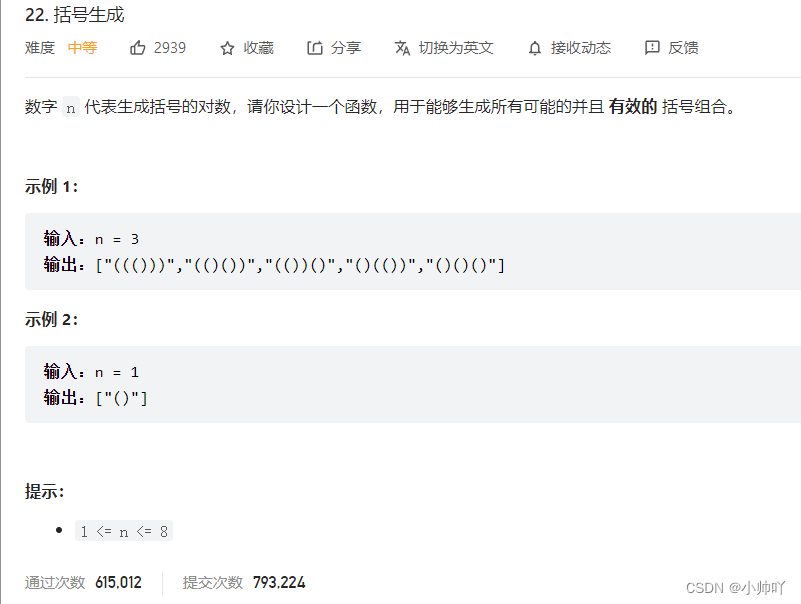
//dfs
//构建一个树形结构,树的宽度为2^n,树的深度为n*2
//剪枝:在生成结果过程中对于left>n(或者right>n的)或者right>left的要进行returnclass Solution { private: vector<string> res; int u = 0; string path; void dfs(int n,int u,int left,int right) { if(left>n||right>left) return; if(u==2*n) { res.push_back(path); return; } path.push_back('('); dfs(n,u+1,left+1,right); path.pop_back(); path.push_back(')'); dfs(n,u+1,left,right+1); path.pop_back(); } public: vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) { //dfs(n,u,right,left) dfs(n,0,0,0); return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
17.lc200 岛屿数量

//用一个bool数组记录是否遍历过,遍历整个数组 //类似对连着的染一下色,遍历的时候没到一个岛屿且没染色的话说明是一个独立的岛屿,最后得到结果 class Solution { public: bool used[310][310]; void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid,int i,int j) { int m = grid.size(); int n = grid[0].size(); used[i][j] = true; int dx[4] = {0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4] = {1,-1,0,0}; for(int k=0;k<4;k++) { int x = i+dx[k], y = j+dy[k]; if(x>=0&&x<m&&y>=0&&y<n&&grid[x][y]=='1'&&used[x][y]==false) { dfs(grid,x,y); } } return; } int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) { int res = 0; int m = grid.size(); int n = grid[0].size(); for(int i = 0;i<m;i++) { for(int j = 0;j<n;j++) { if(grid[i][j]=='1'&&used[i][j]==false) { res++; dfs(grid,i,j); } else continue; } } return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
18.lc79 单词搜索

//需要从每个位置开始遍历,该位置的字符不等与word[0]跳过 //需要用一个bool数组记录每个位置是否用过 //需要判断和word是否相同 //用一个u记录当前层数,看与对应的word的索引下的字符是否相同 class Solution { public: bool flag = false; void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board,string word,int u,bool used[7][7],int i,int j) { if(u==word.size()) flag=true; int m = board.size(); int n = board[0].size(); int dx[4] = {0,0,1,-1}, dy[4] = {1,-1,0,0,}; for(int k = 0;k<4;k++) { int x =i + dx[k],y = j+dy[k]; if(x>=0&&x<m&&y>=0&&y<n) { if(board[x][y]==word[u]&&used[x][y]==false) { used[x][y] = true; dfs(board,word,u+1,used,x,y); used[x][y] = false; } } } } bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) { int m = board.size(); int n = board[0].size(); for(int i = 0;i<m;i++) { for(int j =0;j<n;j++) { if(board[i][j]==word[0]) { bool used[7][7] = {false}; used[i][j] = true; dfs(board,word,1,used,i,j); // dfs(board,word,u); } } } return flag; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
-
相关阅读:
vue3 表单搜索内容回显到地址栏
不懂“数据服务”,聊什么“数据中台”
ES集群搭建及Kibana安装
一键免密登录云平台!ZStack Cloud 4.5.0等你来解锁……
手术麻醉信息系统源码 医院麻醉监护的功能覆盖整个手术与麻醉的全过程
【centos7中使用docker安装KLEE】
touchGFX综合学习十四、基于cubeMX、正点原子H750开发版、RGB4.3寸屏移植touchGFX完整教程+工程(二)
86.(cesium篇)cesium叠加面接收阴影效果(gltf模型)
毫米波雷达在检测、分割、深度估计等多个方向的近期工作及简要介绍
Matlab中clear,close all,clc功能详细说明
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_47997583/article/details/127693362
