-
链表常见面试题分析
目录
接下来我们会从易到难,逐步讲解有关链表的常见面试,部分题目来自Leetcode和牛客
一、移除链表元素

LeetoCode链接: 203. 移除链表元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- class Solution {
- public:
- ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val)
- {
- ListNode* prev = nullptr;
- ListNode* current = head;
- while (current != nullptr)
- {
- if (current->val == val) {
- if(current == head)//头删
- {
- head = head->next;
- delete current;
- current = head;
- }
- else//普通删除
- {
- prev->next = current->next;
- delete current;
- current = prev->next;
- }
- }
- else {
- prev = current;
- current = current->next;
- }
- }
- return head;
- }
- };
二、反转链表

LeetCode链接: 206. 反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路一:
- //头插法
- class Solution {
- public:
- ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
- {
- //if(head == nullptr) return nullptr;
- ListNode* newHead = nullptr, *current = head;
- while(current != nullptr)
- {
- ListNode* next = current->next;
- current->next = newHead;
- newHead = current;
- current = next;
- }
- return newHead;
- }
- };
思路二:
- //三指针
- class Solution {
- public:
- ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
- if(head == nullptr) return nullptr;
- ListNode* n1 = nullptr, *n2 = head, *n3 = head->next;
- while(n2 != nullptr)
- {
- n2->next = n1;
- n1 = n2;
- n2 = n3;
- if(n3 != nullptr) n3 = n3->next;
- }
- return n1;
- }
- };
思路三:
- //递归
- class Solution {
- public:
- ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
- {
- if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
- ListNode* newHead = reverseList(head->next);
- head->next->next = head;
- head->next = nullptr;
- return newHead;
- }
- };
三、链表的中间结点

LeetCode链接: 876. 链表的中间结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
- {
- struct ListNode* slow = head,*fast = head;
- while(fast != NULL&& fast->next != NULL)
- {
- slow = slow->next;
- fast = fast->next->next;
- }
- return slow;
- }
四、链表中倒数第k个结点

牛客网链接: 链表中倒数第k个结点_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
- struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
- if(pListHead == NULL || k == 0) return NULL;
- struct ListNode* slow = pListHead , *fast = pListHead;
- for(int i = 0;i < k ;++i){
- if(fast == NULL) return NULL;
- fast = fast->next;
- }
- while(fast != NULL){
- fast = fast->next;
- slow = slow->next;
- }
- return slow;
- }
五、合并两个有序链表

LeetCode链接: 21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
- struct ListNode* head,*tail;
- head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
- tail->next = NULL;
- while (list1 != NULL && list2 != NULL) {
- if (list1->val < list2->val) {
- tail->next = list1;
- list1 = list1->next;
- }
- else {//list1->val >= list2->val
- tail->next = list2;
- list2 = list2->next;
- }
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- if (list1 != NULL)
- tail->next = list1;
- if (list2 != NULL)
- tail->next = list2;
- struct ListNode* del = head;
- head = head->next;
- free(del);
- return head;
- }
六、链表分割

牛客网链接: 链表分割_牛客题霸_牛客网
- class Partition {
- public:
- ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
- struct ListNode* less_head,*less_tail;
- less_head = less_tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
- less_tail->next = NULL;
- struct ListNode* greater_head,* greater_tail;
- greater_head = greater_tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode*));
- greater_tail->next = NULL;
- struct ListNode* current = pHead;
- while(current != NULL){
- if(current->val < x){
- less_tail->next = current;
- less_tail = less_tail->next;
- }
- else{
- greater_tail->next = current;
- greater_tail = greater_tail->next;
- }
- current = current->next;
- }
- less_tail->next = greater_head->next;
- greater_tail->next = NULL;
- ListNode* head = less_head->next;
- free(less_head);
- free(greater_head);
- return head;
- }
- };
七、链表的回文结构

牛客网链接: 链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网
- class PalindromeList {
- public:
- struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
- struct ListNode* slow = head,*fast = head;
- while(fast && fast->next){
- slow = slow->next;
- fast = fast->next->next;
- }
- return slow;
- }
- struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
- struct ListNode* cur = head;
- struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
- while(cur != NULL){
- struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
- cur->next = newhead;
- newhead = cur;
- cur = next;
- }
- return newhead;
- }
- bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
- struct ListNode* mid = middleNode(A);
- struct ListNode* newhead = reverseList(mid);
- while(A && newhead){
- if(A->val != newhead->val){
- return false;
- }
- A = A->next;
- newhead = newhead->next;
- }
- return true;
- }
- };
八、相交链表
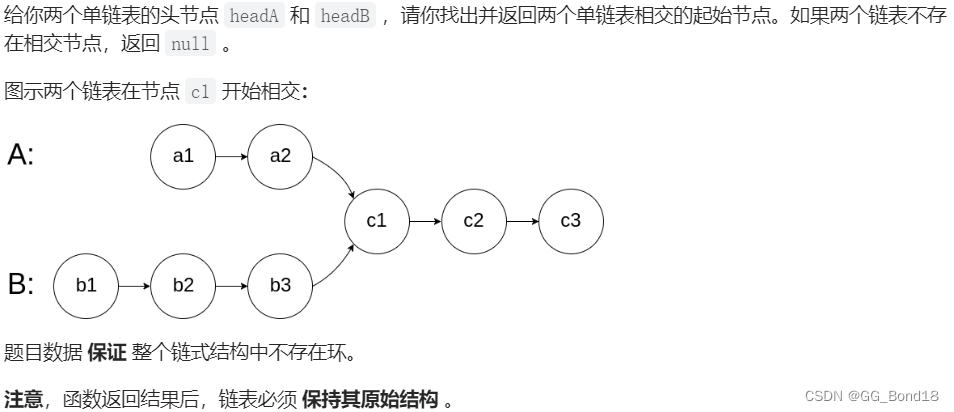
LeetCode链接: 160. 相交链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
- int lenth_A = 0,lenth_B = 0;
- struct ListNode* current_A = headA;
- struct ListNode* current_B = headB;
- while(current_A->next != NULL){
- ++lenth_A;
- current_A = current_A->next;
- }
- while(current_B->next != NULL){
- ++lenth_B;
- current_B = current_B->next;
- }
- if(current_A != current_B) return NULL;//尾结点不同,肯定不为相交链表
- current_A = headA;
- current_B = headB;
- if(lenth_A > lenth_B){
- for(int i = 0;i < lenth_A - lenth_B; ++i){
- current_A = current_A->next;
- }
- }
- else{//lenth_A <= lenth_B
- for(int i = 0;i < lenth_B - lenth_A; ++i){
- current_B = current_B->next;
- }
- }
- while(current_A != current_B){//此时肯定为相交链表
- current_A = current_A->next;
- current_B = current_B->next;
- }
- return current_A;
- }
九、复制带随机指针的链表

LeetCode链接: 138. 复制带随机指针的链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- class Solution {
- public:
- Node* copyRandomList(Node* head)
- {
- Node* current = head;
- //将原链表结点全部拷贝,并将拷贝结点插入原链表其对应的结点的后一个位置
- while(current != nullptr) {
- Node* copy = new Node(current->val);
- copy->next = current->next;
- current->next = copy;
- current = copy->next;
- }
- //copy结点random指针 指向 其对应结点的random指针指向的结点的后一个
- //若对应结点的random指针指向NULL,copy结点的random指针也指向NULL
- current = head;
- while(current != nullptr) {
- Node* copy = current->next;
- if(current->random == nullptr) copy->random = nullptr;
- else copy->random = current->random->next;
- current = copy->next;
- }
- //将插入原链表的所有copy结点,全部解除下来并逐个尾插为一个新的链表,将原链表还原
- current = head;
- Node* newHead = nullptr;
- while(current != nullptr)
- {
- if(newHead == nullptr) newHead = current->next;
- Node* copy = current->next;//根据逻辑,只要current不为空,copy必不为空
- Node* next = copy->next;//copy不为空并不能保证next不为空
- if(next != nullptr) copy->next = next->next;
- current->next = next;
- current = next;
- }
- return newHead;
- }
- };
十、链表的带环问题
问题1
给定一个链表,如何判断链表中是否有环呢?141. 环形链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路: 使用快慢指针,即慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,两个指针从链表起始位置开始运行,若链表带环则一定会在环中相遇,否则快指针率先走到链表的末尾
- bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
- if(head == NULL) return false;
- struct ListNode *slow = head,*fast = head;
- while(fast !=NULL && fast->next != NULL){
- slow = slow->next;
- fast = fast->next->next;
- if(slow == fast) return true;
- }
- return false;
- }

问题2
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL
142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)方法一:
在做这道题之前我们必须了解一个定理:
让一个指针从链表起始位置开始遍历链表,同时让一个指针从判环时相遇点的位置开始绕环运行,两个指针都是每次均走一步,最终肯定会在入口点的位置相遇。但是为什么呢?

接下来,理论上已经解决,用代码将其实现即可。
- struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
- struct ListNode* fast = head,*slow = head;
- while(fast && fast->next){
- slow = slow->next;
- fast = fast->next->next;
- if(slow == fast){
- struct ListNode* meet = fast;
- while(meet != head){
- meet = meet->next;
- head = head->next;
- }
- return meet;
- }
- }
- return NULL;
- }
方法二:
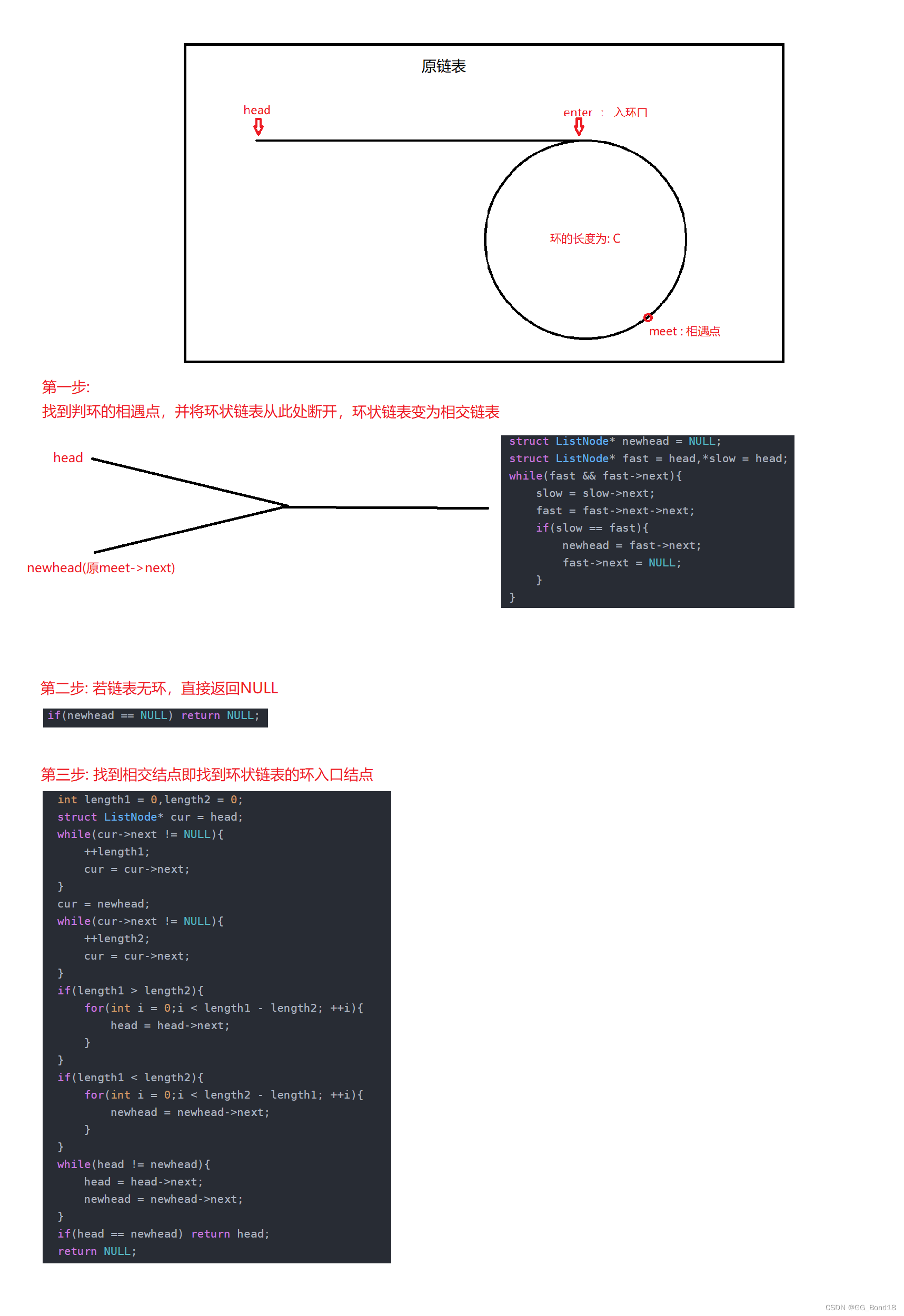
- struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
- struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
- struct ListNode* fast = head,*slow = head;
- while(fast && fast->next){
- slow = slow->next;
- fast = fast->next->next;
- if(slow == fast){
- newhead = fast->next;
- fast->next = NULL;
- }
- }
- if(newhead == NULL) return NULL;
- int length1 = 0,length2 = 0;
- struct ListNode* cur = head;
- while(cur->next != NULL){
- ++length1;
- cur = cur->next;
- }
- cur = newhead;
- while(cur->next != NULL){
- ++length2;
- cur = cur->next;
- }
- if(length1 > length2){
- for(int i = 0;i < length1 - length2; ++i){
- head = head->next;
- }
- }
- if(length1 < length2){
- for(int i = 0;i < length2 - length1; ++i){
- newhead = newhead->next;
- }
- }
- while(head != newhead){
- head = head->next;
- newhead = newhead->next;
- }
- if(head == newhead) return head;
- return NULL;
- }
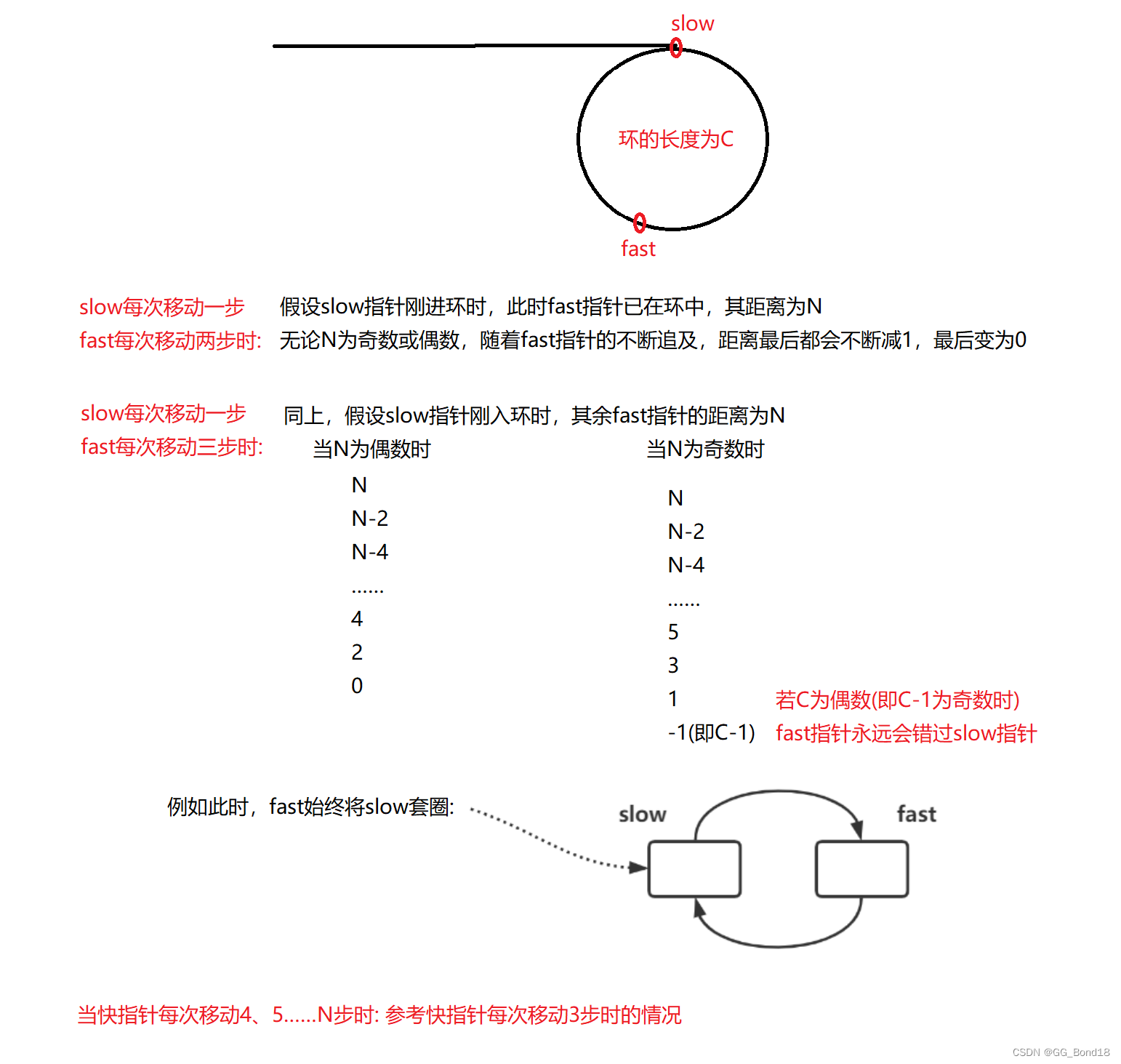
扩展问题1:
为什么快指针每次走两步,慢指针走一步可以?
若链表带环,两个指针最后都会进入环,快指针先进环,慢指针后进环。当慢指针刚进环时,可能就和快指针相遇了,最差情况下两个指针之间的距离刚好就是环的长度 - 1。
此时,两个指针每移动一次,之间的距离就缩小一步,不会出现每次刚好是套圈的情况,因此:在满指针走到一圈之前,快指针肯定是可以追上慢指针的,即相遇
扩展问题2:
快指针一次走3步,走4步,...n步行吗? 不行
十一、顺序表和链表的区别
1.存储空间:
顺序表存储空间连续。支持随机访问O(1)
链表的逻辑结构上连续,但物理结构上不一定连续。不支持随机访问O(n) (使用二分查找等算法时,时间复杂度过大)2.插入与删除操作:
顺序表可能需要移动元素,时间复杂度为O(n)。插入时可能需要扩容,可能存在空间浪费(有一定性能消耗)
链表只需改动指针指向即可。无容量概念,不会浪费空间3.应用场景:
顺序表适用于元素高效存储、频繁访问
链表适用于任意位置插入删除和删除频繁4.缓存利用率:
顺序表CPU高速缓存命中率高
链表CPU高速缓存命中率低CPU缓存命中率

主存、高速缓存和寄存器(带电存储)
磁盘、远程二级存储(不带电存储)
CPU缓存离CPU核心更近,由于电子信号传输是需要时间的,所以离CPU核心越近,缓存的读写速度就越快。但 CPU 的空间很狭小,离 CPU 越近缓存大小受到的限制也越大。所以,综合硬件布局、性能等因素,CPU缓存通常分为大小不等的三级缓存:
L1,L2,L3。级别越小越接近 CPU,所以速度也更快,同时也代表着容量越小。L1 是最接近CPU的, 它容量最小(例如:
32K),速度最快,L1缓存每个核上其实有两个L1缓存, 一个用于存数据的 L1d Cache(Data Cache),一个用于存指令的 L1i Cache(Instruction Cache)。L2缓存更大一些(例如:
256K),速度要慢一些, 一般情况下每个核上都有一个独立的L2缓存;L3缓存是三级缓存中最大的一级,同时也是最慢的一级, 在同一个 CPU 插槽之间的核共享一个 L3 缓存
数据从内存向上,L3->L2->L1,最后到寄存器进行CPU计算。CPU在缓存中找到有用的数据被称为命中率,当缓存中没有CPU所需的数据时(这时称为未命中)CPU才访问内存将数据加载到缓存。CPU并不会一个字节一个字节的加载,效率太低。而是一块一块加载,对于这样的一块一块的数据单位,术语叫“Cache Line”。目前主流的cache line是64字节,也有32和128的。
一般访问某个数据时,先查看其地址是否在缓存中,在就访问,不在则需加载后访问。(一般来说第一次访问都不命中)
缓存命中率 = 从缓存中读取的次数 / 总读取次数
顺序表的存储是一块连续的内存,CPU一块一块地进行数据加载,当访问arr[0]时,arr[1]大概率已经加载到CPU中,减少了加载的时间。
链表空间不连续,每次访问下一个结点大概率需要重新加载。
所以链表缓存命中率低于顺序表,访问速度也低于顺序表
十二、K个一组翻转链表
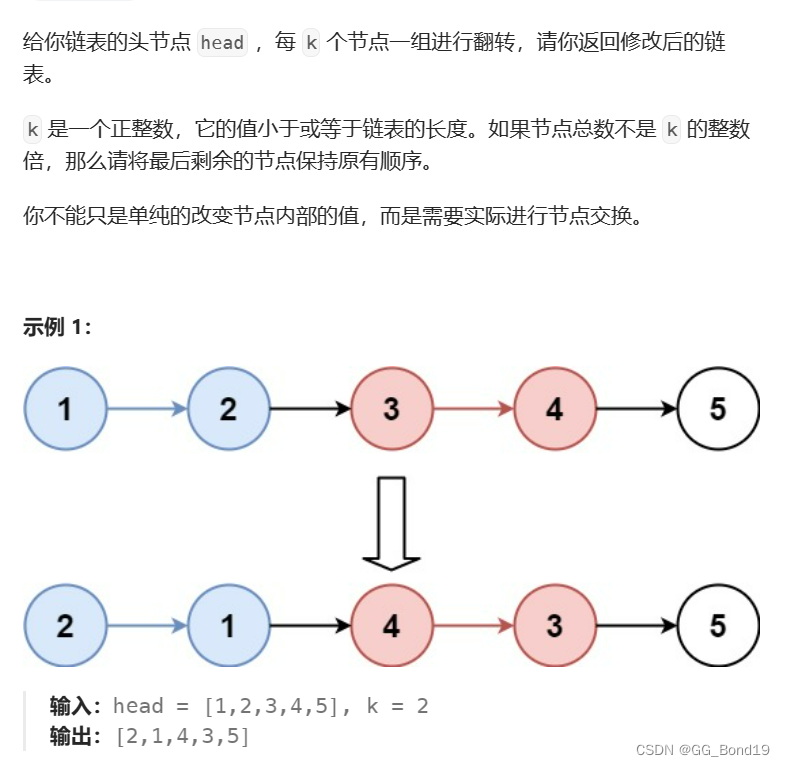
LeetCode链接:25. K 个一组翻转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- /**
- * Definition for singly-linked list.
- * struct ListNode {
- * int val;
- * ListNode *next;
- * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
- * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
- * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
- * };
- */
- class Solution {
- public:
- ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k)
- {
- //计算出需要逆转几次
- int number = 0;
- for(ListNode* current = head; current != nullptr; current = current->next) ++number;
- number /= k;
- //每次反转k个一组的链表
- ListNode* newHead = new ListNode(-1);
- ListNode* tail = newHead;
- ListNode* current = head;
- for(int i = 0; i < number; ++i)
- {
- ListNode* tmp = current;
- for(int j = 0; j < k; ++j)
- {
- ListNode* next = current->next;
- current->next = tail->next;
- tail->next = current;
- current = next;
- }
- tail = tmp;
- }
- //将后续不需反转的结点链接在一起
- tail->next = current;
- current = newHead->next;
- delete newHead;
- return current;
- }
- };
-
相关阅读:
怎么批量保存网页图片-快速批量保存网页的方法
2012年下半年 系统架构设计师 下午试卷 II
Day14——二叉树的前中后序遍历(迭代&&递归)
【算法作业记录】
Debian12安装 Docker
LLaMA 3 源码解读-大语言模型5
网络安全笔记-WebShell与文件上传
5G面试题目和答案,计算机面试
OMS1674 OMS1654 OMS1644 全新原装马可尼SDH设备
sqllab第二十六关通关笔记
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/GG_Bruse/article/details/127625185
