-
说说前端经常考的手写题
实现数组扁平化flat方法
题目描述: 实现一个方法使多维数组变成一维数组
let ary = [1, [2, [3, [4, 5]]], 6]; let str = JSON.stringify(ary);- 1
- 2
第0种处理:直接的调用
arr_flat = arr.flat(Infinity);- 1
第一种处理
ary = str.replace(/(\[|\])/g, '').split(',');- 1
第二种处理
str = str.replace(/(\[\]))/g, ''); str = '[' + str + ']'; ary = JSON.parse(str);- 1
- 2
- 3
第三种处理:递归处理
let result = []; let fn = function(ary) { for(let i = 0; i < ary.length; i++) }{ let item = ary[i]; if (Array.isArray(ary[i])){ fn(item); } else { result.push(item); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
第四种处理:用 reduce 实现数组的 flat 方法
function flatten(ary) { return ary.reduce((pre, cur) => { return pre.concat(Array.isArray(cur) ? flatten(cur) : cur); }, []); } let ary = [1, 2, [3, 4], [5, [6, 7]]] console.log(flatten(ary))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
第五种处理:能用迭代的思路去实现
function flatten(arr) { if (!arr.length) return; while (arr.some((item) => Array.isArray(item))) { arr = [].concat(...arr); } return arr; } // console.log(flatten([1, 2, [1, [2, 3, [4, 5, [6]]]]]));- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
第六种处理:扩展运算符
while (ary.some(Array.isArray)) { ary = [].concat(...ary); }- 1
- 2
- 3
类数组转化为数组
类数组是具有length属性,但不具有数组原型上的方法。常见的类数组有arguments、DOM操作方法返回的结果。
方法一:Array.from
Array.from(document.querySelectorAll('div'))- 1
- 2
方法二:Array.prototype.slice.call()
Array.prototype.slice.call(document.querySelectorAll('div'))- 1
- 2
方法三:扩展运算符
[...document.querySelectorAll('div')]- 1
- 2
方法四:利用concat
Array.prototype.concat.apply([], document.querySelectorAll('div'));- 1
- 2
手写 Promise
const PENDING = "pending"; const RESOLVED = "resolved"; const REJECTED = "rejected"; function MyPromise(fn) { // 保存初始化状态 var self = this; // 初始化状态 this.state = PENDING; // 用于保存 resolve 或者 rejected 传入的值 this.value = null; // 用于保存 resolve 的回调函数 this.resolvedCallbacks = []; // 用于保存 reject 的回调函数 this.rejectedCallbacks = []; // 状态转变为 resolved 方法 function resolve(value) { // 判断传入元素是否为 Promise 值,如果是,则状态改变必须等待前一个状态改变后再进行改变 if (value instanceof MyPromise) { return value.then(resolve, reject); } // 保证代码的执行顺序为本轮事件循环的末尾 setTimeout(() => { // 只有状态为 pending 时才能转变, if (self.state === PENDING) { // 修改状态 self.state = RESOLVED; // 设置传入的值 self.value = value; // 执行回调函数 self.resolvedCallbacks.forEach(callback => { callback(value); }); } }, 0); } // 状态转变为 rejected 方法 function reject(value) { // 保证代码的执行顺序为本轮事件循环的末尾 setTimeout(() => { // 只有状态为 pending 时才能转变 if (self.state === PENDING) { // 修改状态 self.state = REJECTED; // 设置传入的值 self.value = value; // 执行回调函数 self.rejectedCallbacks.forEach(callback => { callback(value); }); } }, 0); } // 将两个方法传入函数执行 try { fn(resolve, reject); } catch (e) { // 遇到错误时,捕获错误,执行 reject 函数 reject(e); } } MyPromise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected) { // 首先判断两个参数是否为函数类型,因为这两个参数是可选参数 onResolved = typeof onResolved === "function" ? onResolved : function(value) { return value; }; onRejected = typeof onRejected === "function" ? onRejected : function(error) { throw error; }; // 如果是等待状态,则将函数加入对应列表中 if (this.state === PENDING) { this.resolvedCallbacks.push(onResolved); this.rejectedCallbacks.push(onRejected); } // 如果状态已经凝固,则直接执行对应状态的函数 if (this.state === RESOLVED) { onResolved(this.value); } if (this.state === REJECTED) { onRejected(this.value); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
实现防抖函数(debounce)
防抖函数原理:在事件被触发n秒后再执行回调,如果在这n秒内又被触发,则重新计时。
那么与节流函数的区别直接看这个动画实现即可。
手写简化版:
// 防抖函数 const debounce = (fn, delay) => { let timer = null; return (...args) => { clearTimeout(timer); timer = setTimeout(() => { fn.apply(this, args); }, delay); }; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
适用场景:
- 按钮提交场景:防止多次提交按钮,只执行最后提交的一次
- 服务端验证场景:表单验证需要服务端配合,只执行一段连续的输入事件的最后一次,还有搜索联想词功能类似
生存环境请用lodash.debounce
参考:前端手写面试题详细解答
数组扁平化
数组扁平化是指将一个多维数组变为一个一维数组
const arr = [1, [2, [3, [4, 5]]], 6]; // => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]- 1
- 2
- 3
方法一:使用flat()
const res1 = arr.flat(Infinity);- 1
- 2
方法二:利用正则
const res2 = JSON.stringify(arr).replace(/\[|\]/g, '').split(',');- 1
- 2
但数据类型都会变为字符串
方法三:正则改良版本
const res3 = JSON.parse('[' + JSON.stringify(arr).replace(/\[|\]/g, '') + ']');- 1
- 2
方法四:使用reduce
const flatten = arr => { return arr.reduce((pre, cur) => { return pre.concat(Array.isArray(cur) ? flatten(cur) : cur); }, []) } const res4 = flatten(arr);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
方法五:函数递归
const res5 = []; const fn = arr => { for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { if (Array.isArray(arr[i])) { fn(arr[i]); } else { res5.push(arr[i]); } } } fn(arr);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
字符串解析问题
var a = { b: 123, c: '456', e: '789', } var str=`a{a.b}aa{a.c}aa {a.d}aaaa`; // => 'a123aa456aa {a.d}aaaa'- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
实现函数使得将str字符串中的
{}内的变量替换,如果属性不存在保持原样(比如{a.d})类似于模版字符串,但有一点出入,实际上原理大差不差
const fn1 = (str, obj) => { let res = ''; // 标志位,标志前面是否有{ let flag = false; let start; for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) { if (str[i] === '{') { flag = true; start = i + 1; continue; } if (!flag) res += str[i]; else { if (str[i] === '}') { flag = false; res += match(str.slice(start, i), obj); } } } return res; } // 对象匹配操作 const match = (str, obj) => { const keys = str.split('.').slice(1); let index = 0; let o = obj; while (index < keys.length) { const key = keys[index]; if (!o[key]) { return `{${str}}`; } else { o = o[key]; } index++; } return o; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
实现日期格式化函数
输入:
dateFormat(new Date('2020-12-01'), 'yyyy/MM/dd') // 2020/12/01 dateFormat(new Date('2020-04-01'), 'yyyy/MM/dd') // 2020/04/01 dateFormat(new Date('2020-04-01'), 'yyyy年MM月dd日') // 2020年04月01日- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
const dateFormat = (dateInput, format)=>{ var day = dateInput.getDate() var month = dateInput.getMonth() + 1 var year = dateInput.getFullYear() format = format.replace(/yyyy/, year) format = format.replace(/MM/,month) format = format.replace(/dd/,day) return format }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
实现字符串的repeat方法
输入字符串s,以及其重复的次数,输出重复的结果,例如输入abc,2,输出abcabc。
function repeat(s, n) { return (new Array(n + 1)).join(s); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
递归:
function repeat(s, n) { return (n > 0) ? s.concat(repeat(s, --n)) : ""; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
字符串查找
请使用最基本的遍历来实现判断字符串 a 是否被包含在字符串 b 中,并返回第一次出现的位置(找不到返回 -1)。
a='34';b='1234567'; // 返回 2 a='35';b='1234567'; // 返回 -1 a='355';b='12354355'; // 返回 5 isContain(a,b);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
function isContain(a, b) { for (let i in b) { if (a[0] === b[i]) { let tmp = true; for (let j in a) { if (a[j] !== b[~~i + ~~j]) { tmp = false; } } if (tmp) { return i; } } } return -1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
实现发布-订阅模式
class EventCenter{ // 1. 定义事件容器,用来装事件数组 let handlers = {} // 2. 添加事件方法,参数:事件名 事件方法 addEventListener(type, handler) { // 创建新数组容器 if (!this.handlers[type]) { this.handlers[type] = [] } // 存入事件 this.handlers[type].push(handler) } // 3. 触发事件,参数:事件名 事件参数 dispatchEvent(type, params) { // 若没有注册该事件则抛出错误 if (!this.handlers[type]) { return new Error('该事件未注册') } // 触发事件 this.handlers[type].forEach(handler => { handler(...params) }) } // 4. 事件移除,参数:事件名 要删除事件,若无第二个参数则删除该事件的订阅和发布 removeEventListener(type, handler) { if (!this.handlers[type]) { return new Error('事件无效') } if (!handler) { // 移除事件 delete this.handlers[type] } else { const index = this.handlers[type].findIndex(el => el === handler) if (index === -1) { return new Error('无该绑定事件') } // 移除事件 this.handlers[type].splice(index, 1) if (this.handlers[type].length === 0) { delete this.handlers[type] } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
Promise.race
Promise.race = function(promiseArr) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { promiseArr.forEach(p => { // 如果不是Promise实例需要转化为Promise实例 Promise.resolve(p).then( val => resolve(val), err => reject(err), ) }) }) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
实现一个队列
基于链表结构实现队列
const LinkedList = require('./实现一个链表结构') // 用链表默认使用数组来模拟队列,性能更佳 class Queue { constructor() { this.ll = new LinkedList() } // 向队列中添加 offer(elem) { this.ll.add(elem) } // 查看第一个 peek() { return this.ll.get(0) } // 队列只能从头部删除 remove() { return this.ll.remove(0) } } var queue = new Queue() queue.offer(1) queue.offer(2) queue.offer(3) var removeVal = queue.remove(3) console.log(queue.ll,'queue.ll') console.log(removeVal,'queue.remove') console.log(queue.peek(),'queue.peek')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
Object.is
Object.is解决的主要是这两个问题:+0 === -0 // true NaN === NaN // false- 1
- 2
- 3
const is= (x, y) => { if (x === y) { // +0和-0应该不相等 return x !== 0 || y !== 0 || 1/x === 1/y; } else { return x !== x && y !== y; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
实现一个迭代器生成函数
ES6对迭代器的实现
JS原生的集合类型数据结构,只有
Array(数组)和Object(对象);而ES6中,又新增了Map和Set。四种数据结构各自有着自己特别的内部实现,但我们仍期待以同样的一套规则去遍历它们,所以ES6在推出新数据结构的同时也推出了一套 统一的接口机制 ——迭代器(Iterator)。ES6约定,任何数据结构只要具备Symbol.iterator属性(这个属性就是Iterator的具体实现,它本质上是当前数据结构默认的迭代器生成函数),就可以被遍历——准确地说,是被for...of...循环和迭代器的next方法遍历。 事实上,for...of...的背后正是对next方法的反复调用。在ES6中,针对
Array、Map、Set、String、TypedArray、函数的arguments对象、NodeList对象这些原生的数据结构都可以通过for...of...进行遍历。原理都是一样的,此处我们拿最简单的数组进行举例,当我们用for...of...遍历数组时:const arr = [1, 2, 3] const len = arr.length for(item of arr) { console.log(`当前元素是${item}`) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
之所以能够按顺序一次一次地拿到数组里的每一个成员,是因为我们借助数组的
Symbol.iterator生成了它对应的迭代器对象,通过反复调用迭代器对象的next方法访问了数组成员,像这样:const arr = [1, 2, 3] // 通过调用iterator,拿到迭代器对象 const iterator = arr[Symbol.iterator]() // 对迭代器对象执行next,就能逐个访问集合的成员 iterator.next() iterator.next() iterator.next()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
丢进控制台,我们可以看到
next每次会按顺序帮我们访问一个集合成员: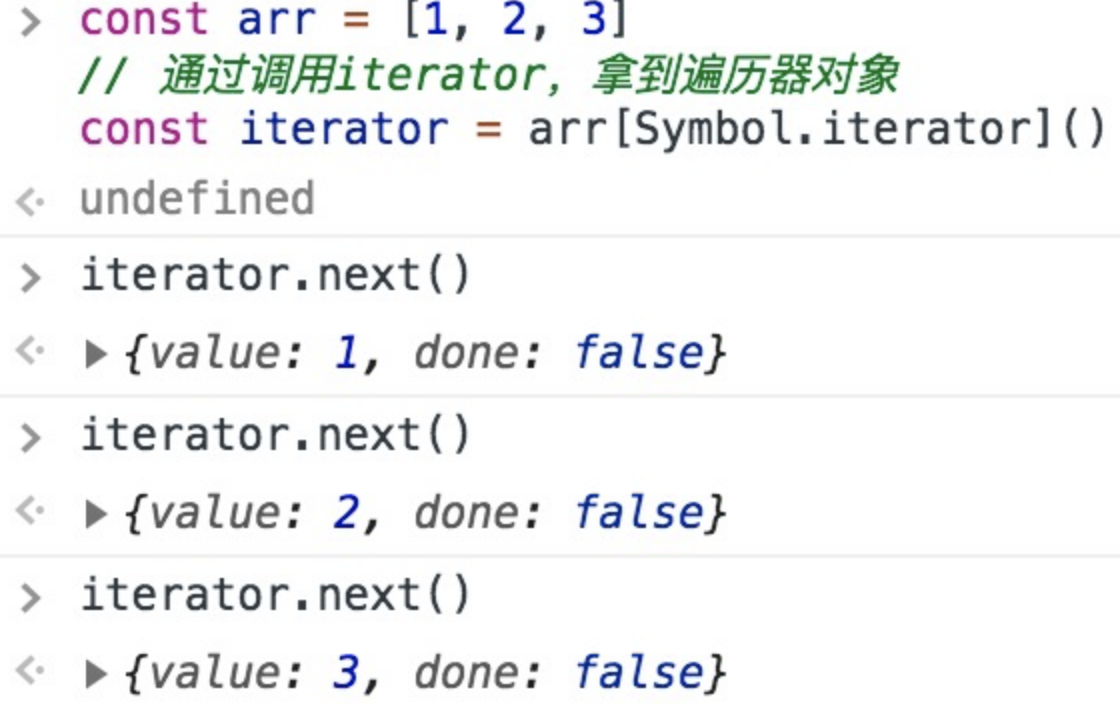
而
for...of...做的事情,基本等价于下面这通操作:// 通过调用iterator,拿到迭代器对象 const iterator = arr[Symbol.iterator]() // 初始化一个迭代结果 let now = { done: false } // 循环往外迭代成员 while(!now.done) { now = iterator.next() if(!now.done) { console.log(`现在遍历到了${now.value}`) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
可以看出,
for...of...其实就是iterator循环调用换了种写法。在ES6中我们之所以能够开心地用for...of...遍历各种各种的集合,全靠迭代器模式在背后给力。ps:此处推荐阅读迭代协议 (opens new window),相信大家读过后会对迭代器在ES6中的实现有更深的理解。
实现Object.create
Object.create()方法创建一个新对象,使用现有的对象来提供新创建的对象的__proto__// 模拟 Object.create function create(proto) { function F() {} F.prototype = proto; return new F(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
验证是否是身份证
function isCardNo(number) { var regx = /(^\d{15}$)|(^\d{18}$)|(^\d{17}(\d|X|x)$)/; return regx.test(number); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
实现一个compose函数
组合多个函数,从右到左,比如:
compose(f, g, h)最终得到这个结果(...args) => f(g(h(...args))).题目描述:实现一个
compose函数// 用法如下: function fn1(x) { return x + 1; } function fn2(x) { return x + 2; } function fn3(x) { return x + 3; } function fn4(x) { return x + 4; } const a = compose(fn1, fn2, fn3, fn4); console.log(a(1)); // 1+4+3+2+1=11- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
实现代码如下
function compose(...funcs) { if (!funcs.length) return (v) => v; if (funcs.length === 1) { return funcs[0] } return funcs.reduce((a, b) => { return (...args) => a(b(...args))) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
compose创建了一个从右向左执行的数据流。如果要实现从左到右的数据流,可以直接更改compose的部分代码即可实现- 更换
Api接口:把reduce改为reduceRight - 交互包裹位置:把
a(b(...args))改为b(a(...args))
event模块
实现node中回调函数的机制,node中回调函数其实是内部使用了观察者模式。
观察者模式:定义了对象间一种一对多的依赖关系,当目标对象Subject发生改变时,所有依赖它的对象Observer都会得到通知。
function EventEmitter() { this.events = new Map(); } // 需要实现的一些方法: // addListener、removeListener、once、removeAllListeners、emit // 模拟实现addlistener方法 const wrapCallback = (fn, once = false) => ({ callback: fn, once }); EventEmitter.prototype.addListener = function(type, fn, once = false) { const hanlder = this.events.get(type); if (!hanlder) { // 没有type绑定事件 this.events.set(type, wrapCallback(fn, once)); } else if (hanlder && typeof hanlder.callback === 'function') { // 目前type事件只有一个回调 this.events.set(type, [hanlder, wrapCallback(fn, once)]); } else { // 目前type事件数>=2 hanlder.push(wrapCallback(fn, once)); } } // 模拟实现removeListener EventEmitter.prototype.removeListener = function(type, listener) { const hanlder = this.events.get(type); if (!hanlder) return; if (!Array.isArray(this.events)) { if (hanlder.callback === listener.callback) this.events.delete(type); else return; } for (let i = 0; i < hanlder.length; i++) { const item = hanlder[i]; if (item.callback === listener.callback) { hanlder.splice(i, 1); i--; if (hanlder.length === 1) { this.events.set(type, hanlder[0]); } } } } // 模拟实现once方法 EventEmitter.prototype.once = function(type, listener) { this.addListener(type, listener, true); } // 模拟实现emit方法 EventEmitter.prototype.emit = function(type, ...args) { const hanlder = this.events.get(type); if (!hanlder) return; if (Array.isArray(hanlder)) { hanlder.forEach(item => { item.callback.apply(this, args); if (item.once) { this.removeListener(type, item); } }) } else { hanlder.callback.apply(this, args); if (hanlder.once) { this.events.delete(type); } } return true; } EventEmitter.prototype.removeAllListeners = function(type) { const hanlder = this.events.get(type); if (!hanlder) return; this.events.delete(type); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
分片思想解决大数据量渲染问题
题目描述: 渲染百万条结构简单的大数据时 怎么使用分片思想优化渲染
let ul = document.getElementById("container"); // 插入十万条数据 let total = 100000; // 一次插入 20 条 let once = 20; //总页数 let page = total / once; //每条记录的索引 let index = 0; //循环加载数据 function loop(curTotal, curIndex) { if (curTotal <= 0) { return false; } //每页多少条 let pageCount = Math.min(curTotal, once); window.requestAnimationFrame(function () { for (let i = 0; i < pageCount; i++) { let li = document.createElement("li"); li.innerText = curIndex + i + " : " + ~~(Math.random() * total); ul.appendChild(li); } loop(curTotal - pageCount, curIndex + pageCount); }); } loop(total, index);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
扩展思考 :对于大数据量的简单
dom结构渲染可以用分片思想解决 如果是复杂的dom结构渲染如何处理?这时候就需要使用虚拟列表了,虚拟列表和虚拟表格在日常项目使用还是很多的
请实现 DOM2JSON 一个函数,可以把一个 DOM 节点输出 JSON 的格式
<div> <span> <a></a> </span> <span> <a></a> <a></a> </span> </div> 把上面dom结构转成下面的JSON格式 { tag: 'DIV', children: [ { tag: 'SPAN', children: [ { tag: 'A', children: [] } ] }, { tag: 'SPAN', children: [ { tag: 'A', children: [] }, { tag: 'A', children: [] } ] } ] }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
实现代码如下:
function dom2Json(domtree) { let obj = {}; obj.name = domtree.tagName; obj.children = []; domtree.childNodes.forEach((child) => obj.children.push(dom2Json(child))); return obj; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
-
相关阅读:
ai电销机器人的语音识别是如何实现的呢?
Redis 7.x 入门和开发实战
重写jar包中的类的方法
RabbitMQ - 消息堆积问题的最佳解决方案?惰性队列
推荐算法之召回模型:DSSM、YoutubeDNN
类和对象(下)
第九章:最新版零基础学习 PYTHON 教程—Python 元组(第二节 -从字符串和列表创建元组Python)
C++初阶作业 Vector作业详解
构建资源的弹性伸缩
Java 开发 6 年了,BAT 面试文档:ActiveMQ(1)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/helloworld1024fd/article/details/127682419
