-
i.MX 6ULL 驱动开发 二十:RTC
一、RTC 概述
RTC(real-time clock)为操作系统中的实时时钟设备,为操作系统提供精准的实时时间和定时报警功能。当设备下电后,通过外置电池供电,RTC继续记录操作系统时间;设备上电后,RTC提供实时时钟给操作系统,确保断电后系统时间的连续性。二、iMX6ULL 的 RTC 原理
三、Linux 内核中 RTC 驱动原理
参考:内核驱动 (三)Linux系统时钟RTC_LouisGou的博客-CSDN博客_linux rtc。
RTC设备驱动是一个标准的字符设备驱动,应用程序通过open、release、read、write和ioctl等函数完成对RTC设备的操作。Linux内核使用rtc_device结构体描述RTC设备,因此RTC设备驱动就是申请并初始化rtc_device,最后将rtc_device注册到Linux内核里面。rtc_device结构体中rtc_class_ops结构体描述RTC设备底层操作函数。rtc_class_ops结构体函数集包括从RTC设备中读取时间、向RTC设备写入新的时间等。
值等。struct rtc_device结构体定义如下:struct rtc_device { struct device dev; struct module *owner; int id; char name[RTC_DEVICE_NAME_SIZE]; const struct rtc_class_ops *ops; struct mutex ops_lock; struct cdev char_dev; unsigned long flags; unsigned long irq_data; spinlock_t irq_lock; wait_queue_head_t irq_queue; struct fasync_struct *async_queue; struct rtc_task *irq_task; spinlock_t irq_task_lock; int irq_freq; int max_user_freq; struct timerqueue_head timerqueue; struct rtc_timer aie_timer; struct rtc_timer uie_rtctimer; struct hrtimer pie_timer; /* sub second exp, so needs hrtimer */ int pie_enabled; struct work_struct irqwork; /* Some hardware can't support UIE mode */ int uie_unsupported; #ifdef CONFIG_RTC_INTF_DEV_UIE_EMUL struct work_struct uie_task; struct timer_list uie_timer; /* Those fields are protected by rtc->irq_lock */ unsigned int oldsecs; unsigned int uie_irq_active:1; unsigned int stop_uie_polling:1; unsigned int uie_task_active:1; unsigned int uie_timer_active:1; #endif };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
dev:设备;id:ID;name:名字;ops:RTC设备底层操作函数;char_dev:字符设备;
struct rtc_class_ops结构体定义如下:/* * For these RTC methods the device parameter is the physical device * on whatever bus holds the hardware (I2C, Platform, SPI, etc), which * was passed to rtc_device_register(). Its driver_data normally holds * device state, including the rtc_device pointer for the RTC. * * Most of these methods are called with rtc_device.ops_lock held, * through the rtc_*(struct rtc_device *, ...) calls. * * The (current) exceptions are mostly filesystem hooks: * - the proc() hook for procfs * - non-ioctl() chardev hooks: open(), release(), read_callback() * * REVISIT those periodic irq calls *do* have ops_lock when they're * issued through ioctl() ... */ struct rtc_class_ops { int (*open)(struct device *); void (*release)(struct device *); int (*ioctl)(struct device *, unsigned int, unsigned long); int (*read_time)(struct device *, struct rtc_time *); int (*set_time)(struct device *, struct rtc_time *); int (*read_alarm)(struct device *, struct rtc_wkalrm *); int (*set_alarm)(struct device *, struct rtc_wkalrm *); int (*proc)(struct device *, struct seq_file *); int (*set_mmss64)(struct device *, time64_t secs); int (*set_mmss)(struct device *, unsigned long secs); int (*read_callback)(struct device *, int data); int (*alarm_irq_enable)(struct device *, unsigned int enabled); };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
注意:
struct rtc_device结构体和struct rtc_class_ops结构体定义在include/linux/rtc.h。Linux内核提供了一个RTC通用字符设备驱动文件,定义在drivers/rtc/rtc-dev.c文件中,rtc-dev.c文件提供了所有RTC设备向应用层提供的file_operations函数操作集,如下所示:static const struct file_operations rtc_dev_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .llseek = no_llseek, .read = rtc_dev_read, .poll = rtc_dev_poll, .unlocked_ioctl = rtc_dev_ioctl, .open = rtc_dev_open, .release = rtc_dev_release, .fasync = rtc_dev_fasync, };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
四、Linux 中 RTC 驱动分析
file_operations、rtc_device和rtc_class_ops结构体建立联系过程如下:1、通过设备树确定驱动源码,设备树内容如下:
snvs_rtc: snvs-rtc-lp { compatible = "fsl,sec-v4.0-mon-rtc-lp"; regmap = <&snvs>; offset = <0x34>; interrupts = <GIC_SPI 19 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>, <GIC_SPI 20 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
通过
fsl,sec-v4.0-mon-rtc-lp字符串确定驱动相关源码。2、驱动源码确定
static const struct of_device_id snvs_dt_ids[] = { { .compatible = "fsl,sec-v4.0-mon-rtc-lp", }, { /* sentinel */ } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
驱动源码路径:
linux\drivers\rtc\rtc-snvs.c。3、驱动源码分析
static struct platform_driver snvs_rtc_driver = { .driver = { .name = "snvs_rtc", .pm = SNVS_RTC_PM_OPS, .of_match_table = snvs_dt_ids, }, .probe = snvs_rtc_probe, }; module_platform_driver(snvs_rtc_driver);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
通过以上信息,可以确定
RTC驱动框架为platform,当设备和驱动匹配成功后,snvs_rtc_probe函数执行。4、
snvs_rtc_probe函数分析struct snvs_rtc_data { struct rtc_device *rtc; struct regmap *regmap; int offset; int irq; struct clk *clk; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
static int snvs_rtc_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) { struct snvs_rtc_data *data; struct resource *res; int ret; void __iomem *mmio; data = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*data), GFP_KERNEL); if (!data) return -ENOMEM; data->regmap = syscon_regmap_lookup_by_phandle(pdev->dev.of_node, "regmap"); if (IS_ERR(data->regmap)) { dev_warn(&pdev->dev, "snvs rtc: you use old dts file, please update it\n"); res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0); mmio = devm_ioremap_resource(&pdev->dev, res); if (IS_ERR(mmio)) return PTR_ERR(mmio); data->regmap = devm_regmap_init_mmio(&pdev->dev, mmio, &snvs_rtc_config); } else { data->offset = SNVS_LPREGISTER_OFFSET; of_property_read_u32(pdev->dev.of_node, "offset", &data->offset); } if (!data->regmap) { dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Can't find snvs syscon\n"); return -ENODEV; } data->irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0); if (data->irq < 0) return data->irq; data->clk = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "snvs-rtc"); if (IS_ERR(data->clk)) { data->clk = NULL; } else { ret = clk_prepare_enable(data->clk); if (ret) { dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Could not prepare or enable the snvs clock\n"); return ret; } } platform_set_drvdata(pdev, data); /* Initialize glitch detect */ regmap_write(data->regmap, data->offset + SNVS_LPPGDR, SNVS_LPPGDR_INIT); /* Clear interrupt status */ regmap_write(data->regmap, data->offset + SNVS_LPSR, 0xffffffff); /* Enable RTC */ snvs_rtc_enable(data, true); device_init_wakeup(&pdev->dev, true); ret = devm_request_irq(&pdev->dev, data->irq, snvs_rtc_irq_handler, IRQF_SHARED, "rtc alarm", &pdev->dev); if (ret) { dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to request irq %d: %d\n", data->irq, ret); goto error_rtc_device_register; } data->rtc = devm_rtc_device_register(&pdev->dev, pdev->name, &snvs_rtc_ops, THIS_MODULE); if (IS_ERR(data->rtc)) { ret = PTR_ERR(data->rtc); dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to register rtc: %d\n", ret); goto error_rtc_device_register; } return 0; error_rtc_device_register: if (data->clk) clk_disable_unprepare(data->clk); return ret; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
-
分配并初始化
rtc_device。 -
调用
devm_rtc_device_register向内核注册RTC设备。 -
devm_rtc_device_register中调用rtc_device_register完成RTC设备注册。
5、
rtc_device_register/** * rtc_device_register - register w/ RTC class * @dev: the device to register * * rtc_device_unregister() must be called when the class device is no * longer needed. * * Returns the pointer to the new struct class device. */ struct rtc_device *rtc_device_register(const char *name, struct device *dev, const struct rtc_class_ops *ops, struct module *owner) { struct rtc_device *rtc; struct rtc_wkalrm alrm; int of_id = -1, id = -1, err; if (dev->of_node) of_id = of_alias_get_id(dev->of_node, "rtc"); else if (dev->parent && dev->parent->of_node) of_id = of_alias_get_id(dev->parent->of_node, "rtc"); if (of_id >= 0) { id = ida_simple_get(&rtc_ida, of_id, of_id + 1, GFP_KERNEL); if (id < 0) dev_warn(dev, "/aliases ID %d not available\n", of_id); } if (id < 0) { id = ida_simple_get(&rtc_ida, 0, 0, GFP_KERNEL); if (id < 0) { err = id; goto exit; } } rtc = kzalloc(sizeof(struct rtc_device), GFP_KERNEL); if (rtc == NULL) { err = -ENOMEM; goto exit_ida; } rtc->id = id; rtc->ops = ops; rtc->owner = owner; rtc->irq_freq = 1; rtc->max_user_freq = 64; rtc->dev.parent = dev; rtc->dev.class = rtc_class; rtc->dev.release = rtc_device_release; mutex_init(&rtc->ops_lock); spin_lock_init(&rtc->irq_lock); spin_lock_init(&rtc->irq_task_lock); init_waitqueue_head(&rtc->irq_queue); /* Init timerqueue */ timerqueue_init_head(&rtc->timerqueue); INIT_WORK(&rtc->irqwork, rtc_timer_do_work); /* Init aie timer */ rtc_timer_init(&rtc->aie_timer, rtc_aie_update_irq, (void *)rtc); /* Init uie timer */ rtc_timer_init(&rtc->uie_rtctimer, rtc_uie_update_irq, (void *)rtc); /* Init pie timer */ hrtimer_init(&rtc->pie_timer, CLOCK_MONOTONIC, HRTIMER_MODE_REL); rtc->pie_timer.function = rtc_pie_update_irq; rtc->pie_enabled = 0; strlcpy(rtc->name, name, RTC_DEVICE_NAME_SIZE); dev_set_name(&rtc->dev, "rtc%d", id); /* Check to see if there is an ALARM already set in hw */ err = __rtc_read_alarm(rtc, &alrm); if (!err && !rtc_valid_tm(&alrm.time)) rtc_initialize_alarm(rtc, &alrm); rtc_dev_prepare(rtc); err = device_register(&rtc->dev); if (err) { put_device(&rtc->dev); goto exit_kfree; } rtc_dev_add_device(rtc); rtc_sysfs_add_device(rtc); rtc_proc_add_device(rtc); dev_info(dev, "rtc core: registered %s as %s\n", rtc->name, dev_name(&rtc->dev)); return rtc; exit_kfree: kfree(rtc); exit_ida: ida_simple_remove(&rtc_ida, id); exit: dev_err(dev, "rtc core: unable to register %s, err = %d\n", name, err); return ERR_PTR(err); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(rtc_device_register);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
rtc_dev_prepare函数中调用cdev_init完成rtc_dev_fops(struct file_operations) 操作集注册。rtc_dev_add_device函数中调用cdev_add完成字符设备驱动注册。
五、Linux 下 RTC 时间相关操作
1、确定 RTC 是否启动
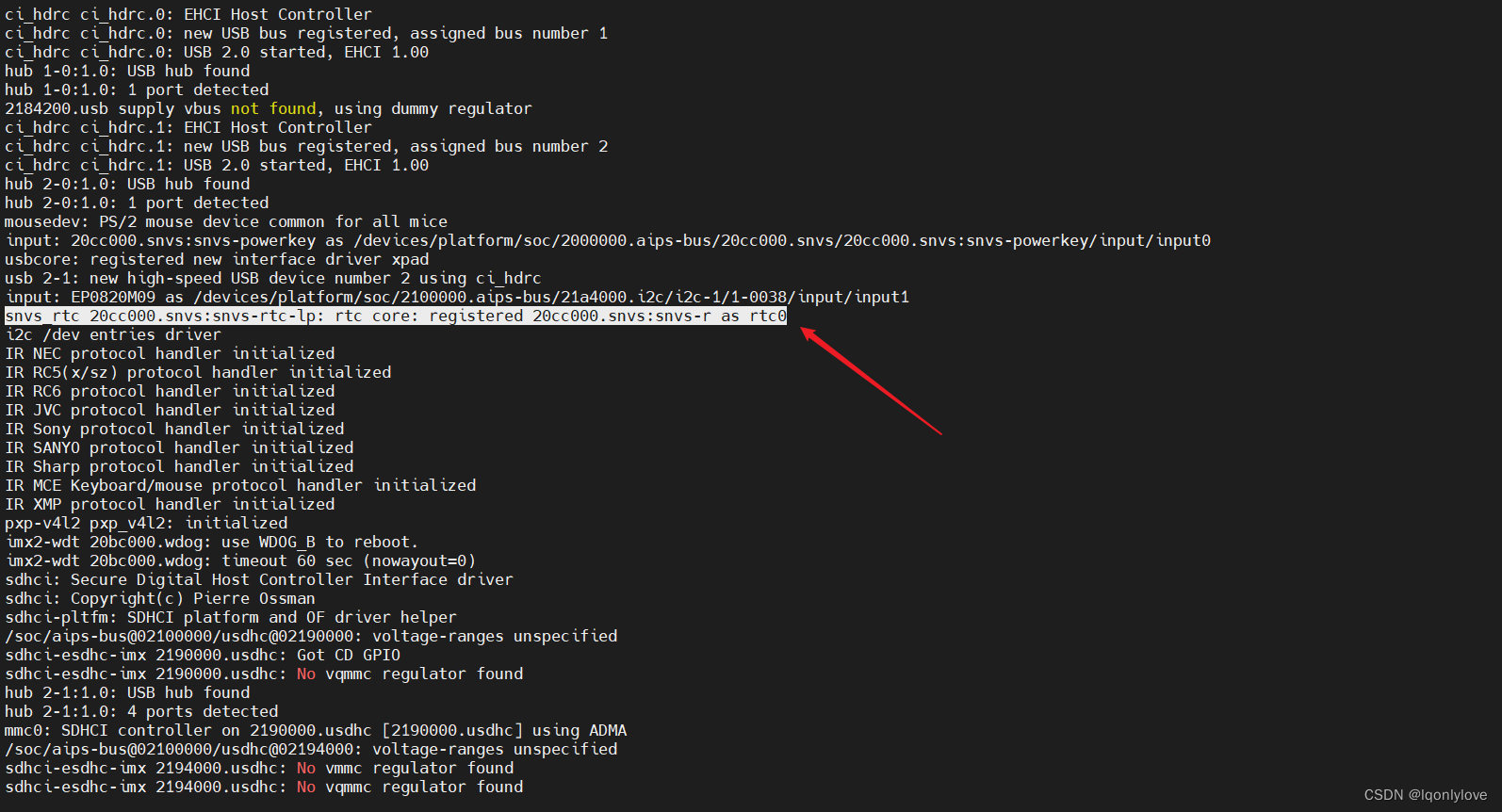
2、查看 RTC 时间
Linux内核通过RTC为系统提供时钟,通过date命令即可查看Linux系统时钟:# date Thu Jan 1 00:04:34 UTC 1970 #- 1
- 2
- 3
3、设置 RTC 时间
# date Thu Jan 1 00:06:53 UTC 1970 # date -s "2022-11-01 21:44:00" Tue Nov 1 21:44:00 UTC 2022 # date Tue Nov 1 21:44:02 UTC 2022 #- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
使用
“date -s”命令仅仅是将当前系统时间设置了,此时间还没有写入到iMX6ULL内部RTC里面或其他的RTC芯片里面,因此系统重启以后时间又会丢失。我们需要将当前的时间写入到RTC里面,这里要用到hwclock命令,输入如下命令将系统时间写入到RTC里面:hwclock -w # 将当前系统时间写入到 RTC 里面- 1
4、date 帮助信息
# date -h date: invalid option -- 'h' BusyBox v1.35.0 (2022-09-25 01:42:03 PDT) multi-call binary. Usage: date [OPTIONS] [+FMT] [[-s] TIME] Display time (using +FMT), or set time -u Work in UTC (don't convert to local time) [-s] TIME Set time to TIME -d TIME Display TIME, not 'now' -D FMT FMT (strptime format) for -s/-d TIME conversion -r FILE Display last modification time of FILE -R Output RFC-2822 date -I[SPEC] Output ISO-8601 date SPEC=date (default), hours, minutes, seconds or ns Recognized TIME formats: @seconds_since_1970 hh:mm[:ss] [YYYY.]MM.DD-hh:mm[:ss] YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm[:ss] [[[[[YY]YY]MM]DD]hh]mm[.ss] 'date TIME' form accepts MMDDhhmm[[YY]YY][.ss] instead #- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
5、hwclock 帮助信息
# hwclock -h hwclock: invalid option -- 'h' BusyBox v1.35.0 (2022-09-25 01:42:03 PDT) multi-call binary. Usage: hwclock [-swul] [--systz] [-f DEV] Show or set hardware clock (RTC) -s Set system time from RTC -w Set RTC from system time --systz Set in-kernel timezone, correct system time if RTC is kept in local time -f DEV Use specified device (e.g. /dev/rtc2) -u Assume RTC is kept in UTC -l Assume RTC is kept in local time (if neither is given, read from /var/lib/hwclock/adjtime) #- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
-
相关阅读:
yapi文档转换jmx脚本
mybatis-plus代码生成工具
设计模式-状态模式(State)
Stable Diffusion 手动安装扩展报错 catch exception for non git extensions
使用TinyPNG API压缩图片
java反序列化专项
Java多线程之线程同步机制(锁,线程池等等)
file Input文件选择框,选择图片后展示在占位区
计算机视觉与深度学习-卷积神经网络-卷积&图像去噪&边缘提取-卷积与边缘提取-[北邮鲁鹏]
盘点3种Python网络爬虫过程中的中文乱码的处理方法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/OnlyLove_/article/details/127658726
