-
Understanding Entity Relationship Behaviors in Microsoft Dynamics 365/CRM
Relationships are one of the core pieces of functionality in Microsoft Dynamics CRM. From time-to-time, I see customers who end up getting surprised by how an action they apply to a record, affects the related records.
A common example of this would be re-assigning an account and how it affects the ownership of the related contacts.
By default, this relationship is configured as a Parental relationship, so in this scenario, all the related contacts are also assigned to the new account owner. In many instances, this is the desired outcome, but in some cases, you’d rather keep the contact ownership the same.
Luckily you are not locked into this behavior if it doesn’t suit your organization’s needs.
In the customization’s area under each entity, you’ll see the lists of 1:N relationships and N:1 relationships. In the earlier example you would find the relationship under 1:N, and then you’d be looking for the relationship whose parent entity is account and related entity is contact.
Once you’ve opened that up you can see the type of behavior for the relationship is configurable. In this case, we can change the behavior from Parental to Configurable Cascading. This would allow you to alter the Assign behavior to another option so it doesn’t update the owners of the child records.
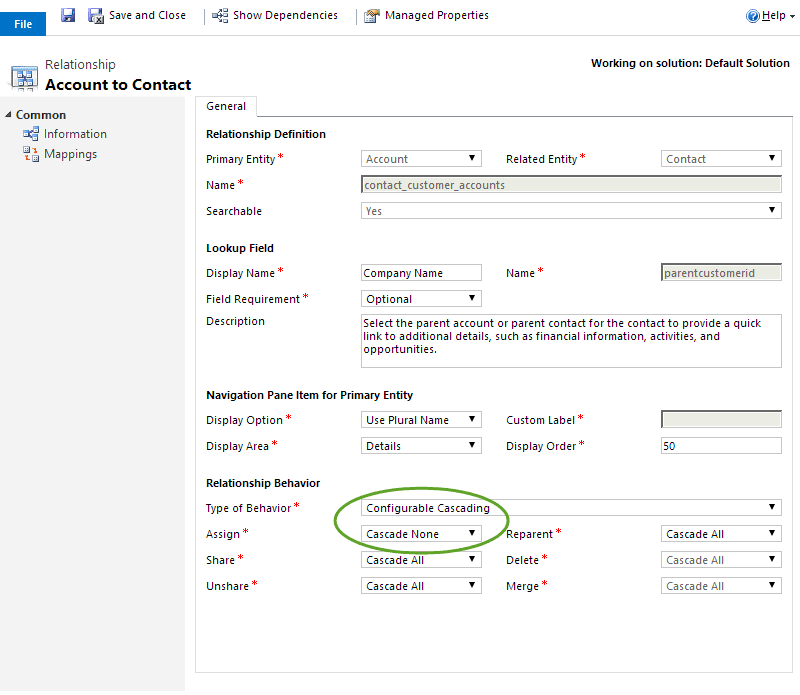
Here are the options that are available, but keep in mind that not all types are available for all relationships in the system.
- Parental: this forces the Cascade All effect to all the individual behaviors
- Referential: this forces the Cascade None effect to all the individual behaviors except Delete which is locked to Remove Link
- Referential, Restrict Delete: this forces the Cascade None effect to all the individual behaviors except Delete which is locked to Restrict
- Configurable Cascading: this allows you to define the individual behaviors independently
- Assign – the record owner changes
- Share – the record is shared with another user
- Unshare – the record is unshared with another user
- Reparent – the referencing attribute of a parental relationship is changed
- Delete – the record is deleted
- Merge – the record is merged with another record
For Assign, Share, Unshare, and Reparent the options are:
- Cascade All – the change is applied to all associated records
- Cascade Active – the change is applied to all associated records that are active
- Cascade User Owned – the change is applied to all associated records owned by the user who owns the original record
- Cascade None – the change is not applied to any other records
For Delete the options are:
- Cascade All
- Remove Link – the link between the original and referenced records is removed
- Restrict – prevents the original record from being deleted when related to child records
For Merge the options are:
- Cascade All
- Cascade None
-
相关阅读:
分享从零开始学习网络设备配置--2.1 交换机基本配置
骚扰电话查询源码
Java基于SSM框架的教室预约申请管理系统 毕业设计
【南外夏令营】线性同余方程
[数据结构]二叉树的链式结构
图像数字化基础
不要再用if-else
猿创征文|[CM311-1A Armbian]-烧录制作 Armbian 系统盘以及写入 CM311-1A 机顶盒的 EMMC 刷成服务器
【数据结构与算法】二叉树的链式访问
计算机未来-发展趋势和未来方向
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lsysunbow/article/details/127646024