-
Spring源码深度解析:五、BeanFactoryPostProcessor的处理
一、前言
文章目录:Spring源码深度解析:文章目录
我们先通过Spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的流程图,来了解Spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的工作流程是什么,接着根据这个工作流程一步一步的阅读源码
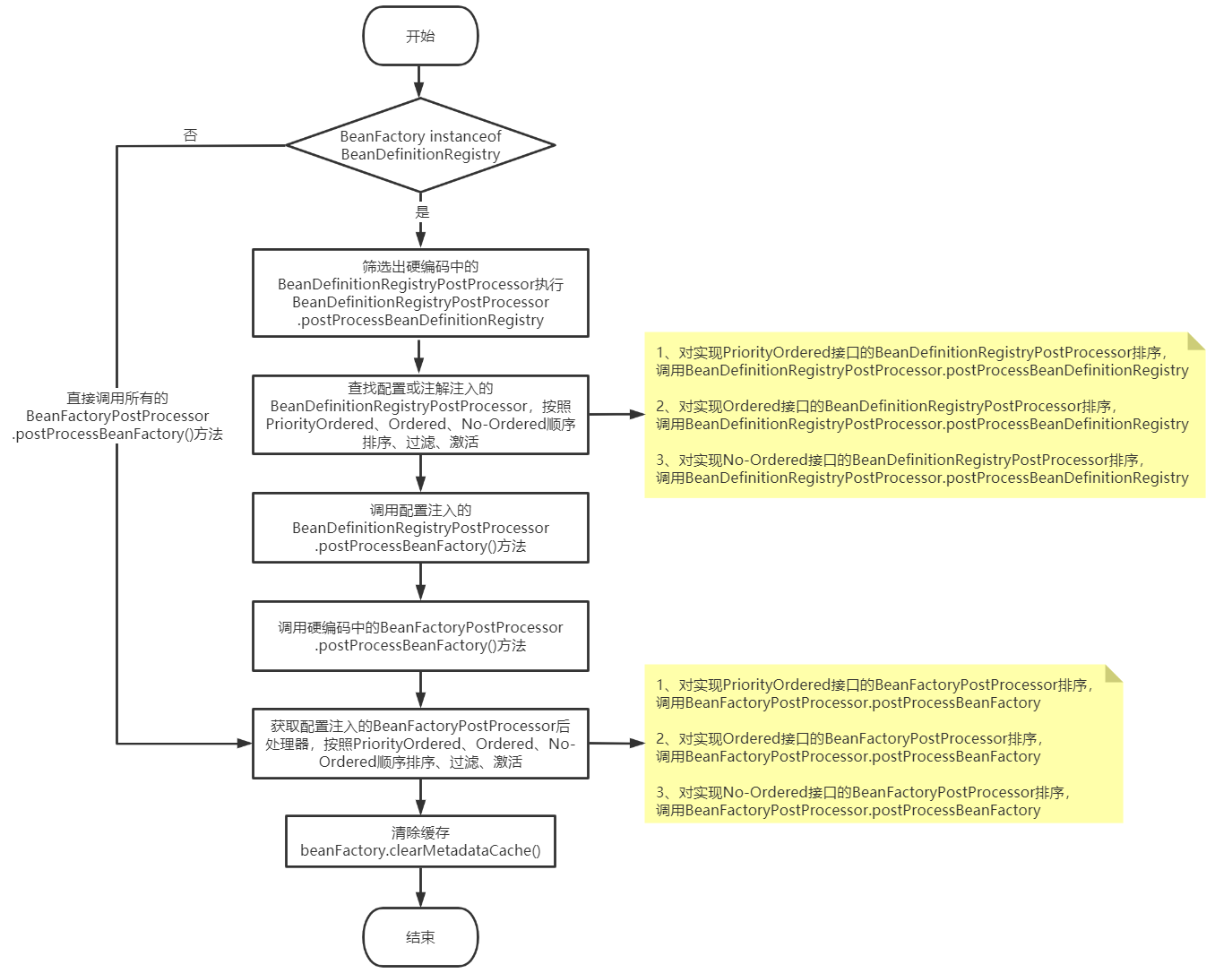
本文分析的方法是 AbstractApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法
PS : 个人感觉,实现IOC的两个核心后处理器 :
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor解析配置类(这里的配置类不仅仅局限于@Configuration注解,还包括@Import、@ImportResource等注解),将解析到的需要注入到Spring容器中的bean的BeanDefinition保存起来AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor解析bean中的 需要自动注入的bean@Autowired和@Inject @Value注解。
二、BeanFactoryPostProcessor & BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
由于
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法中主要就是对BeanFactoryPostProcessor的处理,所以这里简单的介绍一下BeanFactoryPostProcessor及其子接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor。其结构如下图:
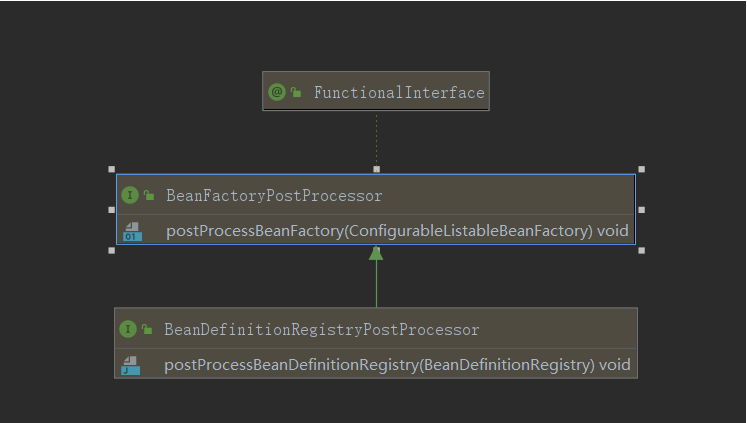
BeanFactoryPostProcessor概述:
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口定义了BeanFactory的后置处理器接口,该接口可以改变已经定义在BeanFactory中已注册Bean的信息(比如参数),Spring 在完成上下文实例化之前,允许我们通过BeanFactoryPostProcessor来对BeanFactory中已注册的Bean进行修改,从而得实例化到我们预期想要的Bean,这种方式兼顾了扩展性,也是 Spring 强大灵活,扩展性高的部分原因。BeanFactoryPostProcessor相比较于BeanPostProcessor方法是很简单的,只有一个方法,其子接口也就一个方法。但是他们俩的功能又是类似的,区别就是作用域并不相同。BeanFactoryPostProcessor的作用域范围是容器级别的。它只和你使用的容器有关。如果你在容器中定义一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor ,它仅仅对此容器中的bean进行后置处理。BeanFactoryPostProcessor不会对定义在另一个容器中的bean进行后置处理,即使这两个容器都在同一容器中。BeanFactoryPostProcessor可以对 bean的定义(配置元数据)进行处理。Spring IOC 容器允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实际实例化任何其他bean之前读取配置元数据,并有可能修改它,也即是说BeanFactoryPostProcessor是直接修改了bean的定义,BeanPostProcessor则是对bean创建过程中进行干涉。BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 和 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的区别在于:
-
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()方法针对是BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的ConfigurableListableBeanFactory,可以实现对BeanDefinition的增删改查等操作,但是对于非ConfigurableListableBeanFactory类型的BeanFactory,并不起作用。 -
BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory()针对的是所有的BeanFactory。 -
postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry的调用时机在postProcessBeanFactory之前。
三、代码分析
1、BeanFactory
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口定义了postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)方法,该方法作用是在BeanFactory实例化Bean之前,对其中的BeanDefinition进行修改参数等一系列操作,入参是一个BeanFactory,但是从我们之前的学习当中我们知道Spring中的BeanFactory其实是一个叫DefaultListableBeanFactory类型的BeanFactory,那么入参当中的ConfigurableListableBeanFactory和DefaultListableBeanFactory为什么关系呢?我们来通过下面提到的DefaultListableBeanFactory的继承关系图。我们看到DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了ConfigurableListableBeanFactory。这一点在 Spring源码深度解析:三、容器的刷新 - refresh()中已经得到证实。下面我们看看
DefaultListableBeanFactory的结构图如下,可以看到DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口。这点在下面的分析中会用到。
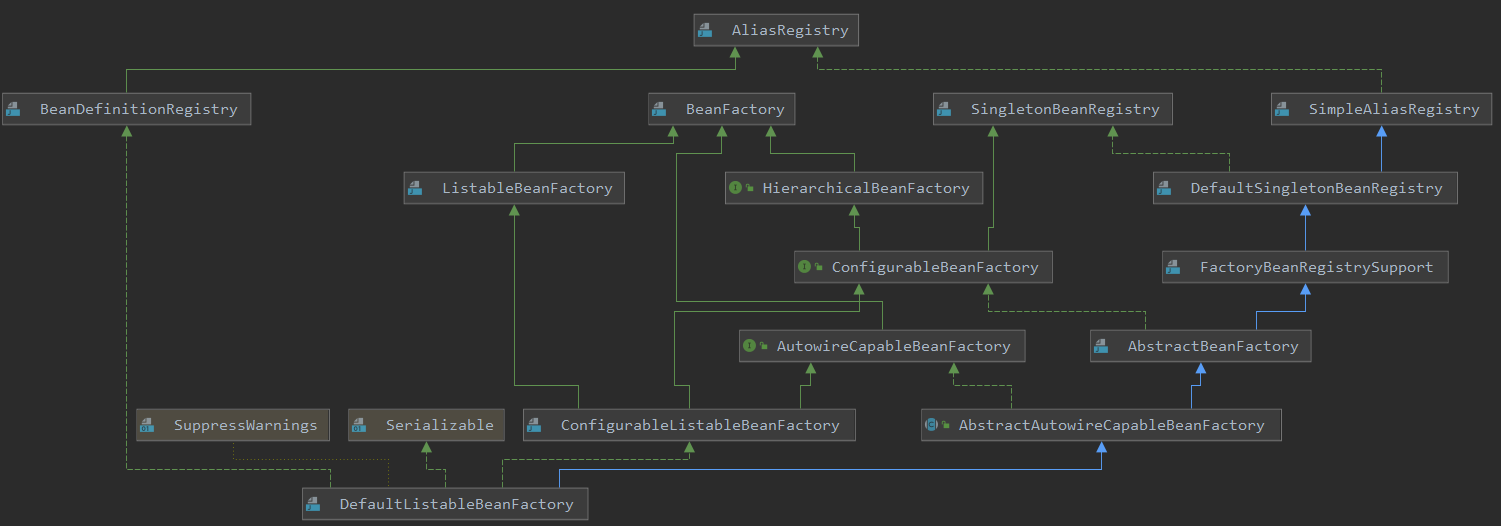
2、代码分析
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法的作用是激活BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor。为了更好的了解下面的代码,我们先了解几个代码中的规则:
-
BeanFactoryPostProcessor在本次分析中分为两种类型:BeanFactoryPostProcessor和其子接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor。BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor相较于BeanFactoryPostProcessor,增加了一个方法如下。
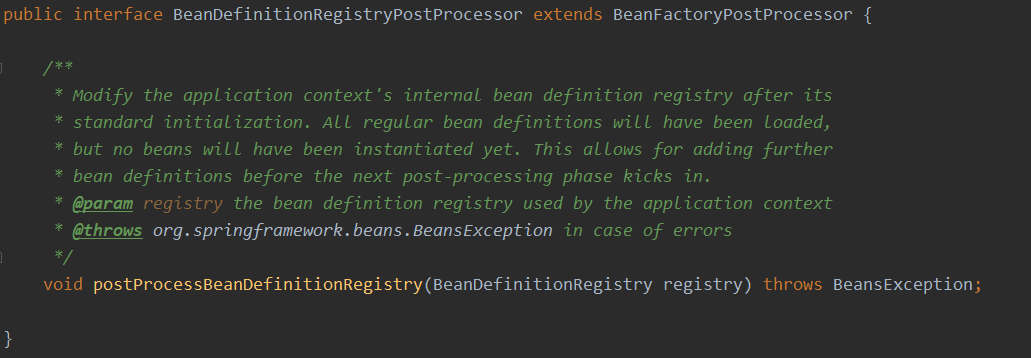
需要注意的是,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 这个方法仅仅针对于BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的BeanFactory生效,这一点根据其入参就可以看到。
总结一下即 :BeanFactoryPostProcessor针对所有的BeanFactory,即对于所有类型的BeanFactory都会调用其方法;BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor仅对BeanDefinitionRegistry子类的BeanFactory起作用,非BeanDefinitionRegistry类型则直接处理即可。 -
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的注入分为两种方式:
1、配置注入方式:即通过注解或者xml的方式动态的注入到容器中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
2、硬编码注入方式: 这种方式是直接调用AbstractApplicationContext#addBeanFactoryPostProcessor方法将BeanFactoryPostProcessor添加到AbstractApplicationContext.beanFactoryPostProcessors属性中。其中硬编码注入的BeanFactoryPostProcessor并不需要也不支持接口排序,而配置注入的方式因为Spring无法保证加载的顺序,所以通过支持PriorityOrdered、Ordered排序接口的排序。 -
在下面代码分析中会有四个集合
1、regularPostProcessors: 记录通过硬编码方式注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的处理器
2、registryProcessors:记录所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的处理器
3、currentRegistryProcessors: 一个临时集合变量,记录通过配置方式注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的处理器
4、processedBeans:记录当前记录所有即将或已经处理的beanName(包含:BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor),用于防止重复处理
其实调用顺序可以归纳为:1)、硬编码先于配置;2)、
postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry先于postProcessBeanFactory下面我们来看具体代码:
AbstractApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors() 方法内容如下protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // getBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法获取了所有硬编码的bean工厂处理器 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()); // 默认情况下这里判断不会为空,在refresh方法调用的prepareBeanFactory方法内已经执行过这段代码了 if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { // 添加bean后置处理器,负责调用实现了LoadTimeWeaverAware接口setLoadTimeWeaver方法的bean beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); // 添加一个临时类加载器 beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
可以看到主要功能还是在
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());这一句上。我们先来看看getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()得到的是什么2.1、getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
AbstractApplicationContext类
// 用来增强或修改bean定义信息的集合 private final List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); @Override public void addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor) { Assert.notNull(postProcessor, "BeanFactoryPostProcessor must not be null"); this.beanFactoryPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } /** * Return the list of BeanFactoryPostProcessors that will get applied * to the internal BeanFactory. */ public List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() { return this.beanFactoryPostProcessors; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
可以看到
getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法仅仅是将beanFactoryPostProcessors集合返回了出去而已。那么beanFactoryPostProcessors集合是通过 add方法添加的。这就是我们上面提到过的,beanFactoryPostProcessors实际上是硬编码形式注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的处理器集合。2.2、invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
通过上一步,我们可以知道 入参中的
beanFactoryPostProcessors集合是硬编码注册的 集合。对于下面的分析我们就好理解了。下面代码主要是对于
BeanDefinitionRegistry类型BeanFactory的处理以及BeanFactoryPostProcessor调用顺序问题的处理。实际上并不复杂。public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { // 记录所有即将或已经处理的beanName,用于防止重复处理 Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>(); // 对BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的处理,这里是交由BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor来处理 // 这里判断BeanFactory如果是BeanDefinitionRegistry子类 则需要进行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的处理,否则直接按照BeanFactoryPostProcessor处理即可。 // 关于为什么BeanDefinitionRegistry比较特殊上面也说过,因为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor只能处理BeanDefinitionRegistry的子类,所以这里需要区分是否是BeanDefinitionRegistry类型 if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { // 下面逻辑看似复杂,其实就两步: // 1. 获取所有硬编码的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型,激活postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法 // 2. 获取所有配置的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,激活postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法 BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; // 记录通过硬编码方式注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的处理器 List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 记录所有注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的处理器(含有硬编码注册的和配置注入注册的) List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 遍历硬编码注册的后处理器(都保存AbstractApplicationContext#beanFactoryPostProcessors中,这里通过参数beanFactoryPostProcessors传递过来) for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); // 将硬编码注册BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor放到registryProcessors中 registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); } else { regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } } // 一个临时变量,记录通过配置方式注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的处理器 List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 获取所有的实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的beanName String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // 筛选出实现了PriorityOrdered接口的实现类,优先执行 for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { // 记录到currentRegistryProcessors中 currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } // 进行排序 sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); // 以配置方式注册的且实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor集合全部放到registryProcessors中 registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); // 激活 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); // 清空临时变量currentRegistryProcessors的内容 currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // 筛选出实现了Ordered接口的实现类,第二执行 for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } // 排序 sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); // 以配置方式注册的且实现了Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor集合全部放到registryProcessors中 registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); // 激活 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); // 清空临时变量currentRegistryProcessors的内容 currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // 最后获取No-Ordered(没有实现排序)接口的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor ,进行激活。 boolean reiterate = true; while (reiterate) { reiterate = false; postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); reiterate = true; } } // 排序 sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); // 将配置方式注册的且没有实现排序(No-Ordered)接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor集合全部放到registryProcessors中 registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); // 激活 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); // 清空临时变量currentRegistryProcessors的内容 currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); } // 到这里,所有的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()方法都已经激活结束。 // 开始激活postProcessBeanFactory方法 // 因为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类,所有这里激活的是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory()方法 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); // regularPostProcessors中记录的是硬编码注入的BeanFactoryPostProcessor invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory); } else { // 如果 beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry = false,那么BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()方法并不生效,就直接激活postProcessBeanFactory()方法即可。 // 激活硬编码注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory()方法 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory); } // 到这一步,所有的硬编码方式注入的后处理器都处理完毕; 配置注入的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor后处理器的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()和postProcessBeanFactory()方法都已经激活。 // 下面开始处理配置注入的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory后处理器。 // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! // 获取所有后处理器的beanName,用于后面处理 String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. // 创建几个保存不同排序的集合,按照实现的排序接口调用 // 筛选出实现了排序接口PriorityOrdered的类 List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 筛选出实现了排序接口Ordered的类 List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); // 筛选出未实现排序接口的类 List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { // skip - already processed in first phase above } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // 排序和激活(实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后处理器) sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // 排序和激活(实现了Ordered接口的后处理器) List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // 排序和激活(没有实现排序接口的后处理器) List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // 清除元数据缓存 beanFactory.clearMetadataCache(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
这里的主要流程:
-
首先执行我们自定义通过
AbstractApplicationContext.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor方法添加进来的BeanFactory后置处理器,然后调用这些beanFactory后置处理器的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,并按类型分装到集合,方便后续统一调用父类BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的postProcessBeanFactory方法 -
获取配置方式注册的所有
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的beanFactory后置处理器,遍历出实现了PriorityOrdered接口的beanFactory后置处理器,进行排序,放到临时存储集合中,然后调用这些beanFactory后置处理器的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法; -
获取配置方式注册的所有
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的beanFactory后置处理器,遍历出实现了Ordered接口的beanFactory后置处理器,进行排序,放到临时存储集合中,然后调用这些beanFactory后置处理器的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法; -
获取配置方式注册的所有
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的beanFactory后置处理器,遍历出既不实现PriorityOrdered接口又不实现Ordered接口的beanFactory后置处理器,放到临时存储集合中,然后调用这些beanFactory后置处理器的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法; -
执行前三步放入临时集合当中配置方式注册的所有
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的beanFactory后置处理器的父类BeanFactoryPostProcessor中的postProcessBeanFactory方法,将前三步中处理的beanFactory后置处理器放到一个临时集合中也是为了这一步操作考虑; -
执行硬编码注入的
beanFactory后置处理器BeanFactoryPostProcessor中的postProcessBeanFactory方法 -
获取获取配置方式注册的所有
BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的beanFactory后置处理器,遍历出实现了PriorityOrdered接口的beanFactory后置处理器,进行排序,然后调用这些beanFactory后置处理器的postProcessBeanFactory方法; -
获取获取配置方式注册的所有
BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的beanFactory后置处理器,遍历出实现了Ordered接口的beanFactory后置处理器,进行排序,然后调用这些beanFactory后置处理器的postProcessBeanFactory方法; -
获取获取配置方式注册的所有
BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的beanFactory后置处理器,遍历出既不实现PriorityOrdered接口又不实现Ordered接口的beanFactory后置处理器,然后调用这些beanFactory后置处理器的postProcessBeanFactory方法;
到这里,所有的
BeanFactory后置处理器就执行完毕了,这里通过分析源码,我们知道了一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor四、模拟测试
- 首先我们创建两个Bean(
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryBean和MyRegularPostProcessorBean)
package com.wts.BeanFactoryPostProcessorTest; public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryBean { private String desc = "Hello World"; public String getDesc() { return desc; } public void setDesc(String desc) { this.desc = desc; } public void method(){ System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionRegistry-method():" + desc); } public MyBeanDefinitionRegistryBean() { System.out.println("我是BeanDefinitionRegistry"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
public class MyRegularPostProcessorBean { private String desc = "Hello World"; public String getDesc() { return desc; } public void setDesc(String desc) { this.desc = desc; } public void method(){ System.out.println("MyRegularPostProcessorBean-method():" + desc); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 创建Spring配置类:
SpringBeanConfig
@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.wts.BeanFactoryPostProcessorTest") public class SpringBeanConfig { /** * 这这方法返回一个MyRegularPostProcessorBean注入到BeanFactory中 * @return */ @Bean("myRegularPostProcessorBean") public MyRegularPostProcessorBean getMyRegularPostProcessorBean(){ return new MyRegularPostProcessorBean(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 创建一个我们自定义的
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和一个我们自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
@Component public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException { System.out.println("BDRPP.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry----start"); // 这里我们将我们要注入的class封装成BeanDefinition RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(MyBeanDefinitionRegistryBean.class); // 将我们的BeanDefinition注入到BeanFactory中 registry.registerBeanDefinition("myBeanDefinitionRegistryBean", beanDefinition); //第一、先调用这个注册c System.out.println("BDRPP.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry----end"); } /** * BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,因此他也有BeanFactoryPostProcessor的功能 * @param beanFactory * @throws BeansException */ @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { // 第二、当bean都完成注册后,调用这个方法 System.out.println("BDRPP.postProcessBeanFactory----start"); // 通过BeanFactory获取我们BeanDefinition BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("myBeanDefinitionRegistryBean"); // 获取Bean的成员变量 MutablePropertyValues pv = beanDefinition.getPropertyValues(); // 将desc变量的值替换 pv.addPropertyValue("desc","Hello! My name is myBeanDefinitionRegistryBean, I was modified by the BDRPP.BeanFactoryPostProcessor"); System.out.println("BDRPP.postProcessBeanFactory----end"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
/** * 这里我们自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor必须是能够注入到BeanFactory中的,否则我们上下文初始化的之后无法从IOC容器中找到他执行方法 * 这里我们用@Component注解来标记它,使IOC容器能够扫描到它并注册 */ @Component public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessors implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("BFPP.postProcessBeanFactory----start"); // 通过BeanFactory获取我们BeanDefinition BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("myRegularPostProcessorBean"); // 获取Bean的成员变量 MutablePropertyValues pv = beanDefinition.getPropertyValues(); // 将desc变量的值替换 pv.addPropertyValue("desc","Hello! My name is myBeanDefinitionRegistryBean, I was modified by the BFPP.BeanFactoryPostProcessor"); System.out.println("BFPP.postProcessBeanFactory----end"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 创建测试类
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringBeanConfig.class); MyRegularPostProcessorBean regularPostProcessor = (MyRegularPostProcessorBean)applicationContext.getBean("myRegularPostProcessorBean"); MyBeanDefinitionRegistryBean beanDefinitionRegistry = (MyBeanDefinitionRegistryBean)applicationContext.getBean("myBeanDefinitionRegistryBean"); regularPostProcessor.method(); System.out.println("----------------------------------------"); beanDefinitionRegistry.method(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 结果:
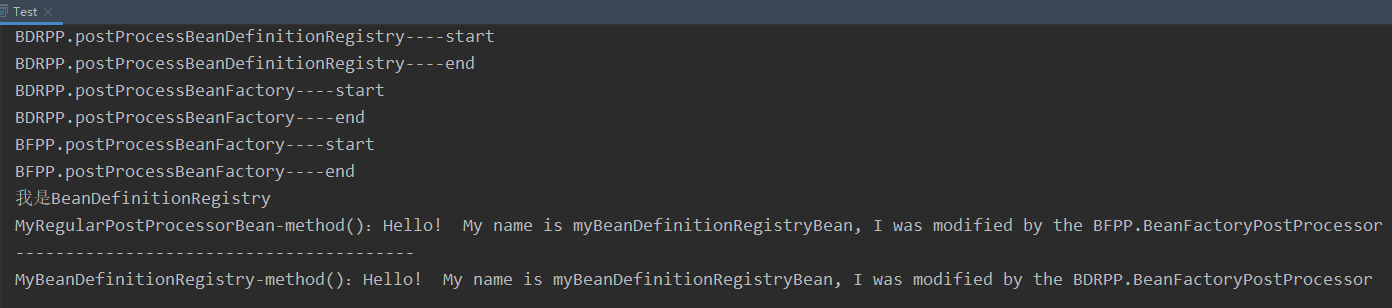
执行结果,可以看到打印出的文本已经不是我们一开始的 Hello World,而是被我们修改成了相应的内容,并且打印的文本和我们分析的主要流程一致。
到此,BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的解析和使用就已经完成了。
以上:内容部分参考
《Spring源码深度解析》
如有侵扰,联系删除。 内容仅用于自我记录学习使用。如有错误,欢迎指正 -
相关阅读:
7.26模拟赛总结
生物通路数据库收录1600+整合的经典通路
Internet Download Manager2023最新版下载器功能介绍
AI也可以算命和占卜?一定要试试这个模型
select、poll、epoll三种IO多路复用的区别
java代理
【SQL性能优化】从磁盘I/O的角度理解SQL查询的成本(优)
Jenkins集成Sonar
十四届蓝桥青少组模拟赛Python-20221108
决策中心:构建企业长期战略竞争力
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/wts563540/article/details/127629689
