-
pytorch 搭建 VGG 网络
目录
1. VGG 网络介绍
VGG16 的网络结构如图:

VGG 网络是由卷积层和池化层构成基础的CNN
它的CONV卷积层的参数全部是由 stride = 1,padding = 1
它的maxpool 最大池化层的参数都是 size = 2 , stride = 2 组成的
VGG 网络的亮点是 它的卷积层全部都是由 3*3 的小型卷积核连续进行的,通过重复进行---卷积层重叠2-4次,然后再由池化层将size 减半进行处理
VGG 网络提出了一个新的概念,就是通过叠加 3*3 的卷积核来替代大的卷积核,这样可以减少网络训练的参数。2 个3*3 卷积核连续卷积代替 5*5 的卷积核,3个 3*3 的卷积核连续卷积代替 7*7 的卷积核
再介绍怎么可以通过连续卷积小的kernel 可以替代大的kernel 之前,先介绍一下感受野
感受野就是说,卷积层的输出 对应的输入区域的范围。例如下图所示,输入是 9*9 大小的图片,经过卷积层的输出size为:output = (9 - 3 + 2 * 0) / 2 + 1 =4 4*4大小的输出,然后经过池化层变为 2*2 的输出,那也就是说最后2*2的一个像素的图像是由卷积后2*2像素的大小决定的,也是由输入图像 5*5 范围内的图像决定的。那么这里的2*2就是池化后一个像素点的感受野,5*5就是卷积后2*2 图像的感受野,也可以说输入的5*5 是卷积-池化后一个像素点的感受野
所以计算卷积后区域大小的公式:
,反过来就是感受野的计算公式
因此感受野size 的计算公式:input = (output - 1)* stride + Ksize
TIP:这里不计算pad的原因,是因为这里pad的作用大都是防止图像缩小,而这里的证明就是为了让图像通过CONV层提取关键特征的

感受野介绍完,我们就可以了解为什么连续小的卷积核等于大的卷积核的运算了
假设输出一个像素点,那么对应 3*3 卷积核的感受野是3*3大小的,再往前对应的 3*3 卷积核的感受野是5*5大小的,再往前对应的 3*3 卷积核的感受野是7*7大小的。那么如果对7*7大小的图片做卷积,用kernel_size 是7*7的话,带入公式output = (7 - 7)/2 + 1 =1 对应的也是一个像素点

因此:2 个3*3 卷积核连续卷积代替 5*5 的卷积核,3个 3*3 的卷积核连续卷积代替 7*7 的卷积核
这样做的好处就是可以减少卷积核的参数:因为3*3*3 = 27 个权重参数,7*7 =49 个权重参数。这样可能感受不到差别,但是算上输出的channel和输出的channel呢?前者就是27*C*C,而后者是49*C*C,这样参数差别就很大了。
所以,CONV卷积层的参数全部是由 stride = 1,padding = 1的情况下,连续2次3*3卷积等于5*5的卷积,连续3次3*3的卷积等于7*7的卷积
2. 搭建VGG 网络
VGG网络的结构有很多种形式,这里常用的是D,16个权重层的形式

首先,先建立一个字典文件存放不同VGG网络的配置列表
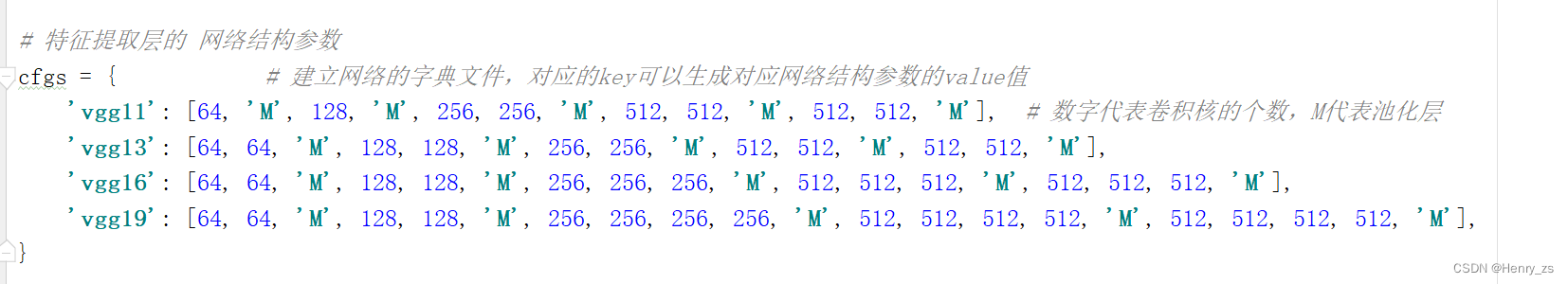
然后通过传入对应的key,建立对应的VGG网络卷积和池化层

然后,通过make_features 创建的特征提取层,可以建立最终的VGG网络

最后就是定义生成VGG网络的函数

这里vgg参数传递的顺序为:
实参里面的vgg16-->形参model_name-->cfgs取出key对应的value赋值给cfg-->cfg传递给make_feature建立卷积层-池化层layers,返回给nn.Sequential-->最后传递给VGG里面的feature生成特征提取层
生成的VGG16为:


vgg网络代码:
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch
- class VGG(nn.Module): # 定义VGG网络
- def __init__(self, features, num_classes=1000,init_weights=False): # num_classed 为分类的个数
- super(VGG, self).__init__()
- self.features = features # 特征提取层通过make_features 创建
- self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Dropout(p=0.5), # dropout 随机失活
- nn.Linear(512 * 7 * 7, 2048), # 特征提取最后的size是(512*7*7)
- nn.ReLU(True),
- nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
- nn.Linear(2048, 1024), # 原论文中,线性层全都是是4096,分为1000类
- nn.ReLU(True), # 最后的分类不能有dropout
- nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
- )
- if init_weights: # 初始化权重
- self._initialize_weights()
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.features(x) # 特征提取层
- x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1) # ddata维度为(batch_size,512,7,7),从第二个维度开始flatten
- x = self.classifier(x) # 分类层
- return x
- def _initialize_weights(self): # 随机初始化权重
- for m in self.modules():
- if isinstance(m,nn.Conv2d):
- nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight) # 初始化权重
- if m.bias is not None:
- nn.init.constant_(m.bias,0) # bias 为 0
- elif isinstance(m,nn.Linear):
- nn.init.normal_(m.weight,mean=0,std=0.01) # 高斯初始化线性层参数
- nn.init.constant_(m.bias,0) # bias 为0
- def make_features(cfg: list): # 生成特征提取层,就是VGG前面的卷积池化层
- layers = [] # 保存每一层网络结构
- in_channels = 3 # 输入图片的深度channels,起始输入是RGB 3 通道的
- for v in cfg: # 遍历配置列表 cfgs
- if v == "M": # M 代表最大池化层,VGG中max pooling的size=2,stride = 2
- layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)] # M 代表最大池化层
- else:
- conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # 数字代表卷积核的个数==输出的channels
- layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)] # 添加卷积层
- in_channels = v # 输出的channels == 下次输入的channels
- return nn.Sequential(*layers) # 解引用,将大的list里面的小list拿出来
- # 特征提取层的 网络结构参数
- cfgs = { # 建立网络的字典文件,对应的key可以生成对应网络结构参数的value值
- 'vgg11': [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'], # 数字代表卷积核的个数,M代表池化层
- 'vgg13': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
- 'vgg16': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
- 'vgg19': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
- }
- # 定义生成VGG 网络函数
- def vgg(model_name="vgg16", **kwargs): # 创建VGG网络,常用的为 VGG16 结构,如果不指定分类个数,默认是10
- cfg = cfgs[model_name] # 先定义特征提取层的结构
- model = VGG(make_features(cfg), **kwargs) # 将cfgs里面某个参数传给make_features,并且生成VGG net
- return model
- # # 测试 vgg net
- # net = vgg(model_name='vgg16', num_classes=10)
- # x = torch.randn((2,3,224,224))
- # print(net(x).shape)
- # # torch.Size([2, 10])
3. train
训练和预测的代码讲解可以参考 pytorch 搭建 LeNet 网络对 CIFAR-10 图片分类
这里用vgg11 对CIFAR10 进行训练,3个epoch
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torchvision
- import torchvision.transforms as transforms
- import torch.optim as optim
- from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
- from model import vgg # 应该导入创建网络的vgg,而不是空的框架VGG
- import json
- from tqdm import tqdm
- # 图像预处理
- data_transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
- transforms.ToTensor(),
- transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
- # 定义超参数
- BATCH_SIZE = 32
- DEVICE = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
- LEARNING_RATE = 0.0001
- WIGHT_SAVE_PATH = './VGG.pth' # 保存的路径
- EPOCHS = 3 # 训练次数
- # 载入训练集
- train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True, download=True,transform=data_transform) # 下载数据集
- train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True) # 读取数据集
- # 载入测试集
- test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False, download=True,transform=data_transform) # 下载数据集
- test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False) # 读取数据集
- # 样本个数
- num_train = len(train_dataset) # 50000
- num_test = len(test_dataset) # 10000
- # 类别和 label
- dataSetClasses = train_dataset.class_to_idx
- #{'airplane': 0, 'automobile': 1, 'bird': 2, 'cat': 3, 'deer': 4, 'dog': 5, 'frog': 6, 'horse': 7, 'ship': 8, 'truck': 9}
- class_dict = dict((val,key) for key,val in dataSetClasses.items())
- #{0: 'airplane', 1: 'automobile', 2: 'bird', 3: 'cat', 4: 'deer', 5: 'dog', 6: 'frog', 7: 'horse', 8: 'ship', 9: 'truck'}
- json_str = json.dumps(class_dict,indent=4)
- '''
- {
- "0": "airplane",
- "1": "automobile",
- "2": "bird",
- "3": "cat",
- "4": "deer",
- "5": "dog",
- "6": "frog",
- "7": "horse",
- "8": "ship",
- "9": "truck"
- }
- '''
- with open('class_indices.json','w') as json_file:
- json_file.write(json_str)
- # 定义网络
- net = vgg(model_name='vgg11', num_classes=10,init_weights=False)
- net.to(DEVICE)
- loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 定义交叉熵损失函数
- optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0001) # 定义优化器
- # train
- best_acc = 0.0
- for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
- net.train() # 开启dropout
- running_loss = 0.0
- for images,labels in tqdm(train_loader):
- images,labels = images.to(DEVICE),labels.to(DEVICE)
- optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度下降
- outputs = net(images) # 前向传播
- loss = loss_function(outputs, labels) # 计算损失
- loss.backward() # 反向传播
- optimizer.step() # 梯度更新
- running_loss += loss.item()
- # test
- net.eval() # 关闭dropout
- acc = 0.0
- with torch.no_grad():
- for x,y in tqdm(test_loader):
- x,y = x.to(DEVICE),y.to(DEVICE)
- outputs = net(x)
- predicted = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
- acc += (predicted == y).sum().item()
- accurate = acc / num_test # 计算正确率
- train_loss = running_loss / num_train # 计算损失
- print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f accuracy: %.3f' %
- (epoch + 1, train_loss, accurate))
- if accurate > best_acc:
- best_acc = accurate
- torch.save(net.state_dict(), WIGHT_SAVE_PATH)
- print('Finished Training....')
训练过程的打印信息:

4. vgg11 在CIFAR10 上的表现
代码为:
- import os
- os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK']='True'
- import torch
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- from model import vgg
- from torchvision.transforms import transforms
- from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
- import torchvision
- import json
- # 预处理
- transformer = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
- # 获取label
- try:
- json_file = open('./class_indices.json','r')
- class_indict = json.load(json_file)
- except Exception as e:
- print(e)
- # 加载模型
- DEVICE = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
- model = vgg(model_name='vgg11',num_classes=10)
- model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./VGG.pth'))
- model.to(DEVICE)
- # 加载数据
- testSet = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data',train=True,download=True,transform=transformer)
- testLoader = DataLoader(testSet,batch_size=8,shuffle=True)
- # 获取一批数据
- imgs,labels = next(iter(testLoader))
- imgs = imgs.to(DEVICE)
- # show
- with torch.no_grad():
- model.eval()
- prediction = model(imgs) # 预测
- prediction = torch.max(prediction, dim=1)[1]
- prediction = prediction.data.cpu().numpy()
- plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
- for i,(img,label) in enumerate(zip(imgs,labels)):
- x = np.transpose(img.data.cpu().numpy(),(1,2,0)) # 图像
- x = x / 2 + 0.5 # 去 normalization
- y = label.numpy().item() # label
- plt.subplot(2,4,i+1)
- plt.imshow(x)
- plt.title('R:{},P:{}'.format(class_indict[str(y)],class_indict[str(prediction[i])]))
- plt.show()
在训练集的表现:

在测试集的表现:

5. 随机预测一张图片
- import os
- os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK']='True'
- import torch
- from PIL import Image
- from torchvision import transforms
- from model import vgg
- import json
- data_transform = transforms.Compose(
- [transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
- transforms.ToTensor(),
- transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
- img = Image.open('./dog.jfif') # 载入图片
- img = data_transform(img) # 预处理
- img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0) # 增加维度
- try:
- json_file = open('./class_indices.json','r')
- class_indict = json.load(json_file)
- # {'0': 'airplane', '1': 'automobile', '2': 'bird', '3': 'cat', '4': 'deer', '5': 'dog', '6': 'frog', '7': 'horse', '8': 'ship', '9': 'truck'}
- except Exception as e:
- print(e)
- model = vgg(model_name="vgg11", num_classes=10)
- model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./VGG.pth')) # 读取网络参数
- model.eval() # 预测的时候不需要随机失活
- with torch.no_grad():
- output = model(img)
- predict = torch.max(output, dim=1)[1]
- predict = predict.data.cpu().numpy()
- print(class_indict[str(predict.item())])
输入图像:

预测结果:

-
相关阅读:
Apache InLong 1.2 单机部署问题记录
Netty
【Java集合】集合是什么?为什么要用集合?
vue3利用 a 标签,文件流,JSZip 压缩包,实现文件下载
[免费专栏] Android安全之Xposed插件开发【从零手把手带】教程
Vue 同步组件和异步组件的差别
JavaWeb项目部署到服务器并连接本地数据库(超详细!)
Golang GMP调度模型:实现高效协程调度和执行
linux安装edge时出现dpkg依赖问题
4.RabbitMQ 消息确认机制
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44886601/article/details/127618573
