-
LeetCode 24.两两交换链表中的节点, 19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点 面试题 02.07. 链表相交 142.环形链表II
文章目录
24.两两交换链表中的节点
题目:
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例1:
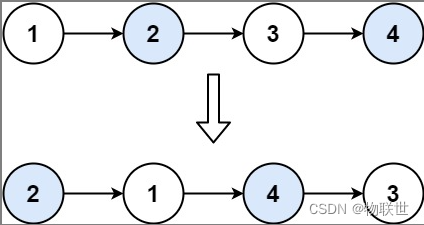
输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]- 1
- 2
示例2:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]- 1
- 2
示例3:
输入:head = [1] 输出:[1]- 1
- 2
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 100
c++ 代码实现
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) { ListNode * dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead->next = head; ListNode * cur = dummyHead; while (cur->next != nullptr && cur->next->next != nullptr) { // 先保存好,交换的值 ListNode *tmp = cur->next; // 下一次的交换节点 ListNode * tmp1 = cur->next->next->next; // 开始交换 cur->next = cur->next->next; cur->next->next = tmp; cur->next->next->next = tmp1; // 移动两位 cur = cur->next->next; } return dummyHead->next; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
python 代码实现
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]: dummy = ListNode(0) dummy.next = head cur = dummy while cur.next != None and cur.next.next != None: tmp = cur.next tmpNext = cur.next.next.next cur.next = cur.next.next cur.next.next = tmp cur.next.next.next = tmpNext cur = cur.next.next return dummy.next- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第
n个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。示例1:
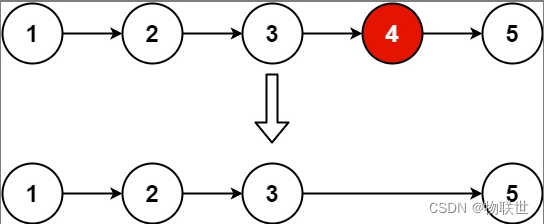
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5]- 1
- 2
示例2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1 输出:[]- 1
- 2
示例3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1 输出:[1]- 1
- 2
提示:
- 链表中结点的数目为
sz 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
c++ 代码实现
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) { ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0, head); ListNode * slow = dummy; ListNode * fast = head; // 先遍历fast , 移动n位置 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { fast = fast->next; } // 同时遍历,直到fast为空,表明slow为倒数个节点 while (fast != nullptr) { fast = fast->next; slow = slow->next; } // 删除节点 slow->next = slow->next->next; return dummy->next; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
python代码实现
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]: dummy = ListNode(0) dummy.next = head slow = dummy fast = head for i in range(n): fast = fast.next while fast != None: slow = slow.next fast = fast.next slow.next = slow.next.next return dummy.next- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
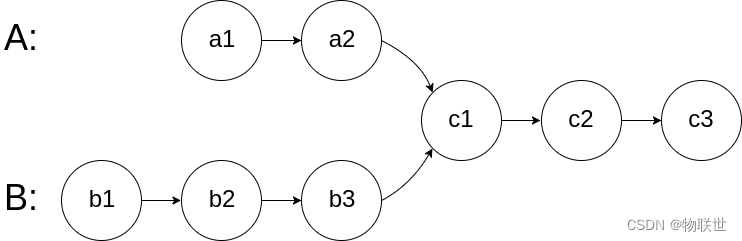
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例1:
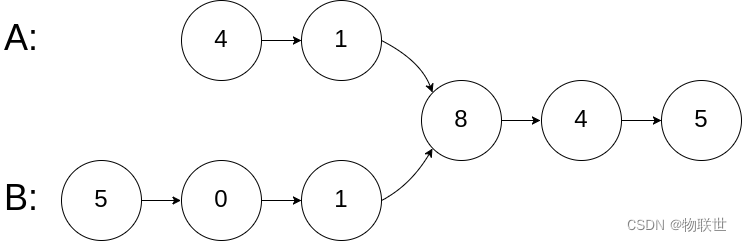
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Intersected at '8' 解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。 在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
示例2:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5yQNGE7i-1667183283625)(./img/160_example_2.png)]
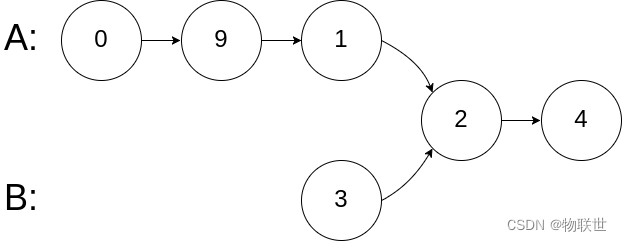
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 输出:Intersected at '2' 解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。 在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
示例3
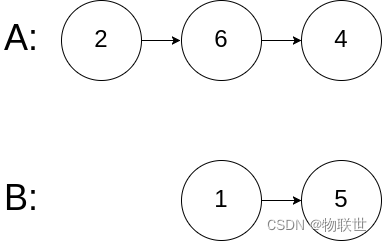
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 输出:null 解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。 由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。 这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
提示:
listA中节点数目为mlistB中节点数目为n0 <= m, n <= 3 * 1041 <= Node.val <= 1050 <= skipA <= m0 <= skipB <= n- 如果
listA和listB没有交点,intersectVal为0 - 如果
listA和listB有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA + 1] == listB[skipB + 1]
**进阶:**你能否设计一个时间复杂度
O(n)、仅用O(1)内存的解决方案?c++ 代码实现
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { if (headA == nullptr || headB == nullptr) return nullptr; ListNode * a = headA; ListNode * b = headB; while ( a != b ) { a = a == nullptr ? headB : a->next; b = b == nullptr ? headA : b->next; } return a; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
python 代码实现
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution: def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode: if (headA == None or headB == None): return None a = headA b = headB while (a != b): if (a == None): a = headB else: a = a.next if (b == None): b = headA else: b = b.next return a- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
142. 环形链表 II
题目:
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例1:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-kVx9FLeR-1667183283627)(./img/ring_1.png)]
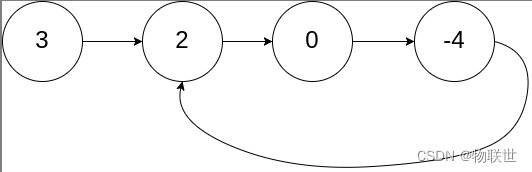 [[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[
[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[[输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。- 1
- 2
- 3
示例2
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-muvxffVF-1667183283627)(./img/ring_2.png)]
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。- 1
- 2
- 3
示例3:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-LFIGc3ZF-1667183283628)(./img/ring_3.png)]
输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:返回 null 解释:链表中没有环。- 1
- 2
- 3
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围在范围
[0, 104]内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105pos的值为-1或者链表中的一个有效索引
**进阶:**你是否可以使用
O(1)空间解决此题?c++代码实现
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { ListNode * fast = head; ListNode * slow = head; while (fast->next != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; // 当slow 和 fast 相遇,证明有环 if (slow == fast) { // 两者同时移动,直到相遇 ListNode * index1 = fast; ListNode * index2 = head; while (index1 != index2) { index1 = index1->next; index2 = index2->next; } return index2; } } return nullptr; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
python 代码实现
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution: def detectCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]: slow = head fast = head while fast!= None and fast.next != None: slow = slow.next fast = fast.next.next if slow == fast: index1 = fast index2 = head while index1 != index2: index1 = index1.next index2 = index2.next return index2 return None- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
-
相关阅读:
安装项目运行环境(python依赖包+allure)
react-native webstorm 无法启动 Android 模拟器
基于罪名法务智能知识图谱(含码源):基于280万罪名预测、20W法务问答与法律资讯问答功能
倒数 3 天|RocketMQ 能力全景图即将发布,定义下一代消息队列未来方向
SpringBoot打包的两种方式 - jar方式 和 war 方式
浅谈基于LoRa技术下智能建筑能耗管理系统的分析与设计
【MYSQL】内置函数
esp8266-01固件信息
网上买手机卡,过来人给你总结了几条经验,得注意了!
矩阵分析与应用+张贤达
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35200479/article/details/127610709
