-
超像素分割 & SLIC算法 & 使用示例
参考博客
介绍超像素分割 & SLIC算法
SLIC超像素分割详解(一):简介_计算机视觉life的博客-CSDN博客_slic超像素分割
机器学习:simple linear iterative clustering (SLIC) 算法_Matrix_11的博客-CSDN博客_简单线性迭代聚类算法
图像处理: 超像素(superpixels)分割 SLIC算法_haoji007的博客-CSDN博客_超像素分割
如何使用SLIC算法
图像分割:Python的SLIC超像素分割_程序媛一枚~的博客-CSDN博客_python slic
Python实现超像素分割_技术挖掘者的博客-CSDN博客_python 超像素分割
python 自带slic代码分析_北落师门XY的博客-CSDN博客_python slic
具体示例
SLIC超像素分割并保存分割得到的超像素块,python代码_LarkMi的博客-CSDN博客_python超像素分割代码
超像素分割, 并获取每一个分区 - 默盒 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
论文&代码
SLIC Superpixels ‒ IVRL ‐ EPFL
http://github.com/laixintao/slic-python-implementation
https://github.com/LarkMi/SLIC
徐其钰/MyProject - Gitee.com (超像素分割、边缘检测)
示例 SLIC分割图

标题示例来自 SLIC Superpixels ‒ IVRL ‐ EPFL 
“怎么不蒜呢”(无恶意.jpg 超像素分割
简介
超像素概念是2003年Xiaofeng Ren提出和发展起来的图像分割技术,是指具有相似纹理、颜色、亮度等特征的相邻像素构成的有一定视觉意义的不规则像素块。它利用像素之间特征的相似性将像素分组,用少量的超像素代替大量的像素来表达图片特征,很大程度上降低了图像后处理的复杂度,所以通常作为分割算法的预处理步骤。在像素网格上按照一定的方式进行像素局部分组,可得到超像素。
它已经广泛用于图像分割、姿势估计、目标跟踪、目标识别等计算机视觉应用。几种常见的超像素分割方法及其效果对比如下:

Graph-based NCut Turbopixel Quick-shift Graph-cut a Graph-cut b SLIC 
使用SLIC的分割示例 其中,SLIC(simple linear iterativeclustering),即简单的线性迭代聚类。它是2010年提出的一种思想简单、实现方便的算法,将彩色图像转化为CIELAB颜色空间和XY坐标下的5维特征向量,然后对5维特征向量构造距离度量标准,对图像像素进行局部聚类的过程。SLIC算法能生成紧凑、近似均匀的超像素,在运算速度,物体轮廓保持、超像素形状方面具有较高的综合评价。
SLIC主要优点
计算效率高、含有更多感知(有意义的)信息、过度分割可减少像素损失、超像素上表示图形更加高效。
- 生成的超像素如同细胞一般紧凑整齐,邻域特征比较容易表达。这样基于像素的方法可以比较容易的改造为基于超像素的方法。
- 不仅可以分割彩色图,也可以兼容分割灰度图。
- 需要设置的参数非常少,默认情况下只需要设置一个预分割的超像素的数量。
- 相比其他的超像素分割方法,SLIC在运行速度、生成超像素的紧凑度、轮廓保持方面都比较理想。
Lab颜色空间
在介绍SLIC之前,插播一下Lab颜色空间的介绍。Lab色彩模型是由亮度(L)和有关色彩的a, b三个要素组成。L表示亮度(Luminosity),L的值域由0(黑色)到100(白色)。a表示从洋红色至绿色的范围(a为负值指示绿色而正值指示品红),b表示从黄色至蓝色的范围(b为负值指示蓝色而正值指示黄色)。
Lab颜色空间的优点:
- 不像RGB和CMYK色彩空间,Lab 颜色被设计来接近人类生理视觉。它致力于感知均匀性,它的 L 分量密切匹配人类亮度感知。因此可以被用来通过修改 a 和 b 分量的输出色阶来做精确的颜色平衡,或使用 L 分量来调整亮度对比。这些变换在 RGB 或 CMYK 中是困难或不可能的。
- 因为 Lab 描述的是颜色的显示方式,而不是设备(如显示器、打印机或数码相机)生成颜色所需的特定色料的数量,所以 Lab 被视为与设备无关的颜色模型。
- 色域宽阔。它不仅包含了RGB,CMYK的所有色域,还能表现它们不能表现的色彩。人的肉眼能感知的色彩,都能通过Lab模型表现出来。
另外,Lab色彩模型的绝妙之处还在于它弥补了RGB色彩模型色彩分布不均的不足,因为RGB模型在蓝色到绿色之间的过渡色彩过多,而在绿色到红色之间又缺少黄色和其他色彩。如果我们想在数字图形的处理中保留尽量宽阔的色域和丰富的色彩,最好选择Lab。
SLIC具体步骤
- 初始化种子点(聚类中心):按照设定的超像素个数,在图像内均匀的分配种子点。假设图片总共有 N 个像素点,预分割为 K 个相同尺寸的超像素,那么每个超像素的大小为N/ K ,则相邻种子点的距离(步长)近似为S=sqrt(N/K)。
- 在种子点的n*n邻域内重新选择种子点(一般取n=3)。具体方法为:计算该邻域内所有像素点的梯度值,将种子点移到该邻域内梯度最小的地方。这样做的目的是为了避免种子点落在梯度较大的轮廓边界上,以免影响后续聚类效果。
- 在每个种子点周围的邻域内为每个像素点分配类标签(即属于哪个聚类中心)。和标准的k-means在整张图中搜索不同,SLIC的搜索范围限制为2S*2S,可以加速算法收敛,如下图。在此注意一点:期望的超像素尺寸为S*S,但是搜索的范围是2S*2S。

- 距离度量。包括颜色距离和空间距离。对于每个搜索到的像素点,分别计算它和该种子点的距离。距离计算方法如下:

其中,dc代表颜色距离,ds代表空间距离,Ns是类内最大空间距离,定义为Ns=S=sqrt(N/K),适用于每个聚类。最大的颜色距离Nc既随图片不同而不同,也随聚类不同而不同,所以取一个固定常数m(取值范围[1,40],一般取10)代替。最终的距离度量D'。
由于每个像素点都会被多个种子点搜索到,所以每个像素点都会有一个与周围种子点的距离,取最小值对应的种子点作为该像素点的聚类中心。
- 迭代优化。理论上上述步骤不断迭代直到误差收敛(可以理解为每个像素点聚类中心不再发生变化为止),实践发现10次迭代对绝大部分图片都可以得到较理想效果,所以一般迭代次数取10。
- 增强连通性。经过上述迭代优化可能出现以下瑕疵:出现多连通情况、超像素尺寸过小,单个超像素被切割成多个不连续超像素等,这些情况可以通过增强连通性解决。主要思路是:新建一张标记表,表内元素均为-1,按照“Z”型走向(从左到右,从上到下顺序)将不连续的超像素、尺寸过小超像素重新分配给邻近的超像素,遍历过的像素点分配给相应的标签,直到所有点遍历完毕为止。
伪代码

SLIC代码使用
直接调库
- from skimage.segmentation import slic,mark_boundaries
- segments = slic(image, n_segments=60, compactness=10)
- # 参数说明:
- # n_segments: 分割块的个数。可能最后分割出的块数与实际设置并不一样,可能是slic算法做了后续处理,将小的超像素合并到大的超像素中。
- # compactness:分割块的边界是否压缩,压缩会使分割快的边沿更光滑。
具体SLIC代码附在文章最后。
超像素分割
例1
项目介绍
SLIC超像素分割并保存分割得到的超像素块,python代码_LarkMi的博客-CSDN博客_python超像素分割代码
完整代码
GitHub - LarkMi/SLIC: SLIC分割并存储分割后的超像素块
- # https://github.com/LarkMi/SLIC/blob/main/SLIC.py
- import skimage
- from skimage.segmentation import slic,mark_boundaries
- from skimage import io
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- from PIL import Image, ImageEnhance
- import numpy as np
- import cv2
- #
- # np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
- path = 'C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\SLIC\\'
- img_name = 'test.png'
- img = io.imread(path + img_name,as_gray=True) #as_gray是灰度读取,得到的是归一化值
- segments = slic(img, n_segments=10, compactness=0.2,start_label = 1)#进行SLIC分割
- out=mark_boundaries(img,segments)
- out = out*255 #io的灰度读取是归一化值,若读取彩色图片去掉该行
- img3 = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(out))
- img3.show()
- seg_img_name = 'seg.png'
- img3.save(path +'\\' +seg_img_name)#显示并保存加上分割线后的图片
- maxn = max(segments.reshape(int(segments.shape[0]*segments.shape[1]),))
- for i in range(1,maxn+1):
- a = np.array(segments == i)
- b = img * a
- w,h = [],[]
- for x in range(b.shape[0]):
- for y in range(b.shape[1]):
- if b[x][y] != 0:
- w.append(x)
- h.append(y)
- c = b[min(w):max(w),min(h):max(h)]
- c = c*255
- d = c.reshape(c.shape[0],c.shape[1],1)
- e = np.concatenate((d,d),axis=2)
- e = np.concatenate((e,d),axis=2)
- img2 = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(e))
- img2.save(path +'\\'+str(i)+'.png')
- print('已保存第' + str(i) + '张图片')
- wid,hig = [],[]
- img = io.imread(path+'\\'+seg_img_name)
- for i in range(1,maxn+1):
- w,h = [],[]
- for x in range(segments.shape[0]):
- for y in range(segments.shape[1]):
- if segments[x][y] == i:
- w.append(x)
- h.append(y)
- font=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX#使用默认字体
- #print((min(w),min(h)))
- img=cv2.putText(img,str(i),(h[int(len(h)/(2))],w[int(len(w)/2)]),font,1,(255,255,255),2)#添加文字,1.2表示字体大小,(0,40)是初始的位置,(255,255,255)表示颜色,2表示粗细
- img = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(img))
- img.show()
- img.save(path +'\\'+seg_img_name+'_label.png')
效果展示:

原图,超像素分割图,下图分割后的标识区域 
各个分割区域 例2
超像素分割, 并获取每一个分区 - 默盒 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
- from skimage.segmentation import slic
- from skimage.segmentation import mark_boundaries
- from skimage.util import img_as_float
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import numpy as np
- import cv2
- # args
- args = {"image": './hand_0.png'}
- # load the image and apply SLIC and extract (approximately)
- # the supplied number of segments
- image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
- segments = slic(img_as_float(image), n_segments=100, sigma=5)
- # show the output of SLIC
- fig = plt.figure('Superpixels')
- ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
- ax.imshow(mark_boundaries(img_as_float(cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)), segments))
- plt.axis("off")
- plt.show()
- print("segments:\n", segments)
- print("np.unique(segments):", np.unique(segments))
- # loop over the unique segment values
- for (i, segVal) in enumerate(np.unique(segments)):
- # construct a mask for the segment
- print("[x] inspecting segment {}, for {}".format(i, segVal))
- mask = np.zeros(image.shape[:2], dtype="uint8")
- mask[segments == segVal] = 255
- # show the masked region
- cv2.imshow("Mask", mask)
- cv2.imshow("Applied", np.multiply(image, cv2.cvtColor(mask, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) > 0))
- cv2.waitKey(0)
例3
项目介绍 & 效果展示
python 超像素分割_Afleve的博客-CSDN博客_python超像素
- 向Cluster类添加了label属性,以便于标记k-means算法得出来的结果
- 对SLICProcessor类方法save_current_image中添加了增加边界的部分,可生成类似3||4.png图像
- 添加了新的类方法generate_result()有一个用户参数K,为设置的Kmeans算法的簇数,根据簇数选择区域合并
- 原码中因为图片通道数不同无法读取同时读取jpg与png图像,小做改动已可以适应。

1:超像素分割图;2:加边界;3:Kmeans聚类后的图;4:原图加边界;5:原图 代码
opencv/超像素分割 · 徐其钰/MyProject - 码云 - 开源中国 (gitee.com)
例4
Python实现超像素分割_技术挖掘者的博客-CSDN博客_python 超像素分割
- # import the necessary packages
- from skimage.segmentation import slic
- from skimage.segmentation import mark_boundaries
- from skimage.util import img_as_float
- from skimage import io
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- # load the image and convert it to a floating point data type
- image = img_as_float(io.imread("image.jpg"))
- # loop over the number of segments
- for numSegments in (100, 200, 300):
- # apply SLIC and extract (approximately) the supplied number
- # of segments
- segments = slic(image, n_segments = numSegments, sigma = 5)
- # show the output of SLIC
- fig = plt.figure("Superpixels -- %d segments" % (numSegments))
- ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
- ax.imshow(mark_boundaries(image, segments))
- plt.axis("off")
- # show the plots
- plt.show()
效果展示:通过超像素分割我们可以将整个图像划分为含有固定个超像素组的感知块,具体如图中的黄色块所示。

边缘检测
- %% Clean up
- clear all
- close all
- clc
- %Generate image
- img = imread('test.jpg');
- img = double(rgb2gray(img));
- %Invert circle brightness
- img = abs(img-1);
- %Blur original image with Gaussian kernel with a blur width (standard
- %deviaion) of 0.9 pixels
- BlurGaussian = 0.9;
- G = fspecial('Gaussian',5,BlurGaussian);
- img = imfilter(img,G,'replicate');
- %Blurring occurs from quantization and from Gaussian
- BlurQuantization = 1/sqrt(12);
- BlurWidth = sqrt( BlurQuantization^2 + BlurGaussian^2);
- %% Create mask
- %Only consider edges on columns 35-50
- M = true(size(img));
- %% Perform edge localization
- %Get pixel-level edges with Sobel operator
- [E] = edge(img,'sobel');
- %Refine to subpixel accuracy
- edges = SubpixelEdge(img,E,BlurWidth,M);
- %% Plot results
- %Show image
- figure(1);
- imshow(uint8(img)),hold on, axis on;
- plot(edges.u,edges.v,'co')
- figure(2);
- imshow(uint8(M)),hold on, axis on;
- plot(edges.u,edges.v,'co')
- % p1 = [edges.u(1), edges.v(1), 0];
- % p2 = [edges.u(100), edges.v(100), 0];
- % p3 = [edges.u(500), edges.v(500), 0];
- % p = CircleCenter(p1, p2, p3);
- %
- % disp('当前圆的半径为%d', p);
- x=edges.u;
- y=edges.v;
- [R,x0,y0]=circ(x,y,edges.NumPts-1);
- disp(['第一个圆的半径是: ' num2str(R),' mm' ]);
- disp(['第一个圆的圆心坐标:( ' num2str(x0) ,',',num2str(y0),')']);
- plot(x0, y0, 'gx');
效果展示:超像素可以准确的检测出齿轮的边缘信息,包括它的内环和外环信息。

SLIC超像素分割算法的应用
应用广泛
详见 superpixels ‒ IVRL ‐ EPFL ,里面列举很多使用超像素算法的论文工作。包括有视频检测、无人机数据对齐、语义分割、目标跟踪、3d重建、数据增强、水印恢复,等等。
IEEE TIP 2014年 的《Robust superpixeltracking》,基于超像素的方法解决外观发生剧烈变化的物体追踪问题。
ICCV 2009年 的《Class segmentation andobject localization with superpixel neighborhoods》,从像素级别的分割迁移到超像素级别的分割。
CVPR 2013年的《Improving an objectdetector and extracting regions using superpixels》,把样本中超像素级的特征通过k-means聚类为超像素级词袋,再结合SVM对难分类样本进一步分类。
IET 2014年的 《Video object segmentation with shape cue based on spatiotemporal superpixel neighbourhood》,用于视频前景分割。
JEI 2015年的《Improving video foreground segmentation with an object-like pool》,在无监督条件下对序列图像中运动目标进行精细的分割。
ECCV 2022年 的 《SPSN: Superpixel Prototype Sampling Network for RGB-D Salient Object Detection》,用超像素分割做显著性检测。
如何设置待分割超像素的数目?
使用超像素对图像进行分割时,设置的超像素数目K比较重要:如果K比较小,每个超像素尺寸会比较大,这样超像素对边界的保持就会变差,如果K比较大,每个超像素的尺寸会比较小,那么会出现类似“过拟合”现象,超像素的形状会变得非常不规则,邻域关系很难保持,而且数目也比较多。

不同尺寸的超像素分割结果对比。
(a)原图,超像素尺寸:(b)100X100,(c)30X30,(d)8X8具体分割数目K和具体应用有关,比如如果对上图做主要人物(左边的小魔女)分割的话,100X100大小的超像素就够了,但是如果对两个骑自行的人物也进行分割的话,需要使用30X30的尺寸,但是此时较小人物的分割精度不高,如果有更高要求,则需要使用8X8甚至更小的尺寸。尺寸也需要根据不同场合选择。
SLIC代码细节
封装工具、C++、Matlab代码:SLIC Superpixels ‒ IVRL ‐ EPFL
1、设定期望分割的超像素数目,打开图片。将彩色RGB图片转换为LAB空间及x、y像素坐标共5维空间。
2、DetectLabEdges。求图片中所有点的梯度=dx+dy.其中
dx=(l(x-1)-l(x+1))*(l(x-1)-l(x+1))+(a(x-1)-a(x+1))*(a(x-1)-a(x+1))+(b(x-1)-b(x+1))*(b(x-1)-b(x+1));
dy=(l(y-1)-l(y+1))*(l(y-1)-l(y+1))+(a(y-1)-a(y+1))*(a(y-1)-a(y+1))+(b(y-1)-b(y+1))*(b(y-1)-b(y+1));
3、GetLABXYSeeds_ForGivenK。给定了要分割的超像素总数K,根据LABXY信息获得种子点。
1) 超像素的种子点间步长Step=sqrt(N/K)。初始化种子点。按照步长均匀播撒种子点,初始化后种子点是均匀分布的(图1中的红色点)。
2) PerturbSeeds。扰乱种子点。在每个种子点的3*3邻域内,计算该种子点的8个邻域内像素点的Lab颜色梯度(同上述步骤2),分别与初始种子点梯度进行比较,取梯度值最小(最“平坦”)的点,并记录其LABXY信息作为新的种子点(图1中绿色点为扰乱后的新种子点)。

扰乱种子点图示 4、超像素的步长Step=sqrt(N/K)+2。加了一个小偏置2是为了避免Step太小,造成超像素太密集的情况。
5、PerformSuperpixelSegmentation_VariableSandM。对于每个超像素,最大的颜色距离M取值范围[1,40],一般取10。最大空间距离取步长为Step。
- 1) 搜索范围2step* 2step,即设置offset=step。 在步长较短时(step<10)可以扩展offset=step*1.5作为搜索范围。
- 2) 初始化distlab、distxy、distvec为无穷大。maxlab初始化为10*10,maxxy初始化为step*step。distlab代表某点与种子点的lab颜色空间距离,计算如下:distlab(i)=(l-kseedsl(n))*(l-kseedsl(n))+(a-kseedsa(n))*(a-kseedsa(n))+(b-kseedsb(n))*(b-kseedsb(n));distxy代表某点与种子点的空间坐标距离,计算如下:distxy(i)=(x-kseedsx(n))*(x-kseedsx(n))+(y-kseedsy(n))*(y-kseedsy(n));dist代表某点与种子点的综合距离(归一化的颜色距离+空间距离),计算如下:dist=distlab/( maxlab)+ distxy/(maxxy);在此提醒一下:如果将C++程序转为matlab代码时特别要注意数据类型。uint16类型变量减去double类型变量的结果是uint16类型,所以如果后者值大于前者,结果就为0。此处容易出错,需要强制类型转换。
- 3) 计算搜索区域内每个点离种子点的距离dist,并将搜索区域内每个点离种子点的距离保存在distvec中。因为某点可能位于多个种子点的搜索区域,所以最后保存的是离相邻种子点最近的距离,并将该像素标号为最近种子点相同的标号。同一个超像素内所有像素的标号相同
- 4) 计算每个新超像素内所有像素的labxy均值和坐标重心。将坐标重心作为该超像素的新种子点位置。
- 5) 上述步骤2)到4)重复迭代10次。
6、EnforceLabelConnectivity。该函数主要有几个作用:保证同一个超像素都是单连通区域;去掉尺寸过小的超像素;避免单个超像素被切割的情况。
- 1) 先计算超像素理想面积大小:SUPSZ = sz/K = N/K;
- 2) 有两种标号向量:上一步骤中得到的旧标号向量labels(即步骤5中得到的klabels),但其存在多连通,过小超像素等问题,需要优化。新标号向量nlabels,初始化值全为-1。
- 3) 首先选择每个超像素的起始点(左上角的第一个点),起始点判断条件:a) 按照从左到右,从上到下的“Z”型顺序查找。b)该点在新标号向量nlabels中未被标记过(值为-1)。将其坐标保存在xvec[0],yvec[0]中。
- 4) 记录前一个相邻超像素的标号值adjlabel。判断条件:a)在步骤3中起始点的四邻域。b)在新标号向量nlabels中被标记过(标号大于0)。记录adjlabel的目的是:如果当前超像素尺寸过小,将当前超像素标号全部用adjlabel代替。即合并到前一个相邻超像素,参考下面步骤6)。
- 5) 扩展当前超像素。首先选择起始点作为当前操作的中心点,然后对其四邻域进行判断是否属于该超像素成员。判断条件:a) 该点在新标号向量nlabels中未被标记过(值为-1);b)该点n和当前操作中心点c在旧标号向量中标号一致,即labels(n)= labels(c),可以理解为原先就是属于同一个超像素的成员。如果判断是超像素的新成员,那么把该新成员作为新的操作中心点,循环直到找不到新成员为止。
- 6) 如果新超像素大小小于理想超像素大小的一半(可以根据需要自己定义),将该超像素标号用前一个相邻超像素的标号值adjlabel代替,并且不递增标号值。
- 7) 迭代上述步骤3)到6)直到整张图片遍历结束。
7、绘制分割结果,退出窗口。

SLIC超像素分割结果,蓝色的点表示最终超像素的种子点。 SLIC Superpixels Compared to State-of-the-art Superpixel Methods,TPAMI 2012
超像素算法将像素组合成感知有意义的原子区域( atomic regions),其可以用于替换像素网格的刚性结构。它们捕获图像冗余,提供计算图像特征的方便原语( primitive ),并且大大降低了后续图像处理任务的复杂性。用下面三点来判断算法的优劣性:
- 超像素应当良好地粘附到图像边界。
- 当作为预处理步骤用于降低的计算复杂度时,超像素应当快速计算,存储 器效率高且易于使用。
- 当用于分割目的时,超像素应当增加速度并提高结果的质量。
论文列举其他超像素方法,再提出SLIC算法进行对比。
用于生成超像素的算法可以大致分类为基于图或梯度上升的方法。

SLIC与现有超像素算法的对比。 基于图形的方法
基于图形的超像素生成方法将每个像素视为图中的节点。两个节点之间的边权重与相邻像素之间的相似性成比例。超像素通过最小化图中定义的成本函数来创建。
NC05,归一化切割算法递归地使用轮廓和纹理线索分割图像中的所有像素的图形,从而全局性地最小化在分割边界处的边缘定义的成本函数。它产生非常规则,视觉上令人愉快的超像素。然而,NC05的边界粘附相对较差,并且它是方法中最慢的(特别是对于大图像),尽管试图加速的算法存在。NC05具有
 的复杂度,其中N是像素的数量。
的复杂度,其中N是像素的数量。GS04,提出了一种替代的基于图形的方法,已被应用于生成超像素。它将像素作为图的节点,使得每个超像素是组成像素的最小生成树。GS04在实践中很好地粘附到图像边界,但是产生具有非常不规则的尺寸和形状的超像素。它的复杂度是
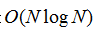 ,在实践中速度很快。然而,它不提供对超像素的量或其紧凑性的明确控制。
,在实践中速度很快。然而,它不提供对超像素的量或其紧凑性的明确控制。SL08,提出了一种通过确定将图像分割成更小的垂直或水平区域的最佳路径或接缝来生成符合网格的超像素的方法。使用类似于SeamCarving的图切割方法找到最佳路径。复杂的是
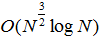 ,但这并不考虑预先计算的边界图,这强烈影响输出的质量和速度。
,但这并不考虑预先计算的边界图,这强烈影响输出的质量和速度。GCa10和GCb10。使用纹理合成工作的全局优化方法。通过将重叠的图像块拼接在一起来获得超像素,使得每个像素仅属于重叠区域中的一个。这个方法有两个变种,一个用于生成紧凑超像素(GCa10),一个用于恒定强度超像素(GCb10)。
基于梯度上升的方法
从粗略的像素初始聚类开始,梯度上升法迭代地修改聚类,直到满足一些收敛标准以形成超像素。
MS02,平均偏移,用于定位密度函数的局部最大值的迭代模式寻找过程被应用于图像的颜色或强度特征空间中的第一模式。会聚到相同模式的像素定义超像素。MS02是一种较旧的方法,产生不均匀尺寸的不规则形状的超像素。它是复杂度
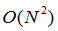 ,使其相对较慢,并且不提供对超像素的量,尺寸或紧密度的直接控制。
,使其相对较慢,并且不提供对超像素的量,尺寸或紧密度的直接控制。QS08,也使用模式查找分割方案。它使用medoid移位过程初始化分割。然后将特征空间中的搜索点移动到最近的邻居,从而增加Parzen密度估计。虽然它具有相对良好的边界粘附,但是QS08的运行速度相当缓慢,具有复杂度
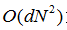 (d是一个小常数)。而且QS08不允许对超像素的大小或数量的显式控制。
(d是一个小常数)。而且QS08不允许对超像素的大小或数量的显式控制。WS91,从局部最小值开始执行梯度上升以产生分水岭,和分离集水盆地的线条。所得到的超像素在尺寸和形状上通常是高度不规则的,并且不表现出良好的边界粘附。具有
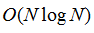 的复杂度),但不提供对超像素量或其紧凑性的控制。
的复杂度),但不提供对超像素量或其紧凑性的控制。TP09,使用基于水平集的几何流动逐渐扩大一组种子位置。几何流依赖于局部图像梯度,目的是在图像平面上规则地分布超像素。与WS91不同,TP09超像素被约束为具有均匀的尺寸,紧凑性和边界粘附。TP09依赖于不同复杂度的算法,但在实践中,如作者所声称的,具有大约
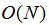 的复杂度,是所检查的最慢的算法之一,并且表现出相对较差的边界粘附。
的复杂度,是所检查的最慢的算法之一,并且表现出相对较差的边界粘附。SLIC
比现有方法更快,更高的记忆效率,展示了目前最优的边界依从性,并提高了分割算法的性能。简单线性迭代聚类(SLIC)采用K均值算法生成超像素,相较与其他算法具有两个重要的区别:
1)通过将搜索空间限制为与超像素大小成比例的区域,显着地减少了优化中的距离计算的数量。这降低了像素数N的线性复杂度,并且与超像素k的数量无关。
2)加权距离度量组合颜色和空间接近度,同时提供对超像素的尺寸和紧凑性的控制。SLiC使用简单,其唯一的参数是所需的超像素数,是产生超体素的为数不多的方法之一。最后,在现有的方法中,SLIC的独特之处在于它能够通过m来控制超像素紧密性和边界粘着性之间的权衡。
python中的slic函数
- def slic(image, n_segments=100, compactness=10., max_iter=10, sigma=0,
- spacing=None, multichannel=True, convert2lab=None,
- enforce_connectivity=True, min_size_factor=0.5, max_size_factor=3,
- slic_zero=False):
- """Segments image using k-means clustering in Color-(x,y,z) space.
- Parameters
- ----------
- image : 2D, 3D or 4D ndarray
- Input image, which can be 2D or 3D, and grayscale or multichannel
- (see `multichannel` parameter).
- n_segments : int, optional
- The (approximate) number of labels in the segmented output image.
- compactness : float, optional
- 控制颜色和空间之间的平衡,约高越方块,和图关系密切,最好先确定指数级别,再微调
- Balances color proximity and space proximity. Higher values give
- more weight to space proximity, making superpixel shapes more
- square/cubic. In SLICO mode, this is the initial compactness.
- This parameter depends strongly on image contrast and on the
- shapes of objects in the image. We recommend exploring possible
- values on a log scale, e.g., 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100, before
- refining around a chosen value.
- max_iter : int, optional
- 最大k均值迭代次数
- Maximum number of iterations of k-means.
- sigma : float or (3,) array-like of floats, optional
- 图像每个维度进行预处理时的高斯平滑核宽。若给定为标量值,则同一个值运用到各个维度。0意味
- 着不平滑。如果“sigma”是标量的,并且提供了手动体素间距,则自动缩放它(参见注释部分)。
- Width of Gaussian smoothing kernel for pre-processing for each
- dimension of the image. The same sigma is applied to each dimension in
- case of a scalar value. Zero means no smoothing.
- Note, that `sigma` is automatically scaled if it is scalar and a
- manual voxel spacing is provided (see Notes section).
- spacing : (3,) array-like of floats, optional
- 代表沿着图像每个维度的体素空间。默认情况下,slic假定均匀的空间(沿x,y,z轴相同的体素分辨
- 率),这个参数控制在k均值聚类中各轴距离的权重
- The voxel spacing along each image dimension. By default, `slic`
- assumes uniform spacing (same voxel resolution along z, y and x).
- This parameter controls the weights of the distances along z, y,
- and x during k-means clustering.
- multichannel : bool, optional
- 二进制参数,代表图像的最后一个轴代表多通道还是另一个空间维度
- Whether the last axis of the image is to be interpreted as multiple
- channels or another spatial dimension.
- convert2lab : bool, optional
- 二进制参数,判断输入需要在分割之前转到LAB颜色空间。输入必须是RGB。当多通道参数为True,
- 输入图片的通道数为3时,该参数默认为True
- Whether the input should be converted to Lab colorspace prior to
- segmentation. The input image *must* be RGB. Highly recommended.
- This option defaults to ``True`` when ``multichannel=True`` *and*
- ``image.shape[-1] == 3``.
- enforce_connectivity: bool, optional
- 二进制参数,控制生成的分割块连接或不连接
- Whether the generated segments are connected or not
- min_size_factor: float, optional
- 与分割目标数有关的要删去的最小分割块比率,(大概是小于长*宽*高/目标数量 的分割结果会被融
- 合掉)
- Proportion of the minimum segment size to be removed with respect
- to the supposed segment size ```depth*width*height/n_segments```
- max_size_factor: float, optional
- 最大融合比率上限
- Proportion of the maximum connected segment size. A value of 3 works
- in most of the cases.
- slic_zero: bool, optional
- 不知所谓的零参数
- Run SLIC-zero, the zero-parameter mode of SLIC. [2]_
- Returns
- -------
- labels : 2D or 3D array
- Integer mask indicating segment labels.
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- If ``convert2lab`` is set to ``True`` but the last array
- dimension is not of length 3.
- Notes
- -----
- * If `sigma > 0`, the image is smoothed using a Gaussian kernel prior to
- segmentation.
- * If `sigma` is scalar and `spacing` is provided, the kernel width is
- divided along each dimension by the spacing. For example, if ``sigma=1``
- and ``spacing=[5, 1, 1]``, the effective `sigma` is ``[0.2, 1, 1]``. This
- ensures sensible smoothing for anisotropic images.
- 如果有平滑参数sigma和体素空间参数spacing,那么空间体素参数会对平滑参数有平分的影响,比如
- 1/[5,1,1]=[0.2,1,1]
- * The image is rescaled to be in [0, 1] prior to processing.
- 图像在预处理之前会被处理为[0,1]之间的标量
- * Images of shape (M, N, 3) are interpreted as 2D RGB images by default. To
- interpret them as 3D with the last dimension having length 3, use
- `multichannel=False`.
- (M,N,3)的图像默认为2维(RGB的图像),要想被理解为3维图需要设置多通道参数=False
- References
- ----------
- .. [1] Radhakrishna Achanta, Appu Shaji, Kevin Smith, Aurelien Lucchi,
- Pascal Fua, and Sabine Süsstrunk, SLIC Superpixels Compared to
- State-of-the-art Superpixel Methods, TPAMI, May 2012.
- .. [2] http://ivrg.epfl.ch/research/superpixels#SLICO
- Examples
- --------
- >>> from skimage.segmentation import slic
- >>> from skimage.data import astronaut
- >>> img = astronaut()
- >>> segments = slic(img, n_segments=100, compactness=10)
- Increasing the compactness parameter yields more square regions:
- >>> segments = slic(img, n_segments=100, compactness=20)
- """
- ###############################################干正事啦
- image = img_as_float(image)
- is_2d = False
- #2D灰度图
- if image.ndim == 2:
- # 2D grayscale image
- image = image[np.newaxis, ..., np.newaxis]
- is_2d = True
- #比如2D RGB的图
- elif image.ndim == 3 and multichannel:
- # Make 2D multichannel image 3D with depth = 1
- image = image[np.newaxis, ...]
- is_2d = True
- #比如3D图
- elif image.ndim == 3 and not multichannel:
- # Add channel as single last dimension
- image = image[..., np.newaxis]
- #控制聚类时各轴权重
- if spacing is None:
- spacing = np.ones(3)
- elif isinstance(spacing, (list, tuple)):
- spacing = np.array(spacing, dtype=np.double)
- #高斯平滑
- if not isinstance(sigma, coll.Iterable):
- sigma = np.array([sigma, sigma, sigma], dtype=np.double)
- sigma /= spacing.astype(np.double)#有可能发生的体素除
- elif isinstance(sigma, (list, tuple)):
- sigma = np.array(sigma, dtype=np.double)
- #高斯滤波处
- if (sigma > 0).any():
- # add zero smoothing for multichannel dimension
- sigma = list(sigma) + [0]
- image = ndi.gaussian_filter(image, sigma)
- #多通道RGB图且需要转lab,用rab2lab即可实现
- if multichannel and (convert2lab or convert2lab is None):
- if image.shape[-1] != 3 and convert2lab:
- raise ValueError("Lab colorspace conversion requires a RGB image.")
- elif image.shape[-1] == 3:
- image = rgb2lab(image)
- depth, height, width = image.shape[:3]
- # initialize cluster centroids for desired number of segments
- #为实现目标分割块数,初始化聚类中心。
- #grid_* 相当于index
- #slices是根据目标数量分的块,有取整需要
- grid_z, grid_y, grid_x = np.mgrid[:depth, :height, :width]
- slices = regular_grid(image.shape[:3], n_segments)
- step_z, step_y, step_x = [int(s.step if s.step is not None else 1)
- for s in slices]
- segments_z = grid_z[slices]
- segments_y = grid_y[slices]
- segments_x = grid_x[slices]
- segments_color = np.zeros(segments_z.shape + (image.shape[3],))
- segments = np.concatenate([segments_z[..., np.newaxis],
- segments_y[..., np.newaxis],
- segments_x[..., np.newaxis],
- segments_color],
- axis=-1).reshape(-1, 3 + image.shape[3])
- segments = np.ascontiguousarray(segments)
- # we do the scaling of ratio in the same way as in the SLIC paper
- # so the values have the same meaning
- step = float(max((step_z, step_y, step_x)))
- ratio = 1.0 / compactness
- #我类个去,分割时方不方的骚操作
- image = np.ascontiguousarray(image * ratio)
- labels = _slic_cython(image, segments, step, max_iter, spacing, slic_zero)
- #把过小过小的处理一下
- if enforce_connectivity:
- segment_size = depth * height * width / n_segments
- min_size = int(min_size_factor * segment_size)
- max_size = int(max_size_factor * segment_size)
- labels = _enforce_label_connectivity_cython(labels,
- min_size,
- max_size)
- if is_2d:
- labels = labels[0]
- return labels
-
相关阅读:
营销妙招:链动2+1渠道搭建团队裂变
【综合类型第 38 篇】如何查看、安装最新版本、旧版本的 Cocoapods
Java-堆和栈的概念和区别-1
海藻酸钠-PEG-马来酰亚胺 MAL-PEG-alginate 马来酰亚胺 修饰海藻酸钠
【Luogu P2221】[HAOI2012] 高速公路(线段树,期望)
有意识的神经网络之对比网络层和后意识层
线上突然查询变慢怎么核查
通关 MySQL获奖名单已公布
Java面试笔试题大汇总一(最全+详细答案)
Python之第七章 函数 --- 基础
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_61899108/article/details/127438117
