-
河南工程学院2022级新生周赛(五)题解
更好的阅读体验 \color{red}{更好的阅读体验} 更好的阅读体验
A. HF 的智能小车车
描述:
众嗦粥汁, H F HF HF 最近天天泡在实验室里做他的智能小车车,但在调试的时候发现控制转向和行进的指令搞混了。这种小事对他来说太简单了,用他的原话说就是:“有手就行”,于是他就懒得继续做下去了。
H F HF HF 把这个做了一半的车子丢给了 L Y S LYS LYS,如果他能解决掉这些问题,这个智能小车车就归 L Y S LYS LYS 辣。
以下是需要解决的问题:
- 当输入右转向指令为
R时,执行左转指令L,反之亦然。 - 当输入前进指令为
U时,执行向后退指令D,反之亦然。
L Y S LYS LYS 肥肠想要这个小车车,可是他啥也不会,现在他来找你帮忙了,你能帮帮他吗?
输入格式:
一行,一个字符 P P P,表示输入的指令。
输出格式:
一行,一个字符,表示执行的指令。
数据范围:
P = { R , L , U , D } P=\{R,L,U,D\} P={R,L,U,D}。
样例输入:
R- 1
样例输出:
L- 1
思想:
- 签到题。
代码:
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr) #define re register #define fi first #define se second #define endl '\n' typedef long long LL; typedef pair<int, int> PII; typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL; const int N = 1e6 + 3; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7; const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1); void solve(){ char op; cin >> op; if(op == 'R') cout << 'L' << endl; else if(op == 'L') cout << 'R' << endl; else if(op == 'U') cout << 'D' << endl; else cout << 'U' << endl; } int main(){ IOS; int _ = 1; // cin >> _; while(_ --){ solve(); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
B. Do you like Van game?
描述:
野兽仙贝想跟你 V a n Van Van 一个游戏,要是你赢了就能让你嘿嘿嘿,反之亦然。
野兽仙贝拿出了三个超大号皮搋子放在桌上,分别编号为 1 , 2 , 3 1,2,3 1,2,3,初始对应位置编号也为 1 , 2 , 3 1,2,3 1,2,3。其中某个的皮搋子下面藏着一个扩音器。
游戏规则:
- 游戏一共进行 k k k 轮。
- 第 k i k_i ki 轮,仙贝会交换某编号为 n i , m i n_i,m_i ni,mi 的皮搋子的位置,若皮搋子下有扩音器,扩音器也会跟着移动。
- 一轮交换结束,你可以猜一个位置 P i P_i Pi。
- 若猜中了扩音器的位置,则本轮得一分,否则不得分。
野兽仙贝其实很想让你赢,所以游戏开始前,他就尽可能的把扩音器放到了你可以得最高分数的位置,现在请你计算出你最高的得分。
输入格式:
第一行,一个整数 k k k,代表游戏进行几轮。
接下来 k k k 行,每行输入两个整数 n i , m i n_i,m_i ni,mi 和一个整数 P i P_i Pi,分别代表皮搋子的编号和你所猜的扩音器的位置编号。
输出格式:
一行,一个整数,表示你可能得到的最高分数。
数据范围:
1 ≤ k ≤ 100 1\le k\le 100 1≤k≤100, 1 ≤ n i , m i , P i ≤ 3 1\le n_i,m_i,P_i\le 3 1≤ni,mi,Pi≤3。
输入样例:
3 1 2 1 3 2 1 1 3 1- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
输出样例:
2- 1
提示:
若扩音器最开始在皮搋子 1 1 1 下面,最终你在第三轮猜中一次。
若扩音器最开始在皮搋子 2 2 2 下面,最终你在第一轮和第二轮猜中,共两次。
若扩音器最开始在皮搋子 3 3 3 下面,最终一次也没有猜中。
思想1:
- 暴力模拟。
- 枚举初始位置,模拟在该开局的条件下的得分。
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr) #define re register #define fi first #define se second #define endl '\n' typedef long long LL; typedef pair<int, int> PII; typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL; const int N = 1e6 + 3; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7; const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1); int pos[N]; struct Operator{ int l, r, p; }op[N]; void solve(){ int n; cin >> n; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){ int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; op[i] = {a, b, c}; } int ans = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i ++){ pos[1] = pos[2] = pos[3] = 0; pos[i] = 1; int cnt = 0; for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++){ swap(pos[op[j].l], pos[op[j].r]); cnt += pos[op[j].p]; } ans = max(ans, cnt); } cout << ans << endl; } int main(){ IOS; int _ = 1; // cin >> _; while(_ --){ solve(); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
思想2:
- 思维题。
- 设位置数组为
pos[N],初始时位置i上的皮搋子编号为i,即pos[1] = 1表示位置 1 1 1 上的皮搋子编号为 1 1 1。 - 设答案数组为
ans[N],表示编号为i的皮搋子被猜中多少次。 - 用
swap()交换位置上的皮搋子,而询问的位置上的皮搋子对应的编号被猜中,记录次数。 - 最后比较哪个编号的皮搋子在交换时被猜中的次数最多,那么一开始扩音器就在这个皮搋子下。
代码2:
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr) #define re register #define fi first #define se second #define endl '\n' typedef long long LL; typedef pair<int, int> PII; typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL; const int N = 1e6 + 3; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7; const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1); int ans[N], pos[N]; void solve(){ int n; cin >> n; for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i ++) pos[i] = i; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){ int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; swap(pos[a], pos[b]); ans[pos[c]] ++; } cout << max(ans[1], max(ans[2], ans[3])) << endl; } int main(){ IOS; int _ = 1; // cin >> _; while(_ --){ solve(); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
C. 好姐姐的三角形
描述:
三角形给人一种稳固的感觉,我们的好姐姐 W J X WJX WJX 最喜欢三角形了,现在她想用一些字母拼出来等腰三角形,你能帮帮她吗?
输入格式:
第一行,一个整数 t t t,表示样例数量。
接下来 t t t 行,第 t i t_i ti 行输入一个整数 n i n_i ni 和一个字符 c i c_i ci,分别表示三角形的高度和用来拼成三角形的字符。
输出格式:
共 t t t 行,每行用所给字符输出对应高度的等腰三角形。
每个样例之间空一行。
数据范围:
1 ≤ t , n i ≤ 10 1\le t,n_i\le 10 1≤t,ni≤10。
样例输入:
2 2 A 3 B- 1
- 2
- 3
样例输出:
A AAA B B B BBBBB- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
思想:
- 模拟。
代码:
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr) #define re register #define fi first #define se second #define endl '\n' typedef long long LL; typedef pair<int, int> PII; typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL; const int N = 1e6 + 3; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1804; const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1); void solve(){ int n; char op; cin >> n >> op; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){ if(i <= n - 1){ //不是最后一行时 for(int j = n - i - 1; j >= 0; j --) cout << ' '; //输出前面的空格 cout << op; for(int j = 1; j <= (i - 1) * 2 - 1; j ++) cout << ' '; //输出中间的空格 if(i > 1) cout << op << endl; //不是第一行再输出一个字符 else cout << endl; } else{ for(int j = 1; j <= i * 2 - 1; j ++) cout << op; //最后一行不含空格 cout << endl; } } cout << endl; } int main(){ IOS; int _ = 1; cin >> _; while(_ --){ solve(); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
D. 帮帮小陈
描述:
我们的好姐姐 W J X WJX WJX 在拼三角形的时候突发奇想,想要考考小陈同学,假如有 n n n 个整数 i i i,以这 n n n 个整数中的三个整数为边长能够构成多少个三角形?
结果小陈同学一时大意,不小心被难住了,你能帮帮他吗?
输入格式:
第一行一个整数 t t t ,表示 t t t 个测试样例。
每个样例第一行一个整数 n n n,表示有 n n n 个可选的边
每个样例第二行 n n n个整数 i i i,表示三角形的边长。
输出格式:
共 t t t 行,每行一个整数,表示该测试样例下能构成的三角形的数量。
数据范围:
1 ≤ t , n , i , ≤ 1 × 1 0 3 1\le t,n, i, \le 1\times 10^3 1≤t,n,i,≤1×103。
样例输入:
1 4 2 2 3 4- 1
- 2
- 3
样例输出:
3- 1
思想:
- 排序,二分。
- 将所有的边按照从小到大的顺序排序。
- 枚举前两个边的长度,二分寻找最大的第三边的位置。
- 将满足的第三边的总数累加即可。
代码:
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr) #define re register #define fi first #define se second #define endl '\n' typedef long long LL; typedef pair<int, int> PII; typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL; const int N = 1e6 + 3; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7; const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1); int a[N]; void solve(){ int n; cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) cin >> a[i]; sort(a, a + n); //排序 LL sum = 0; for(int i = 0; i + 2 < n; i ++){ //枚举第一个边 while(a[i] == 0 && i < n) i ++; //从不是 0 的位置开始 for(int j = i + 1; j + 1 < n; j ++){ //枚举第二个边 int l = j + 1, r = n - 1; int p = a[i] + a[j]; while(l < r){ //二分,找到最大的 a[k] < a[i] + a[j] int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1; if(a[mid] < p) l = mid; else r = mid - 1; } if(a[l] < p) sum += l - j; //特判一下是否满足 else sum += l - j - 1; } } cout << sum << endl; } int main(){ IOS; int _ = 1; cin >> _; while(_ --){ solve(); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
E. 卷点
描述:
小陈同学很感谢你的帮助,作为回报,他也给你出了一个有趣的问题。
现在给出一个“卷点”的定义:在一个正方形内存在某一点,使得这个点和正方形四个顶点连接而划分出的四块三角形的面积比为 a : b : c : d a:b:c:d a:b:c:d。四个数不分顺序;卷点不是唯一的。
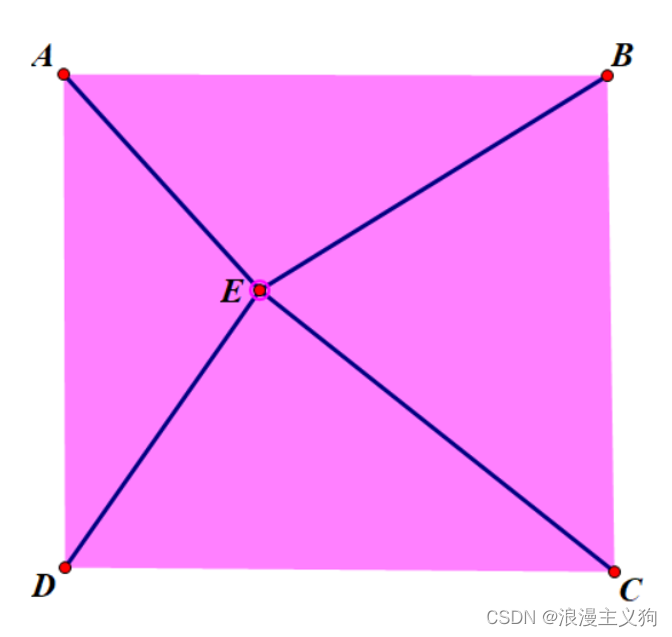
现在有一个正方形,给出 4 4 4个整数 a , b , c , d a,b,c,d a,b,c,d,表示被某点划分出的四个三角形的面积,判断有多少个这样的卷点在正方形内部?
输入格式:
第一行一个整数 n n n ,代表 n n n 个测试样例。
接下来 n n n 行,每行 4 4 4 个整数 a , b , c , d a,b,c,d a,b,c,d,表示四个三角形的面积。
输出格式:
共 n n n 行,每行一个整数,表示卷点的数量。
数据范围:
1 ≤ n ≤ 1 × 1 0 2 1\le n\le 1\times 10^2 1≤n≤1×102, 1 ≤ a , b , c , d ≤ 1 × 1 0 18 1\le a,b,c,d\le1\times10^{18} 1≤a,b,c,d≤1×1018。
样例输入:
3 1 3 3 1 2 4 7 8 2 3 1 4- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
样例输出:
4 0 8- 1
- 2
- 3
思想:
- 思维题。
- 设 a , b , c , d a,b,c,d a,b,c,d 非严格单调递增。
- 则当
a
+
d
=
b
+
c
a+d=b+c
a+d=b+c 时:
- 若 a = b = c = d a=b=c=d a=b=c=d 时,则只有一个卷点;
- 若 a = b , a ≠ d a=b,a\ne d a=b,a=d 时,则存在 4 4 4 个卷点;
- 若 a , b , c , d a,b,c,d a,b,c,d 均不相等时,则存在 8 8 8 个卷点。
- 其他情况不存在卷点。
代码:
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr) #define re register #define fi first #define se second #define endl '\n' typedef long long LL; typedef pair<int, int> PII; typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL; const int N = 1e6 + 3; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7; const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1); LL a[N]; void solve(){ for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++) cin >> a[i]; sort(a, a + 4); if(a[0] + a[3] == a[1] + a[2]){ if(a[0] == a[1] && a[1] == a[2] && a[2] == a[3]) cout << 1 << endl; else if(a[0] == a[1] && a[1] != a[2]) cout << 4 << endl; else cout << 8 << endl; } else cout << 0 << endl; } int main(){ IOS; int _ = 1; cin >> _; while(_ --){ solve(); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
F. 签个到就下班
描述:
给定一个字符串 S S S ,和两个整数 N , M , ( 0 ≤ N ≤ M ≤ 9 ) N,M,(0\le N\le M\le 9) N,M,(0≤N≤M≤9),按照出现的顺序输出其中所有的在 N ∼ M N\sim M N∼M 之间的数字字符。
输入格式:
第一行,两个整数 N , M N,M N,M。
第二行,一个字符串 S S S。
输出格式:
一行,若干个整数,为 S S S 处理后的结果,每个整数间隔一个空格。
数据范围:
保证 S S S 的长度 L ( S ) L_{(S)} L(S) 满足 1 ≤ L ( S ) ≤ 1 × 1 0 5 1\le L_{(S)} \le 1\times 10^5 1≤L(S)≤1×105。
样例输入:
1 2 abc123- 1
- 2
样例输出:
1 2- 1
思想:
- 签到题。
- 按照规则处理即可。
代码:
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr) #define re register #define fi first #define se second #define endl '\n' typedef long long LL; typedef pair<int, int> PII; typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL; const int N = 1e6 + 3; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1804; const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1); void solve(){ int n, m; string s; cin >> n >> m >> s; for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++){ int t = s[i] - '0'; if(t >= n && t <= m) cout << s[i] << ' '; } } int main(){ IOS; int _ = 1; // cin >> _; while(_ --){ solve(); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
G. 现在是摸鱼时间
描述:

L Y S LYS LYS 最喜欢摸鱼了, 现在给出一个长度为 N N N 的序列 A = { A 1 , A 2 , … , A N } A=\{A_1,A_2,\dots,A_N\} A={A1,A2,…,AN},表示 L Y S LYS LYS 的日程表,其中 A i A_i Ai 表示第 i i i 天的摸鱼指数。
为了在排满的日程表里的摸鱼,他向摸鱼大师 H F HF HF 请教,摸鱼大师给出了一个摸鱼公式:
- 1 A i − j A i A j = 1 A j − i A i A j , ( i < j ) \frac{1}{A_i} - \frac{j}{A_iA_j} = \frac{1}{A_j} - \frac{i}{A_iA_j},(i\lt j) Ai1−AiAjj=Aj1−AiAji,(i<j)
由公式可知,当第 i i i 天和第 j j j 天及其对应的摸鱼指数满足上述公式时,他就可以在第 i i i 天和第 j j j 天这两天摸鱼,记为一种摸鱼方案 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)。
虽然只能摸两天的鱼,但是 L Y S LYS LYS 还是想知道,他的日程表有多少种摸鱼方案可选。
输入格式:
第一行,一个整数 N N N,代表天数。
接下来 N N N 个整数,代表第 i i i 天的摸鱼指数 A i A_i Ai。
输出格式:
一行,一个整数,表示方案总数。
数据范围:
1 ≤ N ≤ 1 × 1 0 6 1\le N \le 1\times 10^6 1≤N≤1×106, 1 ≤ A i ≤ 1 × 1 0 3 1\le A_i\le 1\times 10^3 1≤Ai≤1×103。
输入样例:
6 3 5 1 3 9 5- 1
- 2
输出样例:
1- 1
提示:
对于样例,只有 ( 4 , 6 ) (4,6) (4,6) 符合。
思想:
- 思维。
- 化简 1 A i − j A i A j = 1 A j − i A i A j , ( i < j ) \frac{1}{A_i} - \frac{j}{A_iA_j} = \frac{1}{A_j} - \frac{i}{A_iA_j},(i\lt j) Ai1−AiAjj=Aj1−AiAji,(i<j) 得 A j − j = A i − i A_j - j = A_i - i Aj−j=Ai−i。
- 由此,不妨设 B i = A i − i B_i = A_i - i Bi=Ai−i。
- 总方案数即求对于 j j j 之前的与 B j B_j Bj 值相等的 B i B_i Bi 数量之和。
- 记录已经出现过的 B i B_i Bi 数量,之后出现的累加即可。
代码:
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr) #define re register #define fi first #define se second #define endl '\n' typedef long long LL; typedef pair<int, int> PII; typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL; const int N = 1e6 + 3; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7; const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1); void solve(){ LL sum = 0; map<int,int> vis; int n; cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){ int x; cin >> x; x -= i; sum += vis[x]; //加上当前位置之前 x 出现过的次数 vis[x] ++; //更新次数 } cout << sum << endl; } int main(){ IOS; int _ = 1; // cin >> _; while(_ --){ solve(); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
H. 现在是摸鱼时间 PLUS
描述:
在习得摸鱼大师 H F HF HF 给出的公式之后, L Y S LYS LYS 发现 H F HF HF 给的摸鱼公式只适用于地球上的日程表,于是他提出了“宇宙摸鱼大一统理论”,以便适应全宇宙不同摸鱼人群的需求。

现在给出一个长度为 N N N 的序列 A = { A 1 , A 2 , … , A N } A=\{A_1,A_2,\dots,A_N\} A={A1,A2,…,AN},表示某一日程表,其中 A i A_i Ai 表示第 i i i 天的摸鱼指数。
L Y S LYS LYS 提出的理论如下:
- 当第 i i i 天的摸鱼指数 A i A_i Ai 和第 j j j 天的摸鱼指数 A j A_j Aj 互质时,可以在这两天摸鱼,若 i = j i=j i=j 则表示只能在这一天摸鱼。
- i + j i + j i+j 的值越大,摸鱼的质量越高。
按照上述理论,计算在满足摸鱼条件时, i + j i + j i+j 的最大可能值。
输入格式:
第一行,一个整数 N N N,代表天数。
接下来 N N N 个整数,代表第 i i i 天的摸鱼指数 A i A_i Ai。
输出格式:
一行,一个整数,表示某两天满足摸鱼条件的时候 i + j i + j i+j 的最大值。
数据范围:
1 ≤ N ≤ 1 × 1 0 6 1\le N \le 1\times 10^6 1≤N≤1×106, 1 ≤ A i ≤ 1 × 1 0 3 1\le A_i\le 1\times10^3 1≤Ai≤1×103。
输入样例:
6 3 5 1 3 9 5- 1
- 2
输出样例:
11- 1
提示:
互质:当 A A A 和 B B B 的最大公约数为 1 1 1 时,称 A A A 和 B B B 互质。
对于样例,在 i = 5 , j = 6 i=5,j = 6 i=5,j=6 时满足摸鱼条件,且摸鱼质量最高。
思想:
- 离散化,最大公约数。
- 互质的条件为 g c d ( A i , A j ) = 1 gcd(A_i,A_j) = 1 gcd(Ai,Aj)=1。
- 对于相同的 A i A_i Ai,我们记录其所在的下标的最大值即可,不必维护所有 A i A_i Ai 的下标。
- 即将 A A A 序列去重,但保留 A i A_i Ai 原有的最大下标。
- 枚举离散化存储的 A i A_i Ai 判断即可,满足摸鱼的条件则维护 i + j i + j i+j 的最大值。
代码:
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr) #define re register #define fi first #define se second #define endl '\n' typedef long long LL; typedef pair<int, int> PII; typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL; const int N = 1e6 + 3; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 1e9 + 7; const double eps = 1e-6, PI = acos(-1); int gcd(int a, int b){ //求最大公约数 return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } void solve(){ int res = -1; int n; cin >> n; map<int, int> a; //存入出现过的状态 for(re int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){ int x; cin >> x; a[x] = i; //保留最大下标 } for(auto &p : a){ for(auto &t : a){ if(gcd(p.fi, t.fi) == 1) res = max(res, p.se + t.se); //更新答案 } } cout << res << endl; } int main(){ IOS; int _ = 1; // cin >> _; while(_ --){ solve(); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 当输入右转向指令为
-
相关阅读:
【博客486】prometheus-----rate,irate,increase的原理
【牛客刷题】BM20 数组中的逆序对
JDBC MySQL任意文件读取分析
Orphaned pod found - but volume paths are still present on disk的处理
1321_一份BootLoader xmodem部分的协议分析
科技视界杂志科技视界杂志社科技视界编辑部2022年第18期目录
模板进阶:非类型模板参数,特化
深浅拷贝原理+案例解析
K8S入门前奏之VMware虚拟机网络配置
iwebsec靶场 SQL注入漏洞通关笔记10- 双重url编码绕过
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/LYS00Q/article/details/127475993
