-
hisicv500部署yolov5 v5.0完整记录
一、模型训练
配置参数yolov5s.yaml文件# Parameters nc: 5 # number of classes depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple #anchors: # - [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8 # - [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16 # - [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32 anchors: - [48,56, 55,146, 129,94] # P3/8 - [126,221, 80,364, 233,145] # P4/16 - [182,433, 349,259, 396,499] # P5/32 # YOLOv5 backbone backbone: # [from, number, module, args] # [[-1, 1, Focus, [64, 3]], # 0-P1/2 [[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]], # 0-P1/2 [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4 [-1, 3, C3, [128]], [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8 [-1, 9, C3, [256]], [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16 [-1, 9, C3, [512]], [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32 [-1, 1, SPP, [1024, [5, 9, 13]]], [-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 9 ] # YOLOv5 head head: [[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]], # [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']], [-1, 1, nn.ConvTranspose2d, [256, 256, 2, 2]], [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4 [-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13 [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]], # [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']], [-1, 1, nn.ConvTranspose2d, [128, 128, 2, 2]], [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3 [-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small) [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], [[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4 [-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium) [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5 [-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large) [[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5) ]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
导出onnx时去掉detect层,需要修改两个地方:
1.修改yolo.py中的detect层,只留下最后的卷积class Detect(nn.Module): stride = None # strides computed during build onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer super().__init__() self.nc = nc # number of classes self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid a = torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2) self.register_buffer('anchors', a) # shape(nl,na,2) self.register_buffer('anchor_grid', a.clone().view(self.nl, 1, -1, 1, 1, 2)) # shape(nl,1,na,1,1,2) self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment) def forward(self, x): z = [] # inference output for i in range(self.nl): x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv return x[0],x[1],x[2]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
2.对应的修改export.py里的代码
torch.onnx.export(model, img, f, verbose=False, opset_version=opset_version, training=torch.onnx.TrainingMode.TRAINING if train else torch.onnx.TrainingMode.EVAL, do_constant_folding=not train, input_names=['images'], # output_names=output_names, output_names=['output_names1','output_names2','output_names3'], dynamic_axes={'images': {0: 'batch', 2: 'height', 3: 'width'}, # shape(1,3,640,640) 'output': {0: 'batch', 1: 'anchors'} # shape(1,25200,85) } if dynamic else None)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
这就把后边的detect层去掉了
去掉之前:
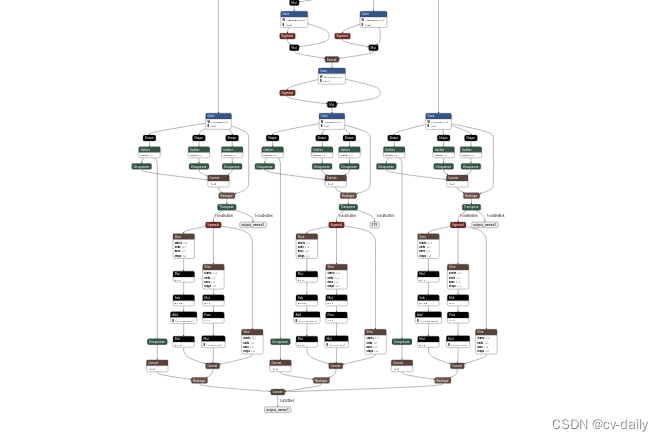 去掉之后:
去掉之后:
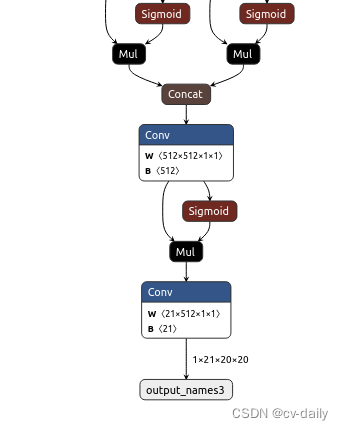
caffe环境配置:需要用到protobuf、opencv、
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41012399/article/details/127249620?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501onnx转caffe
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41012399/article/details/127249620?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
运行:python convertCaffe.py 得到转换好的caffe模型caffe转wk,步骤:
量化之前先修改prototxt文件。
最后三层要是conv+reshape层。上边那样的转化方式只转化到了conv层,还少一个reshape层,所以在prototxt中添加上即可。layer { name: "Sigmoid_200" type: "Sigmoid" bottom: "330" top: "331" } layer { name: "Mul_201" type: "Eltwise" bottom: "330" bottom: "331" top: "332" eltwise_param { operation: PROD } } layer { name: "Conv_202" type: "Convolution" bottom: "292" top: "output_names1" convolution_param { num_output: 30 bias_term: true group: 1 pad_h: 0 pad_w: 0 kernel_h: 1 kernel_w: 1 stride_h: 1 stride_w: 1 dilation: 1 } } layer { name: "Reshape_216" type: "Reshape" bottom: "output_names1" top: "output_names1_reshape" reshape_param { shape { dim: 0 dim: 3 dim: 10 dim: 6400 } } } layer { name: "Conv_203" type: "Convolution" bottom: "312" top: "output_names2" convolution_param { num_output: 30 bias_term: true group: 1 pad_h: 0 pad_w: 0 kernel_h: 1 kernel_w: 1 stride_h: 1 stride_w: 1 dilation: 1 } } layer { name: "Reshape_264" type: "Reshape" bottom: "output_names2" top: "output_names2_reshape" reshape_param { shape { dim: 0 dim: 3 dim: 10 dim: 1600 } } } layer { name: "Conv_204" type: "Convolution" bottom: "332" top: "output_names3" convolution_param { num_output: 30 bias_term: true group: 1 pad_h: 0 pad_w: 0 kernel_h: 1 kernel_w: 1 stride_h: 1 stride_w: 1 dilation: 1 } } layer { name: "Reshape_312" type: "Reshape" bottom: "output_names3" top: "output_names3_reshape" reshape_param { shape { dim: 0 dim: 3 dim: 10 dim: 400 } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
量化步骤,如意工具使用参考链接:
在相机里部署:
本地安装编译链,本地编译sdk
zl@sensoro:~/Hi3516CV500_SDK_V2.0.1.0_biao_bf220221/smp/a7_linux/mpp/sample/svp$ make
编译生成可执行文件,mpp/sample/svp/nnie/sample_nnie_main
相机端操作方式:telnet 10.0.0.0 mount -t nfs -o nolock 10.0.0.10:/home/zl/smp/a7_linux /mnt /mnt/mpp/sample/svp/nnie#./sample_nnie_main Usage : ./sample_nnie_main <index> index: 0) RFCN(VI->VPSS->NNIE->VGS->VO). 1) Segnet(Read File). 2) FasterRcnnAlexnet(Read File). 3) FasterRcnnDoubleRoiPooling(Read File). 4) Cnn(Read File). 5) SSD(Read File). 6) Yolov1(Read File). 7) Yolov2(Read File). 8) Yolov3(Read File). 9) LSTM(Read File). a) Pvanet(Read File). b) Rfcn(Read File). c) Yolov5(Read File). /mnt/mpp/sample/svp/nnie#./sample_nnie_main c -------------------- output_result->left_up_x = 524.761841 output_result->left_up_y = 322.986786 output_result->right_down_x = 550.650879 output_result->right_down_y = 386.360870 output_result->class_index = 0 output_result->score = 0.935751 output_result->left_up_x = 405.818939 output_result->left_up_y = 306.765656 output_result->right_down_x = 420.850739 output_result->right_down_y = 356.835480 output_result->class_index = 0 output_result->score = 0.921844 output_result->left_up_x = 412.485016 output_result->left_up_y = 304.654785 output_result->right_down_x = 420.947723 output_result->right_down_y = 315.355591 output_result->class_index = 2 output_result->score = 0.901636 output_result->left_up_x = 540.785278 output_result->left_up_y = 321.883972 output_result->right_down_x = 549.581665 output_result->right_down_y = 333.090515 output_result->class_index = 2 output_result->score = 0.888724 -------------------- [Level]:Debug,[Func]:SAMPLE_COMM_SVP_CheckSysExit [Line]:94 [Info]:Svp mpi exit ok!- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
修改后处理代码参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41012399/article/details/120866027?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522166606471116782425199191%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334.pc%255Fblog.%2522%257D&request_id=166606471116782425199191&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2blogfirst_rank_ecpm_v1~rank_v31_ecpm-3-120866027-null-null.article_score_rank_blog&utm_term=anchor&spm=1018.2226.3001.4450
替换不同的模型要修改
sample_nnie.cvoid SAMPLE_SVP_NNIE_Yolov5(void) { yolo_result *output_result = NULL; HI_CHAR *pcSrcFile = "./data/nnie_image/rgb_planar/hatsafe/36_44_bgr.bgr"; // HI_CHAR *pcSrcFile = "./data/nnie_image/rgb_planar/fish_640/hat21_bgr_640.bgr"; HI_CHAR *pcModelName = "./data/nnie_model/detection/yolov5s_hatsafe_221017_inst.wk"; anchor_w_h anchor_grids[3][3] = {{{9.0f, 11.0f}, {16.0f, 20.0f}, {14.0f, 38.0f}}, // small yolo layer 层 anchor {{25.0f, 32.0f}, {23.0f, 58.0f}, {34.0f, 70.0f}}, // middle yolo layer 层 anchor {{46.0f, 108.0f}, {68.0f, 140.0f}, {150.0f, 225.0f}}}; // large yolo layer 层 anchor ... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
其中anchor_grids[3][3]是保存在pt模型的detect层中的代码,获取方式:
在export时打印出来,修改yolo.py中的detect层:class Detect(nn.Module): stride = None # strides computed during build onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter ... def forward(self, x): if not self.training: # inference if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4] or self.onnx_dynamic: self.grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny).to(x[i].device) y = x[i].sigmoid() if self.inplace: y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy a=self.anchor_grid[i] print(a) //a就是保存在detect层的anchor- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
测试文件36_44_bgr.bgr的获取代码:
class JPG2BGR_Solver(object): def __init__(self): self.img_size = 640 # save bgr size # jpj2bgr converbgr=true 参数设置 self.imgpath_jpg = r"pose_368.jpg" self.saveimg_bgr = r"pose_368.bgr" self.jpeg_path = r"36_44.jpg" self.path = "36_44_bgr.bgr" self.path2 = "36_44_bgr.jpg" def jpg2bgr_pad(self): save_img_size = self.img_size imgpath = self.jpeg_path img = Image.open(imgpath) saveimg = self.path if img is None: print("img is none") else: ####不变形缩放 iw, ih = img.size w = save_img_size h = save_img_size scale = min(float(w)/float(iw), float(h)/float(ih)) nw = int(iw*scale) nh = int(ih*scale) img = img.resize((nw, nh), Image.BICUBIC) # img.show() new_img = Image.new('RGB', (w, h), (128, 128, 128)) # new_img.show() new_img.paste(img, ((w-nw)//2, (h-nh)//2)) new_img.save(self.path2) new_img = np.array(new_img) ##转成ndarray的 # (R, G, B) = cv2.split(new_img) (B, G, R) = cv2.split(new_img) ####转成rgb with open(saveimg, 'wb')as fp: for i in range(save_img_size): for j in range(save_img_size): fp.write(B[i, j]) print(B[i, j]) for i in range(save_img_size): for j in range(save_img_size): fp.write(G[i, j]) for i in range(save_img_size): for j in range(save_img_size): fp.write(R[i, j]) print("save success") if __name__ == '__main__': converbgr = True solverObj = JPG2BGR_Solver() if (converbgr == True): solverObj.jpg2bgr_pad()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
-
相关阅读:
空间占用计算
【AUTOSAR-CanIf】-2.3-对接收的L-PDU进行的Validation check
javaEE开发配置
MultipartFile 上传文件的踩坑点
记一次 公司.NET项目部署在Linux环境压测时 内存暴涨分析
机器学习笔记 - 深入研究spaCy库及其使用技巧
信号与槽机制
http实现文件分片下载
【操作系统】实验一 Linux初步
BGP—— 边界网关协议
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41012399/article/details/127325224