-
QLayout布局间消除间隙和QLayout边缘空白调整
目录
一、问题
设计了一个
窗口控件,继承了QWidget,里面有两个QLabel,用QHBoxLayout将其并排排列。但是这个控件被调用,但是这个控件边缘太大,看起来很丑,主要原因就是这个QHBoxLayout的边缘设置的太大。
二、QLayout
1、概述
Qt中界面开发的一个优势就是QLayout(布局)和QSpacer(弹簧)的结合。通过在Qt Designer中将需要的控件拖到窗口中,在窗口中添加QLayout和QSpacer以确定控件的位置,将所有可视化的控件全部在窗口中布局好,这样一来,代码只需实现功能就可以了,界面布局的代码就会少很多,而且很方便,可以加快页面的开发速度。
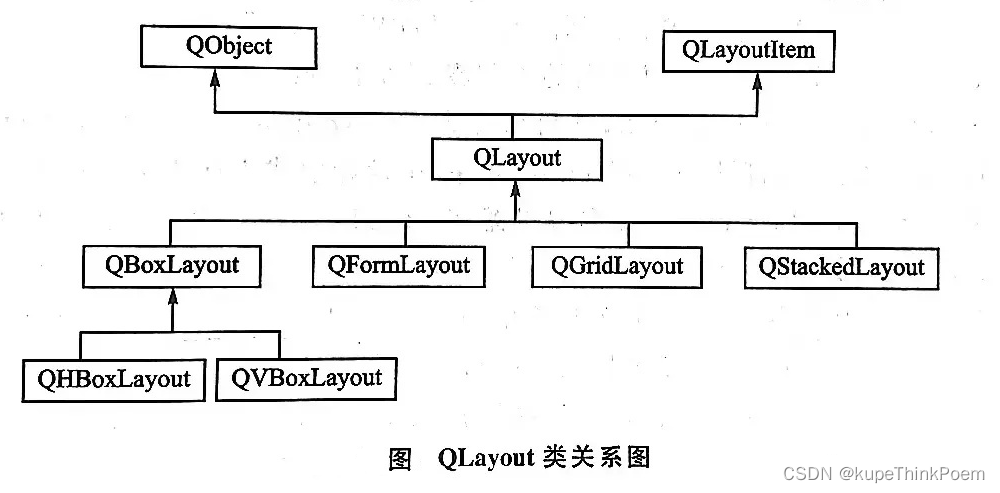
2、布局管理系统
Qt的布局管理系统提供了强大的机制来自动排列窗口中的所有部件,确保它们有效地使用空间。所有QWidget的子类的实例(对象)都可以使用布局管理器管理位于它们之中的子部件,可以通过QWidget::setLayout()函数在一个部件上应用布局管理器,也可以在Qt Designer中右键选中部件,选择布局来添加。QWidget在添加布局时,要先确保QWidget中有子部件的存在,否则这时布局管理是不可用的状态。一旦一个部件设置了布局管理器,那它会完成下面这些事情:
(1)定位子部件;
(2)感知窗口默认大小;
(3)感知窗口最小大小;
(4)窗口大小变化时进行处理;
(5)当内容改变时自动更新:
——字体大小、文本或子部件的其他内容随之改变;
——隐藏或显示子部件;
——移除一个子部件。3、布局管理器
(1)QBoxLayout(基本布局管理器;又分为:QHBoxLayout(水平布局管理器)和QVBoxLayout(垂直布局管理器))
(2)QGridLayout(栅格布局管理器)
(3)QFormLayout(窗体布局管理器)
(4)QStackedLayout(栈布局管理器)
4、布局管理器的一些知识
(1)基本布局管理器(QBoxLayout):基本布局管理器QBoxLayout类可以使子部件在水平方向或者垂直方向排成一列。
(2)栅格布局管理器(QGridLayout):栅格布局管理器QGridLayout类使部件在网格中进行布局,它将所有的控件分隔成网格,将部件放入某一个单元格中。
(3)窗体布局管理器(QFormLayout):用来管理表单的输入部件以及与它们相关的标签。窗体布局管理器将它的子部件分为两列,左边是一些标签,右边是一些输入部件。一般主要应用在登录时输入账号、密码;输入个人信息如:姓名:+输入框。
(4) 当部件加入到一个布局管理其中,然后将这个布局管理器再放到一个窗口部件上时,这个布局以及它包含的所有部件都会重新定义自己的父对象(parent)为这个窗口部件,所以在创建布局管理器和其中的部件时不用指定父部件。(5)在页面上不可能所有控件都排的满满当当,这时就需要用到QSpacer,用来在部件之间产生间隔。QSpacer分为水平分隔符和垂直分隔符。
三、QLayout边缘空白调整
1、原始代码
- #include "testwidget.h"
- #include <QLayout>
- #include <QWidget>
- #include <QFrame>
- #include <QLabel>
- testWidget::testWidget(QWidget *parent, Qt::WFlags flags)
- : QMainWindow(parent, flags)
- {
- ui.setupUi(this);
- QHBoxLayout *pLayout= new QHBoxLayout(this->centralWidget());
- this->centralWidget()->setLayout(pLayout);
- QLabel *pl=new QLabel(this);
- pl->setFrameStyle(QFrame::Panel | QFrame::Raised);
- pl->setText("test1");
- pLayout->addWidget(pl);
- QLabel *p2=new QLabel(this);
- p2->setFrameStyle(QFrame::Panel | QFrame::Raised);
- p2->setText("test2");
- pLayout->addWidget(p2);
- }
- testWidget::~testWidget()
- {
- }
2、setContentsMargins函数
setContentsMargins(0,0,0,0)- void QLayout::setContentsMargins(int left, int top, int right, int bottom)
- /*
- Sets the left, top, right, and bottom margins to use around the layout.
- By default, QLayout uses the values provided by the style. On most platforms, the margin is 11 pixels in all directions.
- This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
- See also contentsMargins(), getContentsMargins(), QStyle::pixelMetric(), PM_LayoutLeftMargin, PM_LayoutTopMargin, PM_LayoutRightMargin, and PM_LayoutBottomMargin.
- */
- void QLayout::setContentsMargins(const QMargins & margins)
- /*
- Sets the margins to use around the layout.
- By default, QLayout uses the values provided by the style. On most platforms, the margin is 11 pixels in all directions.
- This function was introduced in Qt 4.6.
3、修改后代码
- #include "testwidget.h"
- #include <QLayout>
- #include <QWidget>
- #include <QFrame>
- #include <QLabel>
- testWidget::testWidget(QWidget *parent, Qt::WFlags flags)
- : QMainWindow(parent, flags)
- {
- ui.setupUi(this);
- QHBoxLayout *pLayout= new QHBoxLayout(this->centralWidget());
- this->centralWidget()->setLayout(pLayout);
- QLabel *pl=new QLabel(this);
- pl->setFrameStyle(QFrame::Panel | QFrame::Raised);
- pl->setText("test1");
- pLayout->addWidget(pl);
- QLabel *p2=new QLabel(this);
- p2->setFrameStyle(QFrame::Panel | QFrame::Raised);
- p2->setText("test2");
- pLayout->addWidget(p2);
- pLayout->setContentsMargins(0,0,0,0);
- }
- testWidget::~testWidget()
- {
- }
4、效果图

四、QLayout布局间消除间隙
1、原始代码
- #include "testwidget.h"
- #include <QLayout>
- #include <QWidget>
- #include <QFrame>
- #include <QLabel>
- testWidget::testWidget(QWidget *parent, Qt::WFlags flags)
- : QMainWindow(parent, flags)
- {
- ui.setupUi(this);
- QHBoxLayout *pLayout= new QHBoxLayout(this->centralWidget());
- this->centralWidget()->setLayout(pLayout);
- QLabel *pl=new QLabel(this);
- pl->setFrameStyle(QFrame::Panel | QFrame::Raised);
- pl->setText("test1");
- pLayout->addWidget(pl);
- QLabel *p2=new QLabel(this);
- p2->setFrameStyle(QFrame::Panel | QFrame::Raised);
- p2->setText("test2");
- pLayout->addWidget(p2);
- pLayout->setContentsMargins(0,0,0,0);
- }
- testWidget::~testWidget()
- {
- }
2、setSpacing函数
- spacing : int
- This property holds the spacing between widgets inside the layout.
- If no value is explicitly set, the layout's spacing is inherited from the parent layout, or from the style settings for the parent widget.
- For QGridLayout and QFormLayout, it is possible to set different horizontal and vertical spacings using setHorizontalSpacing() and setVerticalSpacing(). In that case, spacing() returns -1.
- Access functions:
- int spacing () const
- void setSpacing ( int )
3、修改后代码
- #include "testwidget.h"
- #include <QLayout>
- #include <QWidget>
- #include <QFrame>
- #include <QLabel>
- testWidget::testWidget(QWidget *parent, Qt::WFlags flags)
- : QMainWindow(parent, flags)
- {
- ui.setupUi(this);
- QHBoxLayout *pLayout= new QHBoxLayout(this->centralWidget());
- this->centralWidget()->setLayout(pLayout);
- QLabel *pl=new QLabel(this);
- pl->setFrameStyle(QFrame::Panel | QFrame::Raised);
- pl->setText("test1");
- pLayout->addWidget(pl);
- QLabel *p2=new QLabel(this);
- p2->setFrameStyle(QFrame::Panel | QFrame::Raised);
- p2->setText("test2");
- pLayout->addWidget(p2);
- pLayout->setContentsMargins(0,0,0,0);
- pLayout->setSpacing(0);
- }
4、效果图

-
相关阅读:
关于C#反射概念,附带案例!
两个node服务共同修改一个计数文件,互相监控服务是否停止
【数据链路层】循环冗余码CRC、后退N帧协议GBN、选择重传协议SR、CSMA/CA
VUE3_Three项目构建(基础模板)
盘点CSV文件在Excel中打开后乱码问题的三种处理方法
Django框架基本语法(一)
银行行测之百炼成钢
python没有重复数字的两位数统计 青少年编程电子学会python编程等级考试二级真题解析2021年6月
MySQL锁机制
界面控件Telerik UI for WPF - 如何使用RadSpreadsheet记录或评论
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/kupe87826/article/details/127457067
