-
源码学习之MyBatis的底层查询原理
导读
本文通过MyBatis一个低版本的bug(3.4.5之前的版本)入手,分析MyBatis的一次完整的查询流程,从配置文件的解析到一个查询的完整执行过程详细解读MyBatis的一次查询流程,通过本文可以详细了解MyBatis的一次查询过程。在平时的代码编写中,发现了MyBatis一个低版本的bug(3.4.5之前的版本),由于现在很多工程中的版本都是低于3.4.5的,因此在这里用一个简单的例子复现问题,并且从源码角度分析MyBatis一次查询的流程,让大家了解MyBatis的查询原理
1 问题现象
1.1 场景问题复现
如下图所示,在示例Mapper中,下面提供了一个方法queryStudents,从student表中查询出符合查询条件的数据,入参可以为student_name或者student_name的集合,示例中参数只传入的是studentName的List集合
List<String> studentNames = new LinkedList<>();studentNames.add("lct");studentNames.add("lct2");condition.setStudentNames(studentNames);<select id="queryStudents" parameterType="mybatis.StudentCondition" resultMap="resultMap">select * from student<where><if test="studentNames != null and studentNames.size > 0 ">AND student_name IN<foreach collection="studentNames" item="studentName" open="(" separator="," close=")">#{studentName, jdbcType=VARCHAR}</foreach></if><if test="studentName != null and studentName != '' ">AND student_name = #{studentName, jdbcType=VARCHAR}</if></where></select>期望运行的结果是
select * from student WHERE student_name IN ( 'lct' , 'lct2' )但是实际上运行的结果是
==> Preparing: select * from student WHERE student_name IN ( ? , ? ) AND student_name = ?
==> Parameters: lct(String), lct2(String), lct2(String)
<== Columns: id, student_name, age
<== Row: 2, lct2, 2
<== Total: 1
通过运行结果可以看到,没有给student_name单独赋值,但是经过MyBatis解析以后,单独给student_name赋值了一个值,可以推断出MyBatis在解析SQL并对变量赋值的时候是有问题的,初步猜测是foreach循环中的变量的值带到了foreach外边,导致SQL解析出现异常,下面通过源码进行分析验证
2 MyBatis查询原理
2.1 MyBatis架构
2.1.1 架构图
先简单来看看MyBatis整体上的架构模型,从整体上看MyBatis主要分为四大模块:
接口层:主要作用就是和数据库打交道
数据处理层:数据处理层可以说是MyBatis的核心,它要完成两个功能:
-
通过传入参数构建动态SQL语句;
-
SQL语句的执行以及封装查询结果集成List
框架支撑层:主要有事务管理、连接池管理、缓存机制和SQL语句的配置方式
引导层:引导层是配置和启动MyBatis 配置信息的方式。MyBatis 提供两种方式来引导MyBatis :基于XML配置文件的方式和基于Java API 的方式
2.1.2 MyBatis四大对象
贯穿MyBatis整个框架的有四大核心对象,ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、StatementHandler和Executor,四大对象贯穿了整个框架的执行过程,四大对象的主要作用为:
-
ParameterHandler:设置预编译参数
-
ResultSetHandler:处理SQL的返回结果集
-
StatementHandler:处理sql语句预编译,设置参数等相关工作
-
Executor:MyBatis的执行器,用于执行增删改查操作
2.2 从源码解读MyBatis的一次查询过程
首先给出复现问题的代码以及相应的准备过程
2.2.1 数据准备
CREATE TABLE `student` (`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`student_name` varchar(255) NULL DEFAULT NULL,`age` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 1;-- ------------------------------ Records of student-- ----------------------------INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (1, 'lct', 1);INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (2, 'lct2', 2);2.2.2 代码准备
1.mapper配置文件
"1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" ><mapper namespace="mybatis.StudentDao"><resultMap id="resultMap" type="mybatis.Student"><id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="BIGINT" /><result column="student_name" property="studentName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" /><result column="age" property="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" /></resultMap><select id="queryStudents" parameterType="mybatis.StudentCondition" resultMap="resultMap">select * from student<where><if test="studentNames != null and studentNames.size > 0 ">AND student_name IN<foreach collection="studentNames" item="studentName" open="(" separator="," close=")">#{studentName, jdbcType=VARCHAR}</foreach></if><if test="studentName != null and studentName != '' ">AND student_name = #{studentName, jdbcType=VARCHAR}</if></where></select></mapper>2.示例代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);//1.获取SqlSessionFactory对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);//2.获取对象SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();//3.获取接口的代理类对象StudentDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);StudentCondition condition = new StudentCondition();List<String> studentNames = new LinkedList<>();studentNames.add("lct");studentNames.add("lct2");condition.setStudentNames(studentNames);//执行方法List<Student> students = mapper.queryStudents(condition);}2.2.3 查询过程分析
1.SqlSessionFactory的构建
先看SqlSessionFactory的对象的创建过程
//1.获取SqlSessionFactory对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);代码中首先通过调用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder中的build方法来获取对象,进入build方法
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {return build(inputStream, null, null);}调用自身的build方法

图1 build方法自身调用调试图例
在这个方法里会创建一个XMLConfigBuilder的对象,用来解析传入的MyBatis的配置文件,然后调用parse方法进行解析

图2 parse解析入参调试图例
在这个方法中,会从MyBatis的配置文件的根目录中获取xml的内容,其中parser这个对象是一个XPathParser的对象,这个是专门用来解析xml文件的,具体怎么从xml文件中获取到各个节点这里不再进行讲解。这里可以看到解析配置文件是从configuration这个节点开始的,在MyBatis的配置文件中这个节点也是根节点
"1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>configurationPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration><properties><property name="dialect" value="MYSQL" /></properties>然后将解析好的xml文件传入parseConfiguration方法中,在这个方法中会获取在配置文件中的各个节点的配置

图3 解析配置调试图例
以获取mappers节点的配置来看具体的解析过程
<mappers><mapper resource="mappers/StudentMapper.xml"/></mappers>进入mapperElement方法
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
图4 mapperElement方法调试图例
看到MyBatis还是通过创建一个XMLMapperBuilder对象来对mappers节点进行解析,在parse方法中
public void parse() {if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);bindMapperForNamespace();}parsePendingResultMaps();parsePendingCacheRefs();parsePendingStatements();}通过调用configurationElement方法来解析配置的每一个mapper文件
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {try {String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");}builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));} catch (Exception e) {throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: " + e, e);}}以解析mapper中的增删改查的标签来看看是如何解析一个mapper文件的
进入buildStatementFromContext方法
private void buildStatementFromContext(Listlist, String requiredDatabaseId ) {for (XNode context : list) {final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);try {statementParser.parseStatementNode();} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);}}}可以看到MyBatis还是通过创建一个XMLStatementBuilder对象来对增删改查节点进行解析,通过调用这个对象的parseStatementNode方法,在这个方法里会获取到配置在这个标签下的所有配置信息,然后进行设置
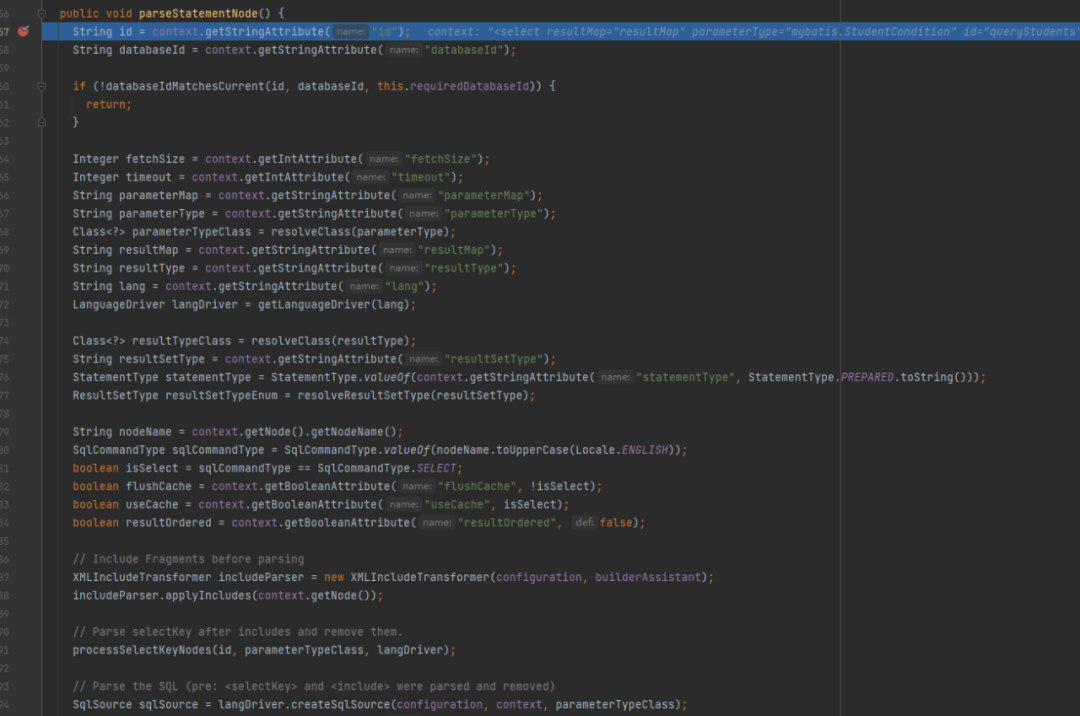
图5 parseStatementNode方法调试图例
解析完成以后,通过方法addMappedStatement将所有的配置都添加到一个MappedStatement中去,然后再将mappedstatement添加到configuration中去
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
图6 增加解析完成的mapper方法调试图例
可以看到一个mappedstatement中包含了一个增删改查标签的详细信息

图7 mappedstatement对象方法调试图例
而一个configuration就包含了所有的配置信息,其中mapperRegistertry和mappedStatements

图8 config对象方法调试图例
具体的流程

图9 SqlSessionFactory对象的构建过程
2.SqlSession的创建过程
SqlSessionFactory创建完成以后,接下来看看SqlSession的创建过程
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();首先会调用DefaultSqlSessionFactory的openSessionFromDataSource方法
@Overridepublic SqlSession openSession() {return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);}在这个方法中,首先会从configuration中获取DataSource等属性组成对象Environment,利用Environment内的属性构建一个事务对象TransactionFactory
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {Transaction tx = null;try {final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);} catch (Exception e) {closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();}}事务创建完成以后开始创建Executor对象,Executor对象的创建是根据 executorType创建的,默认是SIMPLE类型的,没有配置的情况下创建了SimpleExecutor,如果开启二级缓存的话,则会创建CachingExecutor
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;Executor executor;if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);} else {executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);}if (cacheEnabled) {executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);}executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);return executor;}创建executor以后,会执行executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor)方法,这个方法对应的含义是使用每一个拦截器包装并返回executor,最后调用DefaultSqlSession方法创建SqlSession

图10 SqlSession对象的创建过程
3.Mapper的获取过程
有了SqlSessionFactory和SqlSession以后,就需要获取对应的Mapper,并执行mapper中的方法
StudentDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);在第一步中知道所有的mapper都放在MapperRegistry这个对象中,因此通过调用org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperRegistry#getMapper方法来获取对应的mapper
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");}try {return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);} catch (Exception e) {throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);}}在MyBatis中,所有的mapper对应的都是一个代理类,获取到mapper对应的代理类以后执行newInstance方法,获取到对应的实例,这样就可以通过这个实例进行方法的调用
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {private final Class<T> mapperInterface;private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;}public ClassgetMapperInterface() {return mapperInterface;}public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {return methodCache;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")protected T newInstance(MapperProxymapperProxy ) {return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);}public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);return newInstance(mapperProxy);}}获取mapper的流程为

图11 Mapper的获取过程
4.查询过程
获取到mapper以后,就可以调用具体的方法
//执行方法List<Student> students = mapper.queryStudents(condition);首先会调用org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy#invoke的方法,在这个方法中,会调用org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperMethod#execute
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Object result;switch (command.getType()) {case INSERT: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));break;}case UPDATE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));break;}case DELETE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));break;}case SELECT:if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);result = null;} else if (method.returnsMany()) {result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsMap()) {result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);} else {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);}break;case FLUSH:result = sqlSession.flushStatements();break;default:throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());}if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");}return result;}首先根据SQL的类型增删改查决定执行哪个方法,在此执行的是SELECT方法,在SELECT中根据方法的返回值类型决定执行哪个方法,可以看到在select中没有selectone单独方法,都是通过selectList方法,通过调用org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession#selectList(java.lang.String, java.lang.Object)方法来获取到数据
@Overridepublic <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {try {MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);} catch (Exception e) {throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();}}在selectList中,首先从configuration对象中获取MappedStatement,在statement中包含了Mapper的相关信息,然后调用org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor#query()方法

图12 query()方法调试图示
在这个方法中,首先对SQL进行解析根据入参和原始SQL,对SQL进行拼接

图13 SQL拼接过程代码图示
调用MapperedStatement里的getBoundSql最终解析出来的SQL为

图14 SQL拼接过程结果图示
接下来调用org.apache.ibatis.parsing.GenericTokenParser#parse对解析出来的SQL进行解析

图15 SQL解析过程图示
最终解析的结果为

图16 SQL解析结果图示
最后会调用SimpleExecutor中的doQuery方法,在这个方法中,会获取StatementHandler,然后调用org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.PreparedStatementHandler#parameterize这个方法进行参数和SQL的处理,最后调用statement的execute方法获取到结果集,然后 利用resultHandler对结进行处理

图17 SQL处理结果图示
查询的主要流程为


图18 查询流程处理图示
5.查询流程总结
总结整个查询流程如下

图19 查询流程抽象
2.3 场景问题原因及解决方案
2.3.1 个人排查
这个问bug出现的地方在于绑定SQL参数的时候再源码中位置为
@Overridepublic <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);}由于所写的SQL是一个动态绑定参数的SQL,因此最终会走到org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.DynamicSqlSource#getBoundSql这个方法中去
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);}// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();if (rmId != null) {ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);if (rm != null) {hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();}}}return boundSql;}在这个方法中,会调用 rootSqlNode.apply(context)方法,由于这个标签是一个foreach标签,因此这个apply方法会调用到org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.ForEachSqlNode#apply这个方法中去
@Overridepublic boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {Map<String, Object> bindings = context.getBindings();final Iterable<?> iterable = evaluator.evaluateIterable(collectionExpression, bindings);if (!iterable.iterator().hasNext()) {return true;}boolean first = true;applyOpen(context);int i = 0;for (Object o : iterable) {DynamicContext oldContext = context;if (first) {context = new PrefixedContext(context, "");} else if (separator != null) {context = new PrefixedContext(context, separator);} else {context = new PrefixedContext(context, "");}int uniqueNumber = context.getUniqueNumber();// Issue #709if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Map.Entry<Object, Object> mapEntry = (Map.Entry<Object, Object>) o;applyIndex(context, mapEntry.getKey(), uniqueNumber);applyItem(context, mapEntry.getValue(), uniqueNumber);} else {applyIndex(context, i, uniqueNumber);applyItem(context, o, uniqueNumber);}contents.apply(new FilteredDynamicContext(configuration, context, index, item, uniqueNumber));if (first) {first = !((PrefixedContext) context).isPrefixApplied();}context = oldContext;i++;}applyClose(context);return true;}当调用appItm方法的时候将参数进行绑定,参数的变量问题都会存在bindings这个参数中区
private void applyItem(DynamicContext context, Object o, int i) {if (item != null) {context.bind(item, o);context.bind(itemizeItem(item, i), o);}}进行绑定参数的时候,绑定完成foreach的方法的时候,可以看到bindings中不止绑定了foreach中的两个参数还额外有一个参数名字studentName->lct2,也就是说最后一个参数也是会出现在bindings这个参数中的,
private void applyItem(DynamicContext context, Object o, int i) {if (item != null) {context.bind(item, o);context.bind(itemizeItem(item, i), o);}}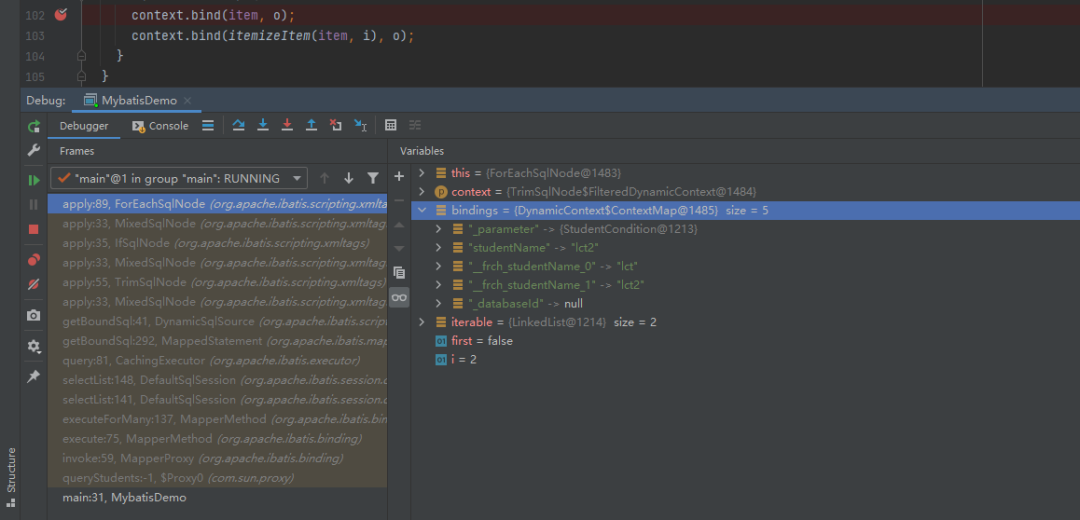
图20 参数绑定过程
最后判定
org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.IfSqlNode#apply
@Overridepublic boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {contents.apply(context);return true;}return false;}可以看到在调用evaluateBoolean方法的时候会把context.getBindings()就是前边提到的bindings参数传入进去,因为现在这个参数中有一个studentName,因此在使用Ognl表达式的时候,判定为这个if标签是有值的因此将这个标签进行了解析
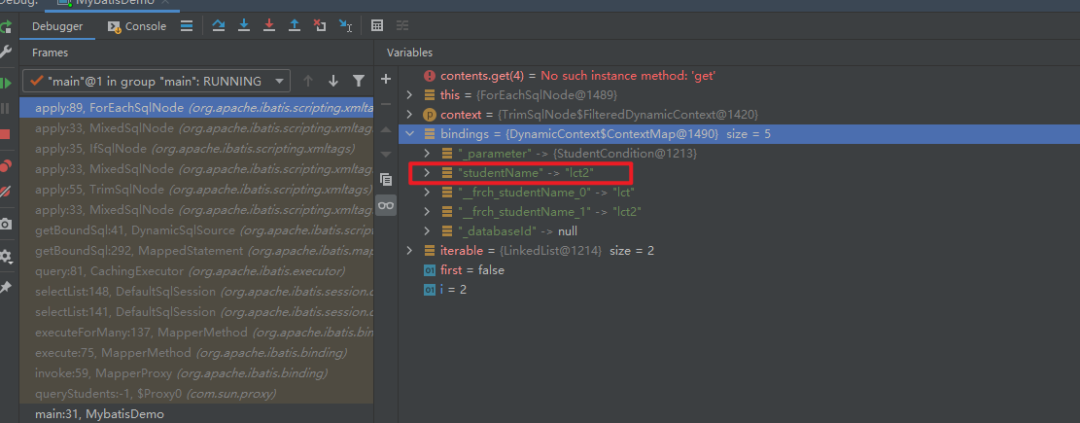
图21 单个参数绑定过程
最终绑定的结果为

图22 全部参数绑定过程
因此这个地方绑定参数的地方是有问题的,至此找出了问题的所在。
2.3.2 官方解释
翻阅MyBatis官方文档进行求证,发现在3.4.5版本发行中bug fixes中有这样一句

图23 此问题官方修复github记录
修复了foreach版本中对于全局变量context的修改的bug
issue地址为https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/pull/966
修复方案为https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/pull/966/commits/84513f915a9dcb97fc1d602e0c06e11a1eef4d6a
可以看到官方给出的修改方案,重新定义了一个对象,分别存储全局变量和局部变量,这样就会解决foreach会改变全局变量的问题。

图24 此问题官方修复代码示例
2.3.3 修复方案
-
升级MyBatis版本至3.4.5以上
-
如果保持版本不变的话,在foreach中定义的变量名不要和外部的一致
3 源码阅读过程总结
理解,首先 MCube 会依据模板缓存状态判断是否需要网络获取最新模板,当获取到模板后进行模板加载,加载阶段会将产物转换为视图树的结构,转换完成后将通过表达式引擎解析表达式并取得正确的值,通过事件解析引擎解析用户自定义事件并完成事件的绑定,完成解析赋值以及事件绑定后进行视图的渲染,最终将目标页面展示到屏幕。
MyBatis源代码的目录是比较清晰的,基本上每个相同功能的模块都在一起,但是如果直接去阅读源码的话,可能还是有一定的难度,没法理解它的运行过程,本次通过一个简单的查询流程从头到尾跟下来,可以看到MyBatis的设计以及处理流程,例如其中用到的设计模式:

图25 MyBatis代码结构图
-
组合模式:如ChooseSqlNode,IfSqlNode等
-
模板方法模式:例如BaseExecutor和SimpleExecutor,还有BaseTypeHandler和所有的子类例如IntegerTypeHandler
-
Builder模式:例如 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder、XMLConfigBuilder、XMLMapperBuilder、XMLStatementBuilder、CacheBuilder
-
工厂模式:例如SqlSessionFactory、ObjectFactory、MapperProxyFactory
-
代理模式:MyBatis实现的核心,比如MapperProxy、ConnectionLogger
4 文档参考
https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
-
-
相关阅读:
从网约车平台合规问题看企业合规难题如何破解
22、Python -- 创建对象和使用对象
Facebook的魅力魔法:探访数字社交的奇妙世界
SpringBoot与Shiro整合详解
特征工程(六)—(2)利用LDA进行特征转换
python绘制云雨图(raincloud plot) 【官方教程翻译】
nvcc编译器之编译选项(chapter 4)
【C++】异常
【GlobalMapper精品教程】005:影像拼接与裁剪案例教程
【Spring】——9、如何指定初始化和销毁的方法?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/jdcdev_/article/details/127118765