-
RabbitMQ 学习(六)---- 路由订阅模型
RabbitMQ 学习(六)---- 路由订阅模型
1、Direct 路由直连模式

在Fanout模式中,一条消息,会被所有订阅的队列都消费。但是,在某些场景下,我们希望不同的消息被不同的队列消费。这时就要用到Direct类型的Exchange。
在Direct模型下:
-
队列与交换机的绑定,不是任意绑定,而是要指定一个
RoutingKey(路由key),相当于是一个队列与交换机连接的规则 -
生产者 在向 Exchange发送消息时,也必须指定消息的
RoutingKey。 -
Exchange不再把消息交给每一个绑定的队列,而是根据消息的
Routing Key进行判断,只有绑定队列的Routingkey与消息的Routing key完全一致,才会接收到消息
(1)生产者
- 声明交换机(exchange)与类型direct
- 生产者通过交换机(exchange),设置路由规则(routineKey),发送消息
生产者代码
发送信息到 "aaa"交换机下“info” 路由key,"warning"路由key
package direct; import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection; import utils.RabbitMQUtils; import java.io.IOException; public class DProvider { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnect(); Channel channel = null; try { // 创建信道 channel = connection.createChannel(); // 声明交换机以及类型 channel.exchangeDeclare("aaa", "direct"); // 设置消息 String body = "direct模式发送消息"; // 在信道中 将消息 发送到交换机 同时设置路由规则 //发送路由为 info的消息 channel.basicPublish("aaa", "info", null,(body+":info").getBytes() ); // 发送路由为 warning的消息 channel.basicPublish("aaa", "warning", null, (body+":warning").getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ RabbitMQUtils.close(channel, connection); } } }
(2)消费者
- 声明交换机与类型(direct),与生产者保持一致
- 声明临时队列(queue)
- 临时队列与交换机绑定(queueBind),同时设置路由规则,队列订阅了交换机中指定路由的信息,一个队列可以绑定多个路由,使用多次 queueBind
消费者1
临时队列订阅了 aaa交换机 中"info" 、“warning” 的路由信息
package direct; import com.rabbitmq.client.*; import utils.RabbitMQUtils; import java.io.IOException; public class DCustomer1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnect(); Channel channel = null; try { // 创建信道 channel = connection.createChannel(); // 声明交换机,与生产者保持一致 channel.exchangeDeclare("aaa", "direct"); // 声明临时队列 String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); // 绑定临时队列 与 交换机,订阅交换机中具体路由规则分发的信息, 交换机和路由规则都是 生产者指定的 // 如果绑定了路由,那么相当于订阅了消息,一种符合规则的广播 channel.queueBind(queue, "aaa", "info"); channel.queueBind(queue, "aaa", "warning"); // 通过队列 接受消息 channel.basicConsume(queue, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println(new String(body)+" routingkey:"+envelope.getRoutingKey()); } }); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
消费者2
临时队列订阅了 aaa 交换机中 “info” 路由下的信息
package direct; import com.rabbitmq.client.*; import utils.RabbitMQUtils; import java.io.IOException; public class DCustomer2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnect(); Channel channel = null; try { // 创建信道 channel = connection.createChannel(); // 声明交换机,与生产者保持一致 channel.exchangeDeclare("aaa", "direct"); // 声明临时队列 String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); // 绑定临时队列 与 交换机,订阅交换机中具体路由规则分发的信息, 交换机和路由规则都是 生产者指定的 // 如果绑定了路由,那么相当于订阅了消息,一种符合规则的广播 channel.queueBind(queue, "aaa", "info"); // 通过队列 接受消息 channel.basicConsume(queue, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println(new String(body)+" routinekey:"+envelope.getRoutingKey()); } }); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
(3)效果展示
消费者1因为 临时队列订阅了 “info”、“warning” 路由,所以生产者的信息都能接收到

消费者2 临时队列因为订阅了 “info” 路由的信息,所有只能接收到 生产者发送的"info"路由中的信息,而 “warning” 路由信息中的信息接收不到。

查看后台交换机路由队列绑定的信息
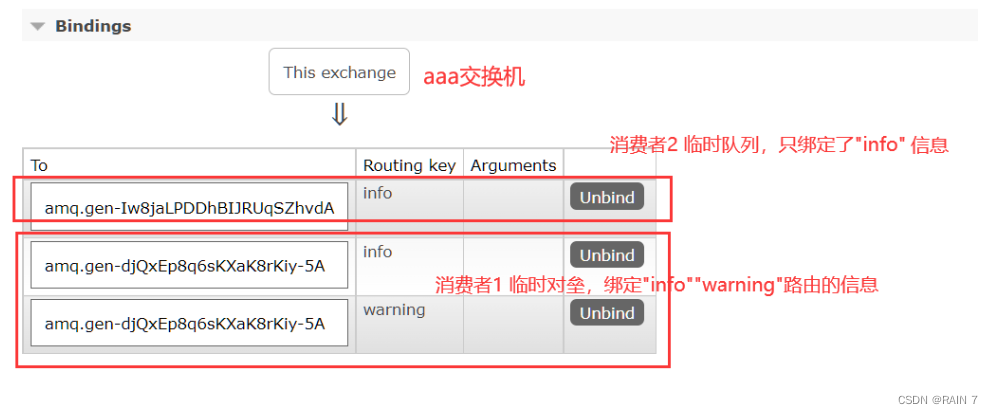
查看队列信息,消费者1 的临时队列,接受了交换机路由 “info”、"warning"的信息

消费者2的临时队列,接受了交换机路由"info" 的信息

2、Topic 路由通配模式
Topic类型的Exchange与Direct相比,都是可以根据RoutingKey把消息路由到不同的队列。只不过Topic类型Exchange可以让队列在绑定Routing key的时候使用通配符!这种模型Routingkey一般都是由一个或多个单词组成,多个单词之间以”.”分割,例如:item.insert
就一句话,与direct模式就是路由匹配多了一个 使用统配符 的功能
(1)通配符使用规则
. 匹配一个单词
# 匹配零个或多个单词
使用如下
admin.* 匹配 admin.staus、admin.item
admin.# 匹配 admin.status.item 、admin
(2)生产者
生产者发送消息到交换机,设置三个不同的路由规则分发消息
routingKey: admin ] message: “生产者 admin 的消息!”
routineKey: admin.user message: “生产者 admin.user 的消息!”
routineKey: admin.user.name message: “生产者 admin.user.name 的消息!”
package topic; import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection; import utils.RabbitMQUtils; import java.io.IOException; public class TProvider { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnect(); Channel channel =null; try { // 创建信道 assert connection != null; channel = connection.createChannel(); // 声明交换机,声明类型Topic channel.exchangeDeclare("bbb", "topic"); // 通过信道,发送交换机设置路由规则 channel.basicPublish("bbb", "admin.user", null, ("生产者 admin.user 的消息!").getBytes()); channel.basicPublish("bbb", "admin", null, ("生产者 admin 的消息").getBytes()); channel.basicPublish("bbb", "admin.user.name", null, ("生产者 admin.user.name 的消息").getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { RabbitMQUtils.close(channel, connection); } } }
(3)消费者
临时队列与交换机绑定(queueBind),同时设置路由规则,不用想direct模式中 需要一个一个规则绑定,直接使用通配符进行绑定即可,可以实现一行语句绑定多个交换机路由
消费者1
临时队列绑定bbb交换机中 admin.* 路由中的消息
package topic; import com.rabbitmq.client.*; import utils.RabbitMQUtils; import java.io.IOException; public class TCustomer1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnect(); try { // 创建信道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); // 声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare("bbb", "topic"); // 声明临时队列 String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); // 队列绑定交换机,并订阅路由(使用通配符) channel.queueBind(queue, "bbb", "admin.*"); // 通过队列接收消息 channel.basicConsume(queue, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println(new String(body)+" 消费者接收路由通配: admin.*"); } }); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
消费者2
临时队列绑定bbb交换机中 admin.# 路由中的消息
package topic; import com.rabbitmq.client.*; import utils.RabbitMQUtils; import java.io.IOException; public class TCustomer2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnect(); try { // 创建信道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); // 声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare("bbb", "topic"); // 声明临时队列 String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); // 队列绑定交换机,并订阅路由(使用通配符) channel.queueBind(queue, "bbb", "admin.#"); // 通过队列接收消息 channel.basicConsume(queue, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println(new String(body)+" 消费者接收路由通配: admin.#"); } }); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
(4)效果展示
后台交换机绑定队列与路由key

消费者2 队列admin.# 匹配零个或多个单词,生产者路由信息全部匹配

消费者1 队列admin.* 匹配一个单词,生产者路由 admin.user 匹配成功
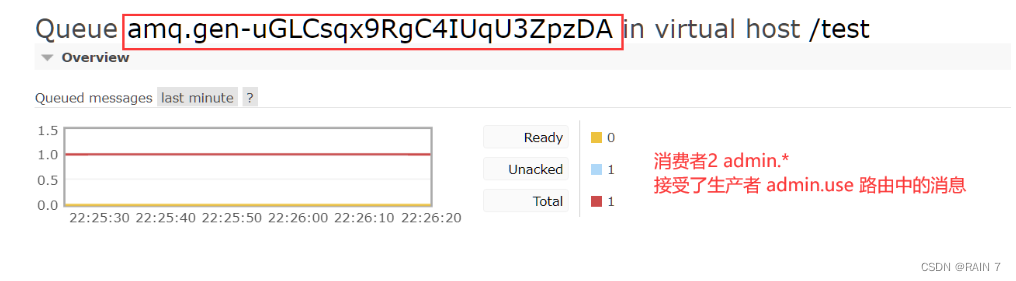
消费者1 的接收到的信息

消费者2 接收到的信息

-
-
相关阅读:
在线渲染3d怎么用?3d快速渲染步骤设置
网络安全(黑客)自学
数据结构-排序
笔记 | 编程经验谈:如何正确的使用内存
java计算机毕业设计SpringBoot在线答疑系统
【Linux】常用工具(下)
mysql面试题51:你是如何监控你们的数据库的?你们的慢日志都是怎么查询的?
STM32连接WIFI-ESP8266实战—AP模式运用
9.15-词向量
黑马苍穹外卖前端求解
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/rain67/article/details/127097517