-
Linux学习笔记——系统文件与目录操作函数
文件操作函数

获取文件属性—stat、lstat、fstat
其函数原型:

这里struct stat结构体如下:struct stat { dev_t st_dev; //文件的设备编号 ino_t st_ino; //节点 mode_t st_mode; //文件的类型和存取的权限 nlink_t st_nlink; //连到该文件的硬连接数目,刚建立的文件值为1 uid_t st_uid; //用户ID gid_t st_gid; //组ID dev_t st_rdev; //(设备类型)若此文件为设备文件,则为其设备编号 off_t st_size; //文件字节数(文件大小) blksize_t st_blksize; //块大小(文件系统的I/O 缓冲区大小) blkcnt_t st_blocks; //块数 time_t st_atime; //最后一次访问时间 time_t st_mtime; //最后一次修改时间 time_t st_ctime; //最后一次改变时间(指属性) };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
st_mode该变量占 2 byte,共 16 位:(1) 掩码的使用: st_mode & 掩码 (2) 其他人权限( 0-2 bit ) (a) S_IROTH 00004 读权限 (b) S_IWOTH 00002 写权限 掩码:S_IRWXO 00007 (c) S_IXOTH 00001 执行权限 (3) 所属组权限(3-5bit) (a) S_IRWXG 00070 读权限 (b) S_IRGRP 00040 写权限 掩码:S_RWXG 00070 (c) S_IXGRP 00010 执行权限 (4) 文件所有者权限(6-8bit) (a) S_IRUSR 00400 读权限 (b) S_IWUSR 00200 写权限 掩码:S_IRWXU 00700 (c) S_IXUSR 00100 执行权限 (5) 文件特权位(9-11bit) (a) S_ISUID 0004000 设置用户ID (b) S_ISGID 0002000 设置组ID 文件特权位很少用 (c) S_ISVTX 0001000 设置黏住位 (6) 文件类型(12-15bit) (a) S_IFSOCK 0140000 socket(套接字) (b) S_IFLNK 0120000 symbolic link(符号链接--软连接) (c) S_IFREG 0100000 regular file(普通文件) (d) S_IFBLK 0060000 block device(块设备) 掩码:S_IFMT 017000 (e) S_IFDIR 0040000 directory(目录) (f) S_IFCHR 0020000 character device(字符设备) (g) S_IFIFO 0010000 FIFO(管道)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
以上三个获取文件属性的函数 若成功,返回0;若失败,返回 -1
stat、lstat、fstat之间的区别
-
fstat函数:系统调用的是一个文件描述符,而另外两个则直接接收文件路径。文件描述符是我们用open系统调用后得到的,而文件全路径直接写就可以了。 -
stat函数与lstat函数的区别: 当一个文件是符号链接时,lstat函数返回的是该符号链接本身的信息(穿透);而stat函数返回的是该链接指向文件的信息(不穿透)。
#include#include #include #include #include int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { if( argc<2 ) { perror("a.out "); exit(1); } struct stat st; int ret = lstat(argv[1],&st); if( ret == -1) { perror("lstat"); exit(1); } int size = st.st_size; printf("file size = %d\n",size); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29


下面使用stat实现一个简单的ls -l指令:#include#include #include #include // 所有者信息 #include // 所属组信息 #include #include #include #include int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { if( argc<2 ) { perror("./a.out filename\n"); exit(1); } struct stat st; int i; for( i = 1; i<argc; i++) { int ret = stat(argv[i],&st); // 获取文件或者目录的所有信息存储于 st 结构体中 if( ret == -1 ) { perror("stat"); exit(1); } // 存储文件类型和访问权限 char perms[11] = {0}; // 判断文件类型 switch( st.st_mode & S_IFMT ) { case S_IFSOCK: // 套接字文件 perms[0] = 's'; break; case S_IFLNK: // 软连接文件 perms[0] = 'l'; break; case S_IFREG: // 普通文件 perms[0] = '-'; break; case S_IFBLK: // 块设备文件 perms[0] = 'b'; break; case S_IFDIR: // 目录文件 perms[0] = 'd'; break; case S_IFCHR: // 字符设备文件 perms[0] = 'c'; break; case S_IFIFO: // 管道文件 perms[0] = 'p'; break; default: break; } // 判断文件的访问权限 // 文件的所有者 perms[1] = (st.st_mode & S_IRUSR) ? 'r':'-'; perms[2] = (st.st_mode & S_IWUSR) ? 'w':'-'; perms[3] = (st.st_mode & S_IXUSR) ? 'x':'-'; // 文件的所属组 perms[4] = (st.st_mode & S_IRGRP) ? 'r':'-'; perms[5] = (st.st_mode & S_IWGRP) ? 'w':'-'; perms[6] = (st.st_mode & S_IXGRP) ? 'x':'-'; // 文件的其他用户 perms[7] = (st.st_mode & S_IROTH) ? 'r':'-'; perms[8] = (st.st_mode & S_IWOTH) ? 'w':'-'; perms[9] = (st.st_mode & S_IXOTH) ? 'x':'-'; // 硬链接计数 int nums = st.st_nlink; // 文件所有者 char *fileuser = getpwuid(st.st_uid)->pw_name; // 文件所属组 char *filegroup = getgrgid(st.st_gid)->gr_name; // 文件大小 int size = (int)st.st_size; // 文件修改时间 char *time = ctime(&st.st_mtime); char mtime[512]=""; strncpy(mtime,time,strlen(time)-1); // 保存输出信息格式 char buf[1024]={0}; // 把对应信息按格式输出到 buf 中 sprintf(buf,"%s %d %s %s %d %s %s",perms,nums,fileuser,filegroup,size,mtime,argv[i]); // 打印 buf printf("%s\n",buf); // drwxrwxr-x 3 arrayli arrayli 4096 11月 13 23:19 day05 // -rw-r--r-- 1 arrayli arrayli 8980 11月 7 22:05 examples.desktop } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
ctime函数是将日历时间(这里是一个结构体)转化为字符串形式。运行结果如下:

文件操作函数还有access、chmod、chown、truncate、link、unlink、rename等,用法都比较简单,参考最上面的图片以及man文档即可。
目录操作

readdir 函数
readdir函数主要用于读目录,其函数原型如下:

dirent结构体内容如下:struct dirent { ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */ // 目录进入点的 inode off_t d_off; /* not an offset; see NOTES */ // 目录文件头开始至此目录进入点的位移 unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */ // d_name的长度,不包括NULL字符 unsigned char d_type; /* type of file; not supported // d_name所指的文件类型 by all filesystem types */ char d_name[256]; /* filename */ // 文件名 };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
其中
dtype有八种类型(1) DT_BLK This is a block device. 块设备 (2) DT_CHR This is a character device. 字符设备 (3) DT_DIR This is a directory. 目录 (4) DT_FIFO This is a named pipe (FIFO). 管道 (5) DT_LNK This is a symbolic link. 软链接 (6) DT_REG This is a regular file. 普通文件 (7) DT_SOCK This is a UNIX domain socket. 套接字 (8) DT_UNKNOWN The file type is unknown. 未知类型- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
下面实现递归读取指定目录所有文件,并输出总的文件数量。
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include // 获取 root 目录下的文件个数 int get_file_count(char *root) { // open dir DIR * dir = NULL; dir = opendir(root); if( NULL == dir ) { perror("opendir"); exit(1); } // 遍历当前打开的目录 struct dirent* ptr = NULL; char path[1024]={0}; int total = 0; while( (ptr = readdir(dir) )!= NULL) { // 过滤掉 . 和 .. if( strcmp(ptr->d_name,".") == 0 || strcmp(ptr->d_name,"..") == 0 ) { continue; } // 如果是目录,递归读目录 if(ptr->d_type == DT_DIR) { sprintf(path,"%s/%s",root,ptr->d_name); total += get_file_count(path); } // 如果是普通文件 if( ptr->d_type == DT_REG ) { total++; } } // 关闭目录 closedir(dir); return total; } int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { if( argc<2 ) { perror("./a.out dir\n"); exit(1); } // 获取文件个数 int count = get_file_count(argv[1]); printf("%s has file numbers : %d\n",argv[1],count); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66

dup和dup2

#include#include #include #include #include #include #include int main(void) { int fd =open("a.txt",O_RDWR); if( fd == -1 ) { perror("open"); exit(1); } printf("file open fd = %d\n",fd); // 找到进程文件描述符表 ======= 第一个========== 可用的文件描述符 // 将参数指定的文件复制到该描述后 返回这个描述符 int ret = dup(fd); if( fd == -1 ) { perror("dup"); exit(1); } printf(" dup fd = %d\n",ret); char *buf = "你是猴子请来的救兵吗??\n"; char *buf1 = "你大爷的,我是程序猿!!!\n"; write(fd,buf,strlen(buf)); write(ret,buf1,strlen(buf1)); close(fd); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40

可以看到 newfd 与 oldfd 对应同一个文件描述,其文件偏移是一样的。#include#include #include #include #include #include #include int main(void) { int fd =open("english.txt",O_RDWR); if( fd == -1 ) { perror("open"); exit(1); } int fd1 =open("a.txt",O_RDWR); if( fd1 == -1 ) { perror("open"); exit(1); } printf("fd = %d\n",fd); printf("fd1 = %d\n",fd1); int ret = dup2(fd1, fd); if( ret == -1 ) { perror("dup2"); exit(1); } printf(" current fd = %d\n",ret); char *buf = "主要看气质 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!\n"; write(fd,buf,strlen(buf)); write(fd1,"hello world!",12); close(fd); close(fd1); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46

可以看到dup2()将newfd关闭了,并且newfd和oldfd对应同一个文件。fcntl

fcntl可以改变已打开文件的属性,下面使用fcntl将一个只写文件改为追加写。#include#include #include #include #include #include #include int main(void) { int flag; int fd; // 测试字符串 char *q ="社会主义好哇!!!\n"; // 以只写方式打开文件 fd = open("test.txt",O_WRONLY); if( fd == -1 ) { perror("open"); exit(1); } // 使用 F_GETFL 命令得到文件状态标志 int flags = fcntl(fd,F_GETFL,0); if( flags == -1 ) { perror("fcntl"); exit(1); }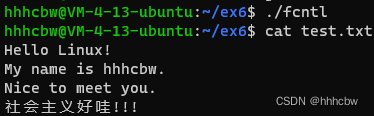 // 将文件状态修改为追加写 if( fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,O_APPEND) == -1 ) { perror("fcntl"); exit(1); } // 输入新的内容,该内容会追加到旧内容对的后面 if( write(fd,q,strlen(q)) == -1 ) { perror("write"); exit(1); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
正常只写文件会覆盖原有文件,而改为追加写,则会在在原有文件之后继续写。

-
相关阅读:
LeetCode——半有序排列
腾讯云双11服务器优惠活动价格表预热!
代码随想录Day52 | 300. 最长递增子序列 | 674. 最长连续递增序列 | 718. 最长重复子数组
网络安全(黑客技术)自学规划
手写 Vue 系列 之 从 Vue1 升级到 Vue2
3D模型格式全解|含RVT、3DS、DWG、FBX、IFC、OSGB、OBJ等70余种
FFplay文档解读-31-视频过滤器六
推理引擎之模型压缩浅析
[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计二手书交易系统
C嘎嘎之类和对象中
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44491423/article/details/126915138
