-
【嵌入式面试题】常见面试题梳理二
注:看面试题时,主要应该以学习为主,面试题有些基本上是我们编程时会遇上的问题,通过学习面试题会提升我们的编程意识和解决一些日常我们编程所遇到的问题,看完这篇面试题后,希望能对你有所帮助,另外题中有问题的地方可以在评论区指出,在这里谢谢您的观看。
一、链表相关
1、链表概念
- 链表是一种物理储存单元上
非连续、非顺序的 存储结构 - 数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针连接次序实现的
- 链表由一系列的结点组成,结点可以动态生成
- 结点分为两部分:
数据域和指针域
2、链表常见应用场景
- 复杂数据结构的基础
- 撤销功能
- 票据
- 员工信息
- linux内核中
- 。。。。。。。。。。
3、链表相关笔试题
判断链表是否有环
思路:使用快慢指针,快的指针一次移动两个节点,慢的指针一次移动一个结点,两个指针都从起始位置出发,当慢指针与快指针相遇时,则说明有环,如下图所示。

代码编写:
list_ring.h:#ifndef LIST_RING_H_ #define LIST_RING_H_ #include#include #include typedef int data_t; //储存的数据类型 typedef struct LinkList //链表结构体 { data_t data; struct LinkList *next; }linknode, *linklist; linklist link_list_init(void); //链表初始化 void link_list_destroy(linklist H); //链表销毁 int link_ring_create(linklist H); //链表环创建 linknode *check_list_ring(linklist H); //检查链表是否存在环 #endif - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
list_ring.c:#include "list_ring.h" linklist link_list_init() { linklist H = (linklist)malloc(sizeof(linknode)); if(H == NULL) return NULL; H->data = 0; H->next = NULL; return H; } void link_list_destroy(linklist H) { assert(H); linknode *p = H; while(p) { H = H->next; free(p); p->next = NULL; p = H; } p = NULL; } int link_ring_create(linklist H) { assert(H); int i; linklist q = H; linknode *p = NULL; for(i = 0; i < 10; i++) { p = (linklist)malloc(sizeof(linknode)); if(p == NULL) { printf("linknode create error!\r\n"); return -1; } p->data = i; p->next = NULL; q->next = p; q = q->next; } p->next = H->next->next->next; return 0; } linknode *check_list_ring(linklist H) { assert(H); linknode *fast, *slow; //快慢指针 fast = H; slow = H; if(fast->next != NULL) { while(fast->next) { fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; if(fast == slow) { return fast; //有环 } } return NULL; //没有环 } else { return NULL; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
test.c:#include "list_ring.h" int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) { int ret = 0; linknode *p = NULL; linklist H = link_list_init(); if(H == NULL) { printf("linklist init error!\r\n"); return -1; } ret = link_ring_create(H); if(ret != 0) { link_list_destroy(H); H = NULL; printf("link ring create error!\r\n"); return -1; } p = check_list_ring(H); if(p != NULL) { printf("list has a ring!\r\n"); printf("The value of the encounter node is %d\r\n", p->data); free(p); } else { printf("list has no ring!\r\n"); } link_list_destroy(H); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
运行结果:

如果有环,得出环的起始位置

思路:根据这张图,在相遇点时,快指针走过的结点为n+2*x+y, 慢指针走过的结点是x+n,快指针是慢指针的2倍,所以有 n+2*x+y = 2*(x+y);得 n = y; 因此得到环的起始点的地址 一个相遇点指针与 一个头结点指针两者同时移动,当两者相等时,指针指向的就是起始点的地址。
代码:
linknode *initial_ring_node_get(linklist H, linknode *p) { assert(H); assert(p); while(p->next != NULL || H->next != NULL) { p = p->next; H = H->next; if(p == H) return H; } return NULL; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
如果有环,得出环的结点数

思路:保存相遇点,让指针从相遇点走一圈计算结点数
代码:
int node_number_get(linknode *p) { assert(p); int i = 1; linknode *q = p->next; while(q != p) { if(q->next == NULL) { return -1; } q = q->next; i++; } return i; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
二、栈和队列
1、栈和队列的概念
栈的概念
栈(stack)是仅限在表尾进行插入和删除的线性表。对于栈来说:
- 表尾端称为栈顶(top)
- 表头端称为栈底(bottom)
- 不含元素的空表为空栈
- 栈遵循后进先出的原则(LIFO)
队列的概念
- 队列是一种特殊的线性表
- 队列允许一端进行插入,一端进行删除
- 队列插入的一端称为队尾,删除的一端称为队头
- 队列不允许中间操作
- 队列是一种
先进先出的线性表(FIFO)
2、栈和队列的应用场景
栈的应用场景
- 语法检查,符号成对出现,例如:“{}”、“[]”、“()”、“<>”。
- 进制转化,例如:十进制的100转化为8进制,先将100除以8,商12余4,将4进栈,将12除以8,商1余4,将4进栈,将1除以8,商0与1,将1进栈,在依次出栈,得8进制数144。
- 浏览器的前进与后退
- 。。。。。。。。。。
队列的应用场景
- 操作系统中,如消息队列、工作队列
- 二叉树按层次遍历
- 排队系统
- 。。。。。。。。。。。。
3、栈和队列的相关笔试题
有效括号
题目:给定一个字符串,由一下字符组成,‘(’、‘[’、‘{’、‘)’、‘]’、‘}’,以‘()’、‘[]’、‘{}’,这样的组合为括号配对成功,示例如下:
s = '()[]{}' 输出为ture s = '[{}()]' 输出为ture s = ‘[{([])}]’ 输出为ture s = ''[{]}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
代码:
stack_symbol.h:#ifndef STACK_SYMBOL_H_ #define STACK_SYMBOL_H_ #include#include #include typedef char data_t; typedef struct Stack_Symbol { data_t *data_space; //数据空间指针 int top; //数据栈顶指针 int maxlen; //数据最大储存空间 }StackSymbol; StackSymbol *stack_symbol_create(int len); void stack_symbol_enter(StackSymbol *st, data_t data); data_t stack_symbol_out(StackSymbol *st); int symbol_judge(StackSymbol *st, const char *str); #endif - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
stack_symbol.c:#include "stack_symbol.h" StackSymbol *stack_symbol_create(int len) { StackSymbol *p = (StackSymbol *)malloc(sizeof(StackSymbol)); if(p == NULL) { printf("symbol stack create error!\r\n"); return NULL; } p->data_space = (data_t *)malloc(len*sizeof(data_t)); if(p->data_space == NULL) { printf("data space create error!\r\n"); return NULL; } p->top = 0; p->maxlen = len; return p; } void stack_symbol_enter(StackSymbol *st, data_t data) { assert(st); int newlen = 0; if(st->top == st->maxlen) //栈满了 { newlen = st->maxlen == 0? 4 : 2*st->maxlen; st->data_space = (data_t *)realloc(st, st->maxlen*sizeof(data_t)); if(st->data_space == NULL) { printf("data space assignment failure!\r\n"); exit(-1); } st->maxlen = newlen; } st->data_space[st->top] = data; st->top++; } data_t stack_symbol_out(StackSymbol *st) { int OutData = 0; assert(st); if(st->top == 0) { printf("stack is empty!\r\n"); return 0; } OutData = st->data_space[st->top-1]; st->data_space[st->top-1] = 0; st->top--; return OutData; } int symbol_judge(StackSymbol *st, const char *str) { assert(st); assert(str); data_t c = 0; while(*str != '\0') { if(*str == '(' || \ *str == '[' || \ *str == '{') { stack_symbol_enter(st, *str); str++; } else { c = stack_symbol_out(st); if(c == 0) return 0; if((c == '(' && *str != ')') || \ (c == '[' && *str != ']') || \ (c == '{' && *str != '}')) { return 0; } else str++; } } return 1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
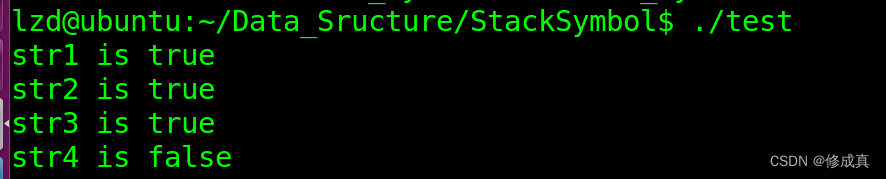
test.c:#include "stack_symbol.h" int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) { int ret = 0; const char *str1 = "()[]{}"; const char *str2 = "[{}()]"; const char *str3 = "[{([])}]"; const char *str4 = "[{]}"; StackSymbol *st = stack_symbol_create(10); if(st == NULL) return -1; ret = symbol_judge(st, str1); if(ret == 1) printf("str1 is true\r\n"); else printf("str1 is false\r\n"); ret = symbol_judge(st, str2); if(ret == 1) printf("str2 is true\r\n"); else printf("str2 is false\r\n"); ret = symbol_judge(st, str3); if(ret == 1) printf("str3 is true\r\n"); else printf("str3 is false\r\n"); ret = symbol_judge(st, str4); if(ret == 1) printf("str4 is true\r\n"); else printf("str4 is false\r\n"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
运行现象:

- 链表是一种物理储存单元上
-
相关阅读:
ATF启动(五):服务注册
关于Pod中进程在节点中的研究
Leetcode406. 根据身高重建队列
R包的尽头是 C/C++
C语言学习之路(基础篇)—— 文件操作(下)
Oracle中的索引碎片
LLM 大模型学习必知必会系列(十):基于AgentFabric实现交互式智能体应用,Agent实战
YOLO v5 实战 中国交通标志识别 原理部分
Xinlinx zynq7010国产替代 FMQL10S400 全国产化 ARM 核心板+扩展板
[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django线上评分分享平台
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_51447215/article/details/126892433
