-
【MybatisPlus】MP的分页查询、多条件查询以及查询过程中解决null的空值判定
文章目录
MP这样一款强大的持久层框架处理起来复杂的SQL来也是得心应手,效率极高,快快与我一同领略Plus的独特魅力吧

一.分页处理
1.调用方法传入参数获取返回值
创建IPage分页对象,设置分页参数,1为当前页码,3为每页显示的记录数,执行分页查询并获取其结果
- @SpringBootTest
- class Mybatisplus{
- @Autowired
- private UserDao userDao;
- //分页查询
- @Test
- void testSelectPage(){
- IPage
page=new Page<>(1,3); - userDao.selectPage(page,null);
- System.out.println("当前页码值:"+page.getCurrent());
- System.out.println("每页显示数:"+page.getSize());
- System.out.println("一共多少页:"+page.getPages());
- System.out.println("一共多少条数据:"+page.getTotal());
- System.out.println("数据:"+page.getRecords());
- }
- }
2.设置分页拦截器
将MP提供的分页拦截器配置成Spring管理的bean对象
- @Configuration
- public class MybatisPlusConfig {
- @Bean
- public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor(){
- //1 创建MybatisPlusInterceptor拦截器对象
- MybatisPlusInterceptor mpInterceptor=new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
- //2 添加分页拦截器
- mpInterceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor());
- return mpInterceptor;
- }
- }
查询结果如下:

二.条件查询
2.1通过QueryWrapper对象来执行分页查询
- @SpringBootTest
- class Mybatisplus{
- @Autowired
- private UserDao userDao;
- @Test
- void testGetAll(){
- QueryWrapper qw = new QueryWrapper();
- qw.lt("age",18);
- List
userList = userDao.selectList(qw); - System.out.println(userList);
- }
- }
注:lt()方法为小于(<) ,对应的SQL为:
SELECT id,name,password,age,tel FROM user WHERE (age < ?)很容易发现, 以字符串形式输出作为查询条件可能会出现字符串拼写错误 ,针对此种情况,可以进行一下小改进!
2.2在QueryWrapper对象的基础上使用lambda表达式
为了解决以字符串形式作为输出而造成拼写错误的问题, 通过lambda来实现实体与属性对应进行查询,就极大地提高了查询的准确性
- @SpringBootTest
- class Mybatisplus{
- @Autowired
- private UserDao userDao;
- @Test
- void testGetAll(){
- QueryWrapper
qw = new QueryWrapper (); - qw.lambda().lt(User::getAge, 10);//添加条件
- List
userList = userDao.selectList(qw); - System.out.println(userList);
- }
- }
与之对应的SQL语句同样也是:
SELECT id,name,password,age,tel FROM user WHERE (age < ?)注:构建LambdaQueryWrapper的时候泛型不能省

当不使用泛型时会提示默认的Object类不是函数接口
而我们的 lambda()的底层又需要传进去一个实体 ,传进去Object显然不能与后面的查询条件相联系!
此时我们再次编写条件的时候,就不会存在写错名称的情况,但是qw后面多了一层lambda()调用
2.3直接通过LambdaQueryWrapper对象
这也是方式二的另一种写法,原理相同都是利用LambdaQueryWrapper
- @SpringBootTest
- class Mybatisplus{
- @Autowired
- private UserDao userDao;
- @Test
- void testGetAll(){
- LambdaQueryWrapper
lqw = new LambdaQueryWrapper (); - lqw.lt(User::getAge, 10);
- List
userList = userDao.selectList(lqw); - System.out.println(userList);
- }
- }
三.多条件查询
对于多条件的情景,MP依然可以简单化解,并且构建多条件的时候,可以支持链式编程
3.1且的情况
场景一:查询数据库表中,年龄在3岁到8岁之间的用户信息
@SpringBootTest class Mybatisplus{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; @Test /** * 多条件查询 */ void testGetAll04() { //方式四 (常用!) LambdaQueryWrapper<Users> qw4 = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>(); qw4.lt(Users::getAge, 8); //上限 qw4.gt(Users::getAge, 3); //下限 // qw4.lt(Users::getAge, 8).gt(Users::getAge, 3); 链式编程! List<Users> users = userDao.selectList(qw4); System.out.println(users); } }注:gt(),大于(>),最终的SQL语句为
SELECT id,name,password,age,tel FROM user WHERE (age < ? AND age > ?)也是迅速查出来了结果

3.2或的情况
场景二:查询数据库表中,年龄小于3或年龄大于8的数据
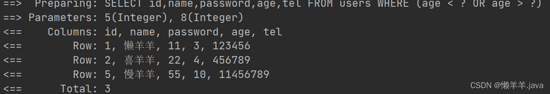
@SpringBootTest class Mybatisplus{ @Autowired private UserDao userDao; @Test void testGetAll(){ LambdaQueryWrapper<User> lqw = new LambdaQueryWrapper<User>(); lqw.lt(User::getAge, 3).or().gt(User::getAge, 8); List<User> userList = userDao.selectList(lqw); System.out.println(userList); } }这里的or()就相当于sql语句中的
or关键字,不加默认是and,最终的sql语句为:SELECT id,name,password,age,tel FROM user WHERE (age < ? OR age > ?)也是顺利的查了出来
四.null判定

以TB为例,我们购物时进行条件筛选时, 可以选择单条件,也可以选择多条件 ,如上,我的条件就变成price>3000,price

显然,这种情况在开发过程中时不被允许的。所以要求我们针对null的情况要解决如下问题:
用户在输入值的时候:
1.如果只输入第一个框,说明要查询大于该价格的商品
2.如果只输入第二个框,说明要查询小于该价格的商品
3.如果两个框都输入了,说明要查询价格在两个范围之间的商品于是,我们可以
新建一个模型类,让其 继承Brand类,并在其中添加price2属性 ,Brand02 在拥有Brand属性后同时添加了price2属性
- @Data
- public class Brand {
- private Long id;
- private String name;
- private Double price;
- }
- @Data
- public class Brand02 extends Brand {
- private Integer price2;
- }
解决了实体的问题,再来解决条件的问题
- "color:#444444">"background-color:#f6f6f6">"color:#1f7199">@SpringBootTest
- "color:#333333">class "color:#880000">Mybatisplus02{
- "color:#1f7199">@Autowired
- "color:#333333">private BrandDao brandDao;
- "color:#1f7199">@Test
- "color:#333333">void testGetAll(){
- BrandQuery bq = "color:#333333">new BrandQuery();
- LambdaQueryWrapper
lqw = "color:#333333">new LambdaQueryWrapper (); - lqw.lt("color:#78a960">null!=bq.getPrice2(),"color:#880000">User"color:#880000">::getPrice, bq.getPrice2());
- lqw.gt("color:#78a960">null!=bq.getPrice(),"color:#880000">User"color:#880000">::getPrice, bq.getPrice());
- List
brands = brandDao.selectList(lqw); - System.out.println(brands);
- }
- }
解读:
如果两个属性不为空,则查询price,price2区间范围内
实现的核心在于lt()、gt()方法,condition为boolean类型上述的
null!=bq.getPrice2()与之对应, 返回true,则添加条件,返回false则不添加条件,条件的生效与否就是靠的这个设计!
最后,也是在null的条件下完成了查询:

-
相关阅读:
接口响应优化方案
精读《素书》精彩语录及感悟篇(二)
矢量图形编辑软件 illustrator 2023 mac 中文软件特点
Viper FTP Mac/ftp管理工具
Java - static 关键字
RPA处理重复工作,助力高效资金管理
Python基础库-JSON库
系分 - 数学与经济管理
Parsec 移动宽带无法登录问题和设置代理方法
人工智能机器学习底层原理剖析,人造神经元,您一定能看懂,通俗解释把AI“黑话”转化为“白话文”
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Candyz7/article/details/126901352
