-
Q-Learning
一、什么是Q-learning
Q-Learning是强化学习中,一种基于值(values-based)的算法,最终的return是一个表格,即Q-Table。这个表格的每一行都代表着一个状态(state),每一行的每一列都代表着一个动作(action),而每个值就代表着如果在该state下,采取该action所能获取的最大的未来期望奖励。通过Q-Table就可以找到每个状态下的最优行为,进而通过找到所有的最优action来最终得到最大的期望奖励。
二、马尔科夫奖励模型(Markov Reward Process,MRP)
马尔科夫奖励模型是带回报值的马尔可夫模型
马尔科夫奖励模型的定义:
1、S 是有限个状态的集合s∈S;
2、P 是一个动态转移模型;
3、R 是一个奖励函数;
4、γ 衰减因子。

回报 & 值函数

马尔可夫决策过程(马尔可夫过程 + 奖励 + 动作)

马尔可夫决策过程的策略:
1、对于MDP,希望得到一个策略
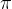 ,对于每一个状态,都能给予一个动作;
,对于每一个状态,都能给予一个动作;2、策略可以是固定的,也可是随机的;
3、更一般地说,我们会将其视为一个条件概率分布;
4、最优策略
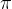 *:一个执行之后能得到最大回报的策略
*:一个执行之后能得到最大回报的策略马尔可夫决策过程的搜索树:

三、贝尔曼方程




收敛性:

四、Q-Learning算法流程

1、建立Q表;
2、选择当前状态的最优action(或设置一定概率随机选择action)
3、执行选择的action,更新当前状态下所选行为的Q值(估计值)
4、更新方法:

五、算法实例1
实例情况:
环境为一个直长廊,直长廊正前方,有一个钻石,直长廊后面,是一个深渊。此处一个Agent,可选择的action有两个,分别是left和right。设定:掉进深渊,score为-1,得到钻石,score为+1 ,其余score均为0 。
可以根据下方图画理解:

如图,这个长得像小人的,就是Agent,它左侧阴影部分,就是深渊,掉进去就-1;离它较远的右侧,有一个粉红的球,就是钻石,得到就是+1.
我们可以画一个表格,来抽象化一下环境和奖励:
深渊-1 Agent起始位置 0 0 0 0 钻石+1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 这个表格第一行就是地图,第二行是地图下标。
我们规定,Agent有只有两种动作,Left和Right,也就是左和右。
代码大致流程可以写出:
1、初始化,初始化环境参数、Agent参数;
2、图画更新,为便于用户观察,动态展示Agent位置;
3、Agent观察环境,看是否经历过这个state,如果经历过就选最优action,如果没有就随机action;
4、执行3所选的action;
5、观察终点,看是否到终点或是否掉入深渊;
6、更新坐标;
7、获取下一环境;
8、学习;
9、参数归零;
10、2-9迭代,直到5成立。
伪代码形式:
- 初始化测试环境对象
- 初始化Agent
- 循环:
- 环境观察
- 图画更新
- while(1):
- 终点观察
- if(到达终点):
- 参数归零
- break;
- 动作选择
- 获取下一步的环境的实际情况
- 学习
- 更新坐标
- 图画更新
下面展示一下实际代码:
首先是环境代码:
Env.py
这是环境代码,主要功能包括:生成图像、获取所在位置、检测是否到终点、更新当前位置、获取下一步的实际情况和初始化地图
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- @Project :Q_learn
- @File :Env.py
- @Author :Hao
- @Date :2022-09-10 010 8:38
- """
- import numpy as np
- class Env:
- def __init__(self, column, start_colum, maze_column):
- self.column = column # 表示地图的长度
- self.maze_column = maze_column - 1 # 宝藏所在的位置
- self.x = start_colum # 初始化x
- self.map = np.arange(column) # 给予每个地点一个标号
- self.count = 0 # 用于记录一共走了多少步
- # 生成图像
- def draw(self):
- a = []
- for j in range(self.column): # 更新图画
- if j == 0:
- a.append('x')
- elif j == self.x:
- a.append('o')
- elif j == self.maze_column:
- a.append('m')
- else:
- a.append('_')
- interaction = ''.join(a)
- print('\r{}'.format(interaction), end='')
- # 获取所在位置
- def get_observation(self):
- return self.map[self.x] # 返回现在所在位置
- # 是否已到达终点
- def get_terminal(self):
- if self.x == self.maze_column: # 如果得到了宝藏,则返回已经完成
- done = True
- elif self.x == 0: # 如果掉入左边边缘,失败,-1
- done = True
- else:
- done = False
- return done
- # 更新当前位置
- def update_place(self, action):
- self.count += 1 # 更新的时候表示已经走了一步
- if action == 'right':
- if self.x < self.column - 1:
- self.x += 1
- elif action == 'left': # left
- if self.x > 0:
- self.x -= 1
- # 获得下一步的环境的实际情况
- def get_target(self, action):
- if action == 'right': # 获得下一步的环境的实际情况
- if self.x + 1 == self.maze_column:
- score = 1
- pre_done = True
- else:
- score = 0
- pre_done = False
- return self.map[self.x + 1], score, pre_done
- elif action == 'left': # left
- if self.x - 1 == self.maze_column:
- score = 1
- pre_done = True
- elif self.x - 1 == 0:
- score = -1
- pre_done = True
- else:
- score = 0
- pre_done = False
- return self.map[self.x - 1], score, pre_done
- # 初始化,位置0,计数器归零
- def retry(self, start_colum): # 初始化
- self.x = start_colum
- self.count = 0
Agent.py
这是智能体的初始化、选择行动和学习的代码。
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- @Project :Q_learn
- @File :Env.py
- @Author :Hao
- @Date :2022-09-10 010 8:38
- @Describe :Agent
- """
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
- class Agent:
- def __init__(self, actions, long, learning_rate=0.05, reward_decay=0.9, e_greedy=0.9):
- self.actions = actions # 初始化可以进行的各种行为,传入为列表
- self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率,用于更新Q_table的值
- self.gamma = reward_decay # 当没有到达终点时,下一环境对当前环境的影响
- # self.epsilon = e_greedy # 随机选择几率为1-e_greedy,当处于e_greedy内时,不随机选择。
- self.q_table = pd.DataFrame(columns=self.actions, dtype=np.float64) # 生成q_table,列向量为columns
- for i in range(long):
- line_table = pd.Series(
- [0.0, 0.0],
- name=i,
- index=actions
- )
- line_table_2_frame = line_table.to_frame()
- self.q_table = pd.concat([self.q_table, line_table_2_frame.T])
- # 选择行动
- def choose_action(self, observation):
- action_list = self.q_table.loc[observation, :] # 取出当前observation所在的不同方向
- # if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon: # 如果在epsilon几率内
- # # 选出当前observation中Q值最大的方向,这里再加一个random.choice是为了防止出现两个概率相同
- # action = np.random.choice(action_list[action_list == np.max(action_list)].index)
- # else:
- # action = np.random.choice(self.actions) # 如果不在epsilon内,则随机选择一个动作
- action = np.random.choice(action_list[action_list == np.max(action_list)].index) # action总选择最优解
- return action # 返回应当做的action
- # 学习
- def learn(self, observation_now, action, score, observation_after, done):
- q_predict = self.q_table.loc[observation_now, action] # 获得当前状态下,当前所作动作所对应的预测得分
- if done:
- q_target = score # 如果完成了则q_target为下一个环境的实际情况得分,本例子中此时score为1
- else:
- # 如果未完成则取下一个环境若干个动作中的最大得分作为这个环境的价值传递给当前环境
- q_target = score + self.gamma * self.q_table.loc[observation_after, :].max()
- # 根据所处的当前环境对各个动作的预测得分和下一步的环境的实际情况更新当前环境的q表
- self.q_table.loc[observation_now, action] += self.lr * (q_target - q_predict)
此处的选择行动,可以设置一定的随机率,比如说设置为0.9的几率为选择Q-table中最优的action,剩下0.1的概率让agent随机选择。或者是不设置随机率,每一步都贪心。
接下来是main
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- @Project :Q_learn
- @File :run_this.py
- @Author :Hao
- @Date :2022-09-10 010 8:40
- """
- from Env import Env
- from Agent import Agent
- import time
- import pandas
- LONG = 7 # 总长度为6
- START_PLACE = 1 # 游戏开始的位置
- MAZE_PLACE = 7 # 宝藏在第六位
- TIMES = 1000 # 限制最大1000次循环,防止死循环
- STOP_FLAG = False
- e = 1e-2
- people = Agent(['left', 'right'], LONG) # 生成QLearn主体的对象,包含left和right,传入两个action
- site = Env(LONG, START_PLACE, MAZE_PLACE) # 生成测试环境
- for episode in range(TIMES):
- state = site.get_observation() # 观察初始环境
- site.draw() # 生成图像
- time.sleep(0.2) # 暂停
- while True:
- done = site.get_terminal() # 判断当前环境是否到达最后
- if done: # 如果到达,则初始化
- interaction = '\n第%s次episode,共使用步数:%s。' % (episode + 1, site.count)
- print(interaction)
- # 存储本次记录,计算与上次最大差值
- fileName = "data/episode" + str(episode) + ".csv"
- people.q_table.to_csv(fileName) # 将本次的q_table存储到本地文件中
- # print(f"\n第{episode}轮数据:\n{people.q_table}\n")
- if episode != 0: # 第一轮不进行判断
- old_file_name = "data/episode" + str(episode - 1) + ".csv" # 读取上一次的q_table
- old_q_table = pandas.read_csv(old_file_name, index_col=0)
- # print(f"\n第{episode - 1}轮数据:\n{old_q_table}\n")
- difference = (people.q_table - old_q_table).abs()
- # print(f"两次差值:\n{difference}\n")
- max_difference = difference.max()[0] \
- if difference.max()[0] >= difference.max()[1] else difference.max()[1]
- # print(f"与上一次最大差值:\n{difference.max()}\n{difference.max()[0]},{difference.max()[1]}\n")
- print(f"最大差值:{max_difference}"
- f"\n------{episode + 1}------")
- if max_difference <= e: # 达到收敛条件
- STOP_FLAG = True
- break
- site.retry(START_PLACE) # 初始化
- time.sleep(0.5)
- break
- action = people.choose_action(state) # 获得下一步方向
- state_after, score, pre_done = site.get_target(action) # 获得下一步的环境的实际情况
- people.learn(state, action, score, state_after, pre_done) # 根据所处的当前环境对各个动作的预测得分和下一步的环境的实际情况更新当前环境的q表
- site.update_place(action) # 更新位置
- state = state_after # 状态更新
- site.draw() # 更新画布
- time.sleep(0.2)
- if STOP_FLAG:
- break
- print(people.q_table)
这里可以设置两种结束条件,一种是比较简单的设置循环次数,比如说循环20次、50次就强制结束,此种方法的缺点是,不能保证此结果已经收敛;还有一种方法是,加上收敛的判定条件,比如以上代码设置了判断收敛的方法,即判断本次Q-table的和上一次Q-table最大的差值,是否小于设定的一个阙值,若小于此阙值,则已经收敛,若不小于,则继续迭代。
六、算法实例2
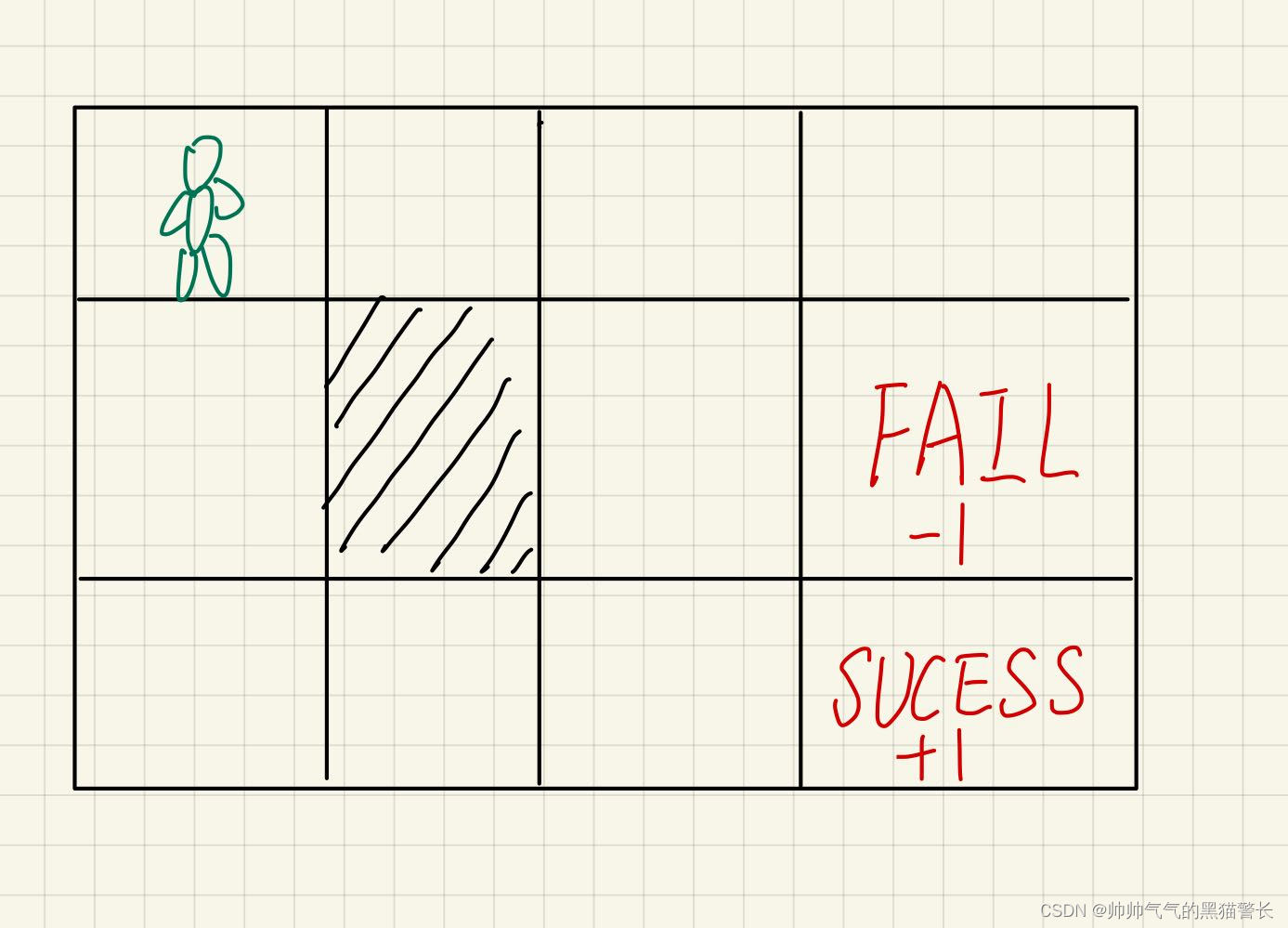
这次实例是上一次的升级版本,这次是二维环境,action也变成了四个,分别是up、down、left和right,同样是一个Agent要获取钻石,即SUCCESS,到达之后会score+1,如果到FAIL,就是score-1,图中阴影部分,是一堵墙,无法穿过,图中的边缘部分,无法穿过,例如在起始位置,往上或者往左,都是无法移动(但是计步器会+1)。而且为了让Agent最快的找到SUCESS,这里设定Agent每走一步,都会获得一个-0.02的score。
此次的Environment.py
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- @Project :Q_learn
- @File :environment.py
- @Author :Hao
- @Date :2022-09-15 015 15:51
- @Describe :
- """
- import numpy as np
- class Environment:
- def __init__(self, map_high, map_width, wall_place, success_place, fail_place):
- self.map_high = map_high # 初始化地图
- self.map_width = map_width
- self.x = 0 # 初始化Agent所在坐标
- self.y = 0
- self.wall_place = wall_place # 初始化墙的位置
- self.success_place = success_place # 初始化成功坐标
- self.fail_place = fail_place # 初始化失败坐标
- self.map = np.arange(map_width * map_high) # 给予每个地点一个标号(width * y + x)
- self.count = 0 # 用于记录一共走了多少步
- print(f"Environment初始化成功!\n"
- f"map_high:{self.map_high}, map_width:{self.map_width}\n"
- f"wall:{self.wall_place},success:{self.success_place},fail:{self.fail_place}")
- # 打印地图
- def print_map(self):
- print(f"\n------MAP------")
- for x in range(self.map_high):
- for y in range(self.map_width):
- if x == self.wall_place[0] and y == self.wall_place[1]:
- print(f"#", end=' ')
- elif x == self.success_place[0] and y == self.success_place[1]:
- print(f"√", end=' ')
- elif x == self.fail_place[0] and y == self.fail_place[1]:
- print(f"X", end=' ')
- else:
- print(f"{x * self.map_width + y}", end=' ')
- print()
- print(f'------MAP------\n')
- # 获取所在位置
- def get_observation(self):
- return self.map[self.x * self.map_width + self.y] # 返回现在所在位置
- # 更新当前位置
- def update_place(self, action):
- self.count += 1
- if action == 'down': # down
- if self.x < self.map_high - 1:
- if self.y == self.wall_place[1] and self.x + 1 == self.wall_place[0]:
- pass
- else:
- # print(f"{self.x, self.y}--> down --> ", end='')
- self.x += 1
- # print(f"{self.x, self.y}")
- elif action == 'up': # up
- if self.x > 0:
- if self.y == self.wall_place[1] and self.x - 1 == self.wall_place[0]:
- pass
- else:
- # print(f"{self.x, self.y}--> up--> ", end='')
- self.x -= 1
- # print(f"{self.x, self.y}")
- elif action == 'left': # left
- if self.y > 0:
- if self.x == self.wall_place[0] and self.y - 1 == self.wall_place[1]:
- pass
- else:
- # print(f"{self.x, self.y}--> left -->", end='')
- self.y -= 1
- # print(f"{self.x, self.y}")
- elif action == 'right': # right
- if self.y < self.map_width - 1:
- if self.x == self.wall_place[0] and self.y + 1 == self.wall_place[1]:
- pass
- else:
- # print(f"{self.x, self.y}--> right --> ", end='')
- self.y += 1
- # print(f"{self.x, self.y}")
- # 是否已到达终点
- def get_terminal(self):
- if self.x == self.success_place[0] and self.y == self.success_place[1]:
- done = True
- elif self.x == self.fail_place[0] and self.y == self.fail_place[1]:
- done = True
- else:
- done = False
- return done
- # 获得下一步的环境的实际情况
- def get_target(self, action):
- if action == 'down':
- if self.x + 1 == self.success_place[0] and self.y == self.success_place[1]:
- score = 1
- pre_done = True
- elif self.x + 1 == self.fail_place[0] and self.y == self.fail_place[1]:
- score = -1
- pre_done = True
- else:
- score = -0.02
- pre_done = False
- if self.x == self.map_high - 1:
- return self.map[self.x * self.map_width + self.y], score, pre_done
- else:
- if self.x + 1 == self.wall_place[0] and self.y == self.wall_place[1]:
- return self.map[self.x * self.map_width + self.y], score, pre_done
- return self.map[(self.x + 1) * self.map_width + self.y], score, pre_done
- elif action == 'up':
- if self.x - 1 == self.success_place[0] and self.y == self.success_place[1]:
- score = 1
- pre_done = True
- elif self.x - 1 == self.fail_place[0] and self.y == self.fail_place[1]:
- score = -1
- pre_done = True
- else:
- score = -0.02
- pre_done = False
- if self.x == 0:
- return self.map[self.x * self.map_width + self.y], score, pre_done
- else:
- if self.x - 1 == self.wall_place[0] and self.y == self.wall_place[1]:
- return self.map[self.x * self.map_width + self.y], score, pre_done
- return self.map[(self.x - 1) * self.map_width + self.y], score, pre_done
- elif action == 'left':
- if self.y - 1 == self.success_place[1] and self.x == self.success_place[0]:
- score = 1
- pre_done = True
- elif self.y - 1 == self.fail_place[1] and self.x == self.fail_place[0]:
- score = -1
- pre_done = True
- else:
- score = -0.02
- pre_done = False
- if self.y == 0:
- return self.map[self.x * self.map_width + self.y], score, pre_done
- else:
- if self.y - 1 == self.wall_place[0] and self.x == self.wall_place[1]:
- return self.map[self.x * self.map_width + self.y], score, pre_done
- return self.map[self.x * self.map_width + self.y - 1], score, pre_done
- elif action == 'right':
- if self.y + 1 == self.success_place[1] and self.x == self.success_place[0]:
- score = 1
- pre_done = True
- elif self.y + 1 == self.fail_place[1] and self.x == self.fail_place[0]:
- score = -1
- pre_done = True
- else:
- score = -0.02
- pre_done = False
- if self.y == self.map_width - 1:
- return self.map[self.x * self.map_width + self.y], score, pre_done
- else:
- if self.y + 1 == self.wall_place[0] and self.x == self.wall_place[1]:
- return self.map[self.x * self.map_width + self.y], score, pre_done
- return self.map[self.x * self.map_width + self.y + 1], score, pre_done
- # 初始化,位置0,计数器归零
- def retry(self, start_colum): # 初始化
- self.x = start_colum
- self.y = start_colum
- self.count = 0
此案例的Agent.py
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- @Project :Q_learn
- @File :agent.py
- @Author :Hao
- @Date :2022-09-15 015 15:51
- @Describe :
- """
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
- class Agent:
- def __init__(self, actions, long, learning_rate=0.05, reward_decay=0.9, e_greedy=1):
- self.actions = actions # 初始化可以进行的各种行为,传入为列表
- self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率,用于更新Q_table的值
- self.gamma = reward_decay # 衰减因子
- self.epsilon = e_greedy # 随机选择几率为1-e_greedy,当处于e_greedy内时,不随机选择。
- self.q_table = pd.DataFrame(columns=self.actions, dtype=np.float64) # 生成q_table,列向量为columns
- for i in range(long): # 向新建的q_table插入与二维格子相同数量的行向量
- line_table = pd.Series(
- [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
- name=i,
- index=actions
- )
- line_table_2_frame = line_table.to_frame()
- self.q_table = pd.concat([self.q_table, line_table_2_frame.T])
- print(f"Agent初始化成功!\n"
- f"{self.q_table}")
- # 贪心选择行动
- def choose_action_greed(self, observation):
- action_list = self.q_table.loc[observation, :] # 取出当前observation所在的不同方向
- action = np.random.choice(action_list[action_list == np.max(action_list)].index) # action总选择最优解
- return action # 返回应当做的action
- # 伴有部分随机选择
- def choose_action(self, observation):
- action_list = self.q_table.loc[observation, :] # 取出当前observation所在的不同方向
- if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon: # 如果在epsilon几率内
- # 选出当前observation中Q值最大的方向,这里再加一个random.choice是为了防止出现两个概率相同
- action = np.random.choice(action_list[action_list == np.max(action_list)].index)
- else:
- action = np.random.choice(self.actions) # 如果不在epsilon内,则随机选择一个动作
- return action # 返回应当做的action
- # 学习
- def learn(self, observation_now, action, score, observation_after, done):
- q_predict = self.q_table.loc[observation_now, action] # 获得当前状态下,当前所作动作所对应的预测得分
- if done:
- # 如果完成了则q_target为下一个环境的实际情况得分,本例子中此时score为1
- q_target = score
- else:
- # 如果未完成则取下一个环境若干个动作中的最大得分作为这个环境的价值传递给当前环境
- q_target = score + self.gamma * self.q_table.loc[observation_after, :].max()
- # 根据所处的当前环境对各个动作的预测得分和下一步的环境的实际情况更新当前环境的q表
- self.q_table.loc[observation_now, action] += self.lr * (q_target - q_predict)
这里给了两种行为选择方式,一种是全部贪心,一种是伴有10%的随机选择。
main.py
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- @Project :Q_learn
- @File :main.py
- @Author :Hao
- @Date :2022-09-15 015 15:50
- @Describe :
- """
- import time
- from environment import Environment
- from agent import Agent
- from find_max import find_max
- import pandas
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- MAP_HIGH = 3
- MAP_WIDTH = 4
- WALL_PLACE = [1, 1]
- SUCCESS_PLACE = [2, 3]
- FAIL_PLACE = [1, 3]
- TIMES = 200
- e = 1e-4
- # site.print_map()
- E_LIST = []
- def train(learn_function):
- robot = Agent(['left', 'right', 'up', 'down'], MAP_HIGH * MAP_WIDTH) # 生成Agent
- site = Environment(MAP_HIGH, MAP_WIDTH, WALL_PLACE, SUCCESS_PLACE, FAIL_PLACE) # 生成环境
- STOP_FLAG = False
- for episode in range(TIMES):
- state = site.get_observation()
- while True:
- done = site.get_terminal() # 判断当前环境是否到达最后
- if done:
- interaction = '\n%s--第%s次episode,共使用步数:%s。' % (learn_function, episode + 1, site.count)
- print(interaction)
- # 存储本次记录,方便后续计算与上次最大差值
- fileName = "data/" + str(learn_function) + "_episode" + str(episode) + ".csv"
- robot.q_table.to_csv(fileName) # 将本次的q_table存储到本地文件中
- if episode != 0:
- old_file_name = "data/" + str(learn_function) + "_episode" + str(
- episode - 1) + ".csv" # 读取上一次的q_table
- old_q_table = pandas.read_csv(old_file_name, index_col=0)
- difference = (robot.q_table - old_q_table).abs()
- max_difference = find_max(difference.max())
- print(max_difference)
- print(f"最大差值:{max_difference}"
- f"\n------{episode + 2}------")
- E_LIST.append(max_difference)
- if max_difference <= e:
- STOP_FLAG = True
- break
- site.retry(0)
- break
- if learn_function == 'greed': # 贪心
- action = robot.choose_action_greed(state) # 获得下一步方向
- else:
- action = robot.choose_action(state) # 获得下一步方向
- state_after, score, pre_done = site.get_target(action) # 获得下一步的环境的实际情况
- robot.learn(state, action, score, state_after, pre_done) # 根据所处的当前环境对各个动作的预测得分和下一步的环境的实际情况更新当前环境的q表
- site.update_place(action) # 更新位置
- # print(f"state_now: {state}, action: {action}, state_after: {state_after}")
- state = state_after
- if STOP_FLAG:
- site.retry(0)
- break
- train('greed')
- random_e_list = E_LIST.copy()
- E_LIST.clear()
- train('random')
- greed_e_list = E_LIST.copy()
- plt.title('greed and random')
- plt.plot(greed_e_list, 'b--', random_e_list, 'g')
- plt.xlabel('Iterations')
- plt.ylabel('Adjacent difference')
- plt.legend(['choose_action_greed', 'choose_action_random1'], loc=1)
- plt.savefig('./photo/greed_random1.svg', dpi=300) # svg文件,可伸缩矢量图形
- plt.show()
- # print(f"greed_e_list:\n{greed_e_list}")
- # print(f"random_e_list:\n{random_e_list}")
还有一个小工具类,find_max.py
- def find_max(different_max):
- max = -9999
- for i in range(4):
- if different_max[i] >= max:
- max = different_max[i]
- return max
代码的最后,最生成图像,可以看到收敛曲线

-
相关阅读:
高效使用python之xlwt库编辑写入excel表内容
数字孪生论文阅读笔记【3】
Ansible自动化部署安装openGauss3.1企业版单机
计算机、通信方向学习考证经验分享
[k8s] kubectl port-forward 和kubectl expose的区别
【算法】Inclusion of a Shuffled String Into another String
鸿蒙Harmony应用开发—ArkTS声明式开发(触摸交互控制:触摸测试控制)
2024Node.js零基础教程(小白友好型),nodejs新手到高手,(九)NodeJS入门——http模块
RUST运算符重载
我来谈谈“人工智能”这个词给我带来了哪些想法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Hao_ge_666/article/details/126894658
