-
RLChina 2022学习笔记——理论课一:机器学习和深度学习基础
Learning note
1. Maching learning
(1)Workflow

(2)Model


①Linear regression
- Model:
y i = F ( x i ) = w x i y_i = F(x_i)=wx_i yi=F(xi)=wxi - Optimization: squared error
min w ∑ i = 1 n ( y i − w x i ) 2 \min_w \sum_{i=1}^n (y_i - wx_i)^2 wmini=1∑n(yi−wxi)2

- Evaluation

②Decision Tree

- Model

- Example


其中, c 1 , c 2 c_1, c_2 c1,c2分别是按照划分点s划分后两个类别的样本在所划分属性上各自的均值。
③Nearest-Neighbor Classifiers
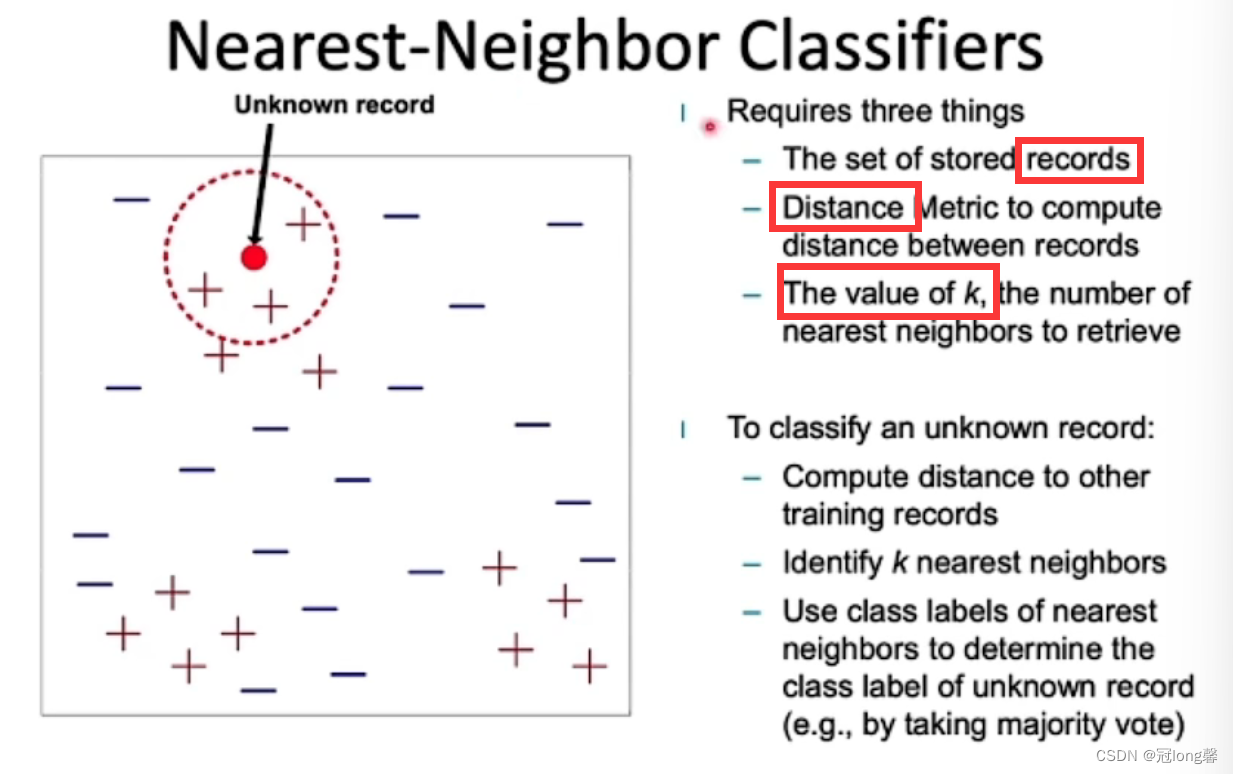
- Distance

- Classification

④Logistic regression

- Optimization


P ( y = 1 ∣ x , w ) P ( y = 0 ∣ x , w ) = 1 1 − P ( y = 1 ∣ x , w ) − 1 \frac{P(y=1|x,w)}{P(y=0|x,w)} = \frac{1}{1-P(y=1|x,w)}-1 P(y=0∣x,w)P(y=1∣x,w)=1−P(y=1∣x,w)1−1
(3)Data
①Distribution


- Testing and Training Dataset
- Observed and Real Dataset (hard to control)
②Sample complexity


其中, ϵ \epsilon ϵ可以理解为精度、 1 − δ 1-\delta 1−δ理解为置信度、 V S H , D VS_{H,D} VSH,D是所有满足精度与置信度条件 ϵ − e x h a u s t e d \epsilon - exhausted ϵ−exhausted的模型集合。当置信度越高、精度越高时,所需要的训练样本数量 m m m增加。
2. Deep Learning
(1)Forward


(2)Backward

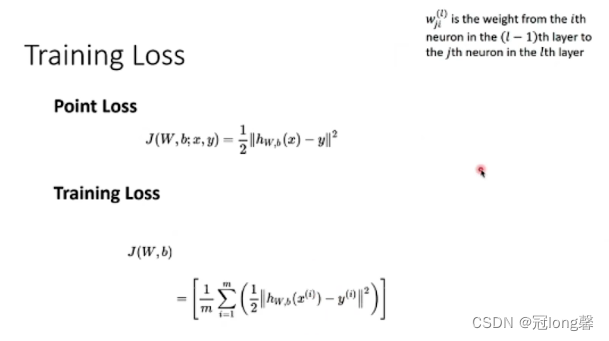






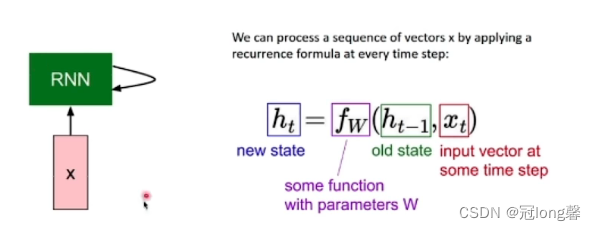
(3)RNN



(4)LSTM


(5)GRU
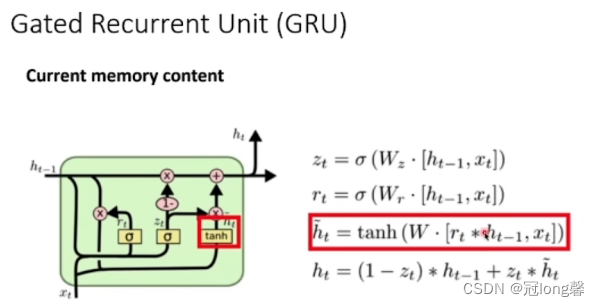
- Model:
-
相关阅读:
java-php-python-ssm基于汽车美容管理计算机毕业设计
AUTOSAR AP 硬核知识点梳理(2)— 架构详解
RabbitMQ消息可靠性(一)-- 生产者消息确认
设计模式(工厂方法-Factory Method)结构|原理|优缺点|场景|示例
Docker高级篇
ITIL4背景下,ITSM产品应具备哪些特点?
【先楫HPM6750系列】RT-Thread SDIO驱动和文件系统
Python面向对象特性——多态(基本概念、代码示例)
MS5611大气压强传感器驱动代码(基于GD32F103)
在ubuntu(20.04)上搭建基于docker的yolov5环境(GPU:3060)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/koulongxin123/article/details/126778946