-
一文带你全面了解Properties类
概述
Properties是JDK1.0中引入的java类,目前也在项目中大量使用,主要用来读取外部的配置,那除了这个,你对它其他的一些api也了解吗? 你了解它是怎么实现的吗? 如果不清楚的话,就通过本篇文章带你一探究竟。
介绍

java.util.Properties继承自java.util.Hashtable,是一个持久化的属性保存对象,可以将属性内容写出到stream中或者从stream中读取属性内容。 它的重要特性如下:
- 在底层的Hashtable中,每一对属性的key和value都是按照string类型来保存的。
- Properties支持文本方式和xml方式的数据存储。在文本方式中,格式为key:value,其中分隔符可以是:冒号(:)、等号(=)、空格。其中空格可以作为key的结束,同时获取的值回将分割符号两端的空格去掉。
- Properties可以将其他的Properties对象作为默认的值。
- Hashtable的所有方法Properties对象均可以访问,但是不建议这么做,因为Hashtable可以存放其他数据类型,这样会导致Properties一些方法调用报错。
- 在properties文件中,可以用井号"#"来作注释。
- 线程安全
- key、value不可以是null
构造方法
- Properties()
创建一个无默认值的空属性列表。
- Properties(Properties defaults)
创建一个带有指定默认值的空属性列表。
关键方法
- getProperty ( String key)
根据指定的key获取对应的属性value值,如果在自身的存储集合中没有找到对应的key,那么就直接到默认的defaults属性指定的Properties中获取属性值。
- getProperty(String, String)
当getProperty(String)方法返回值为null的时候,返回给定的默认值,而不是返回null。
- load ( InputStream inStream)
从byte stream中加载key/value键值对,要求所有的key/value键值对是按行存储,同时是用ISO-8859-1编译的, 不支持中文。
- load(Reader)
从字符流中加载key/value键值对,要求所有的键值对都是按照行来存储的。
- loadFromXML(InputStream)
从xml文件中加载property,底层使用XMLUtils.load(Properties,InputStream)方法来加载。
- setProperty ( String key, String value)
调用 Hashtable 的方法 put 。他通过调用基类的put方法来设置 键 - 值对。
- store ( OutputStream out, String comments)
将所有的property(保存defaults的)都写出到流中,同时如果给定comments的话,那么要加一个注释。
- storeToXML(OutputSteam, comment, encoding)
写出到xml文件中。
- Set stringPropertyNames()
获取所有Properties中所有的key集合
- clear ()
清除所有装载的 键值对。该方法在基类中提供。
使用案例
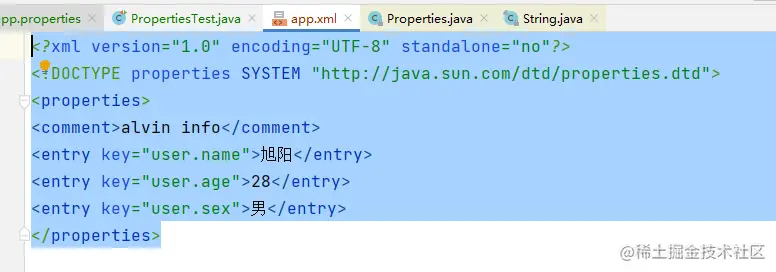
- 新建配置文件app.properties
- ## 用户信息
- user.name:旭阳
- user.age=28
- user.sex 男
- 复制代码
通过idea设置它的格式为UTF-8。

- 验证读取以及中文乱码的问题
- @Test
- public void test1() throws IOException {
- Properties properties = new Properties();
- // 使用load inputstream
- properties.load(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("app.properties"));
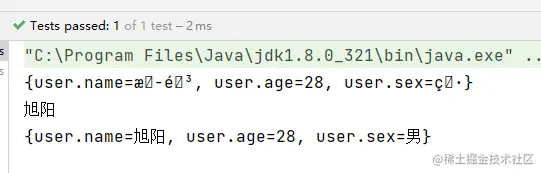
- // 出现乱码
- System.out.println(properties);
- // 转码
- System.out.println(new String(properties.getProperty("user.name").getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
- Properties properties2 = new Properties();
- // 使用load read
- BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("app.properties"), "UTF-8"));
- properties2.load(bf);
- System.out.println(properties2);
- }
- 复制代码
运行结果:
- 保存为xml格式
- @Test
- public void test2() throws IOException {
- Properties properties2 = new Properties();
- // 使用load read
- BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("app.properties"), "UTF-8"));
- properties2.load(bf);
- System.out.println(properties2);
- // 保存到xml
- FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("app.xml");
- properties2.storeToXML(fileOutputStream, "alvin info", "UTF-8");
- }
- 复制代码
运行结果:
源码解析
源码这部分主要分析下load(Reader)和load(InputStream)这两个最常用的方法,这两个方法是指定从文本文件中加载key/value属性值,底层都是将流封装成为LineReader对象,然后通过load0方法来加载属性键值对的。
- public synchronized void load(InputStream inStream) throws IOException {
- load0(new LineReader(inStream));
- }
- 复制代码
将inputStream封装程一个LineReader,每次可以读取一行数据。
LineReader源码分析:
- class LineReader {
- /**
- * 根据字节流创建LineReader对象
- *
- * @param inStream
- * 属性键值对对应的字节流对象
- */
- public LineReader(InputStream inStream) {
- this.inStream = inStream;
- inByteBuf = new byte[8192];
- }
- /**
- * 根据字符流创建LineReader对象
- *
- * @param reader
- * 属性键值对对应的字符流对象
- */
- public LineReader(Reader reader) {
- this.reader = reader;
- inCharBuf = new char[8192];
- }
- // 字节流缓冲区, 大小为8192个字节
- byte[] inByteBuf;
- // 字符流缓冲区,大小为8192个字符
- char[] inCharBuf;
- // 当前行信息的缓冲区,大小为1024个字符
- char[] lineBuf = new char[1024];
- // 读取一行数据时候的实际读取大小
- int inLimit = 0;
- // 读取的时候指向当前字符位置
- int inOff = 0;
- // 字节流对象
- InputStream inStream;
- // 字符流对象
- Reader reader;
- /**
- * 读取一行,将行信息保存到{@link lineBuf}对象中,并返回实际的字符个数
- *
- * @return 实际读取的字符个数
- * @throws IOException
- */
- int readLine() throws IOException {
- // 总的字符长度
- int len = 0;
- // 当前字符
- char c = 0;
- boolean skipWhiteSpace = true;
- boolean isCommentLine = false;
- boolean isNewLine = true;
- boolean appendedLineBegin = false;
- boolean precedingBackslash = false;
- boolean skipLF = false;
- while (true) {
- if (inOff >= inLimit) {
- // 读取一行数据,并返回这一行的实际读取大小
- inLimit = (inStream == null) ? reader.read(inCharBuf) : inStream.read(inByteBuf);
- inOff = 0;
- // 如果没有读取到数据,那么就直接结束读取操作
- if (inLimit <= 0) {
- // 如果当前长度为0或者是改行是注释,那么就返回-1。否则返回len的值。
- if (len == 0 || isCommentLine) {
- return -1;
- }
- return len;
- }
- }
- // 判断是根据字符流还是字节流读取当前字符
- if (inStream != null) {
- // The line below is equivalent to calling a ISO8859-1 decoder.
- // 字节流是根据ISO8859-1进行编码的,所以在这里进行解码操作。
- c = (char) (0xff & inByteBuf[inOff++]);
- } else {
- c = inCharBuf[inOff++];
- }
- // 如果前一个字符是换行符号,那么判断当前字符是否也是换行符号
- if (skipLF) {
- skipLF = false;
- if (c == '\n') {
- continue;
- }
- }
- // 如果前一个字符是空格,那么判断当前字符是不是空格类字符
- if (skipWhiteSpace) {
- if (c == ' ' || c == '\t' || c == '\f') {
- continue;
- }
- if (!appendedLineBegin && (c == '\r' || c == '\n')) {
- continue;
- }
- skipWhiteSpace = false;
- appendedLineBegin = false;
- }
- // 如果当前新的一行,那么进入该if判断中
- if (isNewLine) {
- isNewLine = false;
- // 如果当前字符是#或者是!,那么表示该行是一个注释行
- if (c == '#' || c == '!') {
- isCommentLine = true;
- continue;
- }
- }
- // 根据当前字符是不是换行符号进行判断操作
- if (c != '\n' && c != '\r') {
- // 当前字符不是换行符号
- lineBuf[len++] = c;// 将当前字符写入到行信息缓冲区中,并将len自增加1.
- // 如果len的长度大于行信息缓冲区的大小,那么对lineBuf进行扩容,扩容大小为原来的两倍,最大为Integer.MAX_VALUE
- if (len == lineBuf.length) {
- int newLength = lineBuf.length * 2;
- if (newLength < 0) {
- newLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- }
- char[] buf = new char[newLength];
- System.arraycopy(lineBuf, 0, buf, 0, lineBuf.length);
- lineBuf = buf;
- }
- // 是否是转义字符
- // flip the preceding backslash flag
- if (c == '\') {
- precedingBackslash = !precedingBackslash;
- } else {
- precedingBackslash = false;
- }
- } else {
- // reached EOL
- if (isCommentLine || len == 0) {
- // 如果这一行是注释行,或者是当前长度为0,那么进行clean操作。
- isCommentLine = false;
- isNewLine = true;
- skipWhiteSpace = true;
- len = 0;
- continue;
- }
- // 如果已经没有数据了,就重新读取
- if (inOff >= inLimit) {
- inLimit = (inStream == null) ? reader.read(inCharBuf) : inStream.read(inByteBuf);
- inOff = 0;
- if (inLimit <= 0) {
- return len;
- }
- }
- // 查看是否是转义字符
- if (precedingBackslash) {
- // 如果是,那么表示是另起一行,进行属性的定义,len要自减少1.
- len -= 1;
- // skip the leading whitespace characters in following line
- skipWhiteSpace = true;
- appendedLineBegin = true;
- precedingBackslash = false;
- if (c == '\r') {
- skipLF = true;
- }
- } else {
- return len;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- 复制代码
- readLine这个方法每次读取一行数据;如果我们想在多行写数据,那么可以使用''来进行转义,在该转义符号后面换行,是被允许的。
load0方法源码如下:
- private void load0(LineReader lr) throws IOException {
- char[] convtBuf = new char[1024];
- // 读取的字符总数
- int limit;
- // 当前key所在位置
- int keyLen;
- // value的起始位置
- int valueStart;
- // 当前字符
- char c;
- //
- boolean hasSep;
- // 是否是转义字符
- boolean precedingBackslash;
- while ((limit = lr.readLine()) >= 0) {
- c = 0;
- // key的长度
- keyLen = 0;
- // value的起始位置默认为limit
- valueStart = limit;
- //
- hasSep = false;
- precedingBackslash = false;
- // 如果key的长度小于总的字符长度,那么就进入循环
- while (keyLen < limit) {
- // 获取当前字符
- c = lr.lineBuf[keyLen];
- // 如果当前字符是=或者是:,而且前一个字符不是转义字符,那么就表示key的描述已经结束
- if ((c == '=' || c == ':') && !precedingBackslash) {
- // 指定value的起始位置为当前keyLen的下一个位置
- valueStart = keyLen + 1;
- // 并且指定,去除空格
- hasSep = true;
- break;
- } else if ((c == ' ' || c == '\t' || c == '\f') && !precedingBackslash) {
- // 如果当前字符是空格类字符,而且前一个字符不是转义字符,那么表示key的描述已经结束
- // 指定value的起始位置为当前位置的下一个位置
- valueStart = keyLen + 1;
- break;
- }
- // 如果当前字符为'',那么跟新是否是转义号。
- if (c == '\') {
- precedingBackslash = !precedingBackslash;
- } else {
- precedingBackslash = false;
- }
- keyLen++;
- }
- // 如果value的起始位置小于总的字符长度,那么就进入该循环
- while (valueStart < limit) {
- // 获取当前字符
- c = lr.lineBuf[valueStart];
- // 判断当前字符是否是空格类字符,达到去空格的效果
- if (c != ' ' && c != '\t' && c != '\f') {
- // 当前字符不是空格类字符,而且当前字符为=或者是:,并在此之前没有出现过=或者:字符。
- // 那么value的起始位置继续往后移动。
- if (!hasSep && (c == '=' || c == ':')) {
- hasSep = true;
- } else {
- // 当前字符不是=或者:,或者在此之前出现过=或者:字符。那么结束循环。
- break;
- }
- }
- valueStart++;
- }
- // 读取key
- String key = loadConvert(lr.lineBuf, 0, keyLen, convtBuf);
- // 读取value
- String value = loadConvert(lr.lineBuf, valueStart, limit - valueStart, convtBuf);
- // 包括key/value
- put(key, value);
- }
- }
- 复制代码
- 会将分割符号两边的空格去掉,并且分割符号可以是=,:,空格等。而且=和:的级别比空格分隔符高,即当这两个都存在的情况下,是按照=/:分割的。可以看到在最后会调用一个loadConvert方法,该方法主要是做key/value的读取,并将十六进制的字符进行转换。
总结
本文阐述了Properties的基本作用以及源码实现,是不是对Properties有了更近一步的认识呢。
-
相关阅读:
MySQL索引
嵌入式数据库Sqlite
9.21
Cause: compileSdkVersion is not specified. Please add it to build.gradle
HTML标签学习
大数据调度最佳实践 | 从Airflow迁移到Apache DolphinScheduler
渗透测试基础 | 附带测试点、测试场景
BI财务分析 – 反映盈利水平利润占比的指标如何分析(下)
解决CSDN因版权不明而无法发布博客的问题
【论文精读】TransE 及其实现
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_73311735/article/details/126869971
