-
分布式搜索引擎ElasticSearch-1
1、初识ES
1.1.了解ES
1.1.1.作用
开源搜索引擎,从海量数据中快速找到需要的内容
1.1.2.ELK技术栈
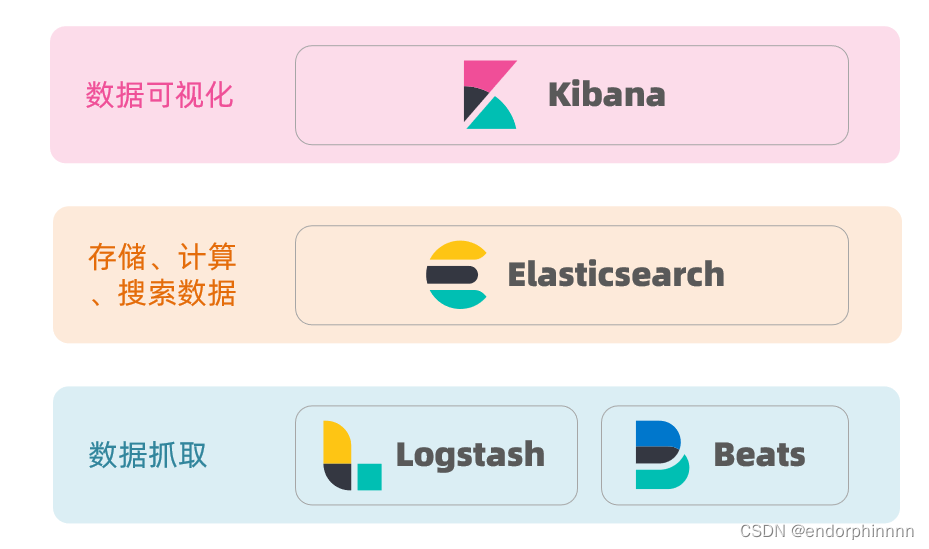
elasticsearch结合kibana、Logstash、Beats,也就是elastic stack(ELK)。被广泛应用在日志数据分析、实时监控等领域。而elasticsearch是elastic stack的核心,负责存储、搜索、分析数据。
1.1.3.elasticsearch和Lucene
elasticsearch底层是基于lucene来实现的。
Lucene是一个Java语言的搜索引擎类库,提供了搜索引擎的核心API
Lucene优势:以扩展、高性能(基于倒排索引)
Lucene缺点:只限于Java语言开发、学习曲线陡峭、不支持水平扩展1.2.倒排索引
倒排索引的概念是基于MySQL这样的正向索引。
1.2.1.正向索引
根据id建立索引。id和title建表,如果基于title做模糊查询,那么只能根据id进行逐行扫描。
是根据文档找词条的过程。
优点:
- 可以给多个字段创建索引
- 根据索引字段搜索、排序速度非常快
缺点: - 根据非索引字段或者索引字段中的部分词条查找时,只能全表扫描
1.2.2.倒排索引
有两个非常重要的概念:
- 文档(Document):用来搜索的数据,其中的每一条数据就是一个文档。
- 词条(Term):对文档数据或用户搜索数据,利用某种算法分词,得到的具体含义的词语就是词条。分词。
创建倒排索引是对正向索引的一种特殊处理:
- 将每一个文档的数据利用算法分词,得到一个个词条
- 创建表,每行数据包括词条、词条所在文档id、位置等信息
- 因为词条唯一性,可以给词条创建索引。
是根据词条找文档的过程。
优点:
- 根据词条搜索、模糊搜索时,速度非常快
缺点: - 只能给词条创建索引,而不是字段
- 无法根据字段做排序
1.3.ES的一些概念
文档
es是面向文档存储的,可以是数据库的一条商品数据、一个订单信息。文档数据会被序列化为json格式后存储在es中。
字段
json文档中往往包含很多的字段(field),类似于数据库中的列。
索引
相同类型的文档的集合,可以把索引当做数据库中的表。
映射
数据库的表会有约束信息,用来定义表的结构、字段的名称、类型等信息。因此索引库中的映射,就是索引中文档的字段约束信息,类似表的结构约束。
mysql
擅长事务类型操作,可以确保数据的安全和一致性
elasticsearch
擅长海量数据的搜索、分析、计算MySQL Elasticsearch 说明 Table Index 索引(index),就是文档的集合,类似数据库的表(table) Row Document 文档(Document),就是一条条的数据,类似数据库中的行(Row),文档都是JSON格式 Column Field 字段(Field),就是JSON文档中的字段,类似数据库中的列(Column) Schema Mapping Mapping(映射)是索引中文档的约束,例如字段类型约束。类似数据库的表结构(Schema) SQL DSL DSL是elasticsearch提供的JSON风格的请求语句,用来操作elasticsearch,实现CRUD - 对于安全性较高的写操作,使用mysql实现
- 对于查询性能较高的搜索需求,使用es实现
- 两者再基于某种方式,实现数据的同步,保证一致性
1.4.分词器
作用- 创建倒排索引时对文档分词
- 用户搜索时,对输入的内容分词
模式 - ik_smart:只能切分,粗粒度
- ik_max_work:最细切分,细粒度
如何扩展词条、停用词条 - 利用config牡蛎的IkAnalyzer.cfg.xml文件添加拓展词典和停用词典
- 在词典中添加拓展词条或者停用词条
在ext.dic文件里添加拓展词条,在stopword.dic文件里添加停用词条。
DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd"> <properties> <comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置comment> <entry key="ext_dict">ext.dicentry> <entry key="ext_stopwords">stopword.dicentry> properties>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
2、索引库操作
Rest(PUT、GET、DELETE)
2.1.mapping映射属性
mapping是对索引库中文档的约束,常见的mapping属性包括:
- type:字段数据类型,常见的简单类型有:
- 字符串:text(可分词的文本)、keyword(精确值,例如品牌、国家等不分词)
- 数值:long、integer等
- 布尔:boolean
- 日期:date
- 对象:object
- index:是否创建索引,默认为true
- analyzer:使用哪种分词器
- properties:该字段的子字段
2.2.索引库的CRUD
2.2.1.创建索引库
# PUT /索引库名称 PUT /heima { "mappings": { "properties": { "info":{ "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_smart" }, "email":{ "type": "keyword", "index": "falsae" }, "name":{ "properties": { "firstName": { "type": "keyword" } } }, // ... 略 } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
2.2.2.修改索引库(添加字段)
索引库一旦创建,无法修改mapping中已有的字段,但是允许添加新字段到mapping中。
PUT /索引库名/_mapping { "properties": { "新字段名":{ "type": "integer" } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
2.2.3.查看索引库
GET /索引库名- 1
2.2.4.删除索引库
DELETE /索引库名- 1
3、文档操作
3.1.新增文档
可以用post和put,但是post新增不指定id系统会自动新建一个id;而get不指定id系统不会分配。
POST /索引库名/_doc/文档id { "字段1": "值1", "字段2": "值2", "字段3": { "子属性1": "值3", "子属性2": "值4" }, // ... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3.2.查询文档
GET /{索引库名称}/_doc/{id}- 1
3.3.删除文档
DELETE /{索引库名}/_doc/id值- 1
3.4.修改文档
- 全量修改(id存在,即为修改;不存在,即为新增)
会删除旧文档,添加新文档
POST /索引库名/_doc/文档id { "字段1": "值1", "字段2": "值2", "字段3": { "子属性1": "值3", "子属性2": "值4" }, // ... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 增量修改
修改指定字段的值
POST /{索引库名}/_update/文档id { "doc": { "字段名": "新的值", } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
4、RestAPI
ES中支持两种地理坐标数据类型:
- geo_point:点
- geo_shape:多个点连接形成的形状
copy_to:将当前字段拷贝到指定字段
核心是client.indices()方法来获取索引库的操作对象。
4.1.初始化RestClient
在elasticsearch提供的API中,与elasticsearch一切交互都封装在一个名为RestHighLevelClient的类中,必须先完成这个对象的初始化,建立与elasticsearch的连接:
1、导入es的RestHighLevelClient依赖:<dependency> <groupId>org.elasticsearch.clientgroupId> <artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-clientartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2、因为SpringBoot默认的ES版本是7.6.2,所以我们需要覆盖默认的ES版本:
<properties> <java.version>1.8java.version> <elasticsearch.version>7.12.1elasticsearch.version> properties>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3、初始化RestHighLevelClient
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder( //填写自己的IP值和端口 HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200") ));- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
4.2.创建索引库
- 1)创建Request对象。因为是创建索引库的操作,因此Request是CreateIndexRequest。
- 2)添加请求参数,其实就是DSL的JSON参数部分。因为json字符串很长,这里是定义了静态字符串常量MAPPING_TEMPLATE,让代码看起来更加优雅。
- 3)发送请求,client.indices()方法的返回值是IndicesClient类型,封装了所有与索引库操作有关的方法。
//MAPPING_TEMPLATE是自己定义的格式 @Test void createHotelIndex() throws IOException { // 1.创建Request对象 CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotel"); // 2.准备请求的参数:DSL语句 request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON); // 3.发送请求 client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
4.3.删除索引库
- 1)创建Request对象。这次是DeleteIndexRequest对象
- 2)准备参数。这里是无参
- 3)发送请求。改用delete方法
@Test void testDeleteHotelIndex() throws IOException { // 1.创建Request对象 DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel"); // 2.发送请求 client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
4.4.判断索引库是否存在
- 1)创建Request对象。这次是GetIndexRequest对象
- 2)准备参数。这里是无参
- 3)发送请求。改用exists方法
@Test void testExistsHotelIndex() throws IOException { // 1.创建Request对象 GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotel"); // 2.发送请求 boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); // 3.输出 System.err.println(exists ? "索引库已经存在!" : "索引库不存在!"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
5、RestClient操作文档
数据库结构和索引库结构会不一致,所以需要新建类库来使结构保持一致。
5.1.新增文档
@Test void testAddDocument() throws IOException { // 1.根据id查询酒店数据 Hotel hotel = hotelService.getById(61083L); // 2.转换为文档类型 HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel); // 3.将HotelDoc转json String json = JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc); // 1.准备Request对象 IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotelDoc.getId().toString()); // 2.准备Json文档 request.source(json, XContentType.JSON); // 3.发送请求 client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
5.2.查询文档
@Test void testGetDocumentById() throws IOException { // 1.准备Request GetRequest request = new GetRequest("hotel", "61082"); // 2.发送请求,得到响应 GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); // 3.解析响应结果 String json = response.getSourceAsString(); HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class); System.out.println(hotelDoc); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
5.3.删除文档
@Test void testDeleteDocument() throws IOException { // 1.准备Request DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest("hotel", "61083"); // 2.发送请求 client.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
5.4.修改文档
- 全量修改:与新增的API完全一致,如果新增时id已存在,则修改;如果新增时id不存在,则新增。
- 增量修改:
@Test void testUpdateDocument() throws IOException { // 1.准备Request UpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest("hotel", "61083"); // 2.准备请求参数 request.doc( "price", "952", "starName", "四钻" ); // 3.发送请求 client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
5.5.批量导入文档
BulkRequest做批量操作,有批量的增、删、查操作。
@Test void testBulkRequest() throws IOException { // 批量查询酒店数据 List<Hotel> hotels = hotelService.list(); // 1.创建Request BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest(); // 2.准备参数,添加多个新增的Request for (Hotel hotel : hotels) { // 2.1.转换为文档类型HotelDoc HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel); // 2.2.创建新增文档的Request对象 request.add(new IndexRequest("hotel") .id(hotelDoc.getId().toString()) .source(JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc), XContentType.JSON)); } // 3.发送请求 client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
-
相关阅读:
【mcuclub】继电器
ArrayList详解
hive on spark 代码方式实现
Uniapp零基础开发学习笔记(1) - 项目初步创建
JAVA毕业设计106—基于Java+Springboot的外卖系统(源码+数据库)
MySQL的分页你还在使劲的limit?
数据结构单链表
大数据生态圈完整知识体系
残差网络(Residual Network,ResNet)原理与结构概述
1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑氯化锌([BMIM][Zn2Cl5])离子液体
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/DOVISSSS/article/details/126776851
