-
音视频从入门到精通——FFmpeg结构体:AVFrame分析
FFmpeg结构体 AVFrame分析

AVFrame结构体一般用于存储原始数据(即非压缩数据,例如对视频来说是YUV,RGB,对音频来说是PCM),此外还包含了一些相关的信息。比如说,解码的时候存储了宏块类型表,QP表,运动矢量表等数据。编码的时候也存储了相关的数据。因此在使用FFMPEG进行码流分析的时候,AVFrame是一个很重要的结构体。
下面看几个主要变量的作用(在这里考虑解码的情况):
uint8_t *data[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]:解码后原始数据(对视频来说是YUV,RGB,对音频来说是PCM) 这个data变量是一个指针数组,对于视频,可以简单地理解为三个一维数组 int linesize[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]:data中“一行”数据的大小。注意:未必等于图像的宽,一般大于图像的宽。 int width, height:视频帧宽和高(1920x1080,1280x720...) int nb_samples:音频的一个AVFrame中可能包含多个音频帧,在此标记包含了几个 int format:解码后原始数据类型(YUV420,YUV422,RGB24...) int key_frame:是否是关键帧 enum AVPictureType pict_type:帧类型(I,B,P...) AVRational sample_aspect_ratio:宽高比(16:9,4:3...) int64_t pts:显示时间戳 int coded_picture_number:编码帧序号 int display_picture_number:显示帧序号 int8_t *qscale_table:QP表 uint8_t *mbskip_table:跳过宏块表 int16_t (*motion_val[2])[2]:运动矢量表 uint32_t *mb_type:宏块类型表 short *dct_coeff:DCT系数,这个没有提取过 int8_t *ref_index[2]:运动估计参考帧列表(貌似H.264这种比较新的标准才会涉及到多参考帧) int interlaced_frame:是否是隔行扫描 uint8_t motion_subsample_log2:一个宏块中的运动矢量采样个数,取log的- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
花屏问题
将图像绘制到界面上,注意AVFrame的一行像素和windowBuffer一行像素长度可能不一致,需要转换好,否则可能花屏。
//代码选自XPlay2.0播放器 void XVideoWidget::Repaint(AVFrame* frame) { if (!frame)return; mux.lock(); //容错,保证尺寸正确 if (!datas[0] || width * height == 0 || frame->width != this->width || frame->height != this->height) { av_frame_free(&frame); mux.unlock(); return; } if (width == frame->linesize[0]) //无需对齐 { memcpy(datas[0], frame->data[0], width * height); memcpy(datas[1], frame->data[1], width * height / 4); memcpy(datas[2], frame->data[2], width * height / 4); } else//行对齐问题 { for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) //Y memcpy(datas[0] + width * i, frame->data[0] + frame->linesize[0] * i, width); for (int i = 0; i < height / 2; i++) //U memcpy(datas[1] + width / 2 * i, frame->data[1] + frame->linesize[1] * i, width); for (int i = 0; i < height / 2; i++) //V memcpy(datas[2] + width / 2 * i, frame->data[2] + frame->linesize[2] * i, width); } mux.unlock(); //刷新显示 update(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
AVFrame中的format视频和音频共用的。
/** * format of the frame, -1 if unknown or unset * Values correspond to enum AVPixelFormat for video frames, * enum AVSampleFormat for audio) */ int format;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
有两个相关结构体
视频enum AVPixelFormat { AV_PIX_FMT_NONE = -1, AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, ///< planar YUV 4:2:0, 12bpp, (1 Cr & Cb sample per 2x2 Y samples) AV_PIX_FMT_YUYV422, ///< packed YUV 4:2:2, 16bpp, Y0 Cb Y1 Cr AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24, ///< packed RGB 8:8:8, 24bpp, RGBRGB... AV_PIX_FMT_BGR24, ///< packed RGB 8:8:8, 24bpp, BGRBGR... AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P, ///< planar YUV 4:2:2, 16bpp, (1 Cr & Cb sample per 2x1 Y samples) AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P, ///< planar YUV 4:4:4, 24bpp, (1 Cr & Cb sample per 1x1 Y samples) AV_PIX_FMT_YUV410P, ///< planar YUV 4:1:0, 9bpp, (1 Cr & Cb sample per 4x4 Y samples) AV_PIX_FMT_YUV411P, ///< planar YUV 4:1:1, 12bpp, (1 Cr & Cb sample per 4x1 Y samples) AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY8, ///< Y , 8bpp ...... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
音频
enum AVSampleFormat { AV_SAMPLE_FMT_NONE = -1, AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8, ///< unsigned 8 bits AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, ///< signed 16 bits AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32, ///< signed 32 bits AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLT, ///< float AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBL, ///< double AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8P, ///< unsigned 8 bits, planar AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16P, ///< signed 16 bits, planar AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32P, ///< signed 32 bits, planar AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP, ///< float, planar, 4 个字节 AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBLP, ///< double, planar AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S64, ///< signed 64 bits AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S64P, ///< signed 64 bits, planar AV_SAMPLE_FMT_NB ///< Number of sample formats. DO NOT USE if linking dynamically };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
关于yuv 的pack(紧缩格式)和planner(平面格式)格式区别
YUV存储格式有两大类:planar 和 packed
- planar,平面格式,先连续存储所有像素点的Y,紧接着存储所有像素点的U,然后是所有像素点的V;将几个分量分开存,比如YUV420中,data[0]专门存Y,data[1]专门存U,data[2]专门存V。
- packed,打包格式,每个像素点的Y,U,V是连续交错存储的,所有数据都存在data[0]中。
FFmpeg AVPacket和AVFrame区别
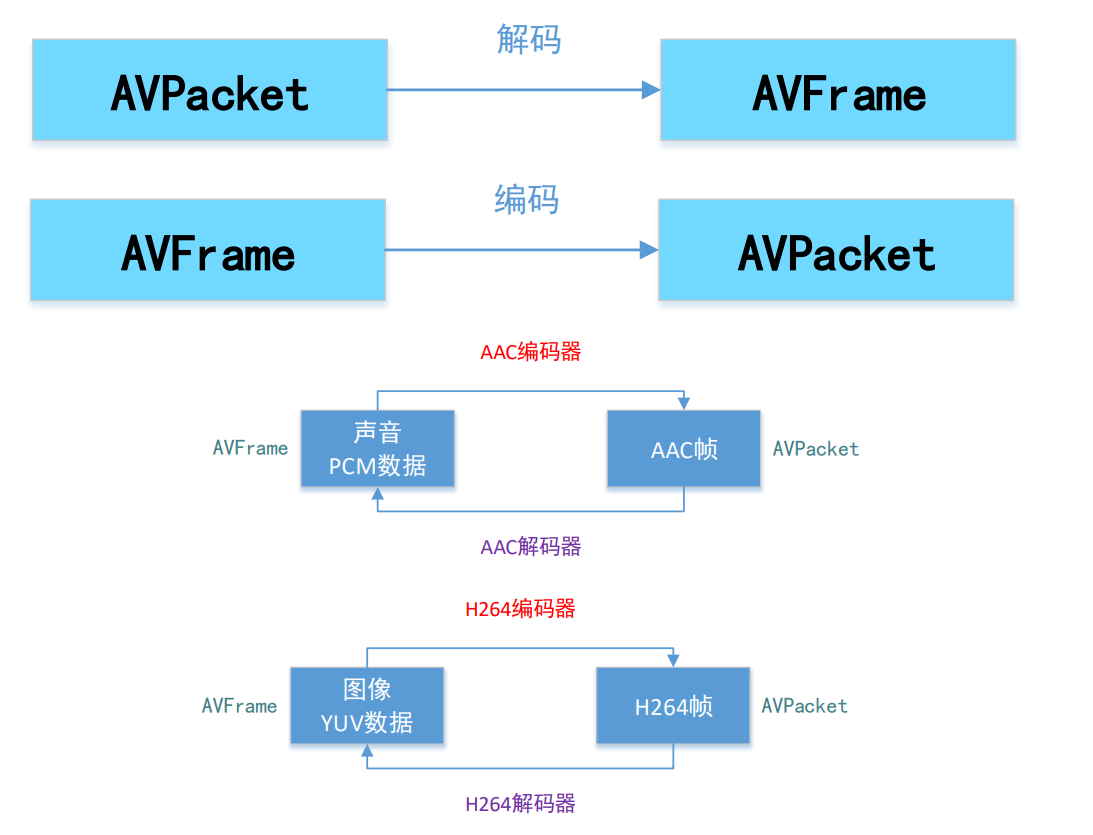
AVPacket:存储压缩数据(视频对应H.264等码流数据,音频对应AAC/MP3等码流数据)
AVFrame:存储非压缩的数据(视频对应RGB/YUV像素数据,音频对应PCM采样数据)AVFrame结构体代码
/** * This structure describes decoded (raw) audio or video data. * * AVFrame must be allocated using av_frame_alloc(). Note that this only * allocates the AVFrame itself, the buffers for the data must be managed * through other means (see below). * AVFrame must be freed with av_frame_free(). * * AVFrame is typically allocated once and then reused multiple times to hold * different data (e.g. a single AVFrame to hold frames received from a * decoder). In such a case, av_frame_unref() will free any references held by * the frame and reset it to its original clean state before it * is reused again. * * The data described by an AVFrame is usually reference counted through the * AVBuffer API. The underlying buffer references are stored in AVFrame.buf / * AVFrame.extended_buf. An AVFrame is considered to be reference counted if at * least one reference is set, i.e. if AVFrame.buf[0] != NULL. In such a case, * every single data plane must be contained in one of the buffers in * AVFrame.buf or AVFrame.extended_buf. * There may be a single buffer for all the data, or one separate buffer for * each plane, or anything in between. * * sizeof(AVFrame) is not a part of the public ABI, so new fields may be added * to the end with a minor bump. * * Fields can be accessed through AVOptions, the name string used, matches the * C structure field name for fields accessible through AVOptions. The AVClass * for AVFrame can be obtained from avcodec_get_frame_class() */ typedef struct AVFrame { #define AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS 8 /** * pointer to the picture/channel planes. * This might be different from the first allocated byte * * Some decoders access areas outside 0,0 - width,height, please * see avcodec_align_dimensions2(). Some filters and swscale can read * up to 16 bytes beyond the planes, if these filters are to be used, * then 16 extra bytes must be allocated. * * NOTE: Except for hwaccel formats, pointers not needed by the format * MUST be set to NULL. */ uint8_t *data[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]; /** * For video, size in bytes of each picture line. * For audio, size in bytes of each plane. * * For audio, only linesize[0] may be set. For planar audio, each channel * plane must be the same size. * * For video the linesizes should be multiples of the CPUs alignment * preference, this is 16 or 32 for modern desktop CPUs. * Some code requires such alignment other code can be slower without * correct alignment, for yet other it makes no difference. * * @note The linesize may be larger than the size of usable data -- there * may be extra padding present for performance reasons. */ int linesize[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]; /** * pointers to the data planes/channels. * * For video, this should simply point to data[]. * * For planar audio, each channel has a separate data pointer, and * linesize[0] contains the size of each channel buffer. * For packed audio, there is just one data pointer, and linesize[0] * contains the total size of the buffer for all channels. * * Note: Both data and extended_data should always be set in a valid frame, * but for planar audio with more channels that can fit in data, * extended_data must be used in order to access all channels. */ uint8_t **extended_data; /** * @name Video dimensions * Video frames only. The coded dimensions (in pixels) of the video frame, * i.e. the size of the rectangle that contains some well-defined values. * * @note The part of the frame intended for display/presentation is further * restricted by the @ref cropping "Cropping rectangle". * @{ */ int width, height; /** * @} */ /** * number of audio samples (per channel) described by this frame */ int nb_samples; /** * format of the frame, -1 if unknown or unset * Values correspond to enum AVPixelFormat for video frames, * enum AVSampleFormat for audio) */ int format; /** * 1 -> keyframe, 0-> not */ int key_frame; /** * Picture type of the frame. */ enum AVPictureType pict_type; /** * Sample aspect ratio for the video frame, 0/1 if unknown/unspecified. */ AVRational sample_aspect_ratio; /** * Presentation timestamp in time_base units (time when frame should be shown to user). */ int64_t pts; #if FF_API_PKT_PTS /** * PTS copied from the AVPacket that was decoded to produce this frame. * @deprecated use the pts field instead */ attribute_deprecated int64_t pkt_pts; #endif /** * DTS copied from the AVPacket that triggered returning this frame. (if frame threading isn't used) * This is also the Presentation time of this AVFrame calculated from * only AVPacket.dts values without pts values. */ int64_t pkt_dts; /** * picture number in bitstream order */ int coded_picture_number; /** * picture number in display order */ int display_picture_number; /** * quality (between 1 (good) and FF_LAMBDA_MAX (bad)) */ int quality; /** * for some private data of the user */ void *opaque; #if FF_API_ERROR_FRAME /** * @deprecated unused */ attribute_deprecated uint64_t error[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]; #endif /** * When decoding, this signals how much the picture must be delayed. * extra_delay = repeat_pict / (2*fps) */ int repeat_pict; /** * The content of the picture is interlaced. */ int interlaced_frame; /** * If the content is interlaced, is top field displayed first. */ int top_field_first; /** * Tell user application that palette has changed from previous frame. */ int palette_has_changed; /** * reordered opaque 64 bits (generally an integer or a double precision float * PTS but can be anything). * The user sets AVCodecContext.reordered_opaque to represent the input at * that time, * the decoder reorders values as needed and sets AVFrame.reordered_opaque * to exactly one of the values provided by the user through AVCodecContext.reordered_opaque */ int64_t reordered_opaque; /** * Sample rate of the audio data. */ int sample_rate; /** * Channel layout of the audio data. */ uint64_t channel_layout; /** * AVBuffer references backing the data for this frame. If all elements of * this array are NULL, then this frame is not reference counted. This array * must be filled contiguously -- if buf[i] is non-NULL then buf[j] must * also be non-NULL for all j < i. * * There may be at most one AVBuffer per data plane, so for video this array * always contains all the references. For planar audio with more than * AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS channels, there may be more buffers than can fit in * this array. Then the extra AVBufferRef pointers are stored in the * extended_buf array. */ AVBufferRef *buf[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]; /** * For planar audio which requires more than AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS * AVBufferRef pointers, this array will hold all the references which * cannot fit into AVFrame.buf. * * Note that this is different from AVFrame.extended_data, which always * contains all the pointers. This array only contains the extra pointers, * which cannot fit into AVFrame.buf. * * This array is always allocated using av_malloc() by whoever constructs * the frame. It is freed in av_frame_unref(). */ AVBufferRef **extended_buf; /** * Number of elements in extended_buf. */ int nb_extended_buf; AVFrameSideData **side_data; int nb_side_data; /** * @defgroup lavu_frame_flags AV_FRAME_FLAGS * @ingroup lavu_frame * Flags describing additional frame properties. * * @{ */ /** * The frame data may be corrupted, e.g. due to decoding errors. */ #define AV_FRAME_FLAG_CORRUPT (1 << 0) /** * A flag to mark the frames which need to be decoded, but shouldn't be output. */ #define AV_FRAME_FLAG_DISCARD (1 << 2) /** * @} */ /** * Frame flags, a combination of @ref lavu_frame_flags */ int flags; /** * MPEG vs JPEG YUV range. * - encoding: Set by user * - decoding: Set by libavcodec */ enum AVColorRange color_range; enum AVColorPrimaries color_primaries; enum AVColorTransferCharacteristic color_trc; /** * YUV colorspace type. * - encoding: Set by user * - decoding: Set by libavcodec */ enum AVColorSpace colorspace; enum AVChromaLocation chroma_location; /** * frame timestamp estimated using various heuristics, in stream time base * - encoding: unused * - decoding: set by libavcodec, read by user. */ int64_t best_effort_timestamp; /** * reordered pos from the last AVPacket that has been input into the decoder * - encoding: unused * - decoding: Read by user. */ int64_t pkt_pos; /** * duration of the corresponding packet, expressed in * AVStream->time_base units, 0 if unknown. * - encoding: unused * - decoding: Read by user. */ int64_t pkt_duration; /** * metadata. * - encoding: Set by user. * - decoding: Set by libavcodec. */ AVDictionary *metadata; /** * decode error flags of the frame, set to a combination of * FF_DECODE_ERROR_xxx flags if the decoder produced a frame, but there * were errors during the decoding. * - encoding: unused * - decoding: set by libavcodec, read by user. */ int decode_error_flags; #define FF_DECODE_ERROR_INVALID_BITSTREAM 1 #define FF_DECODE_ERROR_MISSING_REFERENCE 2 #define FF_DECODE_ERROR_CONCEALMENT_ACTIVE 4 #define FF_DECODE_ERROR_DECODE_SLICES 8 /** * number of audio channels, only used for audio. * - encoding: unused * - decoding: Read by user. */ int channels; /** * size of the corresponding packet containing the compressed * frame. * It is set to a negative value if unknown. * - encoding: unused * - decoding: set by libavcodec, read by user. */ int pkt_size; #if FF_API_FRAME_QP /** * QP table */ attribute_deprecated int8_t *qscale_table; /** * QP store stride */ attribute_deprecated int qstride; attribute_deprecated int qscale_type; attribute_deprecated AVBufferRef *qp_table_buf; #endif /** * For hwaccel-format frames, this should be a reference to the * AVHWFramesContext describing the frame. */ AVBufferRef *hw_frames_ctx; /** * AVBufferRef for free use by the API user. FFmpeg will never check the * contents of the buffer ref. FFmpeg calls av_buffer_unref() on it when * the frame is unreferenced. av_frame_copy_props() calls create a new * reference with av_buffer_ref() for the target frame's opaque_ref field. * * This is unrelated to the opaque field, although it serves a similar * purpose. */ AVBufferRef *opaque_ref; /** * @anchor cropping * @name Cropping * Video frames only. The number of pixels to discard from the the * top/bottom/left/right border of the frame to obtain the sub-rectangle of * the frame intended for presentation. * @{ */ size_t crop_top; size_t crop_bottom; size_t crop_left; size_t crop_right; /** * @} */ /** * AVBufferRef for internal use by a single libav* library. * Must not be used to transfer data between libraries. * Has to be NULL when ownership of the frame leaves the respective library. * * Code outside the FFmpeg libs should never check or change the contents of the buffer ref. * * FFmpeg calls av_buffer_unref() on it when the frame is unreferenced. * av_frame_copy_props() calls create a new reference with av_buffer_ref() * for the target frame's private_ref field. */ AVBufferRef *private_ref; } AVFrame;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
使用
这里使用的是
ffmpeg-n4.4-latest-win64-gpl-shared-4.4.zip。#include#include extern "C" { #include "libavformat/avformat.h" #include "libavcodec/avcodec.h" #include "libswscale/swscale.h" #include "libswresample/swresample.h" } using namespace std; #pragma comment(lib,"avformat.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"avutil.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"avcodec.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"swscale.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"swresample.lib") static double r2d(AVRational r) { return r.den == 0 ? 0 : (double)r.num / (double)r.den; } void XSleep(int ms) { //c++ 11 chrono::milliseconds du(ms); this_thread::sleep_for(du); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { cout << "Test Demux FFmpeg.club" << endl; const char* path = "D:\\javaCode\\androidmaniu2022\\FFmpeg\\input.mp4"; //初始化封装库 av_register_all(); //初始化网络库 (可以打开rtsp rtmp http 协议的流媒体视频) avformat_network_init(); //注册解码器 avcodec_register_all(); //参数设置 AVDictionary* opts = NULL; //设置rtsp流已tcp协议打开 av_dict_set(&opts, "rtsp_transport", "tcp", 0); //网络延时时间 av_dict_set(&opts, "max_delay", "500", 0); //解封装上下文 AVFormatContext* ic = NULL; int re = avformat_open_input( &ic, path, 0, // 0表示自动选择解封器 &opts //参数设置,比如rtsp的延时时间 ); if (re != 0) { char buf[1024] = { 0 }; av_strerror(re, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); cout << "open " << path << " failed! :" << buf << endl; getchar(); return -1; } cout << "open " << path << " success! " << endl; //获取流信息 re = avformat_find_stream_info(ic, 0); //总时长 毫秒 int totalMs = ic->duration / (AV_TIME_BASE / 1000); cout << "totalMs = " << totalMs << endl; //打印视频流详细信息 av_dump_format(ic, 0, path, 0); //音视频索引,读取时区分音视频 int videoStream = 0; int audioStream = 1; //获取音视频流信息 (遍历,函数获取) for (int i = 0; i < ic->nb_streams; i++) { AVStream* as = ic->streams[i]; cout << "codec_id = " << as->codecpar->codec_id << endl; cout << "format = " << as->codecpar->format << endl; //音频 AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO if (as->codecpar->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO) { audioStream = i; cout << i << "音频信息" << endl; cout << "sample_rate = " << as->codecpar->sample_rate << endl; //AVSampleFormat; cout << "channels = " << as->codecpar->channels << endl; //一帧数据?? 单通道样本数 cout << "frame_size = " << as->codecpar->frame_size << endl; //1024 * 2 * 2 = 4096 fps = sample_rate/frame_size } //视频 AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO else if (as->codecpar->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) { videoStream = i; cout << i << "视频信息" << endl; cout << "width=" << as->codecpar->width << endl; cout << "height=" << as->codecpar->height << endl; //帧率 fps 分数转换 cout << "video fps = " << r2d(as->avg_frame_rate) << endl; } } //获取视频流 videoStream = av_find_best_stream(ic, AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, -1, -1, NULL, 0); // ///视频解码器打开 ///找到视频解码器 AVCodec* vcodec = avcodec_find_decoder(ic->streams[videoStream]->codecpar->codec_id); if (!vcodec) { cout << "can't find the codec id " << ic->streams[videoStream]->codecpar->codec_id; getchar(); return -1; } cout << "find the AVCodec " << ic->streams[videoStream]->codecpar->codec_id << endl; AVCodecContext* vc = avcodec_alloc_context3(vcodec); ///配置解码器上下文参数 avcodec_parameters_to_context(vc, ic->streams[videoStream]->codecpar); //八线程解码 vc->thread_count = 8; ///打开解码器上下文 re = avcodec_open2(vc, 0, 0); if (re != 0) { char buf[1024] = { 0 }; av_strerror(re, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); cout << "avcodec_open2 failed! :" << buf << endl; getchar(); return -1; } cout << "video avcodec_open2 success!" << endl; // ///音频解码器打开 AVCodec* acodec = avcodec_find_decoder(ic->streams[audioStream]->codecpar->codec_id); if (!acodec) { cout << "can't find the codec id " << ic->streams[audioStream]->codecpar->codec_id; getchar(); return -1; } cout << "find the AVCodec " << ic->streams[audioStream]->codecpar->codec_id << endl; ///创建解码器上下文呢 AVCodecContext* ac = avcodec_alloc_context3(acodec); ///配置解码器上下文参数 avcodec_parameters_to_context(ac, ic->streams[audioStream]->codecpar); //八线程解码 ac->thread_count = 8; ///打开解码器上下文 re = avcodec_open2(ac, 0, 0); if (re != 0) { char buf[1024] = { 0 }; av_strerror(re, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); cout << "avcodec_open2 failed! :" << buf << endl; getchar(); return -1; } cout << "audio avcodec_open2 success!" << endl; ///ic->streams[videoStream] //malloc AVPacket并初始化 AVPacket* pkt = av_packet_alloc(); AVFrame* frame = av_frame_alloc(); //像素格式和尺寸转换上下文 SwsContext* vctx = NULL; unsigned char* rgb = NULL; //音频重采样 上下文初始化 SwrContext* actx = swr_alloc(); actx = swr_alloc_set_opts(actx, av_get_default_channel_layout(2), //输出格式 AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, //输出样本格式 ac->sample_rate, //输出采样率 av_get_default_channel_layout(ac->channels),//输入格式 ac->sample_fmt, ac->sample_rate, 0, 0 ); re = swr_init(actx); if (re != 0) { char buf[1024] = { 0 }; av_strerror(re, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); cout << "swr_init failed! :" << buf << endl; getchar(); return -1; } unsigned char* pcm = NULL; for (;;) { int re = av_read_frame(ic, pkt); if (re != 0) { //循环播放 cout << "==============================end==============================" << endl; int ms = 3000; //三秒位置 根据时间基数(分数)转换 long long pos = (double)ms / (double)1000 * r2d(ic->streams[pkt->stream_index]->time_base); av_seek_frame(ic, videoStream, pos, AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD | AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME); continue; } cout << "pkt->size = " << pkt->size << endl; //显示的时间 cout << "pkt->pts = " << pkt->pts << endl; //转换为毫秒,方便做同步 cout << "pkt->pts ms = " << pkt->pts * (r2d(ic->streams[pkt->stream_index]->time_base) * 1000) << endl; //解码时间 cout << "pkt->dts = " << pkt->dts << endl; AVCodecContext* cc = 0; if (pkt->stream_index == videoStream) { cout << "图像" << endl; cc = vc; } if (pkt->stream_index == audioStream) { cout << "音频" << endl; cc = ac; } ///解码视频 //发送packet到解码线程 send传NULL后调用多次receive取出所有缓冲帧 re = avcodec_send_packet(cc, pkt); //释放,引用计数-1 为0释放空间 av_packet_unref(pkt); if (re != 0) { char buf[1024] = { 0 }; av_strerror(re, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); cout << "avcodec_send_packet failed! :" << buf << endl; continue; } for (;;) { //从线程中获取解码接口,一次send可能对应多次receive re = avcodec_receive_frame(cc, frame); //直到收不到为止,break退出循环 if (re != 0) break; cout << "recv frame " << frame->format << " " << frame->linesize[0] << endl; //视频 if (cc == vc) { vctx = sws_getCachedContext( vctx, //传NULL会新创建 frame->width, frame->height, //输入的宽高 (AVPixelFormat)frame->format, //输入格式 YUV420p frame->width, frame->height, //输出的宽高 AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA, //输入格式RGBA SWS_BILINEAR, //尺寸变化的算法 0, 0, 0); //if(vctx) //cout << "像素格式尺寸转换上下文创建或者获取成功!" << endl; //else // cout << "像素格式尺寸转换上下文创建或者获取失败!" << endl; if (vctx) { if (!rgb) rgb = new unsigned char[frame->width * frame->height * 4]; uint8_t* data[2] = { 0 }; data[0] = rgb; int lines[2] = { 0 }; lines[0] = frame->width * 4; re = sws_scale(vctx, frame->data, //输入数据 frame->linesize, //输入行大小 0, frame->height, //输入高度 data, //输出数据和大小 lines ); cout << "sws_scale = " << re << endl; } } else //音频 { uint8_t* data[2] = { 0 }; if (!pcm) pcm = new uint8_t[frame->nb_samples * 2 * 2]; data[0] = pcm; re = swr_convert(actx, data, frame->nb_samples, //输出 (const uint8_t**)frame->data, frame->nb_samples //输入 ); cout << "swr_convert = " << re << endl; } } //XSleep(500); } av_frame_free(&frame); av_packet_free(&pkt); if (ic) { //释放封装上下文,并且把ic置0 avformat_close_input(&ic); } getchar(); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
重要结构体之间的关系

FFmpeg 中结构体很多。最关键的结构体可以分成以下几类:
解协议(http, rtsp, rtmp, mms)
- AVIOContext ,URLProtocol ,URLContext 主要存储视音频使用的协议的类型以及状态。URLProtocol 存 储输入视音频使用的封装格式。每种协议都对应一个 URLProtocol 结构(注意:FFmpeg 中文件也被当 做一种协议 “file” )。
解封装(flv, avi, rmvb, mp4)
- AVFormatContext 主要存储视音频封装格式中包含的信息;AVInputFormat 存储输入视音频使用的封装格式。每种视音频封装格式都对应一个 AVInputFormat 结构。
解码(h264, mpeg2, aac, mp3)
- 每个 AVStream 存储一个视频/音频流的相关数据;每个 AVStream 对应一个 AVCodecContext ,存储该视 频/音频流使用解码方式的相关数据;每个 AVCodecContext 中对应一个 AVCodec ,包含该视频/音频对应 的解码器。每种解码器都对应一个 AVCodec 结构。
FFmpeg3与ffmpeg4的区别

存数据
视频的话,每个结构一般是存一帧;音频可能有好几帧
- 解码前数据:AVPacket
- 解码后数据:AVFrame
参考
刻意练习FFmpeg系列:通过思维导图快速了解FFmpeg源码整体结构体
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVFrame
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVFormatContext
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVCodecContext
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVIOContext
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVCodec
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVStream
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVPacket -
相关阅读:
Thinkphp6实现定时任务功能
Spark基础
AMBA 2 AHB、AMBA 3 AHB(AHB_Lite)和AMBA 5 AHB协议比较
二十五、DSL查询文档(全文检索查询、精确查询、地理查询、复合查询)
主动获取用户的ColaKey接口
传统Android 开发与 Android 音视频开发的差距……
JAVA开发中常用RDMS
针对微电网中可时移,柔性,基础负荷的电价响应模型---代码解析
应用层总结(未完待续 )
JavaWeb-JSP+Servlet+Mysql实现JavaWeb基础项目
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/e891377/article/details/126717216
