-
SQL之exists、not exists
函数介绍
-
EXISTS 子查询找到的提交
NOT EXISTS 子查询中 找不到的提交
说明:不要去翻译为存在和不存在,把脑袋搞晕。 -
建立程序循环的概念,这是一个动态的查询过程。如 FOR循环 。
-
Exists执行的流程Exists首先执行外层查询,再执行内层查询,与IN相反。
-
流程为:首先取出外层中的第一元组, 再执行内层查询,将外层表的第一元组代入,若内层查询为真,即有结果时。返回外层表中的第一元 组,接着取出第二元组,执行相同的算法。一直到扫描完外层整表 。
for(int i =0; i<>EOFout;i++) for (int j = 0 ; j<EOFin,j++)- 1
- 2
- 3
性能:
一直以来认为exists比in效率高的说法是不准确的。
如果查询的两个表大小相当,那么用in和exists差别不大。
如果两个表中一个较小,一个是大表,则子查询表大的用exists,子查询表小的用in
Not Exists示例1:
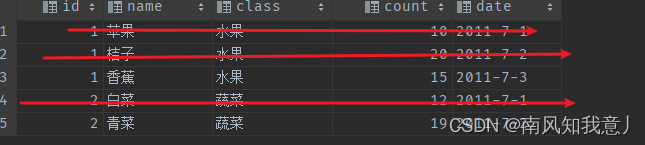
需求:找出每个id,时间最近的行 INSERT INTO fruits (id, name, class, count, date) VALUES (1,'苹果','水果',10,'2011-7-1'), (1 ,'桔子', '水果' ,20 ,'2011-7-2'), (1 ,'香蕉', '水果' ,15 ,'2011-7-3'), (2 ,'白菜', '蔬菜' ,12 ,'2011-7-1'), (2 ,'青菜', '蔬菜' ,19 ,'2011-7-2'); SELECT * FROM fruits f WHERE NOT exists( SELECT 1 FROM fruits WHERE fruits.id = f.id AND fruits.date > f.date # 子查询找不到的提交 ); 等价于(not in): SELECT * FROM fruits f WHERE f.id NOT in( SELECT f.id FROM fruits WHERE fruits.id = f.id AND fruits.date > f.date );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
-
拆解:
SELECT f2.* FROM fruits f1,fruits f2 WHERE f1.id = f2.id AND f1.date > f2.date; #子查询找得到的

-
最终结果就是:
Not Exists示例2:
#查询 a表的name 不在b表中的数据 SELECT * FROM tableln a WHERE NOT exists( SELECT 1 FROM tableex b WHERE a.aname = b.bname 返回A表中A.aname与B.bname不能关联上的数据 );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
select * from tableln A where not exists(select * from tableex B where B.bID=1); ---A表不返回任何数据 select * from tableln A where not exists(select * from tableex B where A.AID=1);---返回A表中AID<>1的数据 select * from tableln A where not exists(select 1 where A.AID=1); ---返回A表中AID<>1的数据- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Exists示例1:
查询 b表的name且在a表中的数据 SELECT * FROM tableex b WHERE exists( SELECT 1 FROM tableln a WHERE b.bname = a.aname # exists返回 b表可以关联上a表 的内容 );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
select * from tableln a where exists(select bid from tableex );---返回A表所有数据 select * from tableln a where exists(select * from tableex where bID=1);---返回A表所有数据 select * from tableln A where exists(select * from tableex B where B.bID=2); ---返回A表所有数据 select * from tableln A where exists(select * from tableex B where B.bID=3); ---返回A表所有数据 select * from tableln A where exists(select * from tableex B where A.AID=1);---返回A表中AID=1的数据 select * from tableln A where exists(select * from tableex B where A.AID=2);---返回A表中AID=2的数据 select * from tableln A where exists(select * from tableex B where A.AID=3);---返回A表中AID=3的数据- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
测试数据
#建表 create table test.tableln (aid varchar(20), aname varchar(20), asex varchar(20)); create table tableex (bid varchar(20), bname varchar(20), bsex varchar(20), baddress varchar(20)); #插入数据 insert into tableln select 1 aa,'张晋娟' bb,'女' cc from dual union all select 2 aa,'张翠兰' bb,'女' cc from dual union all select 3 aa,'李海滨' bb,'男' cc from dual union all select 4 aa,'马艳艳' bb,'女' cc from dual union all select 5 aa,'邓事文' bb,'男' cc from dual; insert into tableex select '1' aa,'马艳艳' bb,'女' cc,'太原' dd from dual union all select '2' aa,'谭建军' bb,'男' cc,'长沙' dd from dual union all select '3' aa,'李红军' bb,'男' cc,'长沙' dd from dual union all select '4' aa,'丁秀娟' bb,'女' cc,'北京' dd from dual union all select '5' aa,'邓事文' bb,'男' cc,'深圳' dd from dual ;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
-
-
相关阅读:
数字孪生技术在智慧城市应用的推进建议
我们为什么做NDH
AI工具在工作中的“大作用”
修改CentOS默认mail发件名称
USB设备枚举
《windows 程序设计》读书笔记 三
想学好C语言,操作符也很重要
Python学习笔记--自定义元类
RabbitMQ系列【11】延迟队列
IP代理安全吗?如何防止IP被限制访问?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Lzx116/article/details/126748500
