-
Spring——AOP(很全很详细,耐心看完有收获)
Spring——AOP
AOP(概念)
1、什么是 AOP
(1)面向切面编程(方面),利用 AOP 可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得
业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
(2)通俗描述:不通过修改源代码方式,在主干功能里面添加新功能
(3)使用登录例子说明 AOP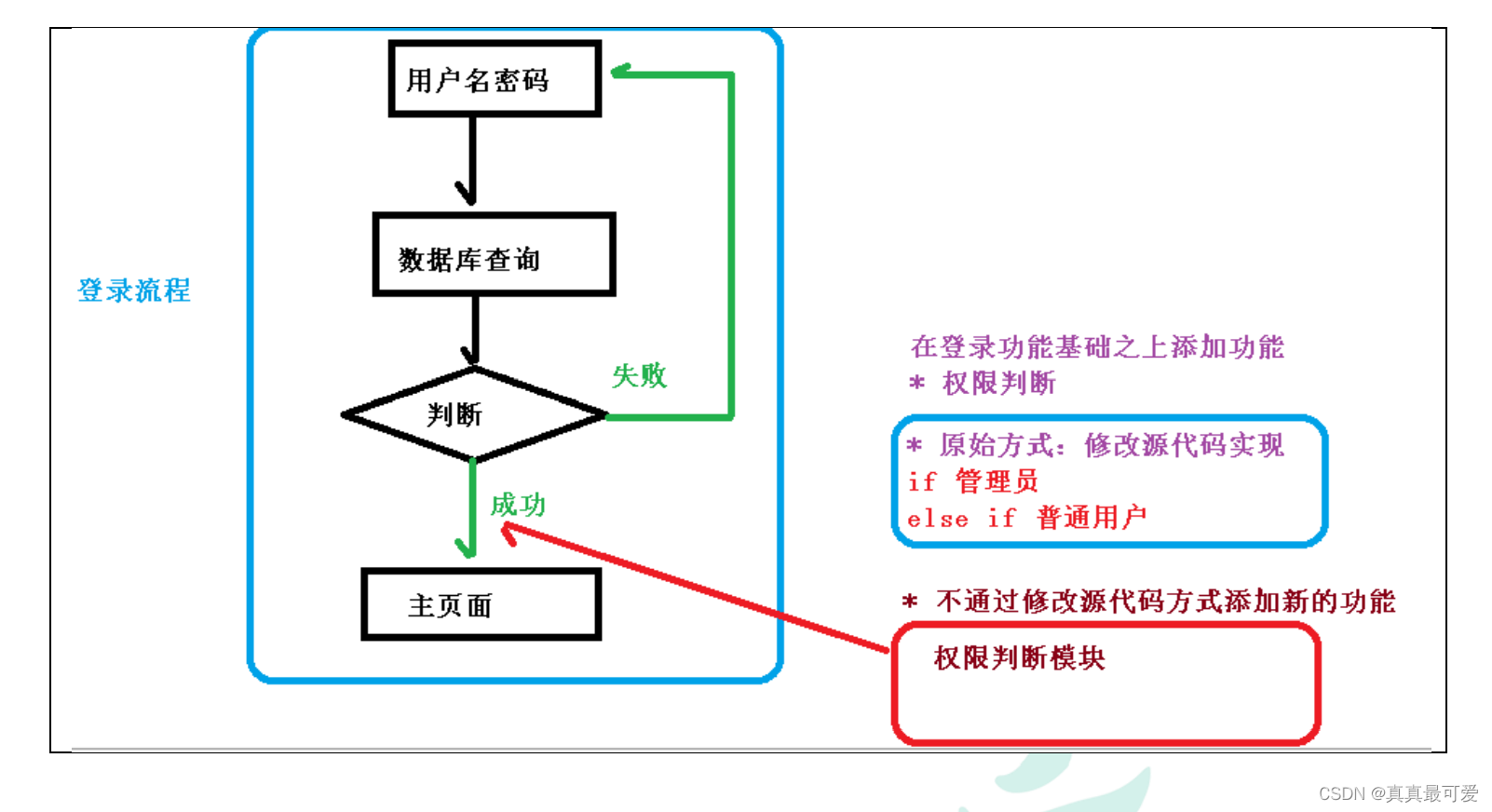
AOP(底层原理)
1、AOP 底层使用动态代理
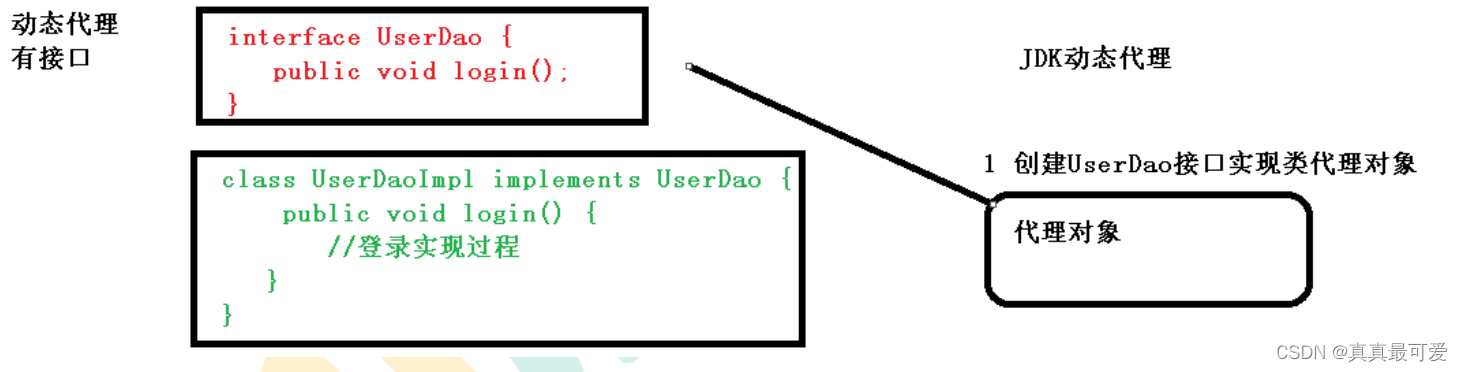
(1)有两种情况动态代理
第一种 有接口情况,使用 JDK 动态代理- 创建接口实现类代理对象,增强类的方法
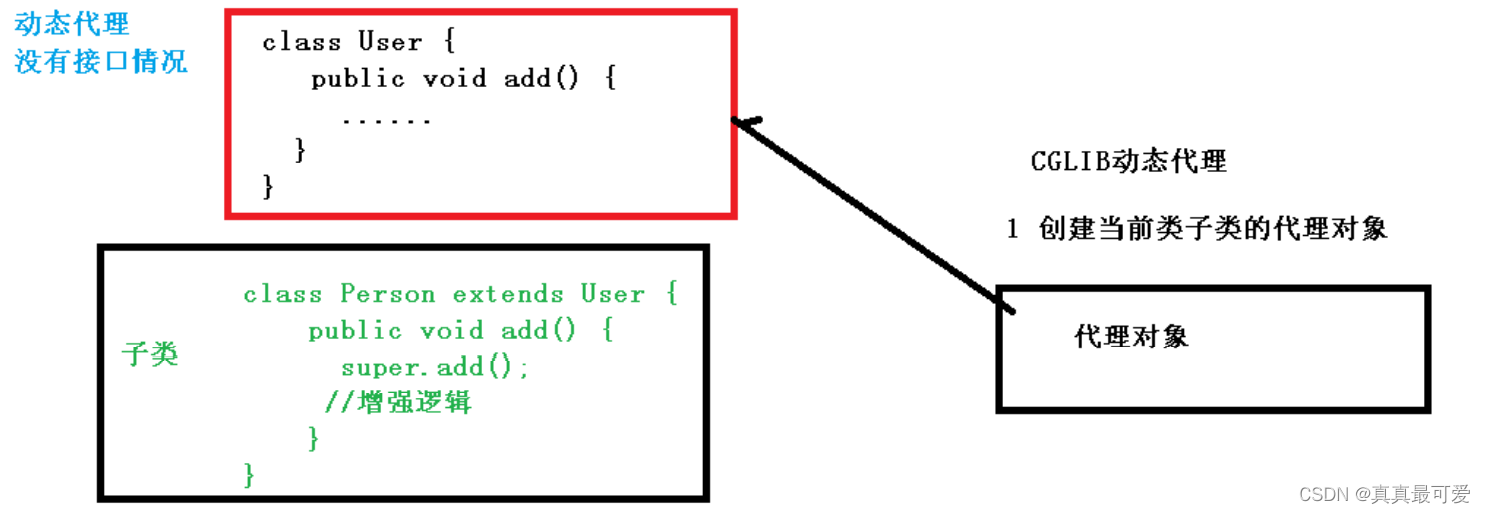
第二种 没有接口情况,使用 CGLIB 动态代理
- 创建子类的代理对象,增强类的方法
AOP(JDK 动态代理——底层原理)
1、使用 JDK 动态代理,使用 Proxy 类里面的方法创建代理对象

(1)调用 newProxyInstance 方法

方法有三个参数:
第一参数,类加载器
第二参数,增强方法所在的类,这个类实现的接口,支持多个接口
第三参数,实现这个接口 InvocationHandler,创建代理对象,写增强的部分2、编写 JDK 动态代理代码
(1)创建接口,定义方法public interface UserDao { public int add(int a,int b); public String update(String id); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
(2)创建接口实现类,实现方法
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { @Override public int add(int a, int b) { return a+b; } @Override public String update(String id) { return id; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
(3)使用 Proxy 类创建接口代理对象
public class JDKProxy { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建接口实现类代理对象 Class[] interfaces = {UserDao.class}; // Proxy.newProxyInstance(JDKProxy.class.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new InvocationHandler() { // @Override // public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { // return null; // } // }); UserDaoImpl userDao = new UserDaoImpl(); UserDao dao = (UserDao)Proxy.newProxyInstance(JDKProxy.class.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new UserDaoProxy(userDao)); int result = dao.add(1, 2); System.out.println("result:"+result); } } //创建代理对象代码 class UserDaoProxy implements InvocationHandler { //1 把创建的是谁的代理对象,把谁传递过来 //有参数构造传递 private Object obj; public UserDaoProxy(Object obj) { this.obj = obj; } //增强的逻辑 @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //方法之前 System.out.println("方法之前执行...."+method.getName()+" :传递的参数..."+ Arrays.toString(args)); //被增强的方法执行 Object res = method.invoke(obj, args); //方法之后 System.out.println("方法之后执行...."+obj); return res; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
AOP(术语)
1、连接点
- 类中的那些方法可以增强,这些方法称为连接点。
2、切入点
- 实际上真正被增强的方法,称为切入点。
3、通知(增强)
- 实际增强的逻辑部分称为通知
- 通知有多种类型
- 前置通知
- 后置通知
- 环绕通知
- 异常通知
- 最终通知
这些在下面的示例中都会讲解到。
4、切面
是动作!把通知应用到切入点的过程。AOP 操作(准备工作)
1、Spring 框架一般都是基于 AspectJ 实现 AOP 操作
(1)AspectJ 不是 Spring 组成部分,独立 AOP 框架,一般把 AspectJ 和 Spirng 框架一起使
用,进行 AOP 操作2、基于 AspectJ 实现 AOP 操作
(1)基于 xml 配置文件实现
(2)基于注解方式实现(实际中只用注解去实现AOP操作)3、在项目工程里面引入 AOP 相关依赖

4、切入点表达式(1)切入点表达式作用:知道对哪个类里面的哪个方法进行增强
(2)语法结构: execution([权限修饰符] [返回类型] [类全路径] [方法名称]]([参数列表]) )举例 1:对 com.atguigu.dao.BookDao 类里面的 add 进行增强
execution(* com.atguigu.dao.BookDao.add(…))举例 2:对 com.atguigu.dao.BookDao 类里面的所有的方法进行增强
execution(* com.atguigu.dao.BookDao.* (…))举例 3:对 com.atguigu.dao 包里面所有类,类里面所有方法进行增强
execution(* com.atguigu.dao.. (…))AOP 操作(AspectJ 注解)
1、创建类,在类里面定义方法
public class User { public void add() { System.out.println("add......."); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
2、创建增强类(编写增强逻辑)
(1)在增强类里面,创建方法,让不同方法代表不同通知类型//增强的类 public class UserProxy { public void before() {//前置通知 System.out.println("before......"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3、进行通知的配置
(1)在 spring 配置文件中,开启注解扫描<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring5.aopanno">context:component-scan>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
(2)使用注解创建 User 和 UserProxy 对象
都在其类上方添加一个注解@Component

(3)在增强类上面添加注解 @Aspect//增强的类 @Component @Aspect //生成代理对象 public class UserProxy {- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
(4)在 spring 配置文件中开启生成代理对象
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy>aop:aspectj-autoproxy>- 1
- 2
4、配置不同类型的通知
(1)在增强类的里面,在作为通知方法上面添加通知类型注解,使用切入点表达式配置//增强的类 @Component @Aspect //生成代理对象 public class UserProxy { //前置通知 //@Before 注解表示作为前置通知 @Before(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))") public void before() { System.out.println("before........."); } //后置通知(返回通知) @AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))") public void afterReturning() { System.out.println("afterReturning........."); } //最终通知 @After(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))") public void after() { System.out.println("after........."); } //异常通知 @AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))") public void afterThrowing() { System.out.println("afterThrowing........."); } //环绕通知 @Around(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))") public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable { System.out.println("环绕之前........."); //被增强的方法执行 proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕之后........."); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
5、相同的切入点抽取(方便我们进行修改切入点表达式)
//相同切入点抽取 @Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))") public void pointdemo() { } //前置通知 //@Before 注解表示作为前置通知 @Before(value = "pointdemo()") public void before() { System.out.println("before........."); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
6、有多个增强类多同一个方法进行增强,设置增强类优先级(都会进行增强,只不过顺序先后的问题。)
(1)在增强类上面添加注解 @Order(数字类型值),数字类型值越小优先级越高@Component @Aspect @Order(1) public class PersonProxy- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
7、完全使用注解开发
(1)创建配置类,不需要创建 xml 配置文件@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.atguigu"}) @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true) //开启 Aspect 生成代理对象 public class ConfigAop { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
AOP 操作(AspectJ 配置文件)
了解就行了,一般不会用配置文件进行AOP。
1、创建两个类,增强类和被增强类,创建方法
2、在 spring 配置文件中创建两个类对象<bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.aopxml.Book">bean> <bean id="bookProxy" class="com.atguigu.spring5.aopxml.BookProxy">bean>- 1
- 2
- 3
3、在 spring 配置文件中配置切入点
<aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="p" expression="execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aopxml.Book.buy(..))"/> <aop:aspect ref="bookProxy"> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="p"/> aop:aspect> aop:config>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 创建接口实现类代理对象,增强类的方法
-
相关阅读:
自然语言处理实战项目17-基于多种NLP模型的诈骗电话识别方法研究与应用实战
数据结构初步(一)- 时间与空间复杂度
QT源码拾贝0-5(qimage和qpainter)
服务器证书是网络信息安全的基础
前端实现批量下载并打包成ZIP文件
go语言多态实现
Python武器库开发-flask篇之error404(二十七)
Eclipse Theia技术揭秘——初识Theia
二本4年Java经验,五面阿里艰苦经历(定薪45K),回馈一波心得体会
JAVA中常用序列化与反序列化合集
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/xiangqian0721/article/details/126697815