-
剑指offer62-67排序-前缀树
剑指 Offer II 062. 实现前缀树
Trie(发音类似 “try”)或者说 前缀树 是一种树形数据结构,用于高效地存储和检索字符串数据集中的键。这一数据结构有相当多的应用情景,例如自动补完和拼写检查。
请你实现 Trie 类:
Trie() 初始化前缀树对象。
void insert(String word) 向前缀树中插入字符串 word 。
boolean search(String word) 如果字符串 word 在前缀树中,返回 true(即,在检索之前已经插入);否则,返回 false 。
boolean startsWith(String prefix) 如果之前已经插入的字符串 word 的前缀之一为 prefix ,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。实现这种结构
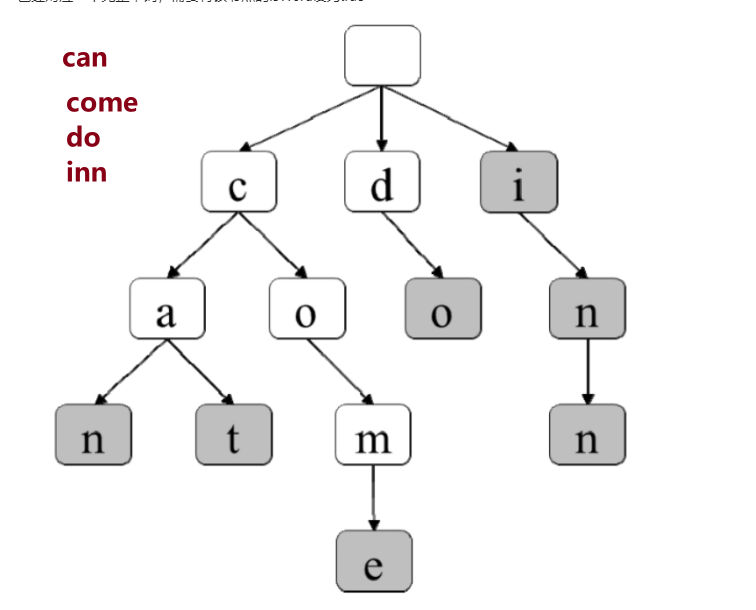
方法
定义一个类,这个类是由一个vector和isEnd组成,前者是存放26个孩子节点,后者表示单词是否已经结束

搜索前缀。比如Anthony,an就是它的一个前缀,下面方法可以检验an是否是这个单词的前缀

搜索这个单词

class Trie { private: vector<Trie*> children; bool isEnd; Trie* searchPrefix(string prefix) { Trie* node = this; for (char ch : prefix) { ch -= 'a'; if (node->children[ch] == nullptr) { return nullptr; } node = node->children[ch]; } return node; } public: Trie() : children(26), isEnd(false) {} void insert(string word) { Trie* node = this; for (char ch : word) { ch -= 'a'; if (node->children[ch] == nullptr) { node->children[ch] = new Trie(); } node = node->children[ch]; } node->isEnd = true; } bool search(string word) { Trie* node = this->searchPrefix(word); return node != nullptr && node->isEnd; } bool startsWith(string prefix) { return this->searchPrefix(prefix) != nullptr; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
剑指 Offer II 063. 替换单词
在英语中,有一个叫做 词根(root) 的概念,它可以跟着其他一些词组成另一个较长的单词——我们称这个词为 继承词(successor)。例如,词根an,跟随着单词 other(其他),可以形成新的单词 another(另一个)。
现在,给定一个由许多词根组成的词典和一个句子,需要将句子中的所有继承词用词根替换掉。如果继承词有许多可以形成它的词根,则用最短的词根替换它。
需要输出替换之后的句子。
输入:dictionary = [“cat”,“bat”,“rat”], sentence = “the cattle was rattled by the battery”
输出:“the cat was rat by the bat”题目意思,cattle有cat,将cattle替换成cat
方法:将给的数组插入前缀树,将句子分解为单词,逐个单词遍历前缀树
// 构造前缀树节点 class Trie { private: bool isWord; vector<Trie*> children; public: Trie () : isWord(false), children(26, nullptr) {} void insert(const string& str) { Trie* node = this; for (auto& ch : str) { if (node->children[ch - 'a'] == nullptr) { node->children[ch - 'a'] = new Trie(); } node = node->children[ch - 'a']; } node->isWord = true; } int countPreFixLen(const string& str) { Trie* node = this; int len = 0; for (auto& ch : str) { if (node->children[ch - 'a'] == nullptr) { return 0; } node = node->children[ch - 'a']; len++; if (node->isWord) { return len; } } return 0; } }; class Solution { public: string replaceWords(vector<string>& dictionary, string sentence) { Trie* root = new Trie(); for (string& word : dictionary) { root->insert(word); } // 分割 vector<string> words{""}; for (auto& ch : sentence) { if (ch != ' ') { words.back().push_back(ch); } else { words.push_back(""); } } // 处理 vector<string> ret; for (auto& word : words) { int len = root->countPreFixLen(word); if (len == 0) { ret.emplace_back(word); } else { ret.push_back(word.substr(0, len)); } } // 拼接 string ans{""}; for (auto& word : ret) { ans += word; ans += " "; } ans.pop_back(); return ans; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
剑指 Offer II 064. 神奇的字典
设计一个使用单词列表进行初始化的数据结构,单词列表中的单词 互不相同 。 如果给出一个单词,请判定能否只将这个单词中一个字母换成另一个字母,使得所形成的新单词存在于已构建的神奇字典中。
实现 MagicDictionary 类:
MagicDictionary() 初始化对象
void buildDict(String[] dictionary) 使用字符串数组 dictionary 设定该数据结构,dictionary 中的字符串互不相同
bool search(String searchWord) 给定一个字符串 searchWord ,判定能否只将字符串中 一个 字母换成另一个字母,使得所形成的新字符串能够与字典中的任一字符串匹配。如果可以,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。输入
inputs = [“MagicDictionary”, “buildDict”, “search”, “search”, “search”, “search”]
inputs = [[], [[“hello”, “leetcode”]], [“hello”], [“hhllo”], [“hell”], [“leetcoded”]]
输出
[null, null, false, true, false, false]解释
MagicDictionary magicDictionary = new MagicDictionary();
magicDictionary.buildDict([“hello”, “leetcode”]);
magicDictionary.search(“hello”); // 返回 False
magicDictionary.search(“hhllo”); // 将第二个 ‘h’ 替换为 ‘e’ 可以匹配 “hello” ,所以返回 True
magicDictionary.search(“hell”); // 返回 False
magicDictionary.search(“leetcoded”); // 返回 False将一个单词替换一个字母能够匹配已经存在的单词,比如已经有了hello,将hhllo中的h替换为e便成了hello
方法 前缀树遍历遇到异常时递归
构造前缀树,定义一个全局变量edit用来表示已经容错的个数,最大是1

class Trie { public: vector<Trie*> children; //当前节点的子孩子 bool isEndPoint; public: Trie() { children.resize(26); isEndPoint = 0; } void insert(string& word) { Trie* node = this; for (char& ch : word) { int idx = ch - 'a'; if (node->children[idx] == nullptr) node->children[idx] = new Trie(); node = node->children[idx]; } node->isEndPoint = 1; } }; class MagicDictionary { private: Trie* trie; public: //pos为word的当前字符位置 bool dfs(Trie* node, string& word, int pos, int& edit) { //如果找到叶子节点都没成功 if (node == nullptr) return false; //如果刚好到达字符串末尾,且node处于根节点,且只被修改过一个字符 if (node->isEndPoint && pos == word.length() && edit == 1) return true; if (pos != word.length() && edit <= 1) { //遍历当前节点的所有子节点, for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) { //如果子节点存在,edit不变;否则,edit加1; int next = (i == (word[pos] - 'a')) ? edit : edit + 1; if (dfs(node->children[i], word, pos + 1, next)) return true; } } return false; } /** Initialize your data structure here. */ MagicDictionary() { trie = new Trie(); } void buildDict(vector<string> dictionary) { for (string& str : dictionary) trie->insert(str); } bool search(string searchWord) { int pos = 0, edit = 0; return dfs(trie, searchWord, pos, edit); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
剑指 Offer II 065. 最短的单词编码
单词数组 words 的 有效编码 由任意助记字符串 s 和下标数组 indices 组成,且满足:
words.length == indices.length
助记字符串 s 以 ‘#’ 字符结尾
对于每个下标 indices[i] ,s 的一个从 indices[i] 开始、到下一个 ‘#’ 字符结束(但不包括 ‘#’)的 子字符串 恰好与 words[i] 相等
给定一个单词数组 words ,返回成功对 words 进行编码的最小助记字符串 s 的长度 。输入:words = [“time”, “me”, “bell”]
输出:10
解释:一组有效编码为 s = “time#bell#” 和 indices = [0, 2, 5] 。
words[0] = “time” ,s 开始于 indices[0] = 0 到下一个 ‘#’ 结束的子字符串,如加粗部分所示 “time#bell#”
words[1] = “me” ,s 开始于 indices[1] = 2 到下一个 ‘#’ 结束的子字符串,如加粗部分所示 “time#bell#”
words[2] = “bell” ,s 开始于 indices[2] = 5 到下一个 ‘#’ 结束的子字符串,如加粗部分所示 “time#bell#”“time”, “me”, “bell” time的me和me重复,所以time ,me变为了time,time和bell没有重复,所以变为了time ,bell
方法:前缀树倒叙插入

最后统计节点的个数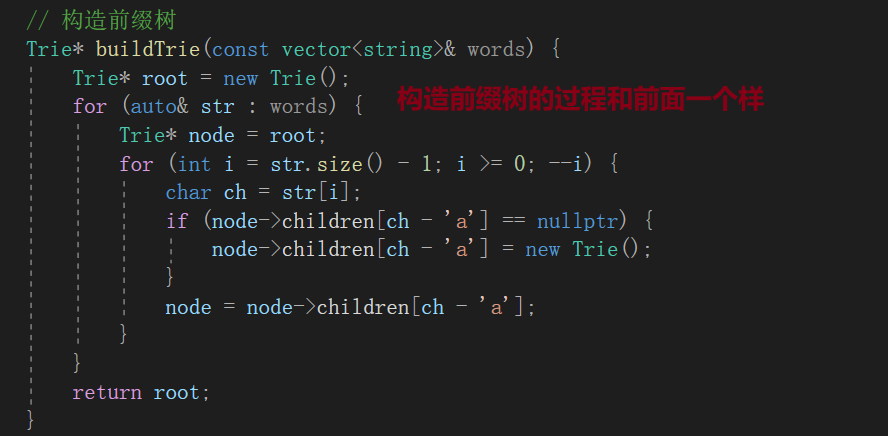

剑指 Offer II 066. 单词之和
实现一个 MapSum 类,支持两个方法,insert 和 sum:
MapSum() 初始化 MapSum 对象
void insert(String key, int val) 插入 key-val 键值对,字符串表示键 key ,整数表示值 val 。如果键 key 已经存在,那么原来的键值对将被替代成新的键值对。
int sum(string prefix) 返回所有以该前缀 prefix 开头的键 key 的值的总和。
输入:
inputs = [“MapSum”, “insert”, “sum”, “insert”, “sum”]
inputs = [[], [“apple”, 3], [“ap”], [“app”, 2], [“ap”]]
输出:
[null, null, 3, null, 5]解释:
MapSum mapSum = new MapSum();
mapSum.insert(“apple”, 3);
mapSum.sum(“ap”); // return 3 (apple = 3)
mapSum.insert(“app”, 2);
mapSum.sum(“ap”); // return 5 (apple + app = 3 + 2 = 5)前缀树,插入时如果分支存在则用新的值替代原来的值,sum时是计算共同前缀的和,比如求a,则将所以单词是a的单词对应的值全部计算
方法前缀树
插入


代码
// 构造前缀树节点 class Trie { public: vector<Trie*> children; Trie() : children(26, nullptr) {} }; // 构造前缀树节点 class Trie { public: int val; vector<Trie*> children; Trie() : val(0), children(26, nullptr) {} // 实现插入字符串 void insert(string& str, int m) { Trie* node = this; for (auto& ch : str) { if (node->children[ch - 'a'] == nullptr) { node->children[ch - 'a'] = new Trie(); } node = node->children[ch - 'a']; } node->val = m; } // 实现返回所有以该前缀 prefix 开头的键 key 的值的总和 int coutSum(string& prefix) { Trie* node = this; for (auto& ch : prefix) { if (node->children[ch - 'a'] == nullptr) { return 0; } node = node->children[ch - 'a']; } // BFS int count = 0; queue<Trie*> que; que.push(node); while (!que.empty()) { Trie* node = que.front(); que.pop(); count += node->val; for (int i = 0; i < node->children.size(); ++i) { if (node->children[i] != nullptr) { que.push(node->children[i]); } } } return count; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
剑指 Offer II 067. 最大的异或
给定一个整数数组 nums ,返回 nums[i] XOR nums[j] 的最大运算结果,其中 0 ≤ i ≤ j < n 。
输入:nums = [3,10,5,25,2,8]
输出:28
解释:最大运算结果是 5 XOR 25 = 28.方法:前缀找相反位





-
相关阅读:
计算机网络学习笔记(II)——应用层(二)
TCP/IP之IP地址分类
input()函数——输入
TIA博途中累计流量的两种计算方法示例
数据库 基础面试第一弹
mysql数据库使用useSSL=true,并配置ca证书和密钥连接
Pytroch Nerf代码阅读笔记(LLFF 数据集pose 处理和Nerf 网络结构)
AI图像行为分析算法 opencv
(续)SSM整合之SSM整合笔记(ContextLoaderListener)(P179-188)
《QT从基础到进阶·三十五》QT插件实现侧边工具栏tabBar
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/baidu_41553551/article/details/126656090
