-
CogView中的Self Attention
入门小菜鸟,希望像做笔记记录自己学的东西,也希望能帮助到同样入门的人,更希望大佬们帮忙纠错啦~侵权立删。
目录
(3)调用ColumnParallelLinear线性变化:h->3h
(4)拆分形成Q,K,V并加入Multi-Head Attention
(10)调用RowParallelLinear线性变化+dropout
(5)attention_probs的dropout方法定义
(3)变形与转换——即加入加入Multi-Head Attention
(5)END OF BLOCK——得到最终GPT2自我注意力机制的输出结果(合并多头)
✨下文中有关ColumnParallelLinear和RowParallelLinear的解说可以看看往期博文
一、原理
1、为什么需要self attention
模仿人类注意力,希望将有限的注意力集中在重点信息上,快速得到最有效的信息。比如说关注图上的“小鸟”,希望把重心放在图中的小鸟上。
如何把关注点放在我们想关注的数据上?最简单的思路就是对数据进行加权处理,关注的部分权重大。
2、基本公式

其中的符号代表:
Q:(query)查询;
K:(key)索引;
V:(value)内容;
 :特征维度;
:特征维度;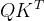 :向量的点积的几何意义是一个向量在另一个向量上的投影,点积越大,两向量间的相关性越强。所以结合Q,K代表的意思,即表示查询的和索引的相关度矩阵,即得到相似度矩阵。
:向量的点积的几何意义是一个向量在另一个向量上的投影,点积越大,两向量间的相关性越强。所以结合Q,K代表的意思,即表示查询的和索引的相关度矩阵,即得到相似度矩阵。除以
 :因为该方法假设 Q 和 K 都是独立的随机变量,满足均值为 0,方差为 1,则点乘后结果均值为 0,方差为
:因为该方法假设 Q 和 K 都是独立的随机变量,满足均值为 0,方差为 1,则点乘后结果均值为 0,方差为 ,所以为了让相似度矩阵中的值变小些,确保梯度稳定性,就来了个
,所以为了让相似度矩阵中的值变小些,确保梯度稳定性,就来了个 的缩放。
的缩放。softmax:然后再来一波归一化处理 :
 ,这样我们就得到了注意力的权重矩阵。
,这样我们就得到了注意力的权重矩阵。再乘上内容矩阵V:则可获得该输入加上注意力后的结果矩阵。
3、Multi-Head Attention
多头注意力机制,其作用是让模型从多个子空间中关注到不同方面的信息(即重复n次self attention)
完成上述公式的计算后需要合并多头,再乘上一个
 矩阵,得到最终结果。
矩阵,得到最终结果。4、具体实现
(1)参数代表
b——batch size;s——sequence length;h——hidden_size;p——number of partitions;
n——num_attention_heads;hp——h/p;np——n/p;hn——h/n;
(2)输入
hidden_states:输入层,shape为(b,s,h),假设为X;
attention mask:shape为(1,1,s,s);
mem:记忆模块(默认没有),若有记忆模块,则将记忆模块与输入层一起拼接;
(3)调用ColumnParallelLinear线性变化:h->3h
这里的W就相当于是
 的集合(其实就是相当于前面是将QW,KW,VW并在一起算)。
的集合(其实就是相当于前面是将QW,KW,VW并在一起算)。Y = XW+B=X*[W_1, ..., W_p]+[b_1, ..., b_p] = [XW_1, ..., XW_p]+[b_1, ..., b_p] = [Y_1, ..., Y_p];
shape变化:(b,s,h)->(b,s,3hp);(第i个GPU上对应Y_i)
(4)拆分形成Q,K,V并加入Multi-Head Attention
然后沿最后一个维度拆成3份,每一个的shape都为(b,s,hp),这就是初步的Q,K,V;
然后加入Multi-Head Attention,进行变形与转换:(b,s,hp) -> (b, np, s, hn);
(5)执行

(b, np, s, hn)->(b,np,s,s);
(6)添加从左到右的attention mask
attention mask默认是一个shape为(1,1,s,s)的下三角矩阵,下三角矩阵使得只能关注前面的东西(乘1),不能关注后面的东西(乘0)。
于是将前面的
 与attention mask相乘,并把不关注的后面部分全部设为-1000(极小值)。
与attention mask相乘,并把不关注的后面部分全部设为-1000(极小值)。(7)softmax归一化操作并dropout
对最后一维做softmax,即可得到每个位置的 attention_probs,然后再根据参数设定进行dropout处理。
(8)再乘上V
最终shape为(b, np, s, hn)
(9)合并Multi-Head
通过一系列变化和展平等操作合并:(b, np, s, hn)->(b, s, np, hn)->(b, s, hp)
(10)调用RowParallelLinear线性变化+dropout
对多头合并结果再乘上
 ,最终shape为(b,s,h);(每块GPU上都一样)
,最终shape为(b,s,h);(每块GPU上都一样)
二、代码解析
1、__init__
(1)参数设定
- class GPT2ParallelSelfAttention(torch.nn.Module):
- """Parallel self-attention layer for GPT2.
- Self-attention layer takes input with size [b, s, h] where b is
- the batch size, s is the sequence length, and h is the hidden size
- and creates output of the same size.
- Arguments:
- hidden_size: total hidden size of the layer (h).
- num_attention_heads: number of attention heads (n). Note that we
- require n to be divisible by number of GPUs
- used to parallelize the model. Also, we
- require hidden size to be divisible by n.
- dropout_prob: dropout probability for the attention scores.
- init_method: weight initialization.
- output_layer_init_method: output layer initialization. If None, use
- `init_method`.
- We use the following notation:
- h: hidden_size
- n: num_attention_heads
- p: number of partitions
- np: n/p
- hp: h/p
- hn: h/n
- b: batch size
- s: sequence length
- """
- def __init__(self, hidden_size, num_attention_heads,
- attention_dropout_prob, output_dropout_prob,
- init_method, output_layer_init_method=None, query_window=128, key_window_times=6):
- super(GPT2ParallelSelfAttention, self).__init__()
- hidden_size:总的隐藏层的大小(h);
- num_attention_heads:自我注意力模块中attention head的数量(n)。注:n可以被用于并行化模型的GPU数整除。此外,h也要求可以被n整除。
- attention_dropout_prob:注意力模块中注意力得分被dropout的概率;
- output_dropout_prob:输出层后的输出被dropout的概率;
- init_method:权重初始化方法;
- output_layer_init_method:输出层初始化方法定义。若为None,则用init_method方法;
- query_window:稀疏处理中的滑动窗口大小;
- key_window_times:可用于调节稀疏处理中的窗口数量;
✨设定:
- h: hidden_size
- n: num_attention_heads
- p: number of partitions
- np: n/p
- hp: h/p
- hn: h/n
- b: batch size
- s: sequence length
(2)输出层的初始化方法定义
- # Set output layer initialization if not provided.
- if output_layer_init_method is None:
- output_layer_init_method = init_method
(3)计算有关分区和attention head的分配情况
- world_size = get_model_parallel_world_size()#获取分布式组中的进程数(每个进程组里有多少个进程)p
- self.hidden_size_per_partition = divide(hidden_size, world_size)#计算每个分区的隐藏层大小
- self.hidden_size_per_attention_head = divide(hidden_size,
- num_attention_heads)#计算每个attention head被分配的隐藏层大小(hn)
- self.num_attention_heads_per_partition = divide(num_attention_heads,
- world_size)#计算每个分区的attention head数目(np)
- self.query_window = query_window
- self.key_window_times = key_window_times
(4)基于模型分片的线性变化层设置(Q,K,V的产生)
- # Strided linear layer.
- self.query_key_value = ColumnParallelLinear(hidden_size, 3*hidden_size,
- stride=3,
- gather_output=False,
- init_method=init_method)
(5)attention_probs的dropout方法定义
- # Dropout. Note that for a single iteration, this layer will generate
- # different outputs on different number of parallel partitions but
- # on average it should not be partition dependent.
- self.attention_dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(attention_dropout_prob)
(6)乘上
 的方法定义与输出层dropout方法定义
的方法定义与输出层dropout方法定义- self.dense = RowParallelLinear(hidden_size,
- hidden_size,
- input_is_parallel=True,
- init_method=output_layer_init_method)
- self.output_dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(output_dropout_prob)
(7)deepspeed激活点检查
- if deepspeed.checkpointing.is_configured():
- global get_cuda_rng_tracker, checkpoint
- get_cuda_rng_tracker = deepspeed.checkpointing.get_cuda_rng_tracker
- checkpoint = deepspeed.checkpointing.checkpoint
2、forward
(1)传入参数
- def forward(self, hidden_states, ltor_mask, pivot_idx=None, is_sparse=0, mem=None):
- # hidden_states: [b, s, h]
- # ltor_mask: [1, 1, s, s]
- # Attention heads. [b, s, hp]
- hidden_states:传入的隐藏层,大小为[b, s, h]
- ltor_mask:attention mask矩阵,大小为[1, 1, s, s]
- pivot_idx:支点index
- is_sparse:是否稀疏处理
- mem:记忆模块
(2)拆分出Q,K,V
首先获取序列长度s(为处理记忆模块做准备);
若有记忆模块,则与输入的隐藏层沿第一维进行拼接;
然后整体进行一个基于模型分片的线性变换;([b, s, h] -> [b, s, 3*hp])
再沿最后一个维度拆分张量(拆成3份)得到Q,K,V;
若有记忆模块,还需要将Q进行裁剪,使他最后的大小是[b,s,hp]
- #拆分出q,k,v
- query_length = hidden_states.size(1)#获得读取的序列长度(s)
- if mem is None:#若没有记忆模块
- mixed_x_layer = self.query_key_value(hidden_states)#整体进行一个基于模型分片的线性变换
- (mixed_query_layer,
- mixed_key_layer,
- mixed_value_layer) = split_tensor_along_last_dim(mixed_x_layer, 3)#沿最后一个维度拆分张量(拆成3份)得到q,k,v
- else:
- cat = torch.cat((mem, hidden_states), 1)#将mem和hidden_states沿一维拼接
- mixed_x_layer = self.query_key_value(cat)#整体进行一个基于模型分片的线性变换
- (mixed_query_layer,
- mixed_key_layer,
- mixed_value_layer) = split_tensor_along_last_dim(mixed_x_layer, 3)#沿最后一个维度拆分张量(拆成3份)得到q,k,v
- mixed_query_layer = mixed_query_layer[:, -query_length:]#截取长度,使q满足大小为[b,s,hp]
这里调用了mpu/utils.py中的split_tensor_along_last_dim函数
- def split_tensor_along_last_dim(tensor, num_partitions,
- contiguous_split_chunks=False):
- """Split a tensor along its last dimension.
- Arguments:
- tensor: input tensor.
- num_partitions: number of partitions to split the tensor
- contiguous_split_chunks: If True, make each chunk contiguous
- in memory.
- """
- # Get the size and dimension.
- last_dim = tensor.dim() - 1
- last_dim_size = divide(tensor.size()[last_dim], num_partitions)
- # Split.
- tensor_list = torch.split(tensor, last_dim_size, dim=last_dim)
- # Note: torch.split does not create contiguous tensors by default.
- if contiguous_split_chunks:
- return tuple(chunk.contiguous() for chunk in tensor_list)
- return tensor_list
(3)变形与转换——即加入加入Multi-Head Attention
首先定义了一个用于分数转换的_transpose_for_scores函数,即将一个shape为[b, s, np*hn]的tensor 变为shape为[b, np, s, hn]的tensor。
注:若模型不分片,np=n,hn=h/n,那就是[b, s, h]变成[b, n, s,hn]
- def _transpose_for_scores(self, tensor):
- """Transpose a 3D tensor [b, s, np*hn] into a 4D tensor with
- size [b, np, s, hn].
- """
- new_tensor_shape = tensor.size()[:-1] + \
- (self.num_attention_heads_per_partition,
- self.hidden_size_per_attention_head)#计算目标矩阵的shape:(b,s) + (np, hn) = (b, s, np, hn)
- # 将当前矩阵分解为目标 shape
- tensor = tensor.view(*new_tensor_shape)#变为(b, s, np, hn)
- return tensor.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)#第一维和第二维互换位置
然后调用_transpose_for_scores函数对q,k,v进行相应变换:[b, s, np*hn]变为[b, np, s, hn]
- query_layer = self._transpose_for_scores(mixed_query_layer)
- key_layer = self._transpose_for_scores(mixed_key_layer)
- value_layer = self._transpose_for_scores(mixed_value_layer)
(4)核心注意力机制代码
分成3种情况:稀疏训练(is_sparse=1),稀疏推断(is_sparse=2)和标准注意力机制(非稀疏处理)—— (is_sparse=0)
最终shape为[b, np, s, hn]
- # ===================== Core Attention Code ======================== #
- if is_sparse == 1:
- context_layer = sparse_attention(query_layer, key_layer, value_layer, pivot_idx, ltor_mask, self.query_window, self.key_window_times, self.attention_dropout)
- elif is_sparse == 2:
- context_layer = sparse_attention_inference(query_layer, key_layer, value_layer, pivot_idx)
- else:
- context_layer = standard_attention(query_layer, key_layer, value_layer, ltor_mask, self.attention_dropout)
稀疏注意那些以后再补吧(懒.gif
✨标准注意力机制——standard_attention函数
- def standard_attention(query_layer, key_layer, value_layer, attention_mask, attention_dropout=None):
- # We disable the PB-relax-Attention and only changes the order of computation, because it is enough for most of training.
- # The implementation in the paper can be done very easily, if you really need it to train very deep transformers.
(1)先对attention mask进行维数限定——必为四维(正常情况下应该是[1, 1, s, s])
- #attention_mask三维变四维
- if len(attention_mask.shape) == 3:#attention_mask是三维的
- attention_mask = attention_mask.unsqueeze(1)
(2)
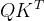 / hn 得到 attention score
/ hn 得到 attention score- # Raw attention scores. [b, np, s, s]
- #qw * kw 得到 attention score
- attention_scores = torch.matmul(query_layer / math.sqrt(query_layer.shape[-1]), key_layer.transpose(-1, -2))
torch.matmul(a,b)——矩阵乘法(最低两维做乘法)
q的shape:[b, np, s, hn];k.transpose(-1, -2)的shape为[b, np,hn ,s](最后两维倒置);
相乘后的结果为[b, np, s, s]。
(3)从左到右attention mask运算
- # Apply the left to right attention mask.
- attention_scores = torch.mul(attention_scores, attention_mask) - \
- 10000.0 * (1.0 - attention_mask)#attention-score的shape是[b, np, s, s];attention_mask(一个上三角全0 下三角全1的矩阵)的shape是[1, 1, s, s];attention-score和attention_mask逐元素相乘,然后只保留当前word之前的attention score,之后的都-1000,即设置为极小值(上三角-1000,下三角不变)
attention-score的shape是[b, np, s, s];attention_mask(一个上三角全0 下三角全1的矩阵)的shape是[1, 1, s, s];
attention-score和attention_mask逐元素相乘,然后只保留当前word之前的attention score,之后的都-1000,即设置为极小值(上三角-1000,下三角不变)
(4)获取attention_probs
- # Attention probabilities. [b, np, s, s]
- attention_probs = torch.nn.Softmax(dim=-1)(attention_scores)#对最后一维做softmax,即可得到每个位置的 attention_probs
(5)对attention_probs 进行 dropout
- if attention_dropout is not None:
- with get_cuda_rng_tracker().fork():
- attention_probs = attention_dropout(attention_probs)
(6)乘上V
attention_probs和V做点积,即[b, np, s, s] * [b, np, s, hn] 变成 [b, np, s, hn]。
- # Context layer.
- # [b, np, s, hn]
- context_layer = torch.matmul(attention_probs, value_layer)
- return context_layer
(5)END OF BLOCK——得到最终GPT2自我注意力机制的输出结果(合并多头)
定shape(合并多头)——乘上
 (RowParallelLinear)——dropout
(RowParallelLinear)——dropout最终shape为[b,s,hp]
- # ===================== END OF BLOCK ======================= #
- # [b, s, np, hn]
- context_layer = context_layer.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).contiguous()# 这里是多头合并,先把维度调换为[b, s, np, hn]
- new_context_layer_shape = context_layer.size()[:-2] + \
- (self.hidden_size_per_partition,)# 然后计算合并后的shape (b,s)+(hp) = (b,s,hp)
- # [b, s, hp]
- context_layer = context_layer.view(*new_context_layer_shape)#按计算的shape进行变化
- # Output. [b, s, h]
- output = self.dense(context_layer)#经过一个RowParallelLinear,[b, s, hp] * [hp, h] -> [b, s, h]
- output = self.output_dropout(output)#再来个dropout
- return output
欢迎大家在评论区批评指正,谢谢~
-
相关阅读:
3dsmax2021软件安装教程
python小记3
RabbitMQ(基于AMQP的开源消息代理软件)
Selenium Web自动化测试 —— 高级控件交互方法!
Spring 中Bean的作用域有哪些?
Knife4j使用教程(五)-- 上传gitee,由Maven管理的SpringBoot项目
设计模式之观察者模式
什么是BT种子!磁力链接又是如何工作的?
网络运行安全
【表白程序】盛开的玫瑰代码
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_55073640/article/details/126491949
